Chapter 19
Java File I/O (NIO.2)
THE OCP EXAM TOPICS COVERED IN THIS PRACTICE TEST INCLUDE THE FOLLOWING:
 Java File I/O (NIO.2)
Java File I/O (NIO.2)
- Use Path interface to operate on file and directory paths
- Use Files class to check, read, delete, copy, move, manage metadata of a file or directory
- Use Stream API with NIO.2
-
Fill in the blanks: A(n)__________ is a file that contains a reference to another file or directory, while a(n)__________ is a file that contains content.
- irregular file, regular file
- regular file, opaque file
- symbolic link, regular file
- symbolic link, symbolic directory
-
Which methods listed below are found in the NIO.2 Path interface?
- getRoot()
- isDirectory()
- listFiles()
- toRealPath()
- I only
- I, II, and III
- I and IV
- II and III
-
Assuming the file /secret/hide.txt exists and is marked hidden, what is result of executing the following program?
package hidden;import java.nio.file.*;public class Finder {public void findHiddenFile(Path p) throws Exception {if(File.isHidden(p)) {System.out.print("Found!");}}public static void main(String[] folders) throws Exception {final Finder f = new Finder();f.findHiddenFile(Paths.get("/secret/hide.txt"));}}- The class does not compile.
- An exception is printed at runtime.
- Found! is printed at runtime.
- Nothing is printed at runtime.
-
Fill in the blanks: Files.walk() performs a __________ traversal, while Files.find() performs a __________ traversal.
- breadth-first, breadth-first
- breadth-first, depth-first
- depth-first, breadth-first
- depth-first, depth-first
-
When reading file information, what is an advantage of using an NIO.2 attribute interface rather than reading the values individually from Files methods?
- Costs fewer round-trips to the file system
- Guarantees performance improvement
- Has support for symbolic links
- Reduces memory leaks
-
What is the result of compiling and executing the following program? Assume the current directory is /stock and the path /stock/sneakers does not exist prior to execution.
package shoe;import java.io.*;import java.nio.file.*;public class Sneaker {public void setupInventory(Path desiredPath) throws Exception {Path suggestedPath = Paths.get("sneakers");if(Files.isSameFile(suggestedPath, desiredPath) // j1&& !Files.exists(suggestedPath))Files.createDirectories(desiredPath); // j2}public static void main(String[] socks) throws Exception {Path w = new File("/stock/sneakers").toPath(); // j3new Sneaker().setupInventory(w);}}- The directory /stock/sneakers is created.
- Line j1 does not compile or produces an exception at runtime.
- Line j2 does not compile or produces an exception at runtime.
- Line j3 does not compile or produces an exception at runtime.
-
Assuming the path referenced below exists and contains a symbolic link that references /again, what is the expected result of executing the following code snippet?
System.out.print(Files.walk(Paths.get("/again/and/again")).count());- An exception is thrown at runtime.
- A number is printed at runtime.
- The process hangs indefinitely.
- The result cannot be determined with the information given.
-
Which method in the NIO.2 Files class is equivalent to the java.io.File method length()?
- length()
- size()
- getLength()
- None of the above
-
Assuming the current working directory is /home, then what is the output of the following program?
1: package magic;2: import java.nio.file.*;3: public class Magician {4: public String doTrick(Path path) {5: return path.subpath(2,3)6: .getName(1)7: .toAbsolutePath()8: .toString();9: }10: public static void main(String... cards) {11: final Magician m = new Magician();12: System.out.print(m.doTrick(13: Paths.get("/bag/of/tricks/.././disappear.txt")));14: } }- /home/tricks
- /home
- The code does not compile.
- The code compiles but prints an exception at runtime.
-
Which methods listed below are found in the NIO.2 Files class?
- isSameFile()
- length()
- relativize()
- mkdir()
- I only
- I, II, and IV
- II and III
- IV only
-
The following code snippet, which attempts to move a file system record from oldHardDrivePath to newHardDrivePath, results in an exception at runtime. Which of the following is the most likely type of exception to be thrown?
