3.9 Augmented Assignments
Augmented assignments abbreviate assignment expressions in which the same variable name appears on the left and right of the assignment’s =, as total does in:
for number in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]:total = total + number
Snippet [2] reimplements this using an addition augmented assignment (+=) statement:
In [1]: total = 0In [2]: for number in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]:...: total += number # add number to total and store in number...:In [3]: totalOut[3]: 15
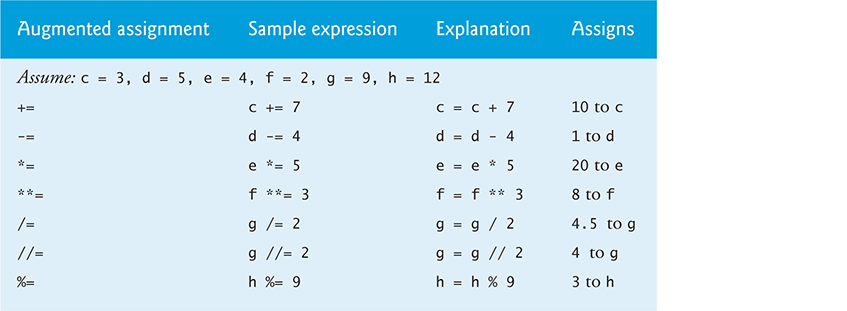
The += expression in snippet [2] first adds number’s value to the current total, then stores the new value in total. The table below shows sample augmented assignments:
 Self Check
Self Check
(Fill-In) If
xis7, the value ofxafter evaluatingx*=5is ___________ .
Answer:35.(IPython Session) Create a variable
xwith the value12. Use an exponentiation augmented assignment statement to squarex’s value. Showx’s new value.
Answer:In [1]: x = 12In [2]: x **= 2In [3]: xOut[3]: 144