Chapter 35 Mediation Analysis Is Harder Than It Looks
Mediators are variables that transmit causal effects from treatments to outcomes. Those who undertake mediation analysis seek
to answer “how” questions about causation: how does this treatment affect that outcome? Typically, we desire answers of the
form “the treatment affects a causally intermediate variable, which in turn affects the outcome.” Identifying these causally
intermediate variables is the challenge of mediation analysis.
Conjectures about political mediation effects are as old as the study of politics. But codification of procedures by which
to test hypotheses about mediation is a relatively new development. The most common procedures are now ubiquitous in psychology
(Quiñones-Vidal et al. 2004) and increasingly popular in the other social sciences, not least political science.
Unfortunately, the most common procedures are not very good. They call for indirect effects – the portions of treatment effects
that are transmitted through mediators – to be estimated via multiequation regression frameworks. These procedures do not
require experimental manipulation of mediators; instead, they encourage the study of mediation with data from unmanipulated
mediators (MacKinnon et al. 2002, 86; Spencer, Zanna, and Fong 2005). The procedures are therefore prone to producing biased estimates of mediation effects. Warnings about this problem have been issued for decades by statisticians, psychologists,
and political scientists.
Recognizing that nonexperimental methods of mediation analysis are likely to be biased, social scientists are slowly turning
to methods that involve experimental manipulation of mediators. This is a step in the right direction. But experimental mediation
analysis is difficult – more difficult than it may seem – because experiment-based inferences about indirect effects are subject
to important but little-recognized limitations. The point of this chapter is to explain the bias to which nonexperimental methods are prone and to describe experimental methods that hold out more promise of generating credible
inferences about mediation. But it is also to describe the limits of experimental mediation analysis.
We begin by characterizing the role that mediation analysis plays in political science. We then describe conventional methods
of mediation analysis and the bias to which they are prone. We proceed by describing experimental methods that can reliably
produce accurate estimates of mediation effects. The experimental approach has several important limitations, and we end the
section by explaining how these limitations imply both best practices and an agenda for future research. We consider objections
to our argument in the next section, including the common objection that manipulation of mediators is often infeasible. Our
last section reviews and concludes.
1. Mediation Analysis in Political Science
The questions that animate political scientists can be classified epistemologically. Some are purely descriptive. Others –
the ones to which experiments are especially well suited – are about treatment effects. (“Does X affect Y? How much? Under what conditions?”) But questions about mediation belong to a different category. When social scientists
seek information about “processes” or demand to know about the “mechanisms” through which treatments have effects, they are
asking about mediation. Indeed, when social scientists speak about “explanation” and “theory,” mediation is usually what they
have in mind.
Social scientists often try to buttress their claims about mediation with data. They use a variety of methods to do so, but
nearly all are based on crosstabulations or multiequation regression frameworks. In this chapter, we focus on one such method:
the one proposed by Baron and Kenny (1986). We focus on it because it is simple, by far the most common method, and similar to almost all other methods in use today.
It originated in social psychology, where its influence is now hard to overstate.1 And within political science, it is most prominent among articles that have explicitly psychological aims. For example, Brader, Valentino, and Suhay (2008) use the procedure to examine whether emotions mediate the effects of news about immigration on willingness to write to members
of Congress. Fowler and Dawes (2008, 586–88) use it to test hypotheses about mediators of the connection between genes and turnout. And several political scientists
have used it to understand the mechanisms that underpin priming and framing effects in political contexts (e.g., Nelson 2004; Malhotra and Krosnick 2007).
To some, the increasing use of the Baron-Kenny method in political science seems a good thing: it promises to bring about “valuable theoretical advances” and
is just what we need to “push the study of voting up a notch or two in sophistication and conceptual payoffs” (Malhotra and
Krosnick 2007, 250, 276). But increasing use of the Baron-Kenny method is not a good thing. Like related methods that do not require manipulation
of mediators, it is biased, and in turn it leads researchers to biased conclusions about mediation.
2. Nonexperimental Mediation Analyses Are Prone to Bias
Like many related procedures, the method proposed by Baron and Kenny (1986) is based on three models:
where Y is the outcome of interest, X is a treatment, M is a potential mediator of the treatment, and α1, α2, and α3 are intercepts. For simplicity, we assume that X and M are binary variables coded either 0 or 1. The unobservable disturbances e1, e2, and e3 are mean-zero error terms that represent the cumulative effect of omitted variables. It is not difficult to extend this framework
to include multiple mediators and other covariates, and our criticisms apply with equal force to models that include such
variables. For notational clarity and comparability to previous articles about mediation analysis, we limit our discussion
to the three-variable regression framework.
 |
(1) |
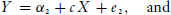 |
(2) |
 |
(3) |
For simplicity, we assume throughout this chapter that X is randomly assigned such that it is independent of the disturbances: e1, e2, e3 ⊥⊥X. As we shall see, randomization of X alone does not ensure unbiased estimation of the effects of mediators. Consequently, we refer to designs in which only X is randomized as nonexperimental for the purpose of mediation analysis, reserving experimental for studies in which both X and M are randomized.
