Appendix II
Molecular Formula/Weight, Physical Properties (Boiling Point, Saturation, Water Solubility) and Partition Coefficients (Air–Water, Measured Direct or Estimated)
II.1 Units
Boiling point in °C:
(1) at normal atmospheric pressure (760 mmHg or 101.3 kPa);
(2) at sub-atmospheric pressure (in mmHg).
Saturation water solubility figure (S) expressed in either, %w/w (w/ws-solutions), or parts of volatile compound (‘j’) per 100 parts of water (‘w’), at T°C given in the superscript figure, though the difference in value is small for percentages below five parts. Qualitative data is given as soluble (s), very slightly soluble (v.sl.s) or insoluble (i).
Partition coefficient (air–water), K j,a-w either directly determined (value preferably with precision data) and given in the literature, or estimated from vapour pressure data/activity coefficient as described in Appendix I, at temperature T°C stated.
II.2 Data sources
Boiling point (vapour pressure) and solubility data are taken from Perry & Green (1997), Kirk-Othmer (1994), Lide (2001) and Burdock (2003).
Directly determined partition coefficients from Buttery et al. (1969, 1971), Gretsch et al. (1995) and Pollien & Yeretzian (2001), loc. cit.
Vapour pressures expressed in mmHg (1 mmHg = 0.133 kPa).
Tables II.1, II.2, II.3, II.4, II.5, II.6, II.7, II.8, II.9 and II.10 are compilations of the available data for each of the groups of the volatile compounds, already described as being present in wines in Chapter 4. The dashes in column positions mean that data is inadequate or not available for calculation. For certain groups of compounds, Pierotti correlations are not given, and calculations are not possible to provide estimates of partition coefficients (K j,a-w).
Table II.1 Volatile esters in wine (multi-referenced). Molecular formula and weight. Physical properties (boiling point; saturation water solubility (S); partition coefficients, Kj,a-w, measured direct or estimated).
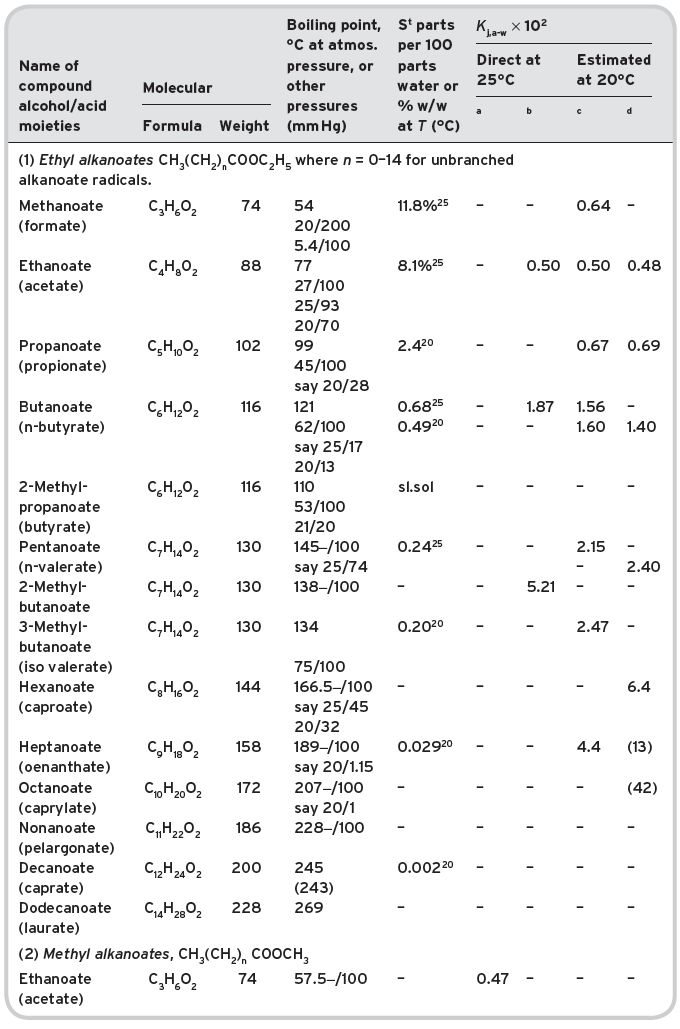
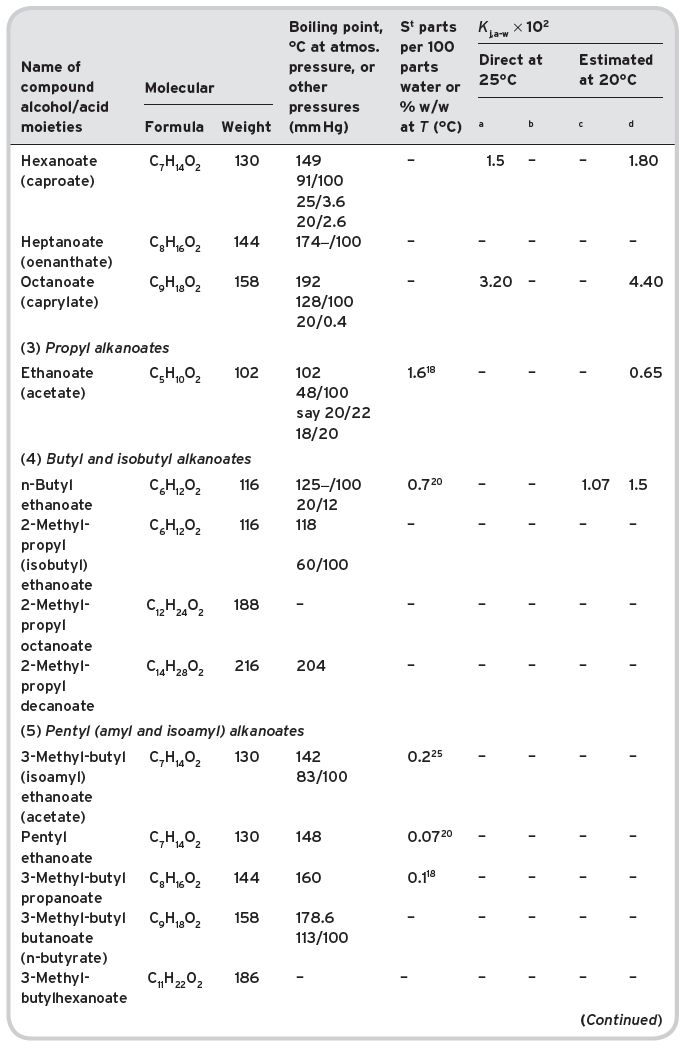
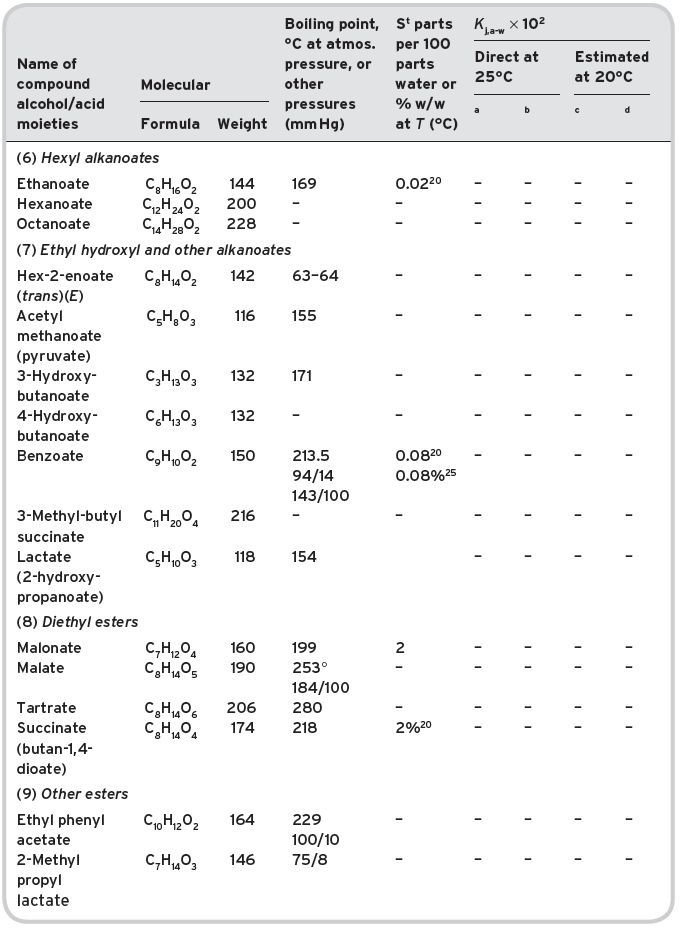
aData from Buttery et al. (1969, 1999) for methyl alkanoates only. bData from Pollien & Yeretzian (2001). cCalculated from solubility data. dCalculated from Pierotti (1959).
