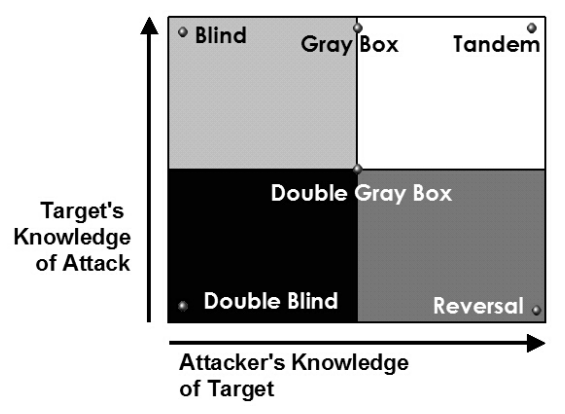
OSSTMM divides the testing types into six broad categories based on the amount of information known to the tester:
- Blind: In this test, the analyst has no knowledge of the target, but the target knows about the audit and has all the details of the analyst. This can be considered a test of the analyst's knowledge.
- Double-Blind: In this test, the analyst has no knowledge of the target, its defenses, assets, and so on. The target is also not notified of the audit. This test is used to check the knowledge and skills of the analyst as well as the preparedness of the target against unknown threats. This is also known as a black box test.
- Gray Box: In this test, the analyst has limited knowledge of the defenses of the target, but has complete knowledge of the assets and workings of the target. The target, in this case, is fully prepared for the audit and knows its full details. This test is also referred to as a Vulnerability Test.
- Double Gray Box: This is also known as the white box test. The target has advance knowledge of the scope and timeframe but has no knowledge of the payloads and test vectors.
- Tandem: This is also referred to as an in-house audit or crystal ball test. In this test, both the target and the analyst know the full details of the audit, but this test does not check the preparedness of the target against unknown variables or vectors.
- Reversal: In this test, an attacker engages with full knowledge of its target's processes and operational security, but the target doesn't know anything about when or how the audit will happen. This is also referred to as a red team exercise.
Here are these types represented in a graph:
Source: https://www.isecom.org/OSSTMM.3.pdf
License: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
License: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Now that we have read through the different OSSTMM test types, let's look at ISSAF.