Chapter 14
Lambda Built-in Functional Interfaces
THE OCP EXAM TOPICS COVERED IN THIS PRACTICE TEST INCLUDE THE FOLLOWING:
 Lambda Built-in Functional Interfaces
Lambda Built-in Functional Interfaces
- Use the built-in interfaces included in the java.util.function package such as Predicate, Consumer, Function, and Supplier
- Develop code that uses primitive versions of functional interfaces
- Develop code that uses binary versions of functional interfaces
- Develop code that uses the UnaryOperator interface
-
Fill in the blanks: The____________ functional interface does not take any inputs, while the____________ functional interface does not return any data.
- IntConsumer, LongSupplier
- IntSupplier, Function
- Supplier, DoubleConsumer
- UnaryOperator, Consumer
-
Which functional interface takes a long value as an input argument and has an accept() method?
- LongConsumer
- LongFunction
- LongPredicate
- LongSupplier
-
What is the output of the following application?
package beach;import java.util.function.*;class Tourist {public Tourist(double distance) {this.distance = distance;}public double distance;}public class Lifeguard {private void saveLife(Predicate<Tourist> canSave, Tourist tourist) {System.out.print(canSave.test(tourist) ? "Saved" : "Too far"); // y1}public final static void main(String... sand) {new Lifeguard().saveLife(s -> s.distance<4, new Tourist(2)); // y2}}- Saved
- Too far
- The code does not compile because of line y1.
- The code does not compile because of line y2.
-
Which of the following statements about DoubleSupplier and Supplier<Double> is not true?
- Both are functional interfaces.
- Lambdas for both can return a double value.
- Lambdas for both cannot return a null value.
- One supports a generic type, the other does not.
-
Which functional interface, when filled into the blank, allows the class to compile?
package space;import java.util.function.*;public class Asteroid {public void mine(____________ lambda) {// TODO: Apply functional interface}public static void main(String[] debris) {new Asteroid().mine((s,p) -> s+p);}}- BiConsumer<Integer,Double>
- BiFunction<Integer,Double,Double>
- BiFunction<Integer,Integer,Double>
- Function<Integer,Double>
-
Assuming the proper generic types are used, which lambda expression cannot be assigned to a ToDoubleBiFunction functional interface reference?
- (Integer a, Double b) -> {int c; return b;}
- (h,i) -> (long)h
- (String u, Object v) -> u.length()+v.length()
- (x,y) -> {int z=2; return y/z;}
-
Which of the following is not a functional interface in the java.util.function package?
- BiPredicate
- DoubleUnaryOperator
- ObjectDoubleConsumer
- ToLongFunction
-
What is the output of the following application?
package zoo;import java.util.function.*;public class TicketTaker {private static int AT_CAPACITY = 100;public int takeTicket(int currentCount, IntUnaryOperator<Integer> counter) {return counter.applyAsInt(currentCount);}public static void main(String...theater) {final TicketTaker bob = new TicketTaker();final int oldCount = 50;final int newCount = bob.takeTicket(oldCount,t -> {if(t>AT_CAPACITY) {throw new RuntimeException("Sorry, max has been reached");}return t+1;});System.out.print(newCount);}}- 51
- The code does not compile because of lambda expression.
- The code does not compile for a different reason.
- The code compiles but prints an exception at runtime.
-
Which functional interface returns a primitive value?
- BiPredicate
- CharSupplier
- LongFunction
- UnaryOperator
-
Which functional interface, when entered into the blank below, allows the class to compile?
package groceries;import java.util.*;import java.util.function.*;public class Market {private static void checkPrices(List<Double> prices,____________scanner) {prices.forEach(scanner);}public static void main(String[] right) {List<Double> prices = Arrays.asList(1.2, 6.5, 3.0);checkPrices(prices,p -> {String result = p<5 ? "Correct" : "Too high";System.out.println(result);});}}- Consumer
- DoubleConsumer
- Supplier<Double>
- None of the above
-
Which of the following three functional interfaces is not equivalent to the other two?
- BiFunction<Double,Double,Double>
- BinaryOperator<Double>
- DoubleFunction<Double>
- None of the above. All three are equivalent.
-
Which lambda expression can be passed to the magic() method?
package show;import java.util.function.*;public class Magician {public void magic(BinaryOperator<Long> lambda) {lambda.apply(3L, 7L);}}- magic((a) -> a)
- magic((b,w) -> (long)w.intValue())
- magic((c,m) -> {long c=4; return c+m;})
- magic((Integer d, Integer r) -> (Long)r+d)
-
What is the output of the following program?
package ai;import java.util.function.*;public class Android {public void wakeUp(Supplier supplier) { // d1supplier.get();}public static void main(String... electricSheep) {Android data = new Android();data.wakeUp(() -> System.out.print("Program started!")); // d2}}- Program started!
