Chapter 11
Java Class Design
THE OCP EXAM TOPICS COVERED IN THIS PRACTICE TEST INCLUDE THE FOLLOWING:
 Java Class Design
Java Class Design
- Implement encapsulation
- Implement inheritance including visibility modifiers and composition
- Implement polymorphism
- Override hashCode, equals, and toString methods from Object class
- Create and use singleton classes and immutable classes
- Develop code that uses static keyword on initialize blocks, variables, methods, and classes
-
Which answer choice can replace line 6 so the code continues to produce the same output?
3: List<String> rug = new ArrayList<>();4: rug.add("circle");5: rug.add("square");6: System.out.println(rug);- System.out.println(rug.asString);
- System.out.println(rug.asString());
- System.out.println(rug.toString);
- System.out.println(rug.toString());
-
Which best describes this code?
class Stats {private int data;public int getData() {return data;}public void setData(int data) {this.data = data;}}- It is a singleton.
- It is well encapsulated.
- It is immutable.
- It is both well encapsulated and immutable.
-
What design pattern or principle ensures that there will be no more than one instance of a class?
- Encapsulation
- Immutability
- Singleton
- Static
-
What is the output of this code?
class Laptop extends Computer {public void startup() {System.out.print("laptop-");}}public class Computer {public void startup() {System.out.print("computer-");}public static void main(String[] args) {Computer computer = new Laptop();Laptop laptop = new Laptop();computer.startup();laptop.startup();}}- computer-laptop-
- laptop-computer-
- laptop-laptop-
- None of the above
-
Which method can be correctly inserted into this class to meet the contract of the equals() method? You may assume that text is not null.
class Button {private String text;public int hashCode() {return text.hashCode();}}-
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if ( o == null ) return true;
if (! (o instanceof Button)) return false;
return text.equals(o.text);
}
-
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if ( o == null ) return true;
Button b = (Button) o;
return text.equals(b.text);
}
-
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (! (o instanceof Button)) return false;
return text.equals(o.text);
}
-
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (! (o instanceof Button)) return false;
Button b = (Button) o;
return text.equals(b.text);
}
-
-
Fill in the blanks: ____________means the state of an object cannot be changed while ____________means that it can.
- Immutability, mutability
- Rigidity, flexibility
- Static, instance
- None of the above
-
Which is the first line to fail to compile?
class Tool {void use() { } // r1}class Hammer extends Tool {private void use() { } // r2public void bang() { } // r3}- r1
- r2
- r3
- None of the above
-
Which of these classes properly implement(s) the singleton pattern?
class ExamAnswers {private static ExamAnswers instance = new ExamAnswers();private List<String> answers = new ArrayList<>();public static List<String> getAnswers() {return instance.answers;}}class TestAnswers {private static TestAnswers instance = new TestAnswers();private List<String> answers = new ArrayList<>();public static TestAnswers getTestAnswers() {return instance;}public List<String> getAnswers() {return answers;}}- ExamAnswers
- TestAnswers
- Both classes
- Neither class
-
What does the following print?
public class Transport {static interface Vehicle {}static class Bus implements Vehicle {}public static void main(String[] args) {Bus bus = new Bus();boolean n = null instanceof Bus;boolean v = bus instanceof Vehicle;boolean b = bus instanceof Bus;System.out.println(n + " " + v + " " + b);}}- true true true
- false true true
- false false false
- None of the above
-
What technique allows multiple variables from the same class to be shared across all instances of a class?
- Encapsulation
- Immutability
- Singleton
- Static
-
Which is not a requirement for a class to be immutable?
- A private constructor is provided.
- Any instance variables are private.
- Methods cannot be overridden.
- There are no setter methods.
-
Which statement is true about encapsulation while providing the broadest access allowed?
- Variables are public and methods are private.
- Variables are public and methods are public.
- Variables are private and methods are public.
- Variables are private and methods are private.