Table II.2 Volatile aldehydes in wines.
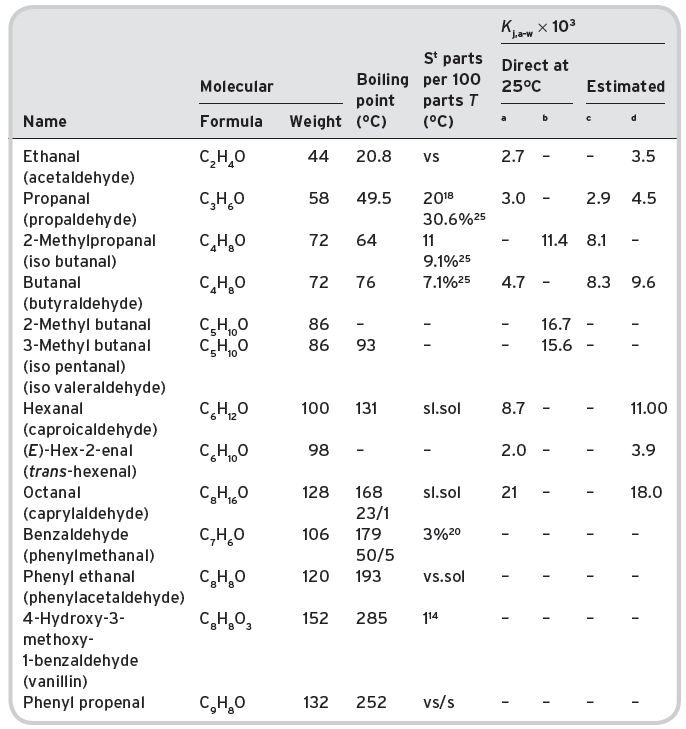
aButtery et al. (1969). bPollien & Yeretzian (2001). cCalculated from S. dCalculated from Pierotti (1959).
Table II.3 Volatile ketones in wines.
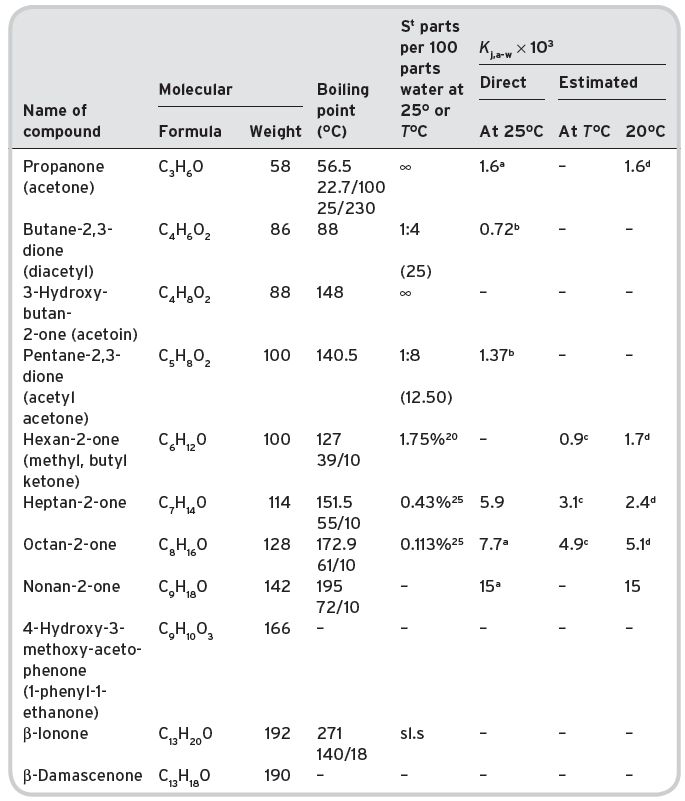
aButtery et al. (1969). bPollien & Yeretzian (2001). cCalculated from S. dCalculated from Pierotti (1959).
