

abatement: The removal of hazardous materials such as asbestos and mold by a licensed contractor. (Compare containment.)
absorption rate: The amount of space of a particular property type that becomes leased compared to the amount of that same type of space available for lease within a certain geographic area during a given period.
abstracting: The process of extracting and condensing the most important terms and financial clauses of the lease into a form that is more easily accessible and understandable.
accelerated cost recovery: Type of depreciation in which the government allows a larger deduction during the early years of the depreciation period. (See also depreciation.)
ACCREDITED COMMERCIAL MANAGER (ACoM): A designation conferred by the Institute of Real Estate Management on onsite managers of commercial buildings.
ACCREDITED MANAGEMENT ORGANIZATION® (AMO®): A designation conferred by the Institute of Real Estate Management on real estate management firms that are under the direction of a CERTIFIED PROPERTY MANAGER® and meet and comply with stipulated standards as to accounting procedures, performance, and protection of funds entrusted to them.
ACCREDITED RESIDENTIAL MANAGER® (ARM®): A professional service award conferred by the Institute of Real Estate Management on individuals who meet specific standards of experience, ethics, and education.
accrual-basis accounting: The method of accounting that involves entering amounts of income when they are earned and amounts of expense when they are incurred—even though the cash may not be received or paid. (Compare cash-basis accounting.)
active shooter: An individual actively engaged in killing or attempting to kill people in a confined and populated area; most use firearms; there is no pattern or method to their actions or selection of victims.
actual cash value (ACV): Insurance that pays a claim based on the purchase price of the item, usually allowing for depreciation because of age and use. (Compare replacement cost coverage.)
adaptive use: The recycling of existing structures through a change of use.
add-on factor: An amount added to the base rent to account for the proration of the common areas among individual commercial tenants. Also called load factor. (See also base rent.)
adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM): A type of variable-rate mortgage (loan) for which the interest rate can be adjusted (raised or lowered) at specific intervals (e.g., semiannually or annually). The adjustment is based on a predetermined index or formula, such as the prime rate plus two percent. (Compare variable-rate mortgage.)
ad valorem tax: A tax levied on the basis of the value of the object taxed. Most often refers to taxes levied by municipalities and counties against real property and personal property.
affidavit of service: A sworn statement completed by a process server that a notice (e.g., eviction) has been properly served.
Affordable Care Act: See Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.
Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA): The federal law that prohibits discrimination against older workers.
agent: A person who enters a legal, fiduciary, and confidential arrangement with a second party and is authorized to act on behalf of that party.
aging in place: The behavior of persons of retirement age who remain in their present residences, whether they own or rent.
air rights: Right to control, occupy, or use the vertical space (air space) above a property, subject to necessary and reasonable use by neighbor(s) and others (such as aircraft). Air rights can be bought, leased, sold, and transferred.
American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE): Professional association that provides information on refrigerant chemicals and equipment modifications and costs.
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): A federal law passed in 1990 that prohibits discrimination in employment on the basis of physical or mental disability and requires places of public accommodation and commercial facilities to be designed, constructed, and altered in compliance with specified accessibility standards. The accessibility requirements may also apply to common areas of residential properties (e.g., rental offices).
amortization: Gradual reduction of a debt, usually through installment payments.
analysis of alternatives: An investigation of the range of possible changes and evaluation of their anticipated effects on a property that is undertaken in the effort to improve the property’s performance.
anchor tenant: A major shopping center tenant that draws the majority of customers.
ancillary tenant: A shopping center tenant that occupies a smaller space and a location that is secondary in relation to the anchor tenant.
annual budget: The most common form of operating budget. Projects the entire year’s income and expenses for each account. There are two types: a historical budget based on a review of income and expenses from previous years; a zero-based budget that consists solely of projections and ignores past operating expenses. (See also operating budget.)
appraisal: An opinion or estimate of the value of a property. An estimate of value that is (usually) prepared by a certified or accredited appraiser. Four methods of appraisal are common—the cost approach, based on the estimated value of the land plus the estimated cost of replacing the improvements on it less depreciation; the market approach (also called sales approach), based on a comparison to similar properties in the market that have been sold recently; the income capitalization approach, based on the net operating income of the property; and the discounted cash flow method, which discounts all future fiscal benefits of an investment property over a predetermined holding period. All four are used to estimate value if sufficient information is gathered in each approach to do so.
appreciation: The increase in the value of an asset over time.
articles of incorporation: A document that states that a condominium association is a corporation under the laws of the state.
artificial breakpoint: See breakpoint.
asbestos: A fibrous mineral formerly used in buildings for flooring, insulation, and fireproofing later determined to be a health hazard.
as-built drawing: Representation of a property that indicates the presence and location of certain utilities for future use.
assessment: An amount paid by each owner or tenant of a property to fund its operation; also used in referring to local (municipal) taxes.
asset management: A specialized field of real estate management that involves the supervision of an owner’s real estate assets at the investment level. In addition to real estate management responsibilities that include maximizing net operating income and property value, an asset manager may recommend, be responsible for, or participate in property acquisition, development, and divestiture. An asset manager may have only superficial involvement with day-to-day operations at the site (e.g., supervision of personnel, property maintenance, tenant relations).
asset manager: A position in real estate management that focuses on the property—residential or commercial—as a financial asset. (See also asset management.)
assignment: The transfer of one person’s interest or right in a property (e.g., a lease) to another; the document by which such an interest or right is transferred.
assisted living facilities: Housing intended for seniors who need assistance with most (or all) daily living tasks—because of age or frailty but not because of illness.
at will employment: Employment in which either the employee or the employer may terminate the relationship at any time for any reason (with or without cause). Important exceptions are antidiscrimination (protected classes) statutes, anti-retaliation (whistleblower) statutes, and specific contractual arrangements, including collective bargaining agreements.
balloon mortgage: A loan with a constant monthly rate of repayment and a much larger (balloon) payment at the end of the term to fully amortize the loan.
bankruptcy: A state of financial insolvency (liabilities exceed assets) of an individual or organization; the inability to pay debts.
Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act: The 2005 federal legislation that changed many provisions of the previous bankruptcy laws; requires all debtors to get credit counseling before they can file a bankruptcy case—and additional counseling on budgeting and debt management before their debts can be wiped out.
base rent: The minimum rent as set forth in a (usually commercial) lease; also called minimum rent.
base year: In an office lease, the stated year that is to be used as a standard in determining rent escalations. During the next year, operating costs are compared with the base year, and the difference (higher or lower) determines the tenant’s rent adjustment.
Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): A stipend military personnel receive for housing.
Better Buildings Initiative: An incentives-based federal program to provide more generous tax credits and more incentives for owners who undertake costly retrofits on existing properties.
blanket policy: Insurance coverage that insures several properties under one policy. May offer more favorable premiums than individual policies.
board of directors: The elected governing body of any corporation, including condominium and other homeowners’ associations. (See also corporation.)
bodily injury insurance: Type of coverage that protects against liability for damages arising out of injury or death occurring on a property.
boiler insurance: Type of coverage that pays for any damage resulting from a boiler malfunction.
BOMA Standard Method: See Building Owners and Managers Association International.
breakpoint: In retail leases, the point at which the tenant’s percentage rent is equal to the base rent and beyond which the tenant will begin to pay overages; also called natural breakpoint. Sometimes a tenant and owner will negotiate an artificial breakpoint that requires the tenant to begin paying percentage rent before or after the natural breakpoint is reached.
broker: A licensed individual who provides owners with the knowledge and expertise needed to buy and sell real estate assets as an investment—acquisition and disposition.
budget: An estimation of income and expenses over a specific period for a particular property, project, or institution. (See also capital budget and operating budget.)
budget variance report: A report produced by most accounting software that compares the operating expenses paid during the month with the amounts budgeted for that month; reflects which expense categories have variances during the month and year (or year-to-date) and can reveal deficiencies in operations.
building engineer: The position in real estate management that manages systems such as HVAC, boilers, elevators, communications, electrical systems, and even green building technologies; must have a wide range of knowledge and expertise in all building systems.
Building Owners and Managers Association International (BOMA): A trade association that serves the commercial real estate building industry and provides operational statistics for office buildings. The BOMA Standard Method computes a tenant’s rentable area by multiplying the tenant’s usable area by an R/U ratio, which is the rentable area of a floor divided by the usable area of that same floor. A pro rata share of the building’s common areas is then added to the basic rentable area to arrive at the tenant’s total rentable square feet.
building standard: A uniform specification that defines the quantity and quality of construction and finish elements a building owner will provide for build-out of space leased to commercial tenants. (See also tenant improvement allowance.)
build out: In retail leasing, to construct the tenant’s space.
build-to-suit: An arrangement in which a landowner constructs (or pays for constructing) a custom building on the land, and both land and building are leased to the tenant; a frequent arrangement in shopping centers (e.g., for pad or outlot spaces) and industrial properties.
business cycle: Four successive stages (recession, depression, recovery, and prosperity) that businesses experience during periods of inflation and deflation of an economy.
bylaws: Regulations that provide specific procedures for handling routine matters in an organization—e.g., a homeowners’ association.
call center-based management: Management approach in which a regional call center equipped with the latest technology allows the management of projects/properties from anywhere an Internet connection is available.
cap: An upper limit on the amount of change allowed in a year and over the term of the loan in a variable-rate mortgage.
capital budget: An estimate of costs of major improvements or replacements; generally a long-range plan for improvements to a property.
capital improvement: A structural addition or betterment to real property that increases its useful life; the use of capital for a betterment that did not exist before.
capitalization: The process employed to estimate the value of a property by the use of a proper investment rate of return and the annual net operating income produced by the property, the formula being expressed as follows:
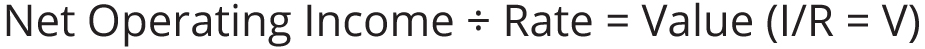
capitalization rate (cap rate): A rate of return used to estimate a property’s value based on that property’s net operating income. This rate is based on the rates of return prevalent in the marketplace for similar properties and is intended to reflect the investment risk associated with a particular property.
cash-basis accounting: The method of accounting that recognizes income and expenses when money is actually received or paid. (Compare accrual-basis accounting.)
cash disbursements report: A chronological record of payments for operating expenses that lists the vendor, the amount, and the check number for all payments and includes items that are not operating expenses (debt service, payment for capital expenditures); also called check register or check voucher.
cash flow: The amount of cash available after all payments have been made for operating expenses, debt service (mortgage principal and interest), and capital reserve funds; also called pretax cash flow to indicate that income taxes have not been deducted.
cash-on-cash return: See return on investment.