The coefficients of interest are a, b, c, and d. The total effect of X on Y is c. To see how c is typically decomposed into “direct” and “indirect” effects, substitute Equation (1) into Equation (3), yielding
The direct effect of X is d. The indirect or “mediated” effect is ab (or, equivalently, c − d).2
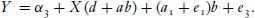 |
Baron and Kenny (1986) do not say how the coefficients in these equations are to be estimated; in practice, ordinary least squares (OLS) is almost
universally used. But the OLS estimator of b in Equation (3) is biased:
The OLS estimator of d is also biased:
(A proof is given in Bullock, Green, and Ha [2008, 39–40].) OLS estimators of direct and indirect effects will therefore be biased as well.
 |
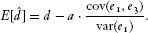 |
In expectation, the OLS estimators of b and d produce accurate estimates only if cov(e1, e3) = 0.3 But this condition is unlikely to hold unless both X and M are randomly assigned. The problem is straightforward: if an unobserved variable affects both M and Y, it will cause e1 and e3 to covary. And even if no unobserved variable affects both M and Y, these disturbances are likely to covary if M is merely correlated with an unobserved variable that affects Y, e.g., another mediator. This “multiple-mediator problem” is a serious threat to social-science mediation analysis because
most of the effects that interest social scientists are likely to have multiple correlated mediators. Indeed, we find it difficult
to think of any political effects that do not fit this description.4
The standard temptation in nonexperimental analysis is to combat this problem by controlling for potential mediators other
than M. But it is normally impossible to measure all possible mediators. Indeed, it may be impossible to merely think of all possible mediators. And controlling for some potential mediators but not all of them is no guarantee of better estimates;
to the contrary, it may make estimates worse (Clarke 2009). Fighting endogeneity in nonexperimental mediation analysis by adding control variables is a method with no clear stopping rule or way
to detect bias – a shaky foundation on which to build beliefs about mediation.
Political scientists who use the Baron-Kenny (1986) method and related methods often want to test hypotheses about several potential mediators rather than one. In these cases,
the most common approach is “one-at-a-time” estimation, whereby Equation (3) is estimated separately for each mediator. This practice makes biased inferences about mediation even more likely. The researcher,
who already faces the spectre of bias due to the omission of variables over which she has no control, compounds the problem
by intentionally omitting variables that are likely to be important confounds. Nonexperimental mediation analysis is problematic
enough, but one-at-a-time testing of mediators stands out as an especially bad practice.
The Baron-Kenny method and related methods are often applied to experiments in which the treatment has been randomized but
the mediator has not, and there seems to be a widespread belief that such experiments are sufficient to ensure unbiased estimates
of direct and indirect effects. But randomization of the treatment is not enough to protect researchers from biased estimates.
It can ensure that X bears no systematic relationship to e1, e2, or e3, but it says nothing about whether M is systematically related to those variables, and thus nothing about whether cov(e1, e3) = 0.5
Stepping back from mediation analysis to the more general problem of estimating causal effects, note that estimators tend
to be biased when one controls for variables that are affected by the treatment. One does this whenever one controls for M in a regression of Y on X, which the Baron-Kenny method requires. This “post-treatment bias” has been discussed in statistics and political science
(e.g., Rosenbaum 1984, 188–94; King and Zeng 2006, 146–48), but its relevance to mediation analysis has gone largely unnoticed. At root, it is one instance of an even more
general rule: estimators of the parameters of regression equations are likely to be unbiased only if the predictors in those
equations are independent of the disturbances. And in most cases, the only way to ensure that M is independent of the disturbances is to randomly assign its values. By contrast, “the benefits of randomization are generally
destroyed by including post-treatment variables” (Gelman and Hill 2007, 192).
Within the past decade, statisticians and political scientists have advanced several different methods of mediation analysis
that do not call for manipulation of mediators. These methods improve on Baron and Kenny (1986), but they do not overcome the problem of endogeneity in nonexperimental mediation analysis. For example, Frangakis and Rubin (2002) propose “principal stratification,” which entails dividing subjects into groups on the basis of their potential outcomes
for mediators. Causal effects are then estimated separately for each “principal stratum.” The problem is that some potential
outcomes for each subject are necessarily unobserved, and those who use principal stratification must infer the values of
these potential outcomes on the basis of covariates. In practice, “this reduces to making the same kinds of assumptions as
are made in typical observational studies when ignorability is assumed” (Gelman and Hill 2007, 193).
In a different vein, Imai, Keele, and Yamamoto (2010) show that indirect effects can be identified even when the mediator is not randomized – provided that we stipulate the size
of cov(e1, e3). This is helpful: if we are willing to make assumptions about the covariance of unobservables, then we may be able to place
bounds on the likely size of the indirect effect. But in no sense is this method a substitute for experimental manipulation
of the mediator. Instead, it requires us to make strong assumptions about the properties of unobservable disturbances, just
as other methods do when they are applied to nonexperimental data. Moreover, Imai, Keele, Tingley, and Yamamoto (2010, 43) note that even if we are willing to stipulate the value of cov(e1, e3), the method that they propose cannot be used whenever the mediator of interest is directly affected by both the treatment
and another mediator. This point is crucial because many effects that interest political scientists seem likely to be transmitted
by multiple mediators that affect each other.
None of these warnings implies that all nonexperimental mediation research is equally suspect. All else equal, research in
which only a treatment is randomized is preferable to research in which no variables are randomized; treatment-only randomization
does not make accurate mediation inference likely, but it does clarify the assumptions required for accurate inference. And
in general, nonexperimental research is better when its authors attempt to justify the assumption that their proposed mediator
is uncorrelated with other variables, including unobserved variables, that may also be mediators. This sort of argument can
be made poorly or well. But even the best arguments of this type typically warrant far less confidence than arguments about
unconfoundedness that follow directly from manipulation of both the treatment and the mediator.
This discussion should make clear that the solution to bias in nonexperimental mediation analyses is unlikely to be another
nonexperimental mediation analysis. The problem is that factors affecting the mediator and the outcome are likely to covary.
We are not likely to solve this problem by controlling for more variables, measuring them more accurately, or applying newer
methods to nonexperimental data. To calculate unbiased estimates of mediation effects, we should look to experiments.
