- Open the sequential file in read-only mode using the following code:
fp = fopen (argv [1],"r");
- If the file does not exist or does not have enough permissions, an error message will be displayed and the program will terminate, as shown in the following code:
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("%s file does not exist\n", argv[1]);
exit(1);
}
- Initialize the counter that will count the number of vowels in the file to 0, as shown in the following code:
count=0;
- One line is read from the file, as shown in the following code:
fgets(buffer, BUFFSIZE, fp);
- Each character of the line is accessed and checked for any lowercase or uppercase vowels, as shown in the following code:
if(buffer[i]=='a' || buffer[i]=='e' || buffer[i]=='i' || buffer[i]=='o' || buffer[i]=='u' || buffer[i]=='A' || buffer[i]=='E' || buffer[i]=='I' || buffer[i]=='O' || buffer[i]=='U')
- If any vowel is found, the value of the counter is incremented by 1, as shown in the following code:
count++;
- Step 5 will be repeated until the end of the line has been reached. Check whether the end of the file has been reached. Repeat from step 4 until the end of the file, as shown in the following code:
while (!feof(fp))
- Display the count of the number of vowels in the file by printing the value in the counter variable on the screen, as shown in the following code:
printf("The number of vowels are %d\n",count);
The preceding steps are shown in the following diagram:
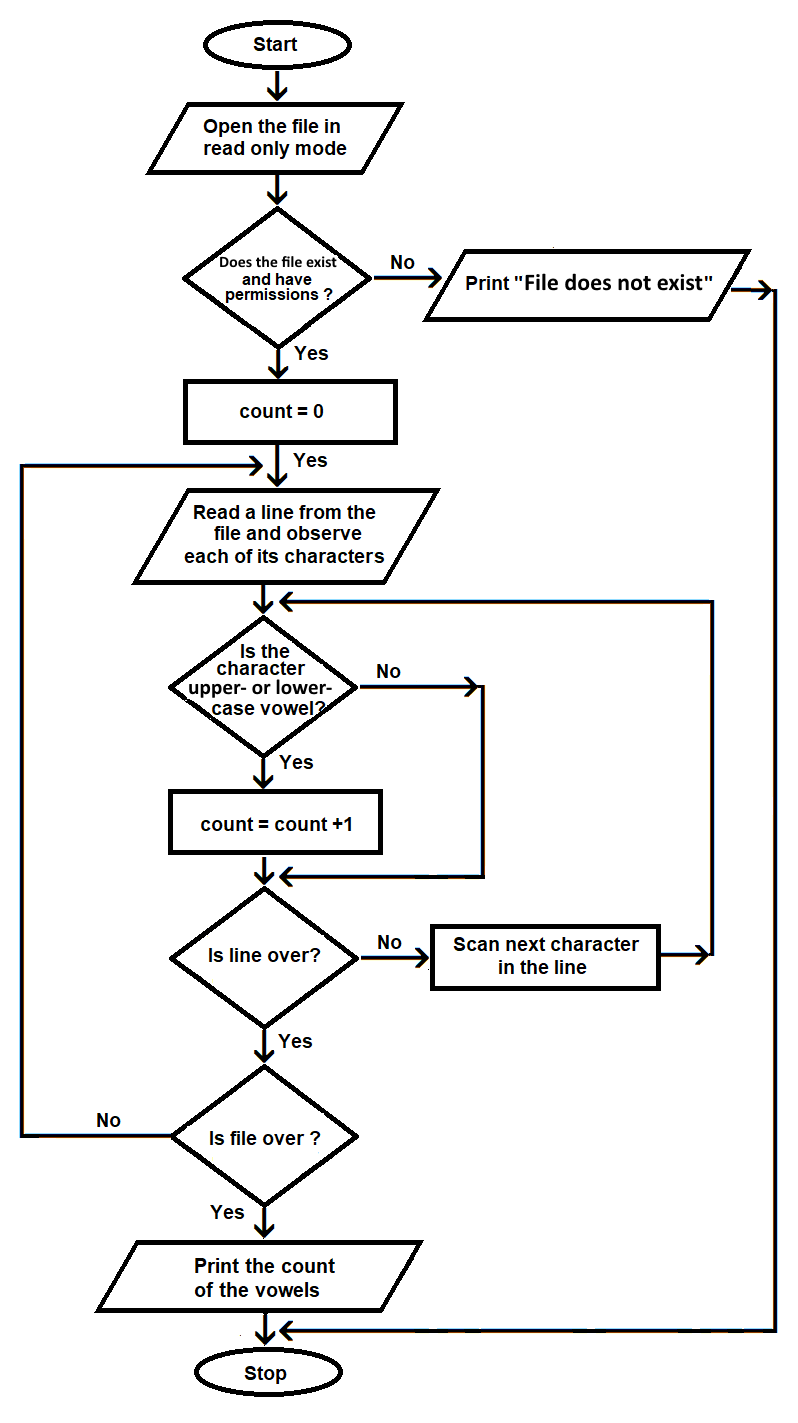
Figure 5.3
The countvowels.c program to count the number of vowels in a sequential text file is as follows:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define BUFFSIZE 255
void main (int argc, char* argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
char buffer[BUFFSIZE];
int n, i, count=0;
fp = fopen (argv [1],"r");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("%s file does not exist\n", argv[1]);
exit(1);
}
printf("The file content is :\n");
while (!feof(fp))
{
fgets(buffer, BUFFSIZE, fp);
puts(buffer);
n=strlen(buffer);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(buffer[i]=='a' || buffer[i]=='e' || buffer[i]=='i' ||
buffer[i]=='o' || buffer[i]=='u' || buffer[i]=='A' ||
buffer[i]=='E' || buffer[i]=='I' || buffer[i]=='O' ||
buffer[i]=='U') count++;
}
}
printf("The number of vowels are %d\n",count);
fclose(fp);
}
Now, let's go behind the scenes.