C corporation: See corporation.
central business district (CBD): The concentration of high-rise buildings within a community.
CERTIFIED PROPERTY MANAGER® (CPM®): The professional designation conferred by the Institute of Real Estate Management on individuals who distinguish themselves in the areas of education, experience, and ethics in property management.
chart of accounts: A classification or arrangement of account items.
chlorofluorocarbon (CFC): Refrigerant chemical that contains two types of halogens—chlorine (Cl) and fluorine (F). It is being phased out and replaced with similar compounds that do not include chlorine.
Civil Rights Act (Title VII): Prohibits discrimination in employment—hiring, compensation, promotion, termination; enforced by the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC).
client trust account: See operating account.
closing ratio: The number of prospects who became residents or tenants due to the efforts of a leasing agent. (See also leasing agent.)
cogeneration plant: One of the most common forms of energy recycling; uses a heat engine or a power station to simultaneously generate both electricity and useful heat; also called a combined heat and power (CHP)plant.
cold calling: Telephoning or personally calling on commercial prospects with whom the leasing agent has had no previous contact in order to interest them in leasing space.
collateral: Property pledged as security for a loan or debt.
combined heat and power (CHP) plant: See cogeneration plant.
commercial property: All real estate development that is not exclusively residential.
commingle: To mix or combine; to combine the money of more than one person or entity into a common fund. A prohibited practice in real estate.
common area: Area of a property that is used by all tenants or owners. In a condominium, the areas of the property in which the unit owners have a shared interest (e.g., lobbies, laundry rooms). In an enclosed mall, the mall corridors, parking lots, escalators, landscaped areas, and other parts of the property that the tenants use in common.
common area maintenance (CAM) clause: Lease clause that specifies exactly what constitutes the common area of the shopping center, what expenses the tenant will pay, and what rights and responsibilities the property owner has. (See also common area.)
common interest development (CID): See common interest realty association.
common interest realty association (CIRA): Real estate that is operated for the mutual benefit of the owners; condominiums, cooperatives, gated communities, and planned unit developments; (PUDs) are examples; also called common interest development (CID).
community shopping center: A shopping center usually anchored by a junior or discount department store, supermarket, or large hardware store. The 25 to 40 ancillary tenants may include men’s and women’s apparel stores, bookstores, card shops, family shoe stores, and fast food operations. Community shopping centers range in size from 150,000 to 400,000 square feet of GLA and usually require a population of 100,000 to 150,000 to sustain them.
comparison grid: A form for price analysis in which the features of a subject property are compared to similar features in comparable properties in the same market. The price (or rent) for each comparable property helps to determine an appropriate market price (or rent) for the subject.
concession: An economic incentive granted by an owner to encourage the leasing of space or the renewal of a lease.
condominium: A multiple-unit structure in which the units and pro rata shares of the common areas are owned individually; a unit in a condominium property.
condominium association: A nonprofit corporation comprised of the unit owners of a condominium that governs its operation. Also called homeowners’ association.
congregate housing: For those who want to remain independent but require some assistance with daily tasks, these arrangements include meals, transportation, and some housekeeping services.
Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA): Federal law that requires employers to offer employees an opportunity to continue their group health care coverage for a time by paying the premiums themselves when they are terminated or leave their jobs.
construction manager: Position in real estate management that provides expertise when an owner or tenant makes improvements to a property.
Consumer Price Index (CPI): A way of measuring consumer purchasing power by comparing the current costs of goods and services to those of a selected base year; sometimes used as a reference point for rent escalations in commercial leases (i.e., as a measure of inflation). (Compare Producer Price Index.)
containment: The process by which a licensed contractor works to maintain a hazardous material such as asbestos safely in place. (Compare abatement.)
Continuing Care Retirement Community (CCRC): A type of senior community in which residents typically pay a substantial entry fee—usually a six-figure amount—which establishes an ownership interest in a community with available nursing services. In addition to the entry fee, a monthly service fee (in essence, rent) is paid by the resident for services rendered by the community; also called buy-in communities.
continuous occupancy clause: Retail lease clause in which the tenant agrees to stay in business for the full term of the lease.
continuous operation clause: Retail lease clause in which the tenant agrees to keep its business operating smoothly and consistently for the full term of the lease.
contract for labor as needed: A work agreement in which money paid is for specific work done and actual hours worked.
convenience shopping center: Shopping center type that usually has a convenience market or a combination gas station and food store anchor and 2 to 10 stores. Most are open all day and all night. Other tenants may be card- or coin-operated laundries, barbershops, dry cleaners, or liquor stores. Usually has 5,000 to 30,000 square feet of GLA. Typical trade area comprises the immediate neighborhood of the site and the traffic on the street. A convenience center can succeed in an area with a population of 1,000 to 2,500. Also called strip shopping center.
conversion ratio: The number of prospects who visit a rental property compared to the number who sign a lease.
cooperative: Ownership of a share or shares of stock in a corporation that holds the title to a multiple-unit residential structure. Shareholders do not own their units outright but have the right to occupy them as co-owners of the cooperative association under proprietary leases.
corporation: A legal entity that is chartered by a state and is treated by courts as an individual entity separate and distinct from the persons who own it. The federal government classifies most corporations C corporations. The entity pays income tax and has no restrictions on the number of shareholders it can have or the types of stock it can issue. An S corporation combines the ownership features of a corporation with those of a partnership. It does not pay federal income tax; profits (and losses) pass directly to the shareholders.
corrective maintenance: Ordinary repairs that must be made to a building and its equipment on a day-to-day basis. (Compare deferred maintenance and preventive maintenance.)
cosmetic maintenance: A type of preventive maintenance that enhances the property’s aesthetic value; aids in the future development of the property by maintaining an up-to-date appearance.
cost approach: See appraisal.
cost-benefit analysis: A method of measuring the benefits expected from a decision (e.g., a change in operating procedures) by calculating the cost of the change and determining whether the benefits justify the costs.
cost recovery: See depreciation.
covenants, conditions, and restrictions (CC&Rs): Documents that affect the management and maintenance of the center as a whole in open-air shopping centers in which parcels of land are owned by different entities.
curb appeal: General cleanliness, neatness, and attractiveness of a building as exemplified by the appearance of the exterior and grounds and the general level of housekeeping.
custodial maintenance: The day-to-day cleaning and other work that is essential to preserving the value of a property; also called janitorial maintenance or housekeeping.
debt service: Regular payments of the principal and interest on a loan.
declaration: A legal document that creates a condominium. The document describes the property, defines the method of determining each unit owner’s share of the common elements, and outlines the responsibilities of the owners and the association. (See also condominium association.)
deductible: In insurance, a specified amount the insured party must pay before the insurer pays on a claim.
deed of trust: Instrument some states use in place of a mortgage. The deed pledges the property as collateral—the buyer holds title to the property as a warranty deed, and the financial institution and the buyer execute a note as evidence of the debt. A mortgage requires a court order for foreclosure, but a deed of trust does not. (Compare mortgage.)
default: Failure to fulfill an obligation; the nonperformance of a duty.
deferred maintenance: Ordinary maintenance of a building that, because it has not been performed, negatively affects the use, occupancy, and value of the property. (Compare corrective maintenance and preventive maintenance.)
deflation: An economic condition that occurs when the money supply declines in relation to the amount of goods available, resulting in lower prices. (Compare inflation.)
demand: The availability of purchasers for a given amount of goods or services.
demised premises: That portion of a property covered by a lease agreement; usually defined by the walls and other structures that separate one tenant’s space from that of another.
demising wall: The partition that separates one tenant’s space from another—the interior of the corridor wall, and the interior of the exterior wall.
demographic profile: A compilation of social and economic statistics (including population density, age, education, occupation, and income) for a specific population, usually within a geographic area (as a neighborhood or region). (Compare psychographic profile.)
density: The number of apartments in relation to the land area; Number of apartments ÷ Land size = Density.
Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD): A department of the U.S. government that supervises the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) and other agencies that administer housing programs.
depreciation: Loss of value due to all causes, including physical deterioration (ordinary wear and tear), structural defects, and changing economic and market conditions (see also obsolescence). The tax deduction that allocates the cost of an asset over its useful life; also called cost recovery.
depression: Part of the business cycle, a period of low economic activity characterized by high unemployment, low levels of investment, falling prices (including rents), reduced purchasing power, decreasing use of resources, and currency deflation.
disability: A physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities, a record of such impairment, or being regarded as having such an impairment.
discounted cash flow method: See appraisal.
discretionary income: Money available for spending after physical needs (food, clothing, shelter) have been met and taxes have been paid.
disposable income: The amount that is left over after personal income taxes have been subtracted from personal income. The amount of money that consumers actually have available to spend or save.
Drug-Free Workplace Act: The federal law that requires employers who contract with the U.S. government to certify that they maintain a drug-free workplace and have a published statement notifying employees that drug activity is prohibited in their workplace and specifying the actions that will be taken against those who violate the prohibition. Employees must abide by the terms of the employer’s drug-free workplace policy as a condition of their employment.
due diligence service: A legal rule that prevents someone from stating a position inconsistent with one previously stated, especially when the earlier representation has been relied upon by others.
Economic Growth and Tax Relief Act of 2001: The federal law that lowered individual tax rates. (See also Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Act of 2003.)
economic obsolescence: See obsolescence.
economic shift: Fluctuation in real estate sales prices and rental rates. (Compare population shift.)
economic vacancy: The percentage of rental units that are not producing income. Includes unoccupied units, leased space that is not yet producing income, delinquencies, and leasable space that is used for other purposes or is otherwise unleasable.
economics: The science that deals with the production, distribution, exchange, and consumption of goods and services.
effective gross income: The total amount of income actually collected during a reporting period; the gross receipts of a property. Gross potential rental income less vacancy and collection losses plus miscellaneous or unscheduled income.
effective rent: The cumulative rental amount collected over the term of a lease expressed as an average monthly rental (residential) or an annual rate per rentable square foot (office, retail, industrial).
eminent domain: The right of a governmental body to acquire private property for public use through a court action called condemnation. The court also determines the compensation to be paid to the owner.
employee onboarding: A comprehensive approach to bringing in new hires that goes beyond simple orientation; intended to make new employees familiar with the overall goals of a management company or specific property and support them as they embark on early projects in an effort to achieve success.
Employee Polygraph Protection Act (EPPA): The federal law that prohibits the use of lie detector tests in most business situations; in the event of an economic loss, it allows the use of polygraph tests, subject to notification and other restrictions.
Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA): The federal law that safeguards employees’ rights to benefits under a company’s pension.
employment at will: See at will employment.
Employment Eligibility Verification form (form I-9): Federal form that verifies the employee’s identity and right to work in the United States. Employees can present a number of documents to verify their identity and right to work. Employers should retain I-9 forms in the employee’s personnel file for at least three years.
employment practices liability insurance (EPL): A type of coverage that protects businesses from the financial consequences associated with a variety of employment-related lawsuits such as charges of racial or age discrimination, sexual harassment, wrongful termination, or noncompliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act; also helps protect businesses against legal dismissals that flare up between employees and third parties, such as vendors or customers.
endorsement: An attachment to an insurance policy that provides or excludes a specific coverage for a specific portion or element of a property; also called a rider.
ENERGY STAR: A joint program of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the U.S. Dept of Energy (DOE) that can help improve a building’s energy performance. (Compare U.S. Green Building Council.)
Enterprise Income Verification (EIV) system: A federal database that provides the information needed to verify a resident’s income—federal wages, quarterly unemployment compensation, monthly social security, and supplemental security income benefits.
entertainment shopping center: Shopping center type that typically consists of entertainment, dining, and other retail stores. Most have a GLA in the range of 150,000 square feet up to 300,000 square feet, but some are much larger. The trade area varies, depending on the location of any other similar center or competition.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): The agency of the U.S. government established to enforce laws that preserve and protect the environment.
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC): A U.S. governmental body created under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 to end discrimination in the workplace.
equity: The interest or value that an owner has in real estate over and above the mortgage against it.
errors and omissions insurance: See professional liability insurance.
escalation clause: In a lease, a provision for increases in rent based on increases in operating costs, sometimes based on a standard index such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) to account for inflation.
estoppel certificate: A document signed by a tenant stating that certain facts about the tenant’s lease are true; the certificate is for the benefit of the property owner and is usually directed to a lender or a new purchaser of the property.
eviction: A legal process to reclaim real estate, usually from a resident’s or a commercial tenant’s failure to perform under the lease (for cause). The two types of causes are monetary (nonpayment of rent) and nonmonetary (breach of a lease covenant).
eviction notice: A written notice to a tenant to cure a breach of the lease immediately or vacate the premises within a specified period.
exclusive use clause: In a retail lease, clause that prohibits other tenants in a shopping center from selling a similar product in order to minimize competition.
Executive Order 13224: See U.S.A. Patriot Act.
executive property manager: A real estate management position often held by an officer of a management firm or its owner; responsible for overseeing management, ensuring profitability, and acquiring new business.
executive summary: A section at the beginning of a management plan that highlights the information presented in the report.
exempt status: See Fair Labor Standards Act.
expense cap: See expense stop.
expense stop: In an office lease, a clause obligating the property owner to pay operating costs up to a certain amount per square foot per year; tenants pay their pro rata share of any costs in excess of that amount. When used in a retail lease, a clause obligating the tenants to pay a pro rata share of operating expenses up to a certain amount (expense cap, cap) per year; the owner pays any costs in excess of that amount. An expense stop in an office lease sets a ceiling on how much the property owner pays; a cap in a retail lease defines a limit on how much the tenant pays.
extended coverage (EC): An endorsement to a standard fire insurance policy that adds coverage against financial loss from certain other specified hazards.
facility manager: A type of real estate manager who, when employed directly by a corporation that owns real estate incidental to its primary business, may be responsible for acquisition and disposition in addition to physical upkeep of the property, record keeping, and reporting on its management, although a corporate asset manager is likely to handle acquisition and disposition. More broadly, the responsibilities involve coordinating the physical workplace with the people and purpose of the organization.
Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA): A federal law that gives people the right to see and correct their credit records at credit reporting bureaus. It also requires real estate managers to inform rental applicants if a credit bureau is contracted to investigate their credit (and to obtain the applicant’s written authorization to do so), advise them in writing if a lease is denied because of a poor credit report, and identify the source of credit information that resulted in their being denied a lease.
Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA): A federal law that created a series of guidelines for debt collectors to follow. Designed to prevent collection agencies from harassing debtors, the law was later expanded to include any organization that collects consumer debt (including real estate managers). The law is governed and regulated by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
fair housing law: Any law that prohibits discrimination against people seeking housing. There are federal, state, and local fair housing laws. Specifically, Title VIII of the U.S. Civil Rights Act of 1968 prohibits discrimination in the sale or rental of housing based on race, color, religion, or national origin. It was amended in 1974 to include sex as a protected class; the Fair Housing Amendments Act of 1988 further prohibits discrimination on the basis of familial status (children) or mental or physical disability.
Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA): The federal law that regulates hourly workers’ wage rates and the number of hours worked and requires overtime compensation for time worked in excess of 40 hours per week. Employers must pay workers for all hours worked, including work performed at home and travel as part of the job. Employees (usually salaried) who do not have to be paid for overtime work are considered to have exempt status. Under new rules put into effect in July of 2009, the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) issued specific guidelines for determining exempt status, including salary level. In addition to hourly workers, real estate managers working in the corporate setting whose annual salary is less than $47,476 must be paid overtime when they work more than 40 hours in a workweek—in the past, the hours per day or per week maximum did not affect exempt employees. The new rules also spell out the duties that define the roles of exempt employees. This act is frequently referred to as the federal Wage and Hour Law.
familial status: The presence in a household of children under age 18 living with parents or guardians, pregnant women, or people seeking custody of children under age 18.
Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA): The federal law that requires employers to grant eligible employees up to 12 weeks of unpaid job-protected leave in the event of a serious health condition or to care for a family member. To be required to participate, the firm must have at least 50 employees within 75 miles.
Federal Housing Administration (FHA): An agency that is part of the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). It administers a variety of housing loan programs.
Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA): The federal law that requires employer and employee to contribute funds equally based on the employee’s income to the Social Security fund and Medicare.
Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA): The federal law that requires employers to contribute funds to compensate employees who are laid off or terminated. The employer alone makes the contributions, and the amount or rate is based on the number of employees and the number of claims made.