3. Experimental Methods of Mediation Analysis
The simplest experimental design that permits accurate estimation of indirect effects entails direct manipulation of treatments
and mediators. We have described such a design elsewhere (Bullock, Green, and Ha 2008), but in many cases, limited understanding of mediators precludes direct manipulation. For example, although we can assign
subjects to conditions in which their feelings of efficacy are likely to be heightened or diminished, we do not know how to
gain direct experimental control over efficacy. That is, we do not know how to assign specific levels of efficacy to different
subjects. The same is true of party identification, emotions, cultural norms, modes of information processing, and other likely
mediators of political processes. These variables and others are beyond direct experimental control.
But even when mediators are beyond direct experimental control, we can often manipulate them indirectly. The key in such cases
is to create an instrument for M, the endogenous mediator. To be a valid instrument for M, a variable must be correlated with M but uncorrelated with e3. Many variables are likely to satisfy the first condition: whatever M is, it is usually not hard to think of a variable that is correlated with it, and once we have measured this new variable,
estimating the correlation is trivial. But satisfying the second condition is more difficult. Because e3 is unobservable, we can never directly test whether it is uncorrelated with the potential instrument. Worse, almost every
variable that is correlated with M is likely to be correlated with other factors that affect Y, and thus likely to be correlated with e3.6
Fortunately, a familiar class of variables meets both conditions: assignment-to-treatment variables. Use of these instrumental
variables is especially common in analyses of field experiments, where compliance with the treatment is likely to be partial.
For example, Gerber and Green (2000) use a field experiment to study various means of increasing voter turnout. They cannot directly manipulate the treatments
of interest: they cannot compel their subjects to read mail, answer phone calls, or speak to face-to-face canvassers. Instead, they use random assignments to these treatments
as instruments for the treatments themselves. Doing so permits them to recover accurate estimates of treatment effects even
though the treatments are beyond direct experimental control. (For elaboration of this point, see Angrist, Imbens, and Rubin [1996] and Gerber's chapter in this volume.)
Although the instrumental variables approach is increasingly used to estimate average treatment effects, it has not yet been
used in political science to study mediation. We think that it should be. It has already been used multiple times to study
mediation in social psychology, and its use in that discipline suggests how it might be used in ours. For example, Zanna and Cooper (1974) hypothesize that attitude-behavior conflict produces feelings of unpleasant tension (“aversive arousal”), which in turn
produces attitude change. They cannot directly manipulate levels of tension, so they use an instrument to affect it indirectly:
subjects swallow a pill and are randomly assigned to hear that it will make them tense, make them relax, or have no effect.
In a related vein, Bolger and Amarel (2007) hypothesize that the effect of social support on the stress levels of recipients is mediated by efficacy: support reduces
recipients’ stress by raising their feelings of efficacy. Bolger and Amarel cannot directly assign different levels of efficacy
to different participants in their experiment. Instead, they randomly assign subjects to receive personal messages that are
designed to promote or diminish their feelings of efficacy. In this way, they indirectly manipulate efficacy.
To see how such instruments might be created and used in political science, consider research on issue framing. A controversial
hypothesis is that framing an issue in a particular way changes attitudes by increasing the accessibility of particular thoughts
about the issue, i.e., the ease with which particular thoughts come to mind (see Iyengar and Kinder 1987, esp. ch. 7; Nelson, Clawson, and Oxley 1997; Miller and Krosnick 2000). Political scientists do not know how to directly manipulate the accessibility of particular thoughts, but they do know
how to indirectly manipulate accessibility by priming people in different ways (e.g., Burdein, Lodge, and Taber 2006, esp. 363–64; see also Lodge and Taber's chapter in this volume). Experimental analysis of the hypothesis is therefore possible.
Following Equation (3), consider the model:
In this model, framing indicates whether subjects were assigned to a control condition (framing = 0) or an issue frame (framing = 1); accessibility is reaction times in milliseconds in a task designed to gauge the accessibility of particular thoughts about the issue; and
e3 is a disturbance representing the cumulative effect of other variables. Crucially, accessibility is not randomly assigned. It is likely to be affected by framing and to be correlated with unobserved variables represented
by e3: age, intelligence, and political predispositions, among others.
 |
The OLS estimator of b, the effect of accessibility, is therefore likely to be biased. (The OLS estimator of d, the direct effect of the framing manipulation, is also likely to be biased.) But suppose that in addition to the framing
manipulation and the measurement of accessibility, some subjects are randomly assigned to a condition in which relevant considerations
are primed. This priming manipulation may make certain thoughts about the issue more accessible. In this case, accessibility
remains nonexperimental, but the priming intervention generates an instrumental variable that we can use to consistently estimate
b. If we also estimate a – for example, by conducting a second experiment in which only framing is manipulated – our estimator of ab, the extent to which priming mediates framing, will also be consistent.
The most common objection to experimental mediation approaches is that they often cannot be used because mediators often cannot
be manipulated. We take up this objection later in this chapter, but for the moment, we stress that researchers need not seek complete experimental control over mediators. They need only seek
some randomization-based purchase on mediators. Consider, for example, one of the best-known and least tractable variables
in political behavior research: party identification. The history of party ID studies suggests that it should be difficult
to manipulate. It is one of the most stable individual-level influences on votes and attitudes, and no one knows how to assign
different levels of party ID to different subjects. But party ID can be changed by experiments, and such experiments are the
key to understanding its mediating power. For example, Brader and Tucker (2008) use survey experiments to show that party cues can change Russians’ party IDs. And Gerber, Huber, and Washington (2010) use a field experiment to show that registering with a party can produce long-term changes
in party ID. The most promising path to secure inferences about party ID as a mediator is to conduct studies in which interventions
like these are coupled with manipulations of policy preferences, candidate evaluations, or other treatments. And in general,
the most promising path to secure inferences about mediation is to design studies that include experimental manipulations
of both treatments and mediators.