Files.move(oldHardDrivePath,newHardDrivePath,REPLACE_EXISTING);- AtomicMoveNotSupportedException
- DirectoryNotEmptyException
- FileAlreadyExistsException
- None of the above since the line of code does not compile
-
Which of the following can be filled into the blank that would allow the method to compile?
public String getPathName(String fileName) {final Path p = ____________________;return p.getFileName();}- new File(fileName).toPath()
- new Path(fileName)
- FileSystems.getDefault().getPath(fileName)
- I and II
- I and III
- II
- None of the above
-
Which statement about the following class is correct?
package clone;import java.io.*;import java.nio.file.*;public class Rewriter {public static void copy(Path source, Path target) throws Exception {try (BufferedReader r = Files.newBufferedReader(source);Writer w = Files.newBufferedWriter(target)) {String temp = null;while((temp = r.readLine()) != null) {w.write(temp);}}}public static void main(String[] tooMany) throws Throwable {Rewriter.copy(Paths.get("/original.txt"),FileSystems.getDefault().getPath("/","unoriginal.txt"));}}- The class compiles without issue.
- The class never throws an exception at runtime.
- The implementation correctly copies a regular file.
- All of the above
-
Fill in the blanks: The Files.__________ method returns a List, while the Files.__________ method returns a Stream.
- lines(), readAllLines()
- lines(), readLines()
- readAllLines(), lines()
- readLines(), lines()
-
What is the output of the following application?
1: package yellow;2: import java.nio.file.*;3: public class Road {4: public boolean findHome() {5: Path oftenTraveled = Paths.get("/highway/street/spot.txt");6: Path lessTraveled = Paths.get("/highway/street/house/../.");7: lessTraveled.resolve("spot.txt");8: return oftenTraveled.equals(lessTraveled.normalize());9: }10: public static void main(String... emerald) {11: System.out.print("AM I HOME? "12: +(new Road().findHome() ? "yes" : " no"));13: }14: }- AM I HOME? no
- AM I HOME? yes
- The class does not compile.
- The class compiles but throws an exception at runtime.
-
Which of the following is not an advantage of using an NIO.2 Path instead of a java.io.File to work with files?
- Contains built-in support for symbolic links
- Has ability to read operating-system-specific attributes
- Provides a single method for deleting a directory tree
- Provides efficient access of file metadata
-
What is the result of executing the following program? Assume the path /driveway exists and is non-empty, and the directory tree is fully accessible within the file system.
package weather;import java.io.*;import java.nio.file.*;public class Snow {public static boolean removeSnow(Path flake) throws IOException {if(!Files.isDirectory(flake) && !Files.isSymbolicLink(flake))return Files.delete(flake);else return true;}public static void main(String[] cones) throws IOException {File driveway = new File("/driveway");for(File f : driveway.listFiles()) {System.out.println(removeSnow(f.toPath()));}}}- The program prints a list of only true values.
- The program prints a mix of true and false values.
- The code does not compile.
- The code compiles but prints an exception at runtime.
-
Which interface name inserted into the blank below allows the code snippet to compile?
Path file = Paths.get("/data/movie.txt");BasicFileAttributes b = Files.readAttributes(file, __________);- BasicFileAttributes.class
- DosFileAttributes.class
- PosixFileAttributes.class
- All of the above
-
What is the output of the following code snippet? Assume that the current directory is the root path.
Path p1 = Paths.get("./locks");Path p2 = Paths.get("/found/red.zip");System.out.println(p1.relativize(p2));System.out.println(p2.relativize(p1));-
../found/red.zip
../../locks
-
../../locks
../found/red.zip
-
locks/../found/red.zip
../found/locks
- None of the above
-
-
What is the output of the following code snippet? Assume that the current directory is the root path.
Path p1 = Paths.get("./found/../keys");Path p2 = Paths.get("/lost/blue.txt");System.out.println(p1.resolve(p2));System.out.println(p2.resolve(p1));-
/lost/blue.txt
./found/../keys
-
/found/../keys/./lost/blue.txt
/lost/blue.txt/keys
-
/lost/blue.txt
/lost/blue.txt/./found/../keys
- None of the above
-
-
What is the output of the following application? Assume the application is called with a valid path that exists and is accessible within the file system.
package charity;import java.nio.file.*;public class Roster {protected void printRoster(Path p) {for(Path f : Files.list(p)) { // n1if(f.toString().endsWith(".per")) // n2System.out.print(f);}}public static void main(String... volunteers) {new Roster().printRoster(Paths.get(volunteers[0]));}}- A list of file names is printed at runtime.
- The class does not compile due to line n1.
- The class does not compile due to line n2.
- None of the above
-
Given the following file system diagram, in which forward is a symbolic link to the java directory, which value does not print /java/Sort.java at runtime?