-
What does the following print?
class Laptop extends Computer {String type = "laptop";}public class Computer {String type = "computer";public static void main(String[] args) {Computer computer = new Laptop();Laptop laptop = new Laptop();System.out.print(computer.type + "," + laptop.type);}}- computer,laptop
- laptop,computer
- laptop,laptop
- None of the above
-
Which of these classes is/are immutable?
public final class Flower {private final String name;private final List<Integer> counts;public Flower(String name, List<Integer> counts) {this.name = name;this.counts = counts;}public String getName() {return name;}public List<Integer> getCounts() {return counts;}}public final class Plant {private final String name;private final List<Integer> counts;public Plant(String name, List<Integer> counts) {this.name = name;this.counts = new ArrayList<>(counts);}public String getName() {return name;}public List<Integer> getCounts() {return new ArrayList<>(counts);}}- Flower
- Plant
- Both classes
- Neither class
-
Which methods compile?
private static int numShovels;private int numRakes;public int getNumShovels() {return numShovels;}public int getNumRakes() {return numRakes;}- Just getNumRakes()
- Just getNumShovels()
- Both methods
- Neither method
-
Which methods compile?
private static int numShovels;private int numRakes;public static int getNumShovels() {return numShovels;}public static int getNumRakes() {return numRakes;}- Just getNumRakes()
- Just getNumShovels()
- Both methods
- Neither method
-
How many lines of the main method fail to compile?
11: static interface Vehicle {}12: static class Bus implements Vehicle {}13:14: public static void main(String[] args) {15: Bus bus = new Bus();16:17: System.out.println(null instanceof Bus);18: System.out.println(bus instanceof Vehicle);19: System.out.println(bus instanceof Bus);20: System.out.println(bus instanceof ArrayList);21: System.out.println(bus instanceof Collection);22: }- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
-
Which variable declaration is the first line not to compile?
class Building {}class House extends Building{}public void convert() {Building b = new Building();House h = new House();Building bh = new House();Building p = (House) b;House q = (Building) h;Building r = (Building) bh;House s = (House) bh;}- p
- q
- r
- s
-
Which statement is true about the code that can fill in the blank?
class Sticker {public int hashCode() {return 1;}public boolean equals(Object o) {return____________ ;}}- It must return false.
- It must return true.
- It can return either true or false.
- None of the above.
-
What change is needed to make Secret well encapsulated?
import java.util.*;public class Secret {private int number = new Random().nextInt(10);public boolean guess(int candidate) {return number == candidate;}}- Change number to use a public access modifier.
- Declare a private constructor.
- Remove the guess method.
- None. It is already well encapsulated.
-
Which of these classes best implement(s) the singleton pattern?
class ExamAnswers {private static ExamAnswers instance = new ExamAnswers();private List<String> answers = new ArrayList<>();private ExamAnswers() {}public ExamAnswers getExamAnswers() {return instance;}public List<String> getAnswers() {return answers;}}class TestAnswers {private static TestAnswers instance = new TestAnswers();private List<String> answers = new ArrayList<>();private TestAnswers() {}public static TestAnswers getTestAnswers() {return instance;}public List<String> getAnswers() {return answers;}}- ExamAnswers
- TestAnswers
- Both classes
- Neither class
-
How many lines does the following code output?
public class Cars {static {System.out.println("static");}private static void drive() {System.out.println("fast");}public static void main(String[] args) {drive();drive();}}- One
- Two
- Three
- None of the above. The code does not compile.
-
Which is not a true statement given this diagram?
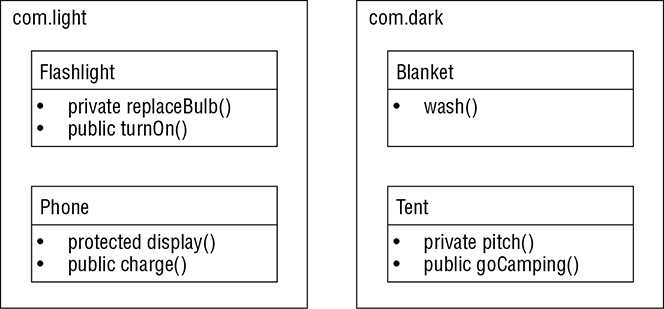
- Instance methods in the Blanket class can call the Flashlight class’s turnOn().
- Instance methods in the Flashlight class can call the Flashlight class’s replaceBulb().
- Instance methods in the Phone class can call the Blanket class’s wash().
- Instance methods in the Tent class can call the Tent class’s pitch().
-
Given the diagram in the previous question, how many of the classes can call the display() method?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
-
What does the following print?