Federal Wage and Hour Law: See Fair Labor Standards Act.
fidelity bond: A surety issued by a third party (usually an insurance company) that protects one individual against financial loss that might result from dishonest acts of another specific individual.
fiduciary: One charged with a relationship of trust and confidence, as between a principal and an agent, trustee and beneficiary, or attorney and client, when one party is legally empowered to act on behalf of another.
financing: The availability, amount, and terms under which money may be borrowed to assist in the purchase of real property, using the property itself as the security (collateral) for such borrowing.
fire insurance: Coverage on property against all direct loss or damage by fire.
fixed-rate mortgage: A loan for real property in which the interest rate is constant over the term of the loan.
flex space: Single-story commercial structure that can be configured to accommodate a single tenant or multiple tenants or to have varying proportions of office and warehouse or manufacturing space according to tenants’ needs.
floor plate: Rentable floor size.
for cause: See eviction.
foreclosure: A court action initiated by the mortgagor, or a lienor, for the purpose of having the court order the debtor’s real estate sold to pay the mortgage or lien.
formaldehyde gas: A foaming agent once used in foam insulation and still present in adhesives used in making pressed-wood products. Its presence in a building can be harmful.
form I-9: See Employment Eligibility Verification form.
fractional ownership: A type of property ownership similar to a timeshare, but it divides a property into more affordable segments for individuals and also matches an individual’s ownership time to their actual usage time. Unlike timeshares, fractional ownership often allows a longer time on the property and a greater chance of property appreciation, while offering the same rights as any other real estate purchase. Although the cost of a fractional property is quite a bit higher than that of a typical timeshare, it is still less expensive than whole ownership of a luxury home in the same location. Also called private residence club. (Compare timeshare.)
frequency: The number of times an ad appears in a marketing medium.
friability: The ease with which a material such as asbestos crumbles.
fully amortized loan: A loan characterized by periodic payments that include a portion applied to interest and a portion applied to principal.
functional obsolescence: See obsolescence.
garden apartment building: A low-rise building designed for multifamily living, usually located in a suburban area.
general partnership: The business activity of two or more persons who agree to pool capital, talents, and other assets according to some agreed formula, and similarly to divide profits and losses, and to commit the partnership to certain obligations. General partners assume unlimited liability. (Compare limited liability limited partnership and limited partnership.)
government-assisted housing: Any residential rental property in which the property owner receives part of the rent payment from a governmental body. As a rule, governmental housing subsidies are either resident based or property based. Also called subsidized housing. (Compare public housing.)
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): Federal law under which property owners fall within the definition of “financial institutions” because they collect personal and financial information from prospective tenants; requires property owners and managers to safeguard personal and financial information collected from prospective tenants and to dispose of it properly to protect against misuse and identity theft.
graphic rating scale: An employee rating system in which the manager checks the appropriate place on a scale for each task listed; typical scale has a five-point rating: 1 is significantly below standard, 3 is standard, and 5 indicates performance significantly above standard.
Great Recession: A severe global economic problem that began in the United States in December 2007, affecting the entire world economy, and is often characterized by various systemic imbalances and was sparked by a liquidity shortfall in the United States banking system. The Great Recession has resulted in the collapse of large financial institutions, the bailout of banks by national governments, and downturns in stock markets around the world.
great room: A living space that combines the living room, dining room, and kitchen.
green movement: Eco-friendly, consumer-driven movement that has affected property management and development through its efforts to minimize urban sprawl and achieve reductions in the carbon footprint.
gross area: The entire floor area of a building measured to the outside finished surface of its permanent walls. (Compare office usable area, rentable area.)
gross domestic product (GDP): Measure of productivity used in the United States since 1991. It indicates the market value of all final goods (tangible objects such as canned food and automobiles) and services (intangible objects such as entertainment activities and transportation) produced only within the United States in one year’s time. (Nearly all other countries measure productivity as GDP, so use of GDP facilitates comparisons of U.S. economic activity with that of other countries.) (Compare gross national product.)
gross floor area: In an enclosed shopping mall, the mall’s GLA plus the common areas—courtyards, escalators, sidewalks, parking areas, etc.—that are not used exclusively by individual tenants. (Compare gross leasable area.)
gross leasable area (GLA): The total square feet of floor space in all store areas of a shopping center, excluding common area space; the size of a retail tenant’s area of exclusive use in a shopping center, usually expressed in square feet. (Compare gross floor area.)
gross lease: A lease under the terms of which the property owner pays all operating expenses of the property and the tenant pays a fixed rent. (Compare net lease, percentage lease.)
gross national product (GNP): The market value of all final goods (tangible objects such as canned food and automobiles) and services (intangible objects such as entertainment activities and transportation) produced by an economy in one year’s time. It measures output attributable to U.S. residents regardless of their geographic location. (Compare gross domestic product.)
gross potential rental income: The sum of the rental rates of all spaces available to be rented in a property, regardless of occupancy; the maximum amount of rent a property can produce.
habitability: A state of being fit for occupancy (e.g., sanitary, safe, in compliance with applicable codes).
heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) system: The combination of equipment and ductwork for producing, regulating, and distributing heat, refrigeration, and fresh air throughout a building.
highest and best use: The use of real property that will produce the highest property value and develop a site to its fullest economic potential.
high-rise apartment building: A multiple-unit dwelling that has 10 or more stories.
historical budget: See annual budget.
homeowners’ association: See condominium association.
home purchase clause: Residential lease clause that allows the resident to break the lease in the event a purchase transaction is closed before the lease term ends.
hoteling: A company’s practice of setting aside one or more spaces for staff members who only need to work in the office periodically rather than maintaining office space for a particular employee.
housekeeping: See custodial maintenance.
Housing and Community Development Act: The 1974 federal law that authorized the Housing Assistance Payments Program commonly referred to as the Section 8 Housing Choice Voucher Program. The program provides rental assistance nationwide to low-income families and elderly and disabled individuals. Public housing agencies (PHAs), which receive funds from the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, locally administer housing choice vouchers.
Housing and Economic Recovery Act of 2008: Legislation that established a tax credit for first-time homebuyers. The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 expanded the first-time homebuyer credit by increasing the credit amount for purchases made in 2009 before December 1, and the Worker, Homeownership and Business Assistance Act of 2009 extended that deadline even further.
illiquid asset: An investment that cannot readily be converted into cash. (Compare liquid asset.)
Immigration Reform and Control Act (IRCA): The federal law that requires the employer to verify an only within the United States employee’s identity and eligibility to work in the United States. Employees must complete Immigration and Nationalization Service (INS) form I-9.
income capitalization approach: See appraisal and capitalization.
income and expense statement: See statement of operations.
individual tax identification number (ITIN): Identification number the Internal Revenue Service issues to a noncitizen who needs to report income for tax purposes but is not eligible for a Social Security number.
indoor air quality (IAQ): An environmental concern specifically related to the work environment. Problems can arise in any type of building, but office buildings are the most susceptible. That is partially because their centralized HVAC systems serve such a large space and partially because they are built new or retrofitted as entirely enclosed systems (the windows cannot be opened), which results in poor air circulation.
inflation: An economic condition occurring when the money supply increases in relation to the amount of goods available, resulting in substantial and continuing increases in prices. (Compare deflation.)
initial investment base: The purchase price of a property; some owners include the cost of initial improvements to make the property operational (rehabilitation) or to enhance its ability to generate income—installation of new appliances to upgrade apartments and achieve higher rental rates.
initial investment basis: The difference between the loan amount and the purchase price of a property (i.e., the owner’s initial equity).
Institute of Real Estate Management (IREM®): A professional association of men and women who meet established standards of experience, education, and ethics with the objective of continually improving their respective managerial skills by mutual education and exchange of ideas and experience. The Institute is an affiliate of the NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF REALTORS®. (See also CERTIFIED PROPERTY MANAGER®.)
institutional owner: A financial institution (bank, trust company, mortgage bank, investment house) or other source of investment capital (insurance companies, pension funds) that invests in real estate.
insurance: An agreement by one party (the insurer, carrier, insurance company) to assume part or all of a financial loss in the event of a specified contingency or peril (e.g., liability, property damage) in consideration of a premium payment by a second party (the insured).
International Council of Shopping Centers (ICSC): The worldwide trade association of the shopping center industry, dedicated to advancing the development of the industry.
inventory control system: A method that provides for each item to be recorded as it is removed from inventory and for the remaining inventory count (item total) to be reduced.
janitorial maintenance: See custodial maintenance.
Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Act of 2003: The federal law that lowered individual tax rates, including reducing the long-term capital gains tax rate from 20 percent to 15 percent. (Those capital gains rate cuts were to be effective for the tax years ending on or after May 6, 2003, through December 31, 2008.)
joint and several liability: A situation in which all the participants in a legal agreement are individually responsible for performing the obligations of the agreement and one or more or all of them can be sued for a breach of the agreement. In real estate management, when a lease is signed by unrelated adults who agree that they are all individually, and as a group, responsible for rent payments and other duties of the tenant.
joint tenancy: Ownership by two or more persons specifically designated as joint tenants, with the right of survivorship—upon the death of one joint tenant, ownership is passed to the other joint tenant(s). (Compare tenancy in common.)
joint venture: An association of two or more persons or businesses to carry out a single business enterprise for profit.
just-in-time delivery: A system manufacturers use to allow them to maintain minimum stocks of raw materials, parts, and packaging by using computer inventory systems coupled with overnight shipping services to supply the materials they need to keep pace with their production levels.
landlord: One who owns real property that is leased to a tenant; a property owner. (See also lessor.)
landlord-tenant law: Laws enacted by various jurisdictions that regulate the relationship between property owner and tenant.
lead-based paint: Type of paint used in housing built prior to 1980 that poses a serious lead-poisoning hazard to resident children. (Its use in the United States was outlawed in 1978.)
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) Certification: An internationally recognized green building certification system; provides building owners and real estate managers the understanding needed to implement practical, environmentally friendly building design, construction, operations, and maintenance solutions.
leaking underground storage tank (LUST): Many older buildings used to maintain their own fuel supply for their boilers, usually in storage tanks on the premises. The threat of contamination of groundwater has led to regulations requiring inspection and replacement of tanks that are still in use. Those no longer in use may have to be removed.
lease: A contract, written or oral, for the possession of part or all of a property for a stipulated period of time in consideration of the payment of rent or other compensation by the tenant. Leases for more than one year generally must be in writing to be enforceable. A residential lease is sometimes called an occupancy agreement.
lease abstract: See abstracting.
leasing agent: A person who is directly responsible for renting space in assigned properties; also called leasing broker.
