Answers and Explanations
Quantitative Reasoning Practice Set 1
- C
Quantity A is a permutation because order matters. The number of ways 3 people chosen from a group of 6 can be arranged in a line, where order matters, is 6 × 5 × 4 = 120. Quantity B is a combination because order does not matter. The number of ways 3 people can be selected from a group of 10, where order does not matter, is
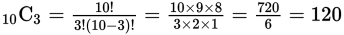
The two quantities are equal.
- C
There are three sets of vertical angles in this diagram: (a, d), (b, e), and (c, f). In Quantity A, you can substitute b for e because they are vertical angles and therefore equal; this leaves the sum a + b + c in Quantity A. Because these are the three angles on one side of a straight line, they sum to 180°. Similarly, after substituting e for b in Quantity B, b + d + f is the same thing as d + e + f, or also 180°. The two quantities are equal. - D
Pick a value for p and see what effect it has on r and s. If p = 1, r = (7 × 1) + 3 = 10, and s = (3 × 1) + 7 = 10, and the two quantities are equal. But if p = 0, r = (7 × 0) + 3 = 3, and s = (3 × 0) + 7 = 7, and Quantity A is less than Quantity B. Because there are at least two different possible relationships, the answer is (D). - A
Use the Picking Numbers strategy to answer this question. Suppose the original selling price of the shirt, x, is $100. After a 10% increase in price, the shirt would sell for 110% of $100, which is $110. If there is a 10% decrease next, the shirt would sell for 90% of the current price. That would be 90% of $110: 0.9 × $110 = $99. This price is less than the original amount, x, so Quantity A is greater. - B
Try to set the quantities equal. If x is 50, then the bookstore started out with 50 dictionaries. Then 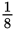 of them were purchased. You can see already that the
quantities can’t be equal, because
of them were purchased. You can see already that the
quantities can’t be equal, because
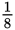 of 50 won’t yield an integer. But go ahead and see whether
the answer is (A) or (B). Because
of 50 won’t yield an integer. But go ahead and see whether
the answer is (A) or (B). Because
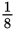 of 50 is close to 6, after these dictionaries were
purchased, the store would have been left with about 50 − 6 or
44 dictionaries. Then it received 10 more, giving a total of about
54 dictionaries. But this is more than the store actually ended up
with; it only had 52. Therefore, it must have started with fewer
than 50 dictionaries, and Quantity B is greater. (The last thing
you care about is how many dictionaries it really had.)
of 50 is close to 6, after these dictionaries were
purchased, the store would have been left with about 50 − 6 or
44 dictionaries. Then it received 10 more, giving a total of about
54 dictionaries. But this is more than the store actually ended up
with; it only had 52. Therefore, it must have started with fewer
than 50 dictionaries, and Quantity B is greater. (The last thing
you care about is how many dictionaries it really had.)
- A
There are n people in a room. One-third of them leave the room. So, there are
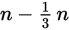 people in the room. Four people enter the room, so you
have
people in the room. Four people enter the room, so you
have
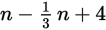 people. There are now
people. There are now
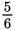 of the original number of people in the room, therefore
of the original number of people in the room, therefore
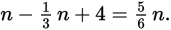 Now solve for n.
Now solve for n.
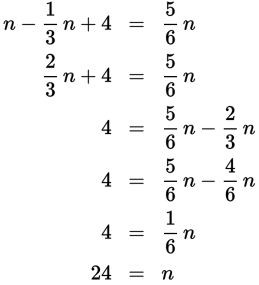
So, n = 24 and Quantity A is larger.