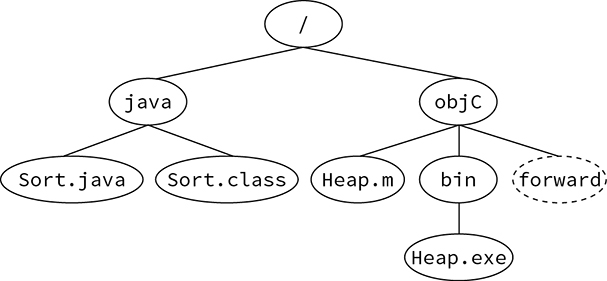
Path p = Paths.get("/", "objC", "bin");System.out.println(p.resolve("__________").toRealPath());- ../backwards/../forward/Sort.java
- ../forward/./Sort.java
- ../java/./forward/Sort.java
- ../../java/Sort.java
-
Using the file system diagram from the previous question, including the symbolic link from forward to java, how many calls to Files.delete() would need to be made before the following line could be executed without throwing an exception?
Files.delete(Paths.get("/objC"));- One
- Four
- Seven
- None of the above. The symbolic link needs to be removed with Files.deleteSymbolicLink() first.
-
Assuming the course.txt file exists and is readable, what is the result of executing the following application?
package schoolwork;import java.io.*;import java.nio.file.*;public class Notes {public void printNotes() {try (OutputStream out = System.out) { // y1Files.copy(out, Paths.get("course.txt"));} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}public static void main(String[] coursework) {new Notes().printNotes();}}- The code compiles but prints an exception at runtime.
- The class does not compile due to line y1.
- The code does not compile for some other reason.
- The program prints the contents of the course.txt file.
-
When reading file information, what is an advantage of loading a BasicFileAttributeView over a BasicFileAttributes?
- Allows the hidden attribute to be set
- Allows the last modified date to be changed
- All of the file information is read in a single round-trip.
- There is no advantage.
-
The Rose application is run with an input argument of /flower. The /flower directory contains five subdirectories, each of which contains five files. How many Path values does the following application print?
import java.nio.file.*;public class Rose {public void tendGarden(Path p) throws Exception {Files.walk(p,1).map(p -> p.toRealPath()).forEach(System.out::println);}public static void main(String... thorns) throws Exception {new Rose().tendGarden(Paths.get(thorns[0]));}}- None
- One
- Six
- Thirty-one
-
Which of the following statements, when run independently, produces a NullPointerException at runtime?
- Paths.get("../sang").getParent().getParent()
- Paths.get("/sing").getParent().getRoot()
- Paths.get("/song").getRoot().getRoot()
- Paths.get("../sung").getRoot().getParent()
- I and III
- I and IV
- II and III
- IV only
-
Which statement about the following Finalize class is correct?
1: package end;2: import java.nio.file.*;3: public class Finalize {4: public Path makeAbsolute(Path p) {5: if(p!=null && !p.isAbsolute())6: return p.toAbsolutePath();7: return p;8: }9: }- It does not compile because IOException is neither handled nor declared.
- It does not compile for some other reason.
- The method compiles and returns a Path value that is always equivalent to the input argument.
- The method compiles and returns a Path value that may not be equivalent to the input argument.
-
Which of the following is a difference between the createDirectory() and createDirectories() methods found in the NIO.2 Files class?
- One takes multiple Path arguments; the other does not.
- One throws an exception if a file already exists at the directory path; the other does not.
- One declares a checked exception; the other does not.
- One creates a single directory while the other may create many directories.
-
Assuming the current working directory is /hail, what is the expected output of executing the following code snippet?
Path w1 = Paths.get("../jungle/.././rain..").toAbsolutePath().normalize();System.out.print(w1.resolve("snow.txt"));- /jungle/snow.txt
- /hail/rain../snow.txt
- /rain../snow.txt
- An exception is printed at runtime.
-
What is the output of the following application?
package med;import java.nio.file.*;public class Surgeon {public Path rebuild(Path p) {Path v = null;for(int i=0; i<p.getNameCount(); i++)if(v==null) v = p.getName(i);else v = v.resolve(p.getName(i));return v;}public static void main(String... tools) {final Surgeon al = new Surgeon();Path original = Paths.get("/tissue/heart/chambers.txt");Path repaired = al.rebuild(original);System.out.print(original.equals(repaired));}}- false
- true
- The code does not compile.
- The code compiles but prints an exception at runtime.
-
Under which circumstances does Files.deleteIfExists() not throw an exception?