Table II.4 Volatile alcohols in wine (alkanols and alkenols).

aButtery (1969). b From solubility data. c From Pierotti (1959).
Table II.5 Volatile furanones/lactones in wines.
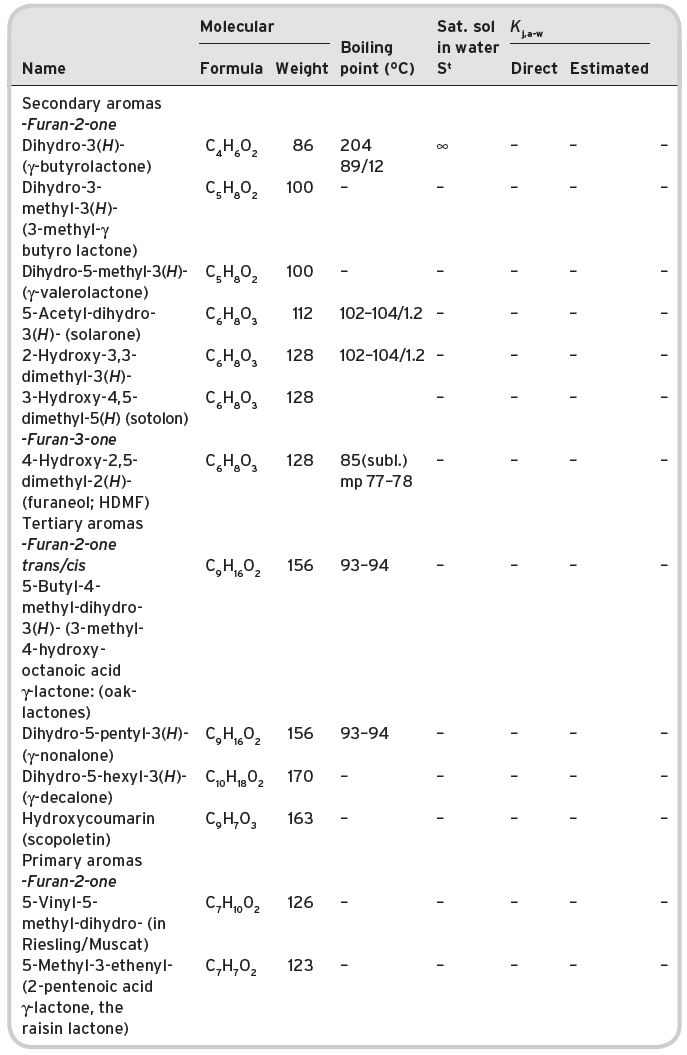
NB: Inadequate or non-available data currently for solubility and vapour pressure. Pierotti correlations not available.
Table II.6 Volatile acids in wines (n-alkanoic acids CH3 (CH2)n COOM, also some iso branched chain variants).