1: class SmartWatch extends Watch {2: private String getType() { return "smart watch"; }3: public String getName(String suffix) {4: return getType() + suffix;5: }6: }7: public class Watch {8: private String getType() { return "watch"; }9: public String getName(String suffix) {10: return getType() + suffix;11: }12: public static void main(String[] args) {13: Watch watch = new Watch();14: SmartWatch smartWatch = new SmartWatch();15: System.out.print(watch.getName(","));16: System.out.print(smartWatch.getName(""));17: }18: }- smart watch,watch
- watch,smart watch
- watch,watch
- None of the above
-
What does the following print?
public class Transport {static interface Vehicle {}static class Bus implements Vehicle {}static class Van extends Bus {}public static void main(String[] args) {Bus bus = new Van();Van van = new Van();Van[] vans = new Van[0];boolean b = bus instanceof Vehicle;boolean v = van instanceof Vehicle;boolean a = vans instanceof Vehicle[];System.out.println(b + " " + v + " " + a);}}- true true true
- false true true
- true false false
- None of the above. The code does not compile
-
Which of the following correctly fills in the blank so this code compiles and prints true?
public class Button {private String text;public int hashCode() {return text.hashCode();}public boolean equals(Object o) {if (____________) return false;Button b = (Button) o;return text.equals(b.text);}public static void main(String[] args) {Button b1 = new Button();Button b2 = new Button();b1.text = "mickey";b2.text = "mickey";System.out.println(b1.equals(b2));}}- (o instanceof Button)
- (o instanceOf Button)
- !(o instanceof Button)
- !(o instanceOf Button)
-
Which is the first line to fail to compile?
class Tool {void use() { } // r1}class Hammer extends Tool {private void use(String s) { } // r2public void bang() { } // r3}- r1
- r2
- r3
- None of the above
-
What is lazy instantiation?
- A technique that can be used in an immutable class to wait until the first use to create the object
- A technique that can be used in a singleton to wait until the first use to create the object
- A technique that can be used in an immutable class to save memory when creating the object
- A technique that can be used in a singleton to save memory when creating the object
-
Which variable declaration is the first line not to compile?
30: class Building {}31: class House extends Building{}32:33: public void convert() {34: Building b = new Building();35: House h = new House();36: Building bh = new House();37: House p = (House) b;38: House q = (House) h;39: House r = (House) bh;40: }- p
- q
- r
- None of the above
-
Which statement about encapsulation is not true?
- Encapsulation allows putting extra logic in the getter and setter methods.
- Encapsulation can use immutable instance variables in the implementation.
- Encapsulation causes two classes to be more tightly tied together.
- Encapsulation makes it easier to change the instance variables in the future.
-
Which of these classes is/are immutable?
public class Flower {private final String name;private final List<Integer> counts;public Flower(String name, List<Integer> counts) {this.name = name;this.counts = new ArrayList<>(counts);}public final String getName() {return name;}public final List<Integer> getCounts() {return new ArrayList<>(counts);}}public class Plant {private final String name;private final List<Integer> counts;public Plant(String name, List<Integer> counts) {this.name = name;this.counts = new ArrayList<>(counts);}public String getName() {return name;}public List<Integer> getCounts() {return new ArrayList<>(counts);}}- Flower
- Plant
- Both classes
- Neither class
-
How many lines does the following code output?
public class Cars {private static void drive() {static {System.out.println("static");}System.out.println("fast");}public static void main(String[] args) {drive();drive();}}- One
- Two
- Three
- None of the above. The code does not compile.
-
How many of the following pairs of values can fill in the blanks to comply with the contract of the hashCode() and equals() methods?
class Sticker {public int hashCode() {return _____________;}public boolean equals(Object o) {return _____________;}}- 1, false
- 1, true
- new Random().nextInt(), false
- new Random().nextInt(), true
- None
- One
- Two
- Three
-
How do you change the value of an instance variable in an immutable class?
- Call the setter method.
- Remove the final modifier and set the instance variable directly.
- Use a method other than Option A or B.
- You can’t.
-
Which technique or pattern requires instance variables to implement?
- Is-a
- Object composition
- Singleton
- None of the above
-
How many lines of output does the following generate?
public class HowMany {static {System.out.println("any");}{System.out.println("more");}public static void main(String[] args) {new HowMany();new HowMany();}}- Two
- Three
- Four
- None of the above. The code does not compile.
-
Which is the first line to fail to compile?
class Tool {default void use() { } // r1}class Hammer extends Tool {public void use() { } // r2public void bang() { } // r3}- r1
- r2
- r3
- None of the above
-
Which variable declaration is the first line to throw a ClassCastException at runtime?
class Building {}class House extends Building{}public void convert() {Building b = new Building();House h = new House();Building bh = new House();House p = (House) b;House q = (House) h;House r = (House) bh;}- p
- q
- r
- None of the above
-
Which of the following values can fill in the blank for the class to be correctly implemented?
class Sticker {public int hashCode(Object o) {return_____________ ;}public boolean equals(Object o) {return true;}}- -1
- 5
- new Random().nextInt()
- I
- I and II
- I, II, and III
- I and III