You have learned how to automatically add targets into WMAP in the data reconnaissance phase. There's another way to load data into WMAP, and that is by manually defining the targets:
- Let's start by creating a new site or a workspace to perform our scan. Let's look at all the options available to us for site creation. Type wmap_sites -h:

- Let's now add the sites. There are two ways of adding sites – one is by going directly through the URL or IP. This can be done using the following command:
wmap_sites -a 151.101.21.32
The following screenshot shows the output of the preceding command:

- The second way is by using virtual hosts. This is very useful when we have to scan multiple virtual hosts. To add virtual hosts, we can use the following command:
wmap_sites -a <subdomain> , <IP Address>
Here's the output of the preceding command:

- Once the sites are added, we can add the targets in a similar way, either by IP/domain or by virtual host (virtual host/domain). To add a target via IP, we can use the following command:
wmap_targets -t <IP Address>
The following screenshot shows the output of the preceding command:

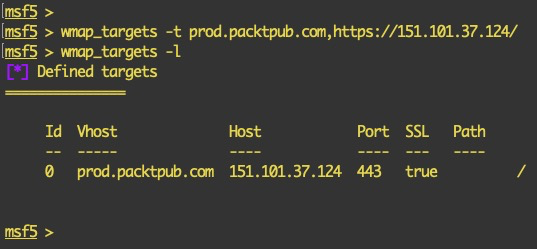
- To add a target via a virtual host, we use the following command:
wmap_targets -t <subdomain > , <IP Address>
The following screenshot shows the output of the preceding command:
- To view the list of all the modules that will be run by WMAP, we can use the wmap_modules -l command. The output of the command is shown in the following screenshot:

The following screenshot shows the modules for file/directory testing:

This phase also includes the WMAP scanning nodes, which can be configured so that you can perform distributed WMAP scanning. The nodes can be managed and configured using the wmap_nodes command. More about this will be discussed in the Clustered Scanning using WMAP section of this chapter. After the final configuration is done, the next phase is to launch WMAP.