Chapter 3 : Python variables, Datatypes & Operators
Important points to note are:
-
In most programming languages, you need to declare the data type of a variable. For example: int
x = 5, String
y = “John” etc, where int
refers to an integer value and String
refers to a sequence of character value.
But in Python, you do not have to declare the data type of a variable. Python understands the data type of any variable simply from its value.
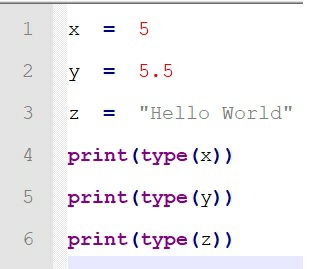
Let us consider the example below:
Output
When we run the above piece of code, Python shows the data types of variable x
, y
and z
.
What is
type( ) function?
type( )
function is used to determine the data type of a variable.
Apart from data types like int
, float
and string
, Python also has list
, tuple
and dictionaries
.
Important points to note are:
3.1.1: What is String Slicing in Python?
Python String slicing is the process of obtaining a sub string of the given string.
Syntax:
string
[
index_number_start
(including its value)
:
index_number_stop
(excluding its value)
]
Example:
Open Notepad++
and create a new python file and write the
following lines of code.
Now run the above piece of code:
Code explanation:
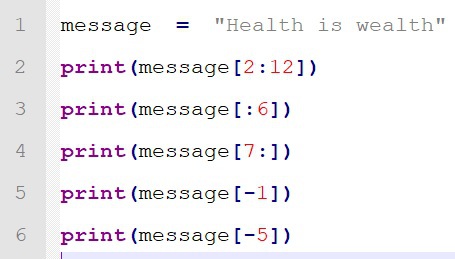
Let’s look into the message “Health is wealth”.
Index number always starts from 0. Letter H
is present at index number 0, letter e
is present at index number 1, letter a
is present at index number 2, letter l
is present at index number 3, letter t
is present at index number 4, letter h
is present at index number 5. Then whitespace is present at index number 6. Letter i
is present at index number 7, letter s
is present at index number 8. Then again whitespace is present at index number 9. Letter w
is present at index number 10, Letter e
is present at index number 11, Letter a
is present at index number 12, Letter l
is present at index number 13, Letter t
is present at index number 14, Letter h
is present at index number 15.
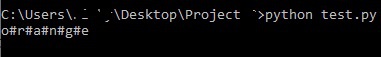
In the above piece of code, the output of message[2:12]
is :
print
values from 2
(including its value at index position 2)
to 12
(excluding its value at index position 12)
alth is we
The output of message[:6]
is : print values from start
(index position 0, including its value)
to 6
(excluding its value at index position 6)
Health
The output of message[7:]
is : print values from 7
(including its value at index position 7)
to end
is wealth
To print letters or values from the end
of a string, minus sign is used. For example: message[-1]
will return
h
,
message[-2]
will return
t
and so on.
3.1.2:
Important and commonly used String methods
-
len( )
function returns the length of the string.
Syntax: len(string)
-
lower( )
function returns the string with lower case characters.
Syntax: string.lower()
-
upper( )
function returns the string with upper case characters.
Syntax: string.upper()
-
strip( )
function gets rid of left or right whitespace.
Syntax: string.strip()
-
lstrip( )
function gets rid of left whitespace.
Syntax: string.lstrip()
-
rstrip( )
function gets rid of right whitespace.
Syntax: string.rstrip()
-
index( )
function returns the index number of the given element.
Syntax: string.index(element
)
Output:
-
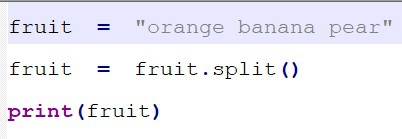
split( )
function returns the list
of substrings separated by whitespace.
Syntax: string.split( )
Output:
-
replace(old,new)
function replaces the old with new.
Syntax: string.replace(old,new)
Output:
-
join( )
string method returns a string by joining all the elements of an iterable (lists, tuples and string) with the delimiter.
Syntax: delimiter.join(iterable)
Output:
3.1.3:
String formatting
format( )
method is used to format a string.
Rules for string formatting:
- Create a placeholder with the help of curly brackets {}.
- Call the format
method and pass variables as parameters. When program executes, the values passed to these parameters will replace the curly brackets placeholders.
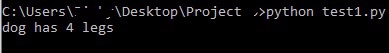
Example 1:
In the above example, the values passed to variable animal
will fill the first
placeholder and the value passed to variable legs
will fill the second
placeholder.