4. Three Limitations of Experimental Mediation Analysis
Despite its promise, the experimental approach has limitations that merit more attention than they typically receive. It requires
researchers to devise experimental manipulations that affect one mediator without affecting others. Even if researchers succeed, their estimates of indirect effects will typically apply only to a subset of the experimental
sample. Finally, if causal effects are not identical for all members of a sample, then even a well-designed experiment may
lead to inaccurate inferences about indirect effects. We discuss these limitations at length in other work (Bullock, Green,
and Ha 2010; Green, Ha, and Bullock 2010); here, we offer a brief overview of each.7
An experimental intervention is useful for mediation analysis if it affects one mediator without affecting others. If the
intervention instead affects more than one mediator, it violates the exclusion restriction – in terms of Equation (3), it
is correlated with e3 – and is not a valid instrument. In this case, the instrumental variables estimator of the indirect effect will be biased.
For example, issue frames may affect attitudes not only by changing the accessibility of relevant considerations, but also
by changing the subjective relevance of certain values to the issue at hand (Nelson et al. 1997). In this case, an experimental intervention can identify the mediating role of accessibility only if it primes relevant
considerations without affecting the subjective relevance of different values. And by the same token, an experimental intervention
will identify the mediating role of value weighting only if it affects the subjective relevance of different values without
changing the accessibility of considerations. The general challenge for experimental researchers, then, is to devise manipulations
that affect one mediator without affecting others.8
Even if researchers isolate particular mediators, they must confront another dilemma: some subjects never take a treatment
even if they are assigned to take it, and a treatment effect cannot be meaningfully estimated for such people. Consequently,
the experimental approach to mediation analysis produces estimates of the average treatment effect not for all subjects but
only for “compliers” who can be induced by random assignment to take it (Imbens and Angrist 1994). For example, if some subjects are assigned to watch a presidential campaign advertisement while others are assigned to
a no-advertisement control group, then the average effect of the ad can be identified not for all subjects but only for 1)
treatment-group subjects who are induced by random assignment to watch the ad, and (2) control-group subjects who would have
been induced to watch the ad if they had been assigned to the treatment group. One may assume that the average indirect effect
is the same for these subjects as for others, but this is an assumption, not an experimental result. Strictly speaking, estimates
of the average indirect effect apply only to a subset of the sample. We can usually learn something about the characteristics
of this subset (Angrist and Pischke 2009, 166–72), but we can never know exactly which subjects belong to it.
An unintuitive consequence follows: even if we use experiments to manipulate both a treatment and a mediator, we may not be
able to estimate an average indirect effect for our experimental sample or any subset of it. To see why, recall that the indirect
effect of X on Y in Equations (1)–(3) is ab. By manipulating X, we can recover â, an estimate of the average effect of X on M among those whose value of X can be affected by the X manipulation. And by manipulating M, we can recover b̂, an estimate of the average effect of M on Y among those whose value of M can be affected by the M manipulation. If these two populations are the same, âb̂ is a sensible estimate of the local average treatment effect. But if these two populations differ – if one set of subjects
is affected by the manipulation of X but a different set is affected by the manipulation of M – âb̂ is the causal effect of X on M for one group of people times the causal effect of M on Y for another group of people. This product has no causal interpretation. It is just an unclear mixture of causal effects for
different groups.9
A related problem is that experiments cannot lead to accurate estimates of indirect effects when the effects of X on M are not the same for all subjects or when the effects of M on Y are not the same for all subjects. When we are not studying mediation, the assumption of unvarying effects does little harm:
if the effect of randomly manipulated X on Y varies across subjects, and we regress Y on X, then the coefficient on X simply indicates the average effect of X. But if the effects of X and M vary across subjects, it will typically be difficult to estimate an average indirect effect (Glynn 2010). To see why, consider an experimental sample in which there are two groups of subjects. In the first group, the effect of
X on M is positive, and the effect of M on Y is also positive. In the second group, the effect of X on M is negative, and the effect of M on Y is also negative. In this case, the indirect effect of X is positive for every subject in the sample: to slightly adapt the notation of Equations (1) and (3), aibi is positive for every subject. But â, the estimate of the average effect of X on M, may be positive, negative, or zero. And b̂, the estimate of the average effect of M on Y, may be positive, negative, or zero. As a result, the estimate of the average indirect effect, âb̂, may be zero or negative – even though the true indirect effect is positive for every subject.
Such problems may arise whenever different people are affected in different ways by X and M. For example, Cohen (2003) wants to understand how reference-group cues (X) affect attitudes toward social policy (Y). In his experiments, politically conservative subjects receive information about a generous welfare policy; some of these
subjects are told that the policy is endorsed by the Republican Party, while others receive no endorsement information. Cohen's findings are consistent with cues (endorsements) promoting systematic thinking (M) about the policy information, and with systematic thinking in turn promoting positive attitudes toward the policy (Cohen 2003, esp. 817).10 On the other hand, Petty and Wegener (1998, 345) and others suggest that reference-group cues inhibit systematic thinking about information, and that such thinking
promotes the influence of policy details – which might be expected to lead, in this case, to negative attitudes toward the
welfare policy among the conservative subjects. For present purposes, there is no need to favor either of these theories or
to attempt a reconciliation. We need only note that they suggest a case in which causal effects may be heterogeneous, and
in which mediation analysis is therefore difficult. Let some subjects in an experiment be “Cohens”: for these people, exposure
to reference group cues heightens systematic thinking (ai is positive), and systematic thinking makes attitudes toward a generous welfare policy more favorable (bi is positive). But other subjects are “Petties”: for them, exposure to reference group cues limits systematic thinking (ai is negative), and systematic thinking makes attitudes toward a generous welfare policy less favorable (bi is negative). Here again, the indirect effect is positive for every subject because aibi > 0 for all i. But if the experimental sample includes both Cohens and Petties, â and b̂ may each be positive, negative, or zero. Conventional estimates of the average indirect effect – âb̂ and related quantities – may therefore be zero or even negative.
