The DNS Question Format consists of a name followed by two 16-bit values—QTYPE and QCLASS. This Question Format is illustrated as follows:
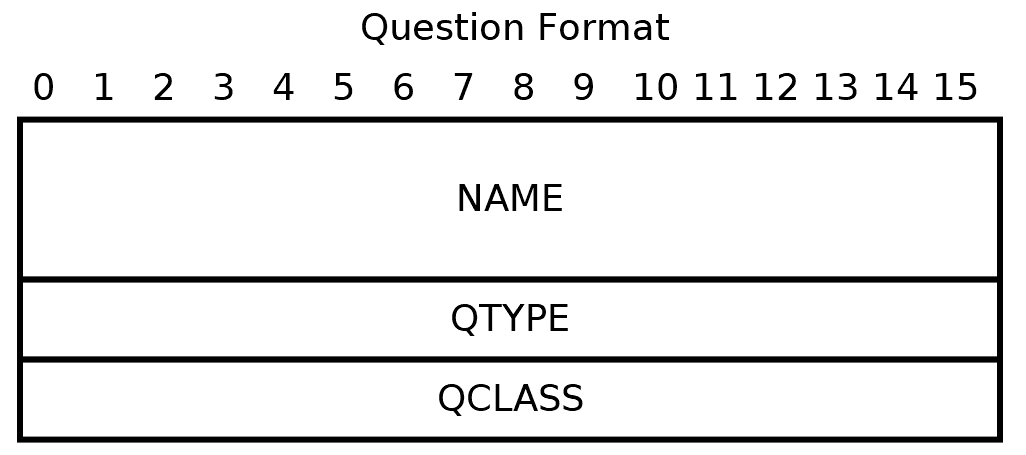
QTYPE indicates the record type we are asking for, and QCLASS should be set to 1 to indicate the internet.
The name field involves a special encoding. First, a hostname should be broken up into its individual labels. For example, www.example.com would be broken up into www, example, and com. Then, each label should be prepended with 1 byte, indicating the label length. Finally, the entire name ends with a 0 byte.
Visually, the name www.example.com is encoded as follows:

If the QTYPE and QCLASS fields were appended to the preceding name example, then it could make up an entire DNS question.
A DNS response is sometimes required to repeat the same name multiple times. In this case, a DNS server may encode a pointer to an earlier name instead of sending the same name multiple times. A pointer is indicated by a 16-bit value with the two most significant bits set. The lower 14 bits indicate the pointer value. This 14-bit value specifies the location of the name as an offset from the beginning of the message. Having the two most significant bits reserved has an additional side-effect of limiting labels to 63 characters. A longer name would require setting both high bits in the label length specifier, but if both high bits are set, it indicates a pointer and not a label length!
The answer format is similar to the question format but with a few more fields. Let's look at that next.