- The file system suddenly becomes unavailable.
- The path does not exist.
- The path represents a non-empty directory.
- The process does not have write access to a path.
-
What is the output of the following code snippet? Assume all referenced paths exist within the file system.
Path v1 = Path.get("/./desert/./").resolve(Paths.get("sand.doc"));Path v2 = new File("/desert/./cactus/../sand.doc").toPath();System.out.print(Files.isSameFile(v1,v2));System.out.print(" "+v1.equals(v2));System.out.print(" "+v1.normalize().equals(v2.normalize()));- false false false
- true false true
- true true true
- None of the above
-
How many lines of the following program contain compilation errors?
public class Song {public static void organize(Path folder, Path file) throws IOException {Path p = folder.resolve(file);BasicFileAttributeView vw = Files.getFileAttributeView(p,BasicFileAttributes.class);if(vw.creationTime().toMillis()<System.currentTimeMillis()) {vw.setTimes(FileTime.fromMillis(System.currentTimeMillis()),null,null);}}public static void main(String[] audio) throws Exception {Song.organize(Paths.get("/", "pub"),new File("/songs").toPath());}}- None
- One
- Two
- Three
-
What is the output of the following application?
package stars;import java.nio.file.*;public class Sun {public void printInfo() {Path halleysComet = Paths.get("stars/./rocks/../m1.meteor") .normalize();Path lexellsComet = Paths.get("./stars/../solar/");lexellsComet = lexellsComet.subpath(0, 2).resolve("m1.meteor").normalize();System.out.print(halleysComet.equals(lexellsComet)? "Same!" : "Different!");}public static void main(String... emerald) {Sun s = new Sun();s.printInfo();}}- Different!
- Same!
- The class does not compile.
- The class compiles but throws an exception at runtime.
-
Assuming the directory /eclipse/projects exists and its contents are accessible, which statement about the following code snippet is correct?
Path p = Paths.get("/eclipse/projects");Files.walk(p).map(z -> z.toAbsolutePath().toString()).filter(s -> s.endsWith(".java")).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.out::println);Files.find(p,Integer.MAX_VALUE,(w,a) -> w.toAbsolutePath().toString().endsWith(".java")).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.out::println);- The first stream statement does not compile.
- The second stream statement does not compile.
- Both statements compile but are unlikely to print the same results at runtime.
- None of the above
-
Assuming the file referenced below exists and is significantly large, which statement about the following program is correct?
public class SpeedRead {public void jenniferReads(Path p) {Files.lines(p);}public void jonReads(Path p) {Files.readAllLines(p);}public static void main(String[] pages) {Path p = Paths.get("/bookshelf/mobydick.txt");final SpeedRead r = new SpeedRead();r.jenniferReads(p);r.jonReads(p);}}- The code does not compile.
- The method jenniferReads() is likely to take longer to run.
- The method jonReads() is likely to take longer to run.
- It is not possible to know which method will take longer to run.
-
What is the result of executing the following program? Assume the files referenced in the application both exist and are fully accessible within the file system.
package duplicate;import static java.nio.file.StandardCopyOption.*;import static java.nio.file.Files.*;import java.io.*;import java.nio.file.*;public class CopyOfACopy {public void main(String[] items) throws Exception {final Path s = new File("apples.zip").toPath();final Path t = FileSystems.getDefault().getPath("oranges.zip");copy(s,t,REPLACE_EXISTING); // q1copy(Files.newBufferedReader(t),t,ATOMIC_MOVE); // q2}}- Line q1 does not compile.
- Line q1 produces an exception at runtime.
- Line q2 does not compile.
- Line q2 produces an exception at runtime.
-
Which of the following Files methods requires the enclosing method to handle or declare a checked exception?
- exists()
- isDirectory()
- isSameFile()
- isSymbolicLink()
-
What is the output of the following application? Assume /all-data exists and is accessible within the file system.
package numbers;import java.nio.file.*;import java.util.stream.Stream;public class TheCount {public static Stream<String> readLines(Path p) {try {return Files.lines(p);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}public static long count(Path p) throws Exception {return Files.list(p).filter(w -> Files.isRegularFile(w)).flatMap(s -> readLines(s)).count();}public final static void main(String[] day) throws Exception {System.out.print(count(Paths.get("/all-data")));}}- The number of lines in all files in a directory tree
- The number of lines in all files in a single directory
- The code does not compile.
- The code compiles but prints an exception at runtime.