- C
You may have thought this was a choice (D) question; after all, you don’t know exactly where the boards overlap, whether in the middle of each board, as pictured, or near the end of one of the boards. But that doesn’t matter; all you need to know is that they overlap and that all the angles are right angles. If the boards did not overlap, it would be easy to find the perimeter: 2 + 2 + 4 + 4 = 12 for each board, or 24 for both boards. Now, because the boards do overlap, the perimeter of the figure will be smaller than that, but how much smaller? It will be smaller by the amount of that “lost perimeter” in the middle; the perimeter of the square where the boards overlap. (You know it’s a square since all the angles are right angles.) The length of a side of that square is the shorter dimension of each of the boards: 2. Therefore, the perimeter of the square is 4 × 2 or 8. The perimeter of the figure, then, is 24 − 8 or 16. The two quantities are equal. - A
Start by simplifying the quantity in Quantity A: 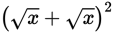 is the same as
is the same as
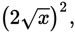 which is 4x. Subtract x from both quantities,
and you’re left with 3x in Quantity A and
which is 4x. Subtract x from both quantities,
and you’re left with 3x in Quantity A and
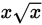 in Quantity B. Now divide both sides by x, and you’re
left with 3 in Quantity A and
in Quantity B. Now divide both sides by x, and you’re
left with 3 in Quantity A and
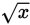 in Quantity B. Square both quantities, and you get 9 in
Quantity A and x in Quantity B. Since x is an integer
between 1 and 9, exclusive, Quantity A is larger. If the algebra
seems too abstract, go ahead and use the Picking Numbers strategy.
If x equals 4, then Quantity A equals (2 +
2)2 = 16, and Quantity B equals
4 + 8 = 12.
in Quantity B. Square both quantities, and you get 9 in
Quantity A and x in Quantity B. Since x is an integer
between 1 and 9, exclusive, Quantity A is larger. If the algebra
seems too abstract, go ahead and use the Picking Numbers strategy.
If x equals 4, then Quantity A equals (2 +
2)2 = 16, and Quantity B equals
4 + 8 = 12.
- B, C, D, E
If 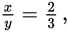 then 3x = 2y and
then 3x = 2y and
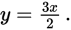 Substitute
Substitute
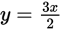 into the equation
into the equation
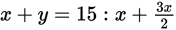 = 15, 2x + 3x = 30, 5x =
30, x = 6. Then,
= 15, 2x + 3x = 30, 5x =
30, x = 6. Then,
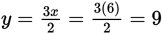 and y2 = 81.
So any answer with greater than 81 under the radical will be greater than
y. Therefore, the correct choices are (B),
(C), (D), and (E).
and y2 = 81.
So any answer with greater than 81 under the radical will be greater than
y. Therefore, the correct choices are (B),
(C), (D), and (E).
- A, B, E
The best place to start here is with pairs of positive integers that have a product of 10. The numbers 5 and 2 have a product of 10, as do 10 and 1. But remember that integers may be negative, so −1 and −10 are possible, as well as −2 and −5. The mean of −1 and −10 is −5.5; the mean of −2 and −5 is −3.5. The mean of 2 and 5 is 3.5. The correct answers are (A), (B), and (E). - C, D, E
The prime factorization of 210 is 2 × 3 × 5 × 7. The sum of the prime factors is 2 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 17. So, the correct choices are (C), (D), and (E). - 9
Use the definition of average to write the sum of the first n bowlers’ scores:
 therefore, n ×
average = sum of scores. Substitute the values given
in the question, and you have 160n
= sum of scores for the initial set of bowlers.
Now write the formula for the average again, using the
additional score of 170. Now there are n + 1 bowlers.
therefore, n ×
average = sum of scores. Substitute the values given
in the question, and you have 160n
= sum of scores for the initial set of bowlers.
Now write the formula for the average again, using the
additional score of 170. Now there are n + 1 bowlers.
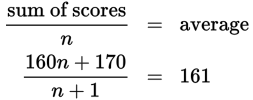
Cross multiply and use algebra to solve for n.
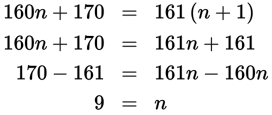
There were 9 bowlers in the original group.
- E
First, identify the numbers in set T: 3, 5, 7, 11, 13. The average of the numbers in set T is 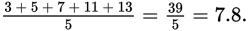 Its standard deviation is given in the question stem
as 3.71. In order to increase the standard deviation of a set of
numbers, you must add a value that is more than one standard
deviation away from the mean. One standard deviation below
the mean for set T would be 7.8
− 3.71 = 4.09, and one standard deviation
above the mean would be 7.8 + 3.71
= 11.51. Any value outside this range 4.09 ≤ x ≤ 11.51
would increase set T’s standard deviation, since it would
make the set more “spread out” from the mean than it currently is.