Moreover, causal effects need not differ so sharply across members of a sample to make mediation analysis problematic. Conventional
estimates of indirect effects will be biased if a and b merely covary among subjects within a sample. For example, if a subset of subjects is more sensitive than the rest of the
sample to changes in X and to changes in M, estimates of indirect effects will be biased. This problem cannot be traced to a deficiency in the methods that are often
used to calculate indirect effects: it is fundamental, not a matter of statistical technique (Robins 2003; Glynn 2010).
5. An Agenda for Mediation Analysis
These limitations of experimental mediation analysis – it requires experimenters to isolate particular mediators, produces
estimates that apply only to an unknown subset of subjects, and cannot produce meaningful inferences about mediation when
causal effects covary within a sample – are daunting. Experiments are often seen as simplifying causal inference, but taken
together, these limitations imply that strong inferences about mediation are likely to be difficult even when researchers
use fully experimental methods of mediation analysis. Still, none of our cautions implies that experiments are useless for
mediation analysis. Nor do they imply that experimental mediation analysis is no better than the nonexperimental alternative. Unlike nonexperimental methods, experiments offer – albeit under limited circumstances – a systematic
way to identify mediation effects. And the limitations that we describe are helpful inasmuch as they delineate an agenda for
future mediation analysis.
First, researchers who do not manipulate mediators should try to explain why the mediators are independent of the disturbances in
their regression equations – after all, the accuracy of their estimates hinges on this assumption. In practice, justifying
this assumption entails describing unmeasured mediators that may link X to Y and explaining why these mediators do not covary with the measured mediators. Such efforts are rarely undertaken, but without
them it is hard to hold out hope that nonexperimental mediation analysis will generate credible findings about mediation.
Second, researchers who experimentally manipulate mediators should explain why they believe that their manipulations are isolating individual mediators. This entails describing the causal paths by which X may affect Y and explaining why each experimental manipulation affects only one of these paths. The list of alternative causal paths may
be extensive, and multiple experiments may be needed to demonstrate that a given intervention tends not to affect the alternative
paths in question.
Third, researchers can improve the state of mediation analysis simply by manipulating treatments and then measuring the effects
of their manipulations on many different outcomes. To see how this can improve mediation analysis, consider studies of the effects of campaign contact on voter turnout. In
addition to assessing whether a particular kind of contact increases turnout, one might also survey participants to determine
whether this kind of contact affects interest in politics, feelings of civic responsibility, knowledge about where and how
to vote, and other potential mediators. In a survey or laboratory experiment, this extra step need not entail a new survey:
relevant questions can instead be added to the post-test questionnaire. Because this kind of study does not include manipulations
of both treatments and mediators, it cannot reliably identify mediation effects. But if some variables seem to be unaffected
by the treatment, one may begin to argue that they do not explain why the treatment works.
Fourth, researchers should know that if the effects of X and M vary from subject to subject within a sample, it may be impossible to estimate the average indirect effect for the entire
sample. To determine whether this is a problem, one can examine the effects of X and M among different types of subjects. If the effects differ little from group to group (e.g., from men to women, whites to nonwhites,
the wealthy to the poor), we can be relatively confident that causal heterogeneity is not affecting our analysis.11 In contrast, if there are large between-group differences in the effects of X or M, then mediation estimates made for an entire sample may be inaccurate even if X and M have been experimentally manipulated. In this case, researchers should aim to make multiple inferences for relatively homogeneous
subgroups rather than single inferences about the size of an indirect effect for an entire sample.
6. Defenses of Conventional Practice
In different ways, statisticians (Rosenbaum 1984; Rubin 2004; Gelman and Hill 2007, 188–94), social psychologists (James 1980; Judd and Kenny 1981, 607), and political scientists (King and Zeng 2006, 146–48; Glynn 2010) have all warned that methods like the one proposed by Baron and Kenny (1986) are likely to produce meaningless or inaccurate conclusions when applied to observational data. Why have their arguments
not taken hold? Some of the reasons are mundane: the arguments are typically made in passing, their relevance to mediation
analysis is not always clear, there are few such arguments in any one discipline, and scholars rarely read outside their own
disciplines. But these are not the only reasons. Another part of the answer lies with three defenses of nonexperimental mediation
analysis, which can also be framed as criticisms of the experimental approach.
The first and most common defense is that many mediators cannot be manipulated and that insistence on experimental mediation
analysis therefore threatens to limit the production of knowledge (e.g., James 2008; Kenny 2008). Manipulation of mediators is indeed difficult in some cases, but we think that this objection falls short on several counts
(Bullock et al. 2008, 28–29). First, it follows from a misunderstanding of the argument. No one maintains that unmanipulable variables should
not be studied or that causal inferences should be drawn only from experiments. The issue lies instead with the accuracy of
nonexperimental inferences and the degree of confidence that we should place in them. In the absence of natural experiments,
dramatic effects, or precise theory about data-generating processes – that is, in almost all situations that social scientists
examine – nonexperimental studies are likely to produce biased estimates of indirect effects and to justify only weak inferences. Moreover, the objection is unduly pessimistic, likely because it springs from a failure to see
that many variables that cannot be directly manipulated can be indirectly manipulated. Perhaps some mediators defy even indirect
manipulation, but in light of increasing experimental creativity throughout the discipline – exemplified by several other
chapters in this volume – we see more cause for optimism than for despair.