- The code does not compile because of line d1 only.
- The code does not compile because of line d2 only.
- The code does not compile because of both lines d1 and d2.
-
Which statement about all UnaryOperator functional interfaces (generic and primitive) is correct?
- The input type must be compatible with the return type.
- Some of them take multiple arguments.
- They each take a generic argument.
- They each return a primitive value.
-
Starting with DoubleConsumer and going downward, fill in the missing values for the table.
Functional Interface # Parameters DoubleConsumer IntFunction LongSupplier ObjDoubleConsumer - 0, 1, 1, 1
- 0, 2, 1, 2
- 1, 1, 0, 2
- 1, 1, 0, 1
-
Starting with DoubleConsumer and going downward, fill in the values for the table. For the choices below, assume R is a generic type.
Functional Interface Return Type DoubleConsumer IntFunction LongSupplier ObjDoubleConsumer - double, R, long, R
- R, int, long, R
- void, int, R, void
- void, R, long, void
-
Fill in the blanks: In the Collection interface, the method removeIf() takes a____________ , while the method forEach() takes a____________ .
- Function, Function
- Predicate, Consumer
- Predicate, Function
- Predicate, UnaryOperator
-
What is the output of the following application?
package nesting;import java.util.function.*;public class Doll {private int layer;public Doll(int layer) {super();this.layer = layer;}public static void open(UnaryOperator<Doll> task, Doll doll) {while((doll = task.accept(doll)) != null) {System.out.print("X");}}public static void main(String[] wood) {open(s -> {if(s.layer<=0) return null;else return new Doll(s.layer––);}, new Doll(5));}}- XXXXX
- The code does not compile because of the lambda expression.
- The code does not compile for a different reason.
- The code compiles but produces an infinite loop at runtime.
-
Which functional interface has a get() method?
- Consumer
- Function
- Supplier
- UnaryOperator
-
The following diagram shows input arguments being applied to three functional interfaces of unknown type. Which three functional interfaces, inserted in order from left to right, could be used to complete the diagram?
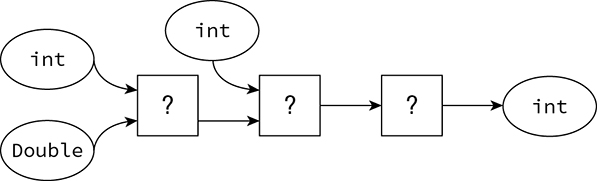
-
DoubleBinaryOperator
ToDoubleBiFunction<Integer,Double>
UnaryOperator<Integer>
-
BinaryOperator<Double>
BiFunction<Integer,Integer,Double>
UnaryOperator<Integer>
-
Function<Double,Integer>
BiFunction<Integer,Integer,Double>
DoubleToIntFunction
-
BiFunction<Integer,Double,Integer>
BinaryOperator<Integer>
IntUnaryOperator
-
-
Which statement about functional interfaces and lambda expressions is not true?
- A lambda expression may be compatible with multiple functional interfaces.
- A lambda expression must be assigned to a functional interface when it is declared.
- A method can return a lambda expression in the form of a functional interface instance.
- The compiler uses deferred execution to skip determining whether a lambda expression compiles or not.
-
Which expression is compatible with the IntSupplier functional interface?
- () -> 1<10 ? "3" : 4
- () -> {return 1/0;}
- () -> return 4
- System.out::print
-
What is the output of the following application?
package tps;import java.util.*;class Boss {private String name;public Boss(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getName() {return name.toUpperCase();}public String toString() {return getName();}}public class Initech {public static void main(String[] reports) {final List<Boss> bosses = new ArrayList(8);bosses.add(new Boss("Jenny"));bosses.add(new Boss("Ted"));bosses.add(new Boss("Grace"));bosses.removeIf(s -> s.equalsIgnoreCase("ted"));System.out.print(bosses);}}- [JENNY, GRACE]
- [tps.Boss@4218224c, tps.Boss@815f19a]
- The code does not compile because of the lambda expression.
- The code does not compile for a different reason.
-
Which of the following method references can be passed to a method that takes Consumer<Object> as an argument?
- ArrayList::new
- String::new
- System.out::println
- I only
- I, II, and III
- I and III
- III only
-
Which of the following is a valid functional interface in the java.util.function package?
- FloatPredicate
- ToDoubleBiFunction
- UnaryIntOperator
- TriPredicate
-
Which functional interface, when filled into the blank, prevents the class from compiling?
package morning;import java.util.function.*;public class Sun {public static void dawn(____________ sunrise) {}public void main(String... rays) {dawn(s -> s+1);}}- DoubleUnaryOperator
- Function<String,String>
- IntToLongFunction
- UnaryOperator
-
Which functional interface does not have the correct number of generic arguments?