The only choice that does that is choice (E).
Its standard deviation is given in the question stem
as 3.71. In order to increase the standard deviation of a set of
numbers, you must add a value that is more than one standard
deviation away from the mean. One standard deviation below
the mean for set T would be 7.8
− 3.71 = 4.09, and one standard deviation
above the mean would be 7.8 + 3.71
= 11.51. Any value outside this range 4.09 ≤ x ≤ 11.51
would increase set T’s standard deviation, since it would
make the set more “spread out” from the mean than it currently is.
The only choice that does that is choice (E).
- C
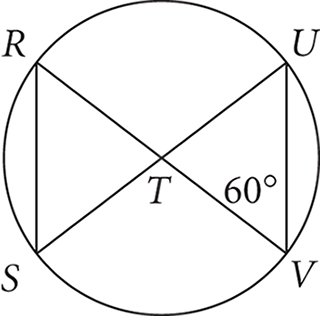
Solving this problem involves several steps, but none is too complicated. The circle has its center at point T. Start with the triangle on the right whose vertices are at T and two points on the circumference of the circle. This makes two of its sides radii of the circle, which we’re told each have a length of 3. Because all radii must have equal length, this makes the triangle an isosceles triangle. In addition, you’re told one of the base angles of this triangle has measure 60°. Thus, the other base angle must also have measure 60° (since the base angles in an isosceles triangle have equal measure). The sum of the two base angles is 120°, leaving 180° − 120° or 60° for the other angle, the one at point T (making ΔTUV an equilateral triangle with sides of 3).
Now, angle RTS is opposite this 60° angle, so its measure must also be 60°. Therefore, ΔRST is another equilateral triangle, and its sides are 3. Therefore, the length of RS is 3, choice (C).
- B
The probability formula is
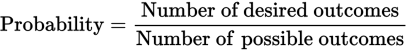
When one die is rolled, there are six possible outcomes. When two dice are rolled, the number of possible outcomes is 6 × 6, or 36. Getting a total value of 7 can be achieved in the following ways: (1, 6), (2, 5), (3, 4), (4, 3), (5, 2), and (6, 1). There are six possible ways.
So the probability of rolling a total of 7 is
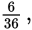 which can be reduced to
which can be reduced to
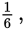 choice (B).
choice (B).
- 8
In the first scenario, each day,
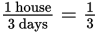 of the house will be built. Because there are 10
workers, each person can build
of the house will be built. Because there are 10
workers, each person can build
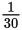 of a house each day. In the second scenario, there are
15 workers, so that means
of a house each day. In the second scenario, there are
15 workers, so that means
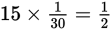 a house can be built each day. Four houses could,
therefore, be built in 8 days:
a house can be built each day. Four houses could,
therefore, be built in 8 days:
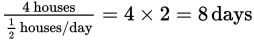
- C
The residential usage (in billions) in 2000 was about 22; the usage was about 52 in 2010. The range is the difference because the residential usage increased over the time period. Therefore, 52 − 22 = 30, and the range is about 30 billion gallons. The correct answer is (C). - C
The two amounts were closest to each other in 2002. The residential amount appears to be about 28; the total appears to be about 32: 28 ÷ 32 = 0.875. Choice (C) is the closest. - D
The three usages with the greatest amounts per person are faucets, washers, and showers, totaling 30 gallons per day. Multiply by 10,000 to get 300,000, choice (D). - B
The residential consumption (in billions) in 2010 was approximately 52. Take half of that amount, 26, to represent the amount of water used by households with efficient appliances and plumbing. Let W represent the amount of water these households would have used otherwise.
Set up a percent equation to solve for W. Remember, the savings were 35%, so subtract 35 from 100 to find the percent that would have been used.

The savings in billions of gallons was 40 − 26 = 14. The correct answer is (B).