A second objection is that the problem of bias in mediation analysis is both well understood and unavoidable. The solution,
according to those who make this objection, is not to embrace experimentation but to “build better models” (e.g., James 1980). The first part of this objection is implausible: those who analyze mediation may claim to be aware of the threat of bias,
but they typically act as though they are not. Potential mediators other than the one being tested are almost never discussed
in conventional analyses, even though their omission makes bias likely. When several mediators are hypothesized, it is common
to see each one analyzed in a separate set of regressions rather than collectively, which further increases the probability
of bias.
This makes the second part of the objection – that the way to secure inferences about mediation is to “build better models”
– infeasible. In the absence of experimental benchmarks (e.g., LaLonde 1986), it is difficult to know what makes a model better. Merely adding more controls to a nonexperimental mediation analysis
is no guarantee of better estimates, common practice to the contrary. It may well make estimates worse (Clarke 2009).
A more interesting argument is that social scientists are not really interested in point estimation of causal effects (Spencer et al. 2005, 846). They report precise point estimates in their tables, but their real concern is statistical significance, i.e., bounding
effects away from zero. And for this purpose, the argument goes, conventional methods of mediation analysis do a pretty good
job. The premise of this argument is correct: many social scientists care more about bounding effects away from zero than
they do about learning the size of effects. But this indifference to the size of effects is regrettable. Our stock of accumulated
knowledge speaks much more to the existence of effects than to their size, and this makes it difficult to know which effects
are important. And even if the emphasis on bounding results away from zero were appropriate, there would not be reason to
think that conventional mediation analysis does a good job of helping us to learn about bounds. As Imai, Keele, Tingley, and Yamamoto (2010, 43) note, even a well-developed framework for sensitivity analysis cannot produce meaningful information about mediation
when important omitted variables are causally subsequent to the treatment.
7. Conclusion
Experiments have taught us much about treatment effects in politics, but our ability to explain these effects remains limited.
Even when we are confident that a particular variable mediates a treatment effect, we are usually unable to speak about its
importance in either an absolute sense or relative to other mediators. Given this state of affairs, it is not surprising that
many political scientists want to devote more attention to mediation.
But conventional mediation analysis, which draws inferences about mediation from unmanipulated mediators, is a step backward.
These analyses are biased, and their widespread use threatens to generate a store of misleading inferences about causal processes
in politics. The situation would be better if we could hazard guesses about the size and direction of the biases. But we can
rarely take even this small step with confidence because conventional mediation analyses rarely discuss mediators other than
those that have been measured. Instead, conventional analyses are typically conducted as though they were fully experimental,
with no consideration of threats to inference.
A second, worse problem is the impression conveyed by the use and advocacy of these methods: the impression that mediation
analysis is easy, or at least no more difficult than running a few regressions. In reality, secure inferences about mediation typically require experimental manipulation
of both treatments and mediators. But experimental inference about mediation, too, is beset by limitations. It requires researchers
to craft interventions that affect one mediator without affecting others. If researchers succeed in this, their inferences
will typically apply only to an unknown subset of subjects in their sample. And if the effects of the treatment and the mediator
are not the same for every subject in the sample, even well-designed experiments may be unable to yield meaningful estimates
of average mediation effects for the entire sample. In the most difficult cases, it may be impossible to learn about mediation
without making strong and untestable assumptions about the relationships among observed and unobserved variables.
The proper conclusion is not that mediation analysis is hopeless but that it is difficult. Experiments with theoretically
refined treatments can help by pointing to mediators that merit further study. Experiments in which mediators are manipulated
are even more promising. And analysis of distinct groups of subjects can strengthen mediation analysis by showing us whether
it is possible to estimate average indirect effects for general populations or whether we must instead tailor our mediation
analyses to specific groups. But because of the threats to inference that we describe, any single experiment is likely to
justify only the most tentative inferences about mediation. Understanding the processes that mediate even a single treatment
effect will typically require a research program comprising multiple experiments – experiments that address the challenges
described here.
It is worthwhile to draw a lesson from other social sciences, where manipulation of mediators is rare but mediation analysis
is ubiquitous. In these disciplines, promulgation of nonexperimental procedures has given rise to a glut of causal inferences
about mediation that warrant little confidence. Even the scholar who has arguably done most to promote nonexperimental mediation
analysis now laments that social scientists often “do not realize that they are conducting causal analyses” and fail to justify
the assumptions that underpin those analyses (Kenny 2008, 356). It would be a shame if political scientists went the same route. We can stay on track by remembering that inference
about mediation is difficult – much more difficult than conventional practice suggests.
References
Angrist, Joshua D., Guido W. Imbens, and Donald B. Rubin. 1996. “Identification of Causal Effects Using Instrumental Variables.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 91: 444–55.
Angrist, Joshua D., Victor Lavy, and Analia Schlosser. 2010. “Multiple Experiments for the Causal Link between the Quantity and Quality of Children.” Journal of Labor Economics 28: 773–824.
Angrist, Joshua D., and Jörn-Steffen Pischke. 2009. Mostly Harmless Econometrics: An Empiricist's Companion. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Baron, Reuben M., and David A. Kenny. 1986. “The Moderator-Mediator Variable Distinction in Social Psychological Research: Conceptual, Strategic, and Statistical Considerations.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 51: 1173–82.
