

PRONUNCIATION | try-SAIR-a-tops
SPECIES | Triceratops horridus
NAME | Three Horn Face
FAMILY | Ceratopsidae
PERIOD | Late Cretaceous
DIET | Herbivore
SIZE | 20 feet (6m)
YEAR DISCOVERED | 1889
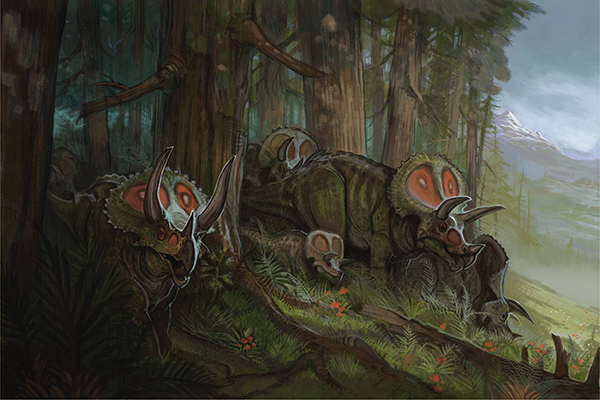
Triceratops is another popular species of dinosaur and a member of the widely varied family of ceratopsids. This large, quadrupedal herbivore was famous for its showy neck frill and fearsome horns. Paleontologists have recently come to the opinion that the frill served more as a display than a defensive function, not unlike modern deer and elk. Fossil remains of triceratops show scar evidence that suggest attacks from predators such as T-rex and rutting damage from other triceratops.
Horns and frills were common to all ceratopsids. A recent paleontological study revealed that separate species of ceratopsids in the triceratops genus were actually true triceratops at various age and gender orientations with a wide range of horn and frill developments.

At twice the size of a rhinoceros, a charging triceratops would be intimidating enough to scare off any predator that threatened the herd.
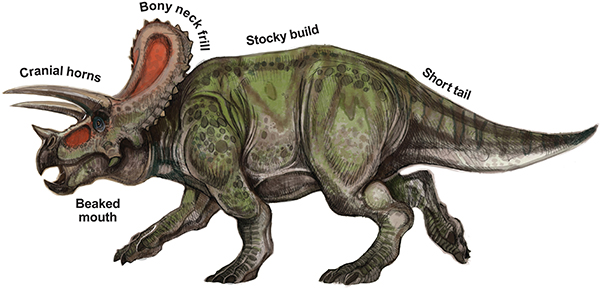
The neck frills and horns are the most recognizable features of all the ceratopsids, and their function has been widely speculated among paleontologists. As an artist, how you choose to decorate the frill is completely open to your imagination.


The horns, frill and patterning on the triceratops is believed to vary greatly between individual specimens. This would make it easier for young to identify family members, and for the age of the dinosaur to be immediately recognizable. Like flukes on whales or horns on elephants it’s likely that each family group had the same distinctive patterning for identification.

Like other herd animals, it is likely that triceratops were social creatures, staying with extended family until old enough to fend for themselves.