LEED Certification. (See Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design Certification.)
lessee: The tenant in a lease.
lessor: The property owner in a lease.
liability insurance: Insurance protection against claims arising out of injury or death of people or physical or financial damage to property.
lien: The legal right of a creditor to have their debt paid out of the property of the debtor.
lifestyle shopping center: A shopping center type that has anchor tenants such as Ann Taylor, Barnes and Noble, and Pottery Barn. These shopping centers have few small shops because they lack the traditional anchor tenants. The trade area may vary greatly from one center to another, depending on the local competition. They generally have 250,000 to 500,000 square feet of GLA.
limited liability company (LLC): Created by state statute, a business ownership form that functions like a corporation—its members are protected from liability— but for income tax purposes is classified as a partnership. Income and expenses flow through to the individual members. The arrangement offers considerable flexibility in its organization and structure.
limited liability limited partnership (LLLP): A form of limited partnership that limits the liability of the general partners. (Compare general partnership and limited partnership.)
limited partnership (LP): A partnership arrangement in which the liability of certain partners is limited to the amount of their investment. Limited partnerships are managed and operated by one or more general partners whose liability is not limited; limited partners have no voice in management. Private limited partnerships have 35 or fewer investors and usually do not have to register with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), although they may have to file a certificate with state authorities. Public limited partnerships have an unlimited number of participants and must register with the SEC when the number of partners and the value of their assets reach certain levels. (Compare general partnership and limited liability limited partnership.)
liquid asset: An investment that can be quickly and easily converted into cash at or near its market value; examples include savings accounts, money market accounts, certificates of deposit, stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and precious metals. (Compare illiquid asset.)
load factor: See add-on factor.
locator service: A business in a major city or other large community whose sole objective is matching prospective tenants with rental spaces.
long-range budget: A budget that illustrates the relationship between operating income and expenses over five or more years in the life of a property. (See also budget.)
loss to lease: The amount of money lost due to rental rates being less than the maximum market rents (or GPI).
low-rise apartment building: Multiple-unit residential dwelling of three or fewer stories. (See also garden apartment building.)
M1: See money supply.
M2: See money supply.
management agreement: A contractual arrangement between the owner(s) of a property and the designated managing agent, describing the duties and establishing the authority and compensation of the agent and detailing the responsibilities, rights, and obligations of both agent and owner(s).
management by objectives: A process in which employees help set objectives for themselves and define what they intend to accomplish within a given period; employer and employees mutually agree on the goals and objectives.
management fee: The monetary consideration paid monthly or otherwise for the performance of management duties.
management plan: An outline of a property’s physical and fiscal management that is directed toward achieving the owner’s goals.
manufactured housing: A dwelling that is built in a factory, transported to and anchored on a site, and used as a year-round residential unit. All manufactured homes must be in compliance with the federal Manufactured Home Construction and Safety Standards Act of 1974 (the HUD code) which became effective in 1976. (Usage note: The term mobile home is commonly used to identify all manufactured housing even though the legal nomenclature is “manufactured homes” for units built after the enactment of the HUD code.)
market: Broadly, any interaction between buyers and sellers. In real estate management, the geographic area within which a rental property competes for tenants.
market analysis: An evaluation of supply and demand conditions in a particular area for a particular type of goods or services. In real estate management, the process of identifying the specific group of prospective tenants for a particular property and then evaluating the property by that market’s standards for rental space.
market approach: See appraisal.
marketing: All business activity a producer uses to expose potential consumers to available goods and services, including selling, advertising, and packaging. For rental property, methods used to attempt to lease space.
marketing director: The position in charge of the entire marketing campaign from lease-up of a new property to managing the leasing activities of the property; typically provides services to large, enclosed shopping malls and large apartment communities or office buildings. Also called marketing manager.
marketing fund: In a shopping center, an account controlled by the landlord that is specifically for funding shopping center promotions and advertising. Merchants and the owner of the shopping center contribute to this fund based on a predetermined amount stated in their leases. (Compare merchants’ association.)
material safety data sheet (MSDS): A compilation of information regarding the hazardous properties of chemicals. Usual information includes composition, physical and chemical properties, and known hazards (e.g., toxicity, flammability, explosion potential); recommended cautions for handling (e.g., protective clothing and devices), storage, and disposal; clean-up procedures, and first aid treatment in the event of exposure. An MSDS is provided when chemicals (e.g., solvents, cleaning compounds) are shipped in bulk in pails or drums and when the information does not fit on the labels of small containers. Maintenance and other onsite personnel must retain these documents for reference.
Medical Office Building (MOB): A building whose space is primarily leased to medical and dental professionals.
megamall: A giant shopping center that may contain five million or more square feet of GLA. Such malls are often connected to or contain hotels, amusement parks, or nightclubs in addition to numerous anchor tenants and hundreds of ancillary tenants.
Megan’s Law: In 1996, the federal government passed legislation called Megan’s Law, which requires disclosure to the public of the presence of convicted sex offenders (names and addresses). This information is available from a variety of sources, including local police departments and the Internet. As interpreted up to 2005, the federal law does not address the responsibility of a property owner to a tenant regarding disclosure.
merchants’ association: An organization formed in shopping centers and controlled jointly by the property owner and the tenants to plan promotions and advertisements for the good of the center as a whole. Usually all tenants are required to participate and both tenants and property owner pay dues. (Compare marketing fund.)
Method B: See Office Building: Standard Methods of Measurement.
micro-market: The neighborhood of an office building.
mid-rise apartment building: A multiple-unit dwelling ranging from four to nine stories tall.
miscellaneous income: Income a property produces from sources other than rent, such as coin-operated laundry equipment, vending machines, and late fees; also called miscellaneous cash receipts, miscellaneous receipts, or unscheduled income.
mixed-use development (MXD): A single property, often found in central business districts, that has more than one use, including retail, office, and hotel space, among other possibilities.
mobile home: See manufactured housing.
modernization: The process of replacing original or outdated equipment with similar features that are of up-to-date design.
money supply: All of the printed currency and coinage in circulation outside of banks, plus those bank deposits that are immediately convertible to cash (savings and checking deposits owned by individuals but held in banks), plus other negotiable instruments such as traveler’s checks, credit union share-draft balances, and negotiable order of withdrawal (NOW) accounts. This amount of money, referred to as M1, is the most frequently cited measure of the U.S. money supply. More broadly, the money supply includes less liquid funds such as money market mutual fund shares and small time deposits (e.g., certificates of deposit) on which penalties are imposed for withdrawal before a specified maturity date. Those less liquid funds are added to M1, and the result is called M2.
mortgage: A conditional transfer or pledge of real property as security for the payment of a debt. The document used to create a mortgage loan. (Compare deed of trust.) (See also collateral.)
mullion: A vertical bar that separates the panes of glass in a window. In newer buildings that have expansive windows, the spacing of the mullions usually determines the placement of the walls.
narrative of operations: A report that explains any differences or variances between the actual income and expenses and the amounts projected for them in the budget.
National Apartment Association (NAA): A professional association that compiles statistics on rental apartments.
National Association of Industrial and Office Properties (NAIOP): A professional association that provides operational statistics for industrial properties.
natural breakpoint: See breakpoint.
negative balance of trade: The economic condition in which a country imports more goods than it exports.
negligent hiring: An instance of employee hiring in which proper collection and verification of pre-employment information was not done; if a background check would have revealed a prior conviction for a felony (e.g., assault), the employer of an individual who assaults someone on the job could be sued successfully.
negligent retention: Failure on the part of an employer to prevent an employee who exhibits dangerous behavior on the job (e.g., showing a weapon, making or carrying out threats of harm) from repeating the behavior and harming another person.
negligent supervision: An employment situation in which training and oversight of an employee is inadequate and an incident results in injury to another person, employee, tenant, or visitor.
negotiation: The process of bargaining that precedes an agreement; in commercial leasing, the bargaining to reach a mutual agreement on rental rates, term of the lease, and other points.
neighborhood analysis: A study of a neighborhood and comparison with the broader economic and geographic area of which it is a part to determine why individuals and businesses are attracted to the area.
neighborhood shopping center: A shopping center type in which the most common anchor tenant is a supermarket, a super drugstore, or a combination of the two. This type of center usually has 15 to 25 small shops. Ancillary tenants include dry cleaners, bank branches, beauty salons, and card and gift shops. The GLA of a typical neighborhood center is between 30,000 and 150,000 square feet. A neighborhood shopping center usually thrives in an area with a population of 5,000 to 40,000.
net lease: A lease that requires the tenant to pay a share of specific property operating expenses in addition to base rent. Three types of net leases are common: net (or single-net), net-net (or double-net), and net-net-net (or triple-net), depending on the extent of the costs that are passed through to the tenant. Used most often for commercial tenants, the definitions of the terms vary with location and types of property—e.g., office, retail, industrial. (Compare gross lease, percentage lease.)
net operating income (NOI): Total collections (gross receipts) less operating expenses.
new urbanism: See urban village.
no-cause action: Termination of a tenancy by a property owner without stating a cause if the tenant has a month-to-month lease.
obsolescence: Lessening of value due to being out-of-date (obsolete) because of changes in design and use; an element of depreciation. Physical obsolescence is a condition of aging (wear and tear) or deferred maintenance of a property; functional obsolescence is a condition of obsolete design or use of a property; and economic obsolescence is a loss of value due to external causes (e.g., market conditions) such that the property cannot generate enough income to offset operating expenses.
occupancy agreement: See lease.
Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA): A law passed in 1970 requiring employers to comply with job safety and health standards issued by the U.S. Department of Labor. It mandates use of protective clothing and devices for certain types of tasks.
Office Building: Standard Methods of Measurement: A publication (ANSI/BOMA Z65.1 2010) that can be obtained from BOMA; includes definitions, illustrations, and calculations. This standard, which is commonly referred to as Method B, discusses the single load factor method, which is an updated calculation applied to the occupant area of each floor to determine the rentable area and is the same for all floor levels of a building.
office condominium: An office space that a business purchases as an alternative to leasing. The most common purchasers are medical and dental practitioners, real estate firms, financial planners, entrepreneurs, and small companies that need 1,000 to 10,000 square feet of space. (See also condominium.)
office park: A discrete business center near an airport, major highway, or other suburban attraction.
office usable area: The rentable area less certain common areas that all tenants share, such as the corridors, storage facilities, and restrooms; basically, the actual space occupied by tenants. (Compare gross area, rentable area.)
off-price center: See outlet shopping center.
onboarding: See employee onboarding.
operating account: Bank account set up as an important provision of the management agreement through which the client’s (owner’s) receipts and expenditures flow; also called a client trust account.
operating budget: A listing of all anticipated income from and expenses of operating a property, usually projected on an annual basis. (See also annual budget.)
operating expense: Any expenditure made in connection with operating a property with the exception of debt service, capital reserves (and/or capital expenditures), and income taxes.
operating expense escalation clause: A lease clause under which any increases in operating costs are passed on to tenants on a pro rata basis.
operations manual: An authoritative collection of information that describes the organization and its goals, explains policies that guide its operations, outlines specific procedures for implementing those policies, assigns responsibility for performing various functions, and contains the various documents (forms) for performing the work; also called standard operating procedures manual. (Compare property operations manual.)
option: The right to obtain a specific condition within a specified time. An option is often written into a lease as an addendum.
option to cancel: An option that grants the tenant the right to cancel the lease before its expiration and, if granted, usually requires a financial penalty; also called termination right.
option to expand: An option that requires the property owner to offer specific additional space at a stated time in the future, often at the end of the lease term.
option to renew: An option that allows a tenant to renew a lease on the same terms and conditions as the original lease.
outlet shopping center: A shopping center in which at least 50 percent of the stores are factory outlet stores. They may include off-price and discount merchants. At an off-price center, retailers offer name-brand merchandise at well-below-normal retail prices. Outlet centers may attract customers from a radius of 20 miles to as far away as several hundred miles in rural areas. They traditionally require a minimum population of 200,000.
outlot: In a shopping center, a separate site that is not attached to the main center. Also called a pad. Banks, restaurants, automotive service centers, and movie theaters are common tenants for these spaces.
overage rent: See breakpoint and percentage rent.
owner, landlord, and tenant (OLT) liability insurance: Type of insurance that covers claims against a property owner, a landlord, or a tenant arising out of injury to a person or persons on the property.
pad: See outlot.
parking area ratio: The relationship between the size of the parking area and the size of the building it is intended to serve.
parking index: For a retail property, the number of spaces per 1,000 square feet of GLA.
partnership: See general partnership and limited partnership.
passive activity income: See Tax Reform Act of 1986.
passive loss rules: See Tax Reform Act of 1986.
pass-through charges: In commercial leasing, operating expenses of a property that are paid by the tenants, usually on a pro rata basis and in addition to base rent.
pass-through clause: A provision that allows property owners to pass to tenants increases in certain operating expenses and rent escalations.
Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA): This 2010 federal legislation makes insurance more affordable by providing small businesses (50 employees or less) with a tax credit to provide healthcare coverage and by providing tax credits to those who need help buying insurance. Also called the Affordable Care Act.
payback period: The amount of time required to recover the cost of a capital investment.
percentage lease: A lease contract sometimes used for retail properties; the rent is a percentage of the tenant’s gross sales made on the premises. The lease usually states a fixed minimum rent, and the tenant pays a percentage of its gross sales in excess of that amount, depending on the volume of business.
percentage rent: In retail leasing, rent that is based on a percentage of a tenant’s gross sales (or sometimes net income or profits), often set against a guaranteed minimum or base rent and referred to as overage rent. (See also breakpoint.)
physical obsolescence: See obsolescence.
physical vacancy: The percentage of units (apartments, office suites, store spaces) that are unoccupied and available for lease.
planned unit development (PUD): A zoning classification that allows flexibility in the design of a subdivision, usually setting an overall density limit that allows clustering of units to provide for common open space. A PUD is a departure from conventional residential zoning; therefore, the term planned unit development also refers to a special zoning apparatus that permits the undertaking.
point: One percent of the total loan amount.
polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB): A chemical present in electrical transformers that is relatively harmless if left undisturbed. However, if a PCB-containing transformer leaks or burns, lethal dioxin gas may be released. Local or state law may require removal of PCBs during rehabilitation.
population shift: A fluctuation in numbers of individuals in different age and income groups and changes in household sizes. (Compare economic shift.)
portfolio manager: The position in real estate management that is responsible for assembling real estate assets to achieve specific investment plans and goals—similar to the management of a mutual fund or other pooled investment.
power shopping center: A type of super community shopping center. Several large, strong, high-volume, heavy-advertising retailers occupy most of the space. Home furnishings, office supplies, sporting goods, home improvements, toys, and consumer electronics (computers, major appliances) stores are common anchor tenants in these centers. Power centers have GLAs ranging from 200,000 to 600,000 square feet and at least four category-specific off-price anchors, each occupying 20,000 or more square feet of GLA. The trade area may extend up to 30 miles, depending on local competition; they need a minimum population of 150,000.
prelease: To lease before construction of a building begins or while the construction is taking place. For proposed developments, lending institutions usually require a certain percentage of a planned property to be leased before construction loans will be approved.
pretax cash flow: See cash flow.
preventive maintenance: A program of regular inspection and care that allows potential problems to be prevented or at least detected and solved before major repairs are needed. (Compare corrective maintenance and deferred maintenance.)
primary trade area: The immediate area around a shopping center; accounts for 60 to 75 percent of the center’s sales. (Compare secondary trade area, trade area, tertiary trade area.)
prime rate: The lowest interest rate available from banks for short-term loans to their most creditworthy customers.
primogeniture: A rule of inheritance in which estates could be passed to descendants.
principal: In real estate, one who owns property; in real estate management, the property owner who contracts for the services of an agent; in finance, the amount of money that is borrowed in a loan as distinct from the interest on such loan.
private limited partnership: See limited partnership.
private residence club: See fractional ownership.
Producer Price Index (PPI): A measurement of inflation at the wholesale level. (Compare Consumer Price Index.)
professional liability insurance: In real estate management, insurance to protect against liabilities resulting from honest mistakes and oversights (no protection is provided in cases of gross negligence); also called errors and omissions insurance.
professional real estate management: The profession of conducting a property’s management, operations, marketing, leasing, and financial reporting to meet the objectives of the owner. It also involves planning for the future of the property by proposing physical and fiscal strategies that will enhance the value of the real estate.
progressive discipline: A system of employee reprimand that provides ample opportunity for the employee to change or correct their behavior; such a system usually involves verbal warnings, written warnings, probation, and termination.
Project-Based Rental Assistance HUD: Section 8 program under which HUD makes up the difference between the rent a low- or very low-income household can afford and the approved rent for an adequate housing unit in a multifamily project. Eligible renters pay rent based on their income.
property analysis: A study of a property referring to such items as deferred maintenance, functional and economic obsolescence, land location and zoning, exterior construction and condition, plant and equipment, unit mix, facilities, and expected income and expenses.
property damage insurance: Coverage that protects against liability for damage to the property of others that occurs on the insured property.
property management: See real estate management.
property manager: A position in real estate management that may be responsible for operating a single large property or a portfolio of several properties, while also supervising the site managers. Also called property supervisor. (Compare site manager.)
property operations manual: A manual that a real estate manager or management firm develops for a specific managed property. Some policies and procedures may duplicate or only slightly modify many of the firm’s operational policies, others will be property-specific. (Compare operations manual.)
proprietary lease: See cooperative.
pro rata: Proportionately; in real estate ownership and leasing, based on the size of individually owned or leased spaces in relation to the whole. Condominium owners and commercial tenants commonly pay proportionate shares of operating expenses and other costs.
prospect: A potential tenant or management client.
prospect report: A record of information about prospective tenants for office space, their space needs, current space and lease expiration data, how they were contacted, whether they were qualified for tenancy, and their status as prospects—if they received a brochure or were given a tour of the property.
protected class: See fair housing laws.
psychographic profile: An analysis of a retail trade area that goes beyond the numbers to examine the interests and shopping habits of the people who live in the shopping center’s trade area. (Compare demographic profile.)
public housing: Housing owned by and/or managed for a local or state governmental agency; the principal form of low-income housing available in the United States. (Compare government-assisted housing.)
public housing agency (PHA): See Housing and Community Development Act.
public limited partnership: See limited partnership.
public relations (PR): Any form of promotion that is not paid for, such as press releases and word-of-mouth endorsement.