Bartels, Larry M. 1991. “Instrumental and ‘Quasi-Instrumental’ Variables.” American Journal of Political Science 35: 777–800.
Bolger, Niall, and David Amarel. 2007. “Effects of Social Support Visibility on Adjustment to Stress: Experimental Evidence.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 92: 458–75.
Bound, John, David A. Jaeger, and Regina M. Baker. 1995. “Problems with Instrumental Variables Estimation When the Correlation between the Instruments and the Endogenous Explanatory
Variable Is Weak.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 90: 443–50.
Brader, Ted A., and Joshua A. Tucker. 2008. “Reflective and Unreflective Partisans? Experimental Evidence on the Links between Information, Opinion, and Party Identification.”
Manuscript, New York University.
Brader, Ted, Nicholas A. Valentino, and Elizabeth Suhay. 2008. “What Triggers Public Opposition to Immigration? Anxiety, Group Cues, and Immigration Threat.” American Journal of Political Science 52: 959–78.
Bullock, John G., Donald P. Green, and Shang E. Ha. 2008. “Experimental Approaches to Mediation: A New Guide for Assessing Causal Pathways.” Unpublished manuscript, Yale University.
Bullock, John G., Donald P. Green, and Shang E. Ha. 2010. “Yes, But What's the Mechanism? (Don't Expect an Easy Answer).” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 98: 550–58.
Burdein, Inna, Milton Lodge, and Charles Taber. 2006. “Experiments on the Automaticity of Political Beliefs and Attitudes.” Political Psychology 27: 359–71.
Campbell, Angus, Philip E. Converse, Warren Miller, and Donald Stokes. 1960. The American Voter. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
Clarke, Kevin A. 2009. “Return of the Phantom Menace: Omitted Variable Bias in Political Research.” Conflict Management and Peace Science 26: 46–66.
Cohen, Geoffrey L. 2003. “Party over Policy: The Dominating Impact of Group Influence on Political Beliefs.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 85: 808–22.
Downs, Anthony. 1957. An Economic Theory of Democracy. New York: HarperCollins.
Fowler, James H., and Christopher T. Dawes. 2008. “Two Genes Predict Voter Turnout.” Journal of Politics 70: 579–94.
Frangakis, Constantine E., and Donald B. Rubin. 2002. “Principal Stratification in Causal Inference.” Biometrics 58: 21–29.
Gelman, Andrew, and Jennifer Hill. 2007. Data Analysis Using Regression and Multilevel Hierarchical Models. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Gerber, Alan S., and Donald P. Green. 2000. “The Effects of Canvassing, Telephone Calls, and Direct Mail on Voter Turnout: A Field Experiment.” American Political Science Review 94: 653–62.
Gerber, Alan S., Gregory A. Huber, and Ebonya Washington. 2010. “Party Affiliation, Partisanship, and Political Beliefs: A Field Experiment.” American Political Science Review 104: 720–44.
Glynn, Adam N. 2010. “The Product and Difference Fallacies for Indirect Effects.” Unpublished manuscript, Harvard University.
Green, Donald P., Shang E. Ha, and John G. Bullock. 2010. “Enough Already about ‘Black Box’ Experiments: Studying Mediation Is More Difficult Than Most Scholars Suppose.” Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Sciences 628: 200–8.
Imai, Kosuke, Luke Keele, Dustin Tingley, and Teppei Yamamoto. 2010. “Unpacking the Black Box: Learning about Causal Mechanisms from Experimental and Observational Studies.” Unpublished manuscript,
Princeton University. Retrieved from http://imai.princeton.edu/research/files/mediationP.pdf (November 21, 2010).
Imai, Kosuke, Luke Keele, and Teppei Yamamoto. 2010. “Identification, Inference, and Sensitivity Analysis for Causal Mediation Effects.” Statistical Science 25: 51–71.
Imbens, Guido W., and Joshua D. Angrist. 1994. “Identification and Estimation of Local Average Treatment Effects.” Econometrica 62: 467–75.
Iyengar, Shanto, and Donald R. Kinder. 1987. News That Matters: Television and American Opinion. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
James, Lawrence R. 1980. “The Unmeasured Variables Problem in Path Analysis.” Journal of Applied Psychology 65: 415–21.
James, Lawrence R. 2008. “On the Path to Mediation.” Organizational Research Methods 11: 359–63.
Judd, Charles M., and David A. Kenny. 1981. “Process Analysis: Estimating Mediation in Treatment Evaluations.” Evaluation Review 5: 602–19.
Kenny, David A. 2008. “Reflections on Mediation.” Organizational Research Methods 11: 353–58.
King, Gary, and Langche Zeng. 2006. “The Dangers of Extreme Counterfactuals.” Political Analysis 14: 131–59.
LaLonde, Robert J. 1986. “Evaluating the Econometric Evaluations of Training Programs with Experimental Data.” American Economic Review 76: 604–20.
MacKinnon, David P., Chondra M. Lockwood, Jeanne M. Hoffman, Stephen G. West, and Virgil Sheets. 2002. “A Comparison of Methods to Test Mediation and Other Intervening Variable Effects.” Psychological Methods 7: 83–104.
Malhotra, Neil, and Jon A. Krosnick. 2007. “Retrospective and Prospective Performance Assessments during the 2004 Election Campaign: Tests of Mediation and News Media
Priming.” Political Behavior 29: 249–78.
Miller, Joanne M., and Jon A. Krosnick. 2000. “News Media Impact on the Ingredients of Presidential Evaluations.” American Journal of Political Science 44: 295–309.