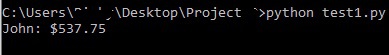
Output:
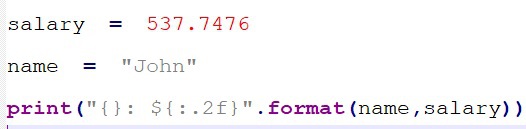
Example 2:
If you want to display a float number with two digits after the decimal dot, formatting expression {:.2f}
is used.
Output:
●
A Python List
is very similar to an Array
. It contains a list of elements separated by commas and its elements are written with square brackets [
…. ]
.
●
Python list are mutable meaning that we can modify list elements.
●
A value from a List
can be accessed from its index value.
Syntax for accessing the values from a List is:
List_name
[
index_num
]
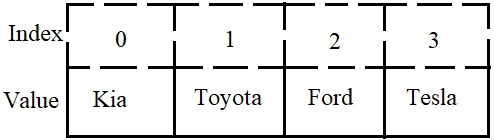
An Array is a collection of items or elements all having the same datatype. An element from an array can only be accessed from its index value. Example:
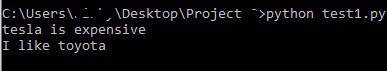
Let’s create an array of cars.
cars
= [“Kia”, “Toyota”, “Ford”, “Tesla”]
In order to get the value Ford
as output, we need to write print
(
cars
[
2
] )
Example:
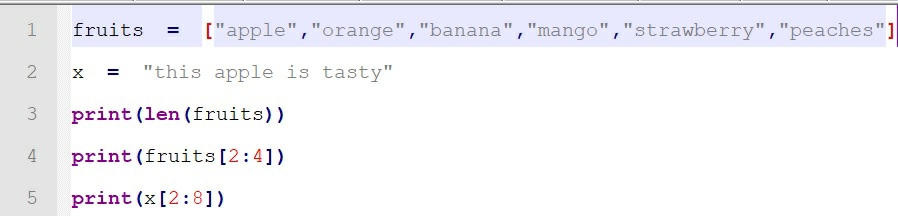
Create a new Python file (variables.py
) and write the following lines of code:
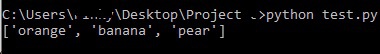
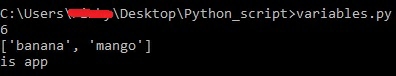
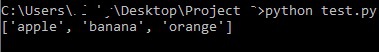
After running the above piece of code, we get an output of:
Code explanation:
●
In the above piece of code, fruits
is a List
containing 6 elements. The value at position 0 is “apple
”, at position 1 is “orange
” and so on.
●
x
is a variable holding a string value. The value at position 0 is “t”
, at position 1 is “h
” and so on.
●
len( )
function is used to get the length of the list
.
●
In Line 4 and 5 we are performing Slicing operation
.
Output:
[‘banana’, ‘mango’]
Output:
is app
3.2.1:
Important and commonly used List methods
-
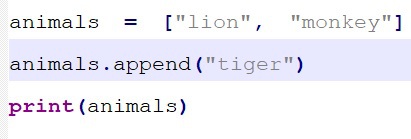
append( ) method inserts the element at the end of the list.
Syntax: list.append(element
)
Output:
-
insert( ) method inserts an element at the specified index number.
Syntax: list.index(index_num
, element
)
Output:
-
remove( ) method removes the first occurrence of element specified.
Syntax: list.remove(element
)
Output:
●
A Tuple
is very much like a List
. It contains elements separated by commas within open and close parenthesis (
…. )
.
●
Python tuple are immutable meaning once a tuple is declared, it cannot be modified.
Difference between Tuple and List
|
Tuple
|
List
|
|
Tuple contains elements within (… ) parenthesis
|
List contains elements within [ …] square brackets
|
|
Once a tuple is created, no item can be added, updated or deleted
|
List gives us the ability to add, update and delete items.
|
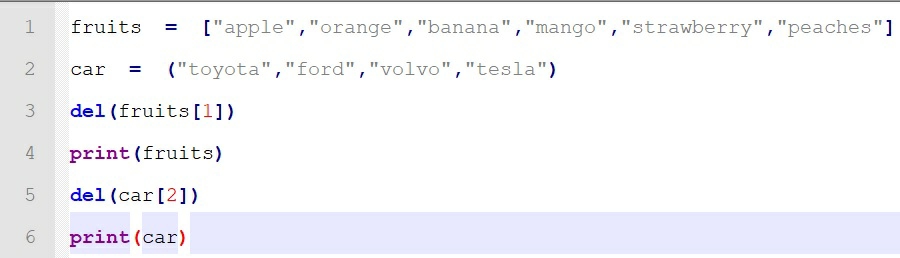
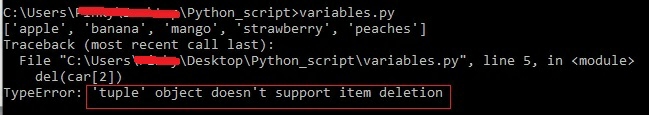
Example:
After running the above piece of code, we get an output of:
del ( ) function
is used to delete element from a certain position.