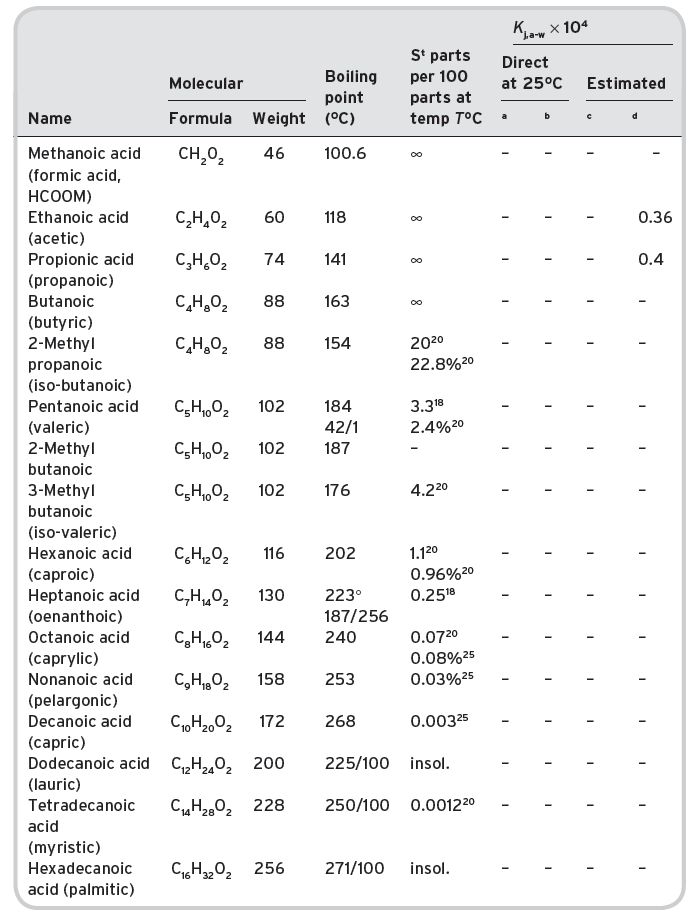
a,bData not available. cData inadequate. dPierotti correlations.
Table II.7 Volatile phenols in wines.
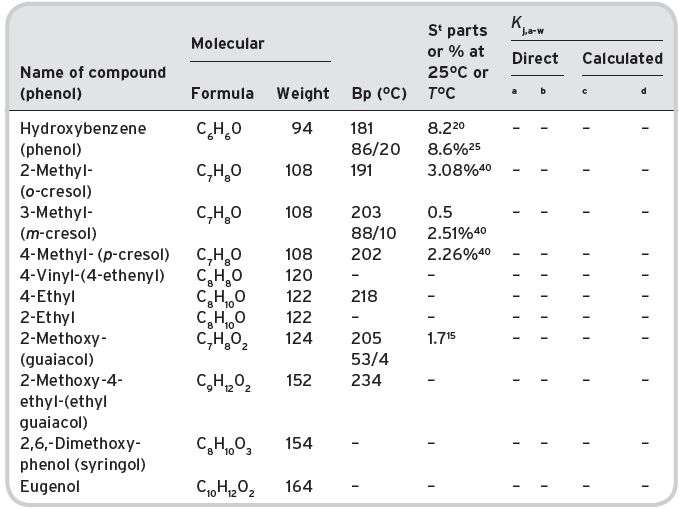
a,bData not available. cData inadequate. dPierotti correlations not available.
Table II.8 Volatile terpenes in wines.
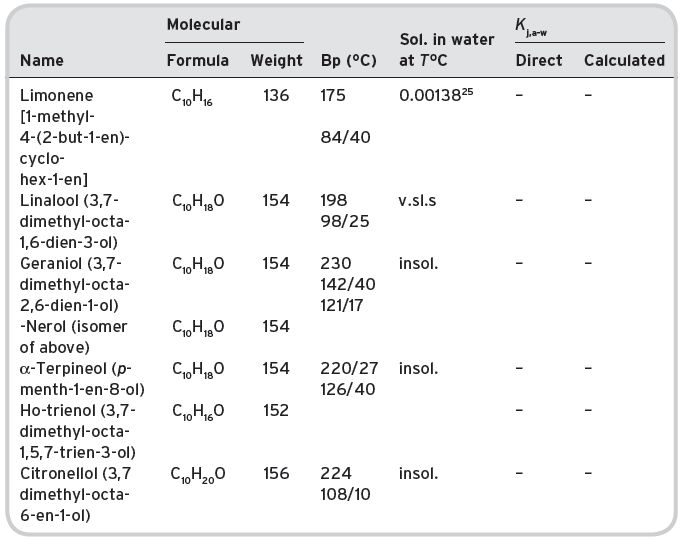
Table II.9 Volatile methoxy pyrazines in wines.