Morgan, Stephen L., and Christopher Winship. 2007. Counterfactuals and Causal Inference. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Nelson, Thomas E. 2004. “Policy Goals, Public Rhetoric, and Political Attitudes.” Journal of Politics 66: 581–605.
Nelson, Thomas E., Rosalee A. Clawson, and Zoe M. Oxley. 1997. “Media Framing of a Civil Liberties Conflict and Its Effect on Tolerance.” American Political Science Review 91: 567–94.
Pearl, Judea. 2010. “The Mediation Formula: A Guide to the Assessment of Causal Pathways in Non-Linear Models.” Unpublished manuscript, University
of California, Los Angeles. Retrieved from http://ftp.cs.ucla.edu/~kaoru/r363.pdf (November 21, 2010).
Petty, Richard E., and Duane T. Wegener. 1998. “Attitude Change: Multiple Roles for Persuasion Variables.” In The Handbook of Social Psychology. vol. 1, 4th ed., eds. Daniel T. Gilbert, Susan T. Fiske, and Gardner Lindzey. New York: McGraw-Hill, 323–90.
Quiñones-Vidal, Elena, Juan J. López-Garcia, Maria Peñaranda-Ortega, and Francisco Tortosa-Gil. 2004. “The Nature of Social and Personality Psychology as Reflected in JPSP, 1965–2000.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 86: 435–52.
Robins, James M. 2003. “Semantics of Causal DAG Models and the Identification of Direct and Indirect Effects.” In Highly Structured Stochastic Systems, eds. Peter J. Green, Nils Lid Hjort, and Sylvia Richardson. New York: Oxford University Press, 70–81.
Rosenbaum, Paul R. 1984. “The Consequences of Adjustment for a Concomitant Variable That Has Been Affected by the Treatment.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A 147: 656–66.
Rubin, Donald B. 2004. “Direct and Indirect Causal Effects via Potential Outcomes.” Scandinavian Journal of Statistics 31: 161–70.
Spencer, Steven J., Mark P. Zanna, and Geoffrey T. Fong. 2005. “Establishing a Causal Chain: Why Experiments Are Often More Effective Than Mediational Analyses in Examining Psychological
Processes.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 89: 845–51.
Zanna, Mark P., and Joel Cooper. 1974. “Dissonance and the Pill: An Attribution Approach to Studying the Arousal Properties of Dissonance.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 29: 703–9.
A previous version of this chapter was presented at the Experimentation in Political Science Conference at Northwestern University,
May 28–29, 2009. We thank Jamie Druckman, Alan Jacobs, Scott Matthews, Nora Ng, David Nickerson, Judea Pearl, Dustin Tingley,
and Lynn Vavreck for comments. Particular thanks to Donald Green, our coauthor on several related papers, for many helpful
discussions.
1 Quiñones-Vidal et al. (2004) show that the article is already the best-cited in the history of the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. Our own search turned up more than 20,000 citations. Analogous searches suggest that Downs (1957) has been cited fewer than 14,000 times and that The American Voter (Campbell et al. 1960) has been cited fewer than 4,000 times.
2 This discussion of direct and indirect effects elides a subtle but important assumption: the effect of M on Y is the same regardless of the value of X. This additivity or “no-interaction” assumption is implied in linear models, e.g., Equation (3). See Robins (2003, 76–77) for a detailed consideration.
3 Imai, Keele, and Yamamoto (2010, 3) show that the indirect effect ab is identified under the assumption of sequential ignorability, i.e., independence of X from the potential outcomes of M and Y, and independence of M from the potential outcomes of Y. This is a stronger identifying assumption than cov(e1, e3) = 0 (Imai, Keele, and Yamamoto 2010, 10), but it has the virtue of being grounded in a potential-outcomes framework.
4 An occasional defense of the Baron-Kenny method is that the method itself is unbiased: the problem lies in its application
to nonexperimental data, and it would vanish if the method were applied to studies in which both X and M are randomized. This is incorrect. In fact, when both X and M are randomized, the Baron-Kenny method calls for researchers to conclude that M does not mediate X even when M strongly mediates X. For details, see Bullock et al. (2008, 10–11).
5 This warning is absent from Baron and Kenny (1986), but it appears clearly in one of that article's predecessors, which notes that what would come to be known as the Baron-Kenny
procedure is “likely to yield biased estimates of causal parameters…even when a randomized experimental research design has been used” (Judd and Kenny 1981, 607, emphasis in original).
7 We do not take up two other limitations. One is the unreliability of instrumental-variable approaches to mediation in nonlinear
models (Pearl 2010). The other is the “weak instruments” problem: when instruments are weakly correlated with the endogenous variables, IV estimators
have large standard errors, and even slight violations of the exclusion restriction (cov[Z, e3] = 0 where Z is the instrument for the endogenous mediator) may cause the estimator to have a large asymptotic bias (Bartels 1991; Bound, Jaeger, and Baker 1995). This is a large concern in econometric studies, where instruments are often weak and exclusion-restriction violations likely.
But instruments that are specifically created by random assignment to affect endogenous mediators are likely to meet the exclusion
restriction and unlikely to be “weak” by econometric standards.
8 Econometric convention permits the use of multiple instruments to simultaneously identify the effects of a single endogenous
variable. But estimators based on multiple instruments have no clear causal interpretation in a potential-outcomes framework;
they are instead difficult-to-interpret mixtures of local average treatment effects (Morgan and Winship 2007, 212). This is why we recommend that experimenters create interventions that isolate individual mediators.
10 This is only one aspect of Cohen (2003). As far as mediation is concerned, Cohen's main suggestion is that reference-group cues affect policy attitudes not by changing
the extent to which people think systematically about policy information but by otherwise changing perceptions of the policies
under consideration.