When applying delete function to fruits
list
, the value at position 1 (orange
) was deleted successfully. But in case of tuple
, when we tried to delete an element at position 2, it threw an error.
3.3.1: What is unpacking a tuple mean?
When we create a tuple and assign new values into it. This is called packing a tuple.
When we extract those values and store them into a variable. This is called unpacking a tuple.
Output:
Example:
After running the above piece of code, we get an output of:
3.4.1:
Important Dictionary operations and methods
-
Now let’s insert
some new records.
To insert new records into the dictionary, the syntax is:
dictionary_name
[
key
] =
value
Output:
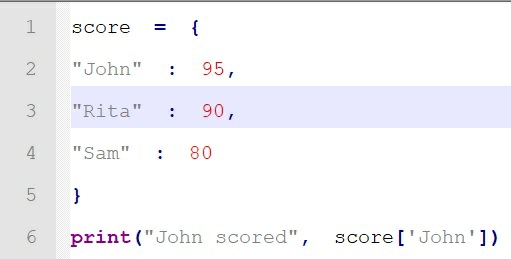
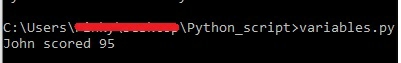
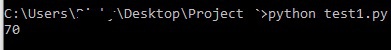
-
Update a record
To update a record, the syntax is same as insert a new record.
Output:
In the above piece of code, we see the new value (70
) assigned to key John
replaces the old value (95
).
-
Delete a record
To delete a record from a dictionary, del
keyword is used. Syntax:
del
dictionary_name
[
key
]
Important Dictionary Methods:
1. To iterate through dictionary, items( )
method is used. Syntax:
dictionary.items( )
(example present in chapter 5
)
2. To display only dictionary keys, key( )
method is used.
Syntax:
dictionary.keys( )
3. To display only dictionary values, values( )
method is used.
Syntax:
dictionary.values( ).
3.5.1: Commonly used Arithmetic operators
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
+
|
Addition
|
|
-
|
Subtraction
|
|
*
|
Multiplication
|
|
/
|
Division
|
|
%
|
Modulus. This sign returns the remainder.
|
|
**
|
Exponentiation. For example: 2 ** 3 means 2 to the power of 3 and that is equal to 8
|
|
//
|
Floor division. This operator returns only the whole integer number. For example: 23 // 2 will give 11
|
3.5.2: Commonly used Comparison Operators
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
= =
|
Equals: x = = y
|
|
!=
|
Not Equals: x != y
|
|
<
|
Less than: x < y
|
|
<=
|
Less than or equal to: x <= y
|
|
>
|
Greater than: x > y
|
|
>=
|
Greater than or equal to: x >= y
|
3.5.3: Commonly used Logical Operators
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
and
|
Example:
x = 123 and
y = “John” executes certain block of code if both
statements are TRUE
|
|
or
|
Example:
x = 123 or
y = “John” executes certain block of code if one
of the statements is TRUE
|
|
in
|
Example:
x = [ 123 , 345 ]
if 123 in
x returns TRUE, then executes certain block of code
|
|
not in
|
Example:
x = [ 123 , 345 ]
if 12 not in
x returns TRUE, then executes certain block of code
|
3.5.4: Commonly used Assignment Operators
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
=
|
Example: x = 2, this means value 2 is assigned to x
|
|
+=
(x += 1)
|
This is same as x = x + 1. If value of x = 3, then the new value of x is 3 + 1 = 4
|
|
-=
(x -= 2)
|
This is same as x = x – 2. If value of x = 5, then the new value of x is 5 – 2 = 3
|
|
*=
(x *= 5)
|
This is same as x = x * 5. If value of x = 2, then the new value of x is 2 * 5 = 10
|
|
/=
(x /= 2)
|
This is same as x = x / 2. If value of x is 10, then the new value of x is 10 / 2 = 5
|
|
%=
(x %= 2)
|
This is same as x = x % 2. If value of x is 10, then the new value of x is 10 % 2 = 0
|