- BiFunction<T,U,R>
- DoubleFunction<T,R>
- ToDoubleFunction<T>
- ToIntBiFunction<T,U>
-
Which lambda expression, when filled into the blank, allows the code to compile?
package ballroom;import java.util.function.*;public class Dance {public static Integer rest(BiFunction<Integer,Double,Integer> takeABreak) {return takeABreak.apply(3, 10.2);}public static void main(String[] participants) {rest(____________);}}- (int n, double e) -> (int)(n+e)
- (n,w,e) -> System.out::print
- (s,w) -> 2*w
- (s,e) -> s.intValue()+e.intValue()
-
Fill in the blank: ____________is the only functional interface that does not involve double, int, or long.
- BooleanSupplier
- CharPredicate
- FloatUnaryOperator
- ShortConsumer
-
What is the output of the following application?
package savings;import java.util.function.*;public class Bank {private int savingsInCents;private static class ConvertToCents {static DoubleToIntFunction f = p -> p*100;}public static void main(String... currency) {Bank creditUnion = new Bank();creditUnion.savingsInCents = 100;double deposit = 1.5;creditUnion.savingsInCents += ConvertToCents.f.applyAsInt(deposit); // j1System.out.print(creditUnion.savingsInCents);}}- 200
- 250
- The code does not compile because of line j1.
- None of the above
-
Which functional interface takes a double value and has a test() method?
- DoubleConsumer
- DoublePredicate
- DoubleUnaryOperator
- ToDoubleFunction
-
Given the following class, how many lines contain compilation errors?
1: package showtimes;2: import java.util.*;3: import java.util.function.*;4: public class FindMovie {5: private Function<String> printer;6: protected FindMovie() {7: printer = s -> {System.out.println(s); return s;}8: }9: void printMovies(List<String> movies) {10: movies.forEach(printer);11: }12: public static void main(String[] screen) {13: List<String> movies = new ArrayList<>();14: movies.add("Stream 3");15: movies.add("Lord of the Recursion");16: movies.add("Silence of the Lambdas");17: new FindMovie().printMovies(movies);18: }19: }- None. The code compiles as is.
- One
- Two
- Three
-
Which lambda expression cannot be assigned to a DoubleToLongFunction functional interface?
- a -> null==null ? 1 : 2L
- e -> (int)(10.0*e)
- (double m) -> {long p = (long)m; return p;}
- (Double s) -> s.longValue()
-
Which of the following is not a functional interface in the java.util.function package?
- DoublePredicate
- LongUnaryOperator
- ShortSupplier
- ToIntBiFunction
-
Which functional interface, when filled into the blank, allows the class to compile?
package sleep;import java.util.function.*;class Sheep {}public class Dream {int MAX_SHEEP = 10;int sheepCount;public void countSheep( ____________backToSleep) {while(sheepCount<MAX_SHEEP) {// TODO: Apply lambdasheepCount++;}}public static void main(String[] dark) {new Dream().countSheep(System.out::println);}}- Consumer<Sheep>
- Function<Sheep,void>
- UnaryOperator<Sheep>
- None of the above
-
What is the output of the following application?
package pet;import java.util.*;import java.util.function.*;public class DogSearch {void reduceList(List<String> names, Predicate<String> tester) {names.removeIf(tester);}public static void main(String[] treats) {int MAX_LENGTH = 2;DogSearch search = new DogSearch();List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();names.add("Lassie");names.add("Benji");names.add("Brian");MAX_LENGTH += names.size();search.reduceList(names, d -> d.length()>MAX_LENGTH);System.out.print(names.size());}}- 2
- 3
- The code does not compile because of lambda expression.
- The code does not compile for a different reason.
-
Which functional interface takes two values and has an apply() method?
- BiConsumer
- BiFunction
- BiPredicate
- DoubleBinaryOperator
-
Which of the following lambda expressions can be passed to a method that takes IntFunction<Integer> as an argument?
- (Integer f) -> f
- (v) -> null
- s -> s
- I, II, and III
- II and III only
- III only
- None of the above
-
What is the output of the following application?
package lot;import java.util.function.*;public class Warehouse {private int quantity = 40;private final BooleanSupplier stock;{stock = () -> quantity>0;}public void checkInventory() {if(stock.get())System.out.print("Plenty!");else {System.out.print("On Backorder!");}}public static void main(String... widget) {final Warehouse w13 = new Warehouse();w13.checkInventory();}}- Plenty!
- On Backorder!
- The code does not compile because of the checkInventory() method.
- The code does not compile for a different reason.
-
Which of the following statements about functional interfaces is true?
- It is possible to define a functional interface that returns two data types.
- It is possible to define a primitive functional interface that uses float, char, or short.
- It is not possible to define a functional interface that does not take any arguments nor return any value.
- None of the primitive functional interfaces include generic arguments.