JBoss has a simplified directory structure. By browsing to the JBoss home directory and listing the contents, we can see the structure shown in the following screenshot:
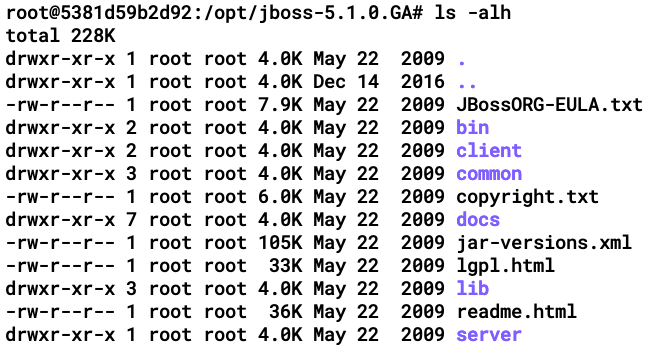
Let's try to understand what these directories are and what files and folders they contain:
- bin: This directory contains all the entry point Java Archives (JARs) and scripts, including startup and shutdown.
- client: This directory stores the configuration files that may be used by an external Java client application.
- common: This directory contains all of the server's common JAR and config files.
- docs: This directory contains the JBoss documentation and schemas, which are helpful during the development process.
- lib: This directory contains all the JARs required for JBoss to start up.
- server: This directory contains the files related to different server profiles, including production and testing.
By going further into the server directory and listing the contents, we can see the structure shown in the following screenshot:

Let's open one of these profiles and learn about the structure. The following screenshot shows the listing of the default folder:
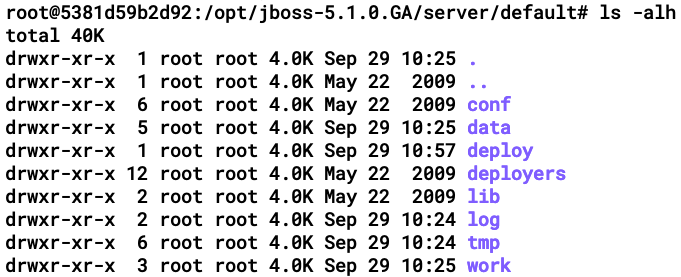
Let's look at a breakdown of the directories in the preceding screenshot:
- conf: This directory contains config files, including login-config and bootstrap config.
- data: This directory is available for services that store content in the filesystem.
- deploy: This directory contains the WAR files that are deployed on the server.
- lib: The lib directory is the default location for static Java libraries that are loaded to the shared classpath at startup.
- log: This directory is where all the logs are written to.
- tmp: This directory is used by JBoss to store temporary files.
- work: This directory contains the compiled JSP and class files.
By going further into the deploy directory and listing the contents, we can see various WAR files, XML files, and so on, as in the following screenshot:
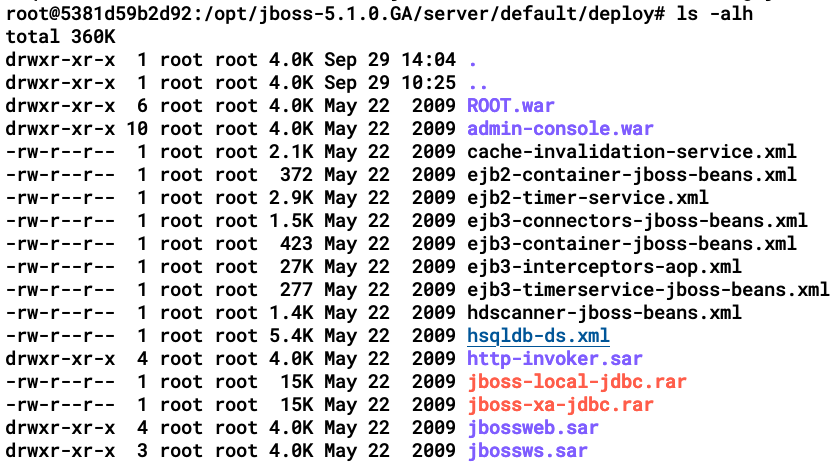
Some of the files we need to know about are as follows:
- admin-console.war is the admin console for JBoss AS.
- ROOT.war is the /root web application.
- jbossweb.sar is the Tomcat servlet engine deployed on the server.
- jbossws.sar is the JBoss service that supports web services.
Most of the time, we will find admin-console missing from the server as JBoss administrators remove the admin-console, web-console, and JMX-console applications from the server. Though it's a pretty neat way of protecting the JBoss instance, this won't work against threat actors. JBoss AS can also be managed using MBeans. Even though they are a feature for administrators, MBeans also work as a live door that allows actors to penetrate the network. To access MBeans, let's first learn about the file and directory structure, as that will help us learn how to access the MBeans in the process. The vast number of MBeans deployed in JBoss AS can be accessed directly via JMX-console and web-console, which raises many security concerns regarding deployment.
Before jumping into the JBoss exploitation, let's first understand how we can perform reconnaissance and enumeration on a JBoss AS deployment.