qualification: The process of judging a prospective tenant’s financial status or creditworthiness. In real estate management, the process of determining whether a prospect can afford the rent on the unit applied for and has a good history of bill payments.
quiet enjoyment: A covenant that promises that the grantee or tenant of an estate in real property will be able to possess the premises in peace, without disturbance by hostile claimants. Quiet enjoyment is a right to the undisturbed use and enjoyment of real property by a tenant or property owner.
radius clause: A provision in a retail lease that prevents a retailer from opening and operating a similar—and therefore competitive—business within a certain radius from the shopping center.
radon: A colorless, odorless, tasteless gas that occurs naturally in the radioactive decay of radium and uranium. It became a problem with the advent of energy-efficient buildings that allow only minimal transfer of air between the building’s interior and exterior.
reach: The specific audience exposed to a marketing medium; should be the largest possible number of prospects who mirror the target market.
real estate: Land and all improvements in or on it.
real estate cycle: Recurring periods of high and low activity in real estate markets. The cycle has four components: overbuilding, adjustment, stabilization, and development. They generally follow their business cycle counterparts.
real estate executive: A supervisory role that manages multiple real estate managers, numerous personnel within an entire firm, or even several apartment communities that have regional real estate managers that supervise onsite personnel. Also called senior portfolio manager, director of real estate services, director of client services.
real estate investment trust (REIT): An entity that sells shares of beneficial interest to investors and uses the funds to invest in real estate or mortgages. Real estate investment trusts must meet certain requirements such as a minimum number of investors and widely dispersed ownership. No corporate taxes need to be paid as long as a series of complex IRS qualifications are met. (See also shares of beneficial interest.)
real estate management: A profession in which someone other than the owner (a real estate manager) supervises the operation of a property according to the owner’s objectives or consults with the owner on the definition of those objectives and the property’s profitability.
receivables ledger: See statement of receipts report.
receivership: Court-ordered turnover of a property to an impartial third party (receiver) so that it may be preserved for the benefit of the affected parties.
reconciliation: The process of comparing estimated operating expenses paid by tenants throughout the year to actual operating expenses at year-end when the true costs are known and then billing or crediting the adjusted amounts to the tenants.
recovery: Part of the business cycle, a period or economic upturn following a depression characterized by increasing demand for goods and services and rising prices.
regional analysis: A detailed study of a region, usually the area surrounding and including one or more neighboring cities, to determine the force of various factors affecting the economic welfare of a section of the region, such as population growth and movement, employment, industrial and business activity, transportation facilities, tax structures, topography, improvements, and trends.
regional mall: A large shopping center that has one or more full-line department stores as anchor tenants. The presence of a department store tends to attract such ancillary tenants as men’s and women’s apparel stores, optical shops, electronic equipment stores, and jewelers. Many include small fast-food outlets arranged in a food court. Some also have cinemas. Regional malls contain 400,000 to one million square feet of GLA. Their trade area has a radius of 7 to 10 miles, and they usually serve a population of 150,000 to 300,000.
regional manager: A position in real estate management that supervises onsite residential or commercial property managers and sometimes the property managers within the management firm. Also called regional property manager, portfolio supervisor, or senior property manager.
rehabilitation: The process of renewing the equipment and materials in the building; entails correcting deferred maintenance.
rent: In real estate, payment made for the use of space; periodic payments made under a lease.
rentable area: The area in an office building on which rent is based and which generally includes the space available for tenants’ exclusive use plus identified common areas less any major vertical penetrations (air shafts, stairways, elevators) in the building. The term is applied to the building as a whole, to individual floors, and to portions of floors. (Compare gross area, office usable area.)
rental agreement: See lease.
rental ledger: A record of rent received, date of receipt, period covered, and other related information for each individual tenant. (Compare rent roll.)
rent control law: A law that regulates rental rates, usually to limit the amount of rent increases and their frequency.
rent loss insurance: Coverage that protects the owner from loss of income resulting from damage that makes all or part of the property unleasable.
rent roll: A listing of all rental units, showing the rental rate, tenant’s name, and lease expiration date as well as the status of rent and other payments. (Compare rental ledger.)
replacement cost coverage: Insurance to replace or restore a building or its contents to its preexisting condition and appearance. (Compare actual cash value.)
request for proposal (RFP): A request for a formal proposal that requires a bidder to provide written specifications for services.
reserve account transactions report: A report that lists deposits to and withdrawals from the reserve fund.
reserve fund: Money set aside to provide funds for anticipated future expenditures.
resident: One who lives (or resides) in a place. Many real estate professionals prefer to refer to residential tenants as “residents.” (Compare tenant.)
Resident-Based Rental Assistance HUD Section 8 program: The individual or family who receives a housing voucher is responsible for finding a suitable housing unit. The public housing agency pays the subsidy directly to the property owner on behalf of the participating renter. The renter then pays the difference between the amount subsidized by the program and the actual rent charged by the owner (usually limited to 30 percent of the renter’s adjusted monthly income).
Residential Lead-Based Paint Hazard Reduction Act: The federal law that requires owners and managers of apartment buildings constructed before 1978 to give renters (1) a disclosure form detailing the presence of lead-based paint; (2) a government pamphlet on lead paint hazards; and (3) a copy of any existing reports that describe lead paint hazards at the property.
residential manager: One who manages a residential property or properties.
resident manager: See site manager.
Resolution Trust Corporation (RTC): A governmental agency created to manage and dispose of the assets of thrifts that were in receivership; contracted with real estate management firms to manage and market many of those assets for disposition.
retrofit: To replace fixtures or facilities in a building with new equipment that is more efficient, usually in terms of energy consumption, fire protection codes, or accommodations for new technology.
return on investment (ROI): A measure of profitability expressed as a percentage and calculated by comparing periodic income to the owner’s equity in the property. (income ÷ equity = % ROI) It can be calculated either before or after deduction of income tax. Also called cash-on-cash return.
rider: See endorsement.
right of first offer: As an alternative approach to granting an option to expand, a tenant may be granted a first choice to rent a particular space subject to availability of that space.
right of first refusal: An option that gives a tenant the first choice to lease contiguous space or other space in the building when it becomes available. The lease clause specifies the area.
right of reentry: The property owner’s right to enter an occupied apartment to make repairs, provide agreed-upon services, and show the apartment to prospective tenants and others, subject to certain limitations.
R/U ratio: See Building Owners and Managers Association International.
sales approach: See appraisal.
S corporation: See corporation.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): Legislation that expanded repercussions for destroying, altering, or fabricating records in federal investigations or for attempting to defraud shareholders; required compliance from property management companies.
secondary trade area: The area around a shopping center that usually extends three to seven miles from the site (for a regional shopping center) and accounts for 10 to 20 percent of sales. (Compare primary trade area, tertiary trade area, trade area.)
Section 202: Federal housing program that covers supportive housing for the elderly.
Section 8 housing: Privately owned residential rental units that participate in the low-income rental assistance program created by the 1974 amendments to Section 8 of the 1937 Housing Act. Under this program, the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) pays a rent subsidy to the property owner on behalf of qualified low-income residents so they pay a limited portion of their incomes for rent.
Section 811: Federal housing program that covers supportive housing for the disabled.
security deposit: An amount of money advanced by the tenant and held by an owner or manager to ensure the faithful performance of the lease terms by the tenant. Part or all of the deposit may be retained to pay for rent owed, miscellaneous charges owed, unpaid utility bills, and damage to the leased space that exceeds normal wear and tear. Limitations on withholding may be imposed by local and state ordinances.
self-storage facilities: Storage facilities that resemble rows of attached garages in which individuals and businesses store and secure their goods themselves. Many of these facilities include living quarters for an onsite manager.
semimonthly payroll system: A payroll method that pays employees twice a month—usually on the 15th and the last day of the month.
shares of beneficial interest: Shares sold by real estate investment trusts (REITs); they are traded on the stock markets similar to corporate common stock. (See also real estate investment trust.)
shell space: Condition in which new office space and store space is commonly leased—enclosed by outside walls and a roof, with a concrete slab floor and utilities brought in. The plumbing and electrical installations are unfinished, and the space has no partitioning walls, ceiling tiles, wall coverings, or flooring. (Compare vanilla shell space.)
shopping center: A generic term applied to a collection of retail stores enclosed in one building or adjacent to each other in separate buildings. Shopping centers are categorized based on their gross leasable area, type of tenancy, and the extent of their geographic trade area (customer base).
single-family home: A residence that has its own entry. Townhouses, which by definition share a common wall but have private entrances, are also classified as single-family homes.
single load factor method: See Office Building: Standard Methods of Measurement.
site management: A profession that involves maintaining the physical structure of a property as well as maintaining and updating property-related documents and information.
site manager: An employee who oversees and administers the day-to-day affairs of a property in accordance with directions from the property manager or the owner. For residential properties, the manager may live in the building they manage (resident manager) or off site. For commercial properties, the manager may occupy an office on site or off site. (Compare property manager.)
sole proprietorship: A business enterprise carried on by one person.
space planning: The process of designing an office configuration for maximum functional efficiency based on a prospective tenant’s space utilization needs, aesthetic requirements, and financial limitations.
special assessment: A special tax levied by a local government to fund public improvements (sidewalks, curbs, or other infrastructure) within a small area; only properties directly benefiting from the improvements are assessed the tax. In a condominium, monies collected from owners to fund a capital expenditure (e.g., roof replacement) when reserve funds are insufficient. This is in addition to the regular assessment for maintenance of common areas. (See also assessment.)
special form insurance: Coverage that pays for all losses except those that are specifically excluded in the policy. (Formerly all-risk insurance.)
special improvement district: A narrowly defined area—a single block or several blocks along a thoroughfare—in dense urban areas in which owners of buildings may band together to form a nonprofit corporation with a specific purpose, such as to clean up the area, to increase security, or simply to give the area a specific identity, such as using signs or banners. The taxing body may levy a special assessment for this purpose. (See also special assessment.)
Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons (SDN) list: See U.S.A. Patriot Act.
specialty shopping center: A dominant theme or image characterizes this type of shopping center. Those in downtown areas are often the result of adaptive use of a historic building. They do not always have an anchor tenant, and many rely on tourists for most of their sales. Their uniqueness is their main attraction. They usually vary in size from 25,000 to 70,000 square feet, although some of these centers can be as large as 375,000 square feet of GLA. The specific use defines the trade area, and it may extend beyond the radiuses usually associated with centers of this size. Specialty shopping centers require an area population in excess of 150,000 to survive.
standard operating procedures manual: See operations manual.
standard tenant improvement allowance: See tenant improvement allowance.
statement of operations: An at-a-glance view of the property’s gross amounts of income and expenses for a period. It emphasizes the cash flow paid to the owner. Also called an income and expense statement.
statement of receipts report: Chronological report of rents and income from sources other than rents that identifies the source and amount of all monies received; also called receivables ledger.
steering: An illegal discriminatory practice that encourages a prospective tenant to look at another site for housing or conceals vacancies from a prospect.
store hours clause: A retail lease clause that authorizes the management of the property to set store hours for the center as a whole. It may include provisions for seasonal adjustments and special hours for holiday shopping periods.
strip shopping center: A shopping center designed in a line. The term is sometimes used for convenience shopping centers and can refer to other types of centers as well.
sublet: The leasing of part or all of the premises by a tenant to a third party for part or all of the tenant’s remaining term.
sublet clause: A clause in a residential lease that states that, in order for the resident to vacate the premises before the end of the term, he or she must find a suitable resident to sublet the space for the remainder of the lease obligation. The manager must approve that person, and the resident or the subtenant must pay for the credit check.
submarket: A segment of the overall market that is limited by a particular market influence.
subrogation: The substitution of one creditor for another such that the substituted person succeeds to the legal rights and claims of the original claimant; in insurance, the right of an insurer to attempt to recover amounts from an at-fault third party for claims paid to the insured party.
subsidized housing: See government-assisted housing.
substitute check: See Check 21 Act.
super-regional mall: A large shopping center that includes four or more full-line department stores and 100 to 150 small shops. May include outlots or pads. It usually has one million to three million square feet of GLA. Its trade area has a radius of 10 to 20 miles, and it serves a population of 300,000 or more.
supply: The availability of goods and services.
surety: A formal guarantee.
syndicate: A type of professionally managed limited partnership formed to invest in different types of real estate.
syndication: A method of selling property in which a sponsor sells ownership interests to investors.
tax: An amount assessed by government for public purposes, usually based on the relative value of property or income.
Tax Reform Act of 1980: Federal legislation that offered numerous incentives for real estate investment and fueled unprecedented development. (See also Tax Reform Act of 1986.)
Tax Reform Act of 1986: Legislation that restructured federal income tax and its associated deductions. Of primary importance in real estate are its definitions of passive activity income (and loss), which include real property income, and its restrictions against using passive losses to offset active income—i.e., salary. (The Technical and Miscellaneous Revenue Act of 1988 delineated technical corrections to the Tax Reform Act of 1986.)
telecommute: To work at home using a computer linked to an employer’s location via a telephone network.
tenancy in common (TIC): Ownership by two or more persons in which each holds an undivided interest in the property. Upon the death of one tenant, that tenant’s interest in the property passes to his or her heirs—not to the other tenant(s); the right of survivorship does not apply. A tenancy in common is a fractionalized fee-simple interest in real property used in certain tax-deferred exchanges. While technically a real estate transaction, TICs are in fact sold as securities. (Compare joint tenancy.)
tenant: One who pays rent to occupy real estate. Real estate managers often limit the use of the term “tenant” to commercial tenants and refer to residential tenants as “residents.” (See also lessee and resident.)
tenant improvement allowance (TIA): In commercial leasing, an amount a landlord agrees to spend to improve the leased shell space for a tenant before move-in or as a condition of lease renewal. A standard tenant improvement allowance is a fixed dollar amount allowed by the owner for items that may be installed in the leased premises at no charge to the tenant. Payment for tenant improvements is part of the lease negotiations. (See also building standard.)
tenant mix: The combination of types of businesses and services that lease space in a shopping center, an office building, or (sometimes) an industrial park.
term: The duration of a tenant’s lease; the duration of a mortgage (e.g., a 30-year term).
termination right: See option to cancel.
terrorism: As defined in the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations, the unlawful use of force and violence against persons or property to intimidate or coerce a government, the civilian population, or any segment thereof, in furtherance of political or social objectives.
Terrorism Risk Insurance Act (TRIA) of 2007: This federal legislation provides for a transparent system of shared public and private compensation for insured losses resulting from acts of terrorism.
tertiary trade area: The area around a major shopping center that extends 15 to 50 miles from the center and accounts for 5 to 15 percent of sales. (Compare primary trade area, secondary trade area, trade area.)
timeshare: A specialized form of condominium found mostly in resort areas. As the name implies, the owner has the right to occupy the unit for a specific period. (Compare fractional ownership.)
time value of money: The assumption that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar at some future date. The basis of compounding to determine future value or discounting to determine present value.
Title VIII: See fair housing law.
trade area: The geographic area from which a shopping center obtains most of its customers, its size depends on the type of center, location of competition, and other factors. (Compare primary trade area, secondary trade area, tertiary trade area.)
traffic report: A record of the number of prospects who visit or make inquiries at a property and the factors that attracted them to it.
transfer clause: A residential lease clause that allows the resident to break the lease without penalty in case of a job transfer.
tuckpointing: The periodic replacement of mortar.
umbrella liability insurance: Extra liability coverage that exceeds the limits of a basic liability policy.
unemployment rate: The number of unemployed divided by the number in the labor force (the number of employed plus the number of unemployed).
unit deed: A document that legally transfers title to a condominium unit and a share of the common areas from one owner to another.
unscheduled income: Income that may be unanticipated and/or not planned.
Urban Land Institute (ULI): An independent nonprofit research and educational organization dedicated to improving the quality and standards of land use and development. It publishes comparison data on shopping centers and multifamily housing.
urban renewal: A federal program that opens land in cities to development or redevelopment and new uses.
urban village: A parcel of land that was previously home to an industrial use or an apartment complex that is redeveloped to incorporate a variety of residential and commercial uses into a “pedestrian-friendly” neighborhood. This phenomenon, called new urbanism, includes higher-density development with narrow streets complemented by wide sidewalks. This strategy is revitalizing urban areas and creating an identifiable downtown in suburbs that do not have one.
usable area: The area in an office building that is available for the exclusive use of a tenant. (Compare rentable area.)
U.S.A. Patriot Act: This federal legislation, along with Executive Order 13224, has increased federal government scrutiny of financial transactions, including real estate transactions. The purpose is to curb and prevent business interactions with terrorist organizations. Commercial property managers in particular should periodically check the Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons (SDN) list to ensure that current and prospective tenants are not on that list. Residential property managers should also check prospects and existing residents against the list since known terrorists have leased apartments in the United States.
U.S. Civil Rights Act of 1968: See fair housing law.
use clause: In a retail lease, a clause that prevents a tenant from using the premises in a different way than originally intended.
useful life: The period of years over which a building will produce income and to recover the cost of the building; the period varies for different types of properties. Also called depreciation period.
U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC): A federal program for improving a building’s performance that offers a Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) Certification. (Compare ENERGY STAR.)
valuation: An estimation or calculation of the worth of an object or service; the process of determining an object’s or service’s worth.
vanilla shell space: A rental space that usually has an American Disabilities Act (ADA) compliant restroom, walls ready for paint, floor ready for floor coverings, and ceiling tiles and lighting in place. (Compare shell space.)
variable-rate mortgage: A mortgage in which the lending institution can raise or lower the interest rate of an existing loan depending on prevailing loan rates or a prescribed index. (Compare adjustable-rate mortgage.)
wage and hour law: See Fair Labor Standards Act.
walk-up: An older four-story apartment building that has stairs only.
weighted checklist: An employee evaluation method in which the appraiser is given a list of statements and checks the items on the list that describe or apply to the employee; some items may be weighted higher than others to arrive at an overall tabulated result.
Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification (WARN) Act: The federal law that requires employers of large numbers of workers to give affected workers 60 days’ advance notice of a layoff if it impacts 33 percent of the employer’s workforce, provided that at least 50 employees are to be laid off.
Worker, Homeownership and Business Assistance Act of 2009: See Housing and Economic Recovery Act of 2008.
workers’ compensation insurance: Coverage obtained by an employer to pay compensation and benefits awarded to an employee in the event of employment-related sickness or injury.
zero-based budget: See annual budget.
zoning: Regulation of the character and use of property by areas or “zones,” usually by local (municipal) government.