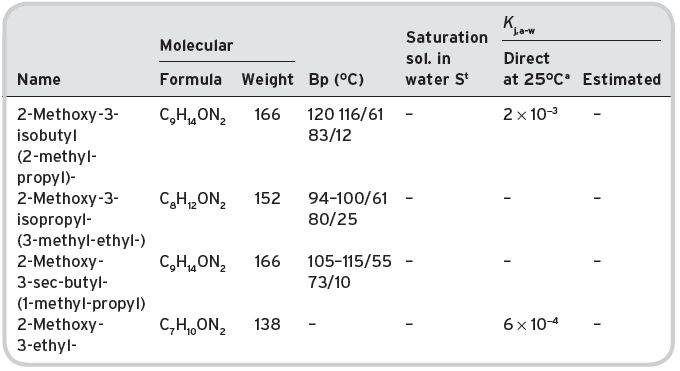
aData from Buttery et al. (1971).
Table II.10 Volatile sulfur compounds in wines.
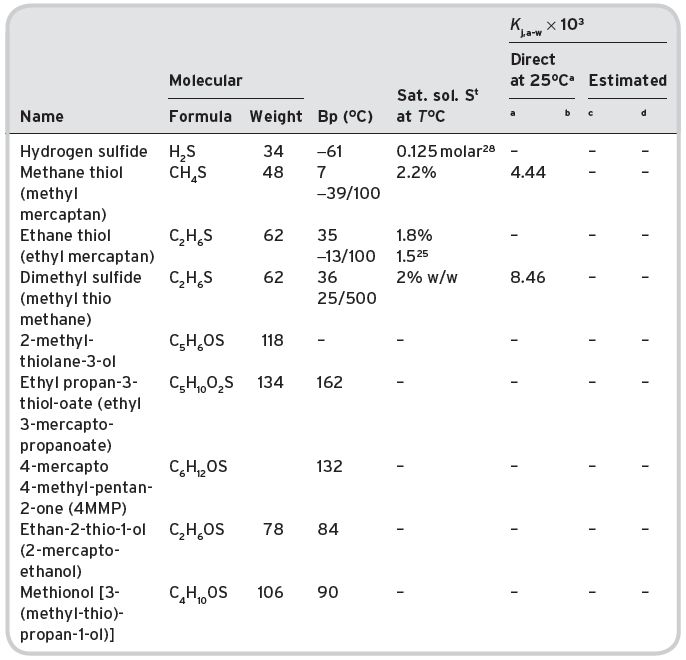
aPollien & Yeretzian (2001). bNo other data. cCalculated from St. dCalculated from Pierotti (1959). c,dData not available or inadequate.
References
Buckingham, J. & McDonald, F. (eds.) (1982, 1996) Dictionary of Organic Compounds 6th edn. Chapman and Hall/CRC Press, London.
Kirk-Othmer (1994) Kirk-Othmer Encyclopaedia of Chemical Technology, 4th edn. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
Lide, D. (ed.) (2001) Handbook of Chemistry and Physic, 81st edn., CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Burdock, G.H. (2003) Fenaroli’s Handbook of Food Flavour Ingredients, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Buttery, R.G., Guadagni, D.E. & Ling, L.C. (1969) Volatilities of aldehydes, ketones and esters in dilute solution. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 17(2), 385–389.
Buttery, R.G., Bomben, J.L., Guadagni, D.G. & Ling, L.C. (1971) Volatilities of organic compounds in foods. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 19, 1045–1048.
Buttery, R.G. (1999) Flavour chemistry and odour thresholds. In: Flavour Chemistry: Thirty years of progress (eds. R. Teranishi, E.L. Wick & J. Hornstein), pp. 353–365. Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New York.
Gretsch, C., Grandjean, G., Maering, M., Liardon, K. & Westfall, S. (1995) Determination of the partition coefficients of coffee volatiles using static head-space. In: Proceedings of the 16th ASIC Colloquium (Kyoto), pp. 326–31, ASIC, Paris, France.
Perry, R.H. & Green, D.W. (eds.) (1997) Perry’s Chemical Engineer’s Handbook, 7th edn. McGraw-Hill.
Pierotti, G.J., Deal, C.H. & Derr, E.L. (1959) Activity Coefficients and Molecular Structure. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 51, 95–102.
Pollien, P. & Yeretzian, C. (2001) Measurement of partition coefficients. Proceedings of the 19th ASIC Colloquium on Coffee, CD-ROM, ASIC, Paris.