1 Introduction
One of the key conditions for a timely response to critical undesirable deviations that are substantial, extreme and exert significant negative impact on the enterprises operation is the availability of an effective stress management system. The multidimensional and diverse nature of these deviations necessitates the appropriate theoretical and practical training of managers engaged in such processes.
Identification and determination of potential vulnerabilities in the production and economic activity of the enterprise from the point of view of emergence of critical undesirable deviations;
Development, implementation and formalization of the key elements of the stress management system;
Development of a list of potential critical undesirable deviations for each key business process of the company;
Development of a complex of potential measures for influence on critical undesirable deviations;
Establishment of criteria for the interpretation of critical undesirable deviations in such a way as to necessitate the use of managerial measures to influence them.
Critical undesirable deviations in the activities of business entities may take different forms determined by a number of parameters, namely: duration of the individual stages of deviations, the reasons behind their occurrence, level of influence on business processes, tools for managing them, etc.
The study of theory and practice makes it possible to conclude that the low level of process management within the stress management systems determines not only the increase in critical undesirable deviations, but also their negative impact on the activities of business entities. Therefore, it is important to have effective tools for simulating and reengineering such processes.
To build stress management systems at enterprises, it is expedient to use the simulation tools. It makes it possible to clearly identify the functional boundaries of each manager within this process, recipients and disseminators of information, timing for the implementation of the relevant work, level of responsibility and authority, etc. Simulation also provides for transparency of stress management systems since it allows you to understand the directions of documentation, information, communications, etc.
In addition, since in terms of their content the absolute majority of parameters for simulating the impact of a potential or actual incident that causes undesirable deviation for each link in the supply-production-marketing chain are fuzzy, it is feasible and necessary to use fuzzy set tools to solve the specified problem.
2 Paper Preparation
2.1 Features of Incident Criticality Simulation in the Stress Management Systems
 :
: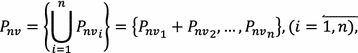
 is the number of potential incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain, each of which can be represented as a function similar to [2–4]:
is the number of potential incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain, each of which can be represented as a function similar to [2–4]:
-

is the designation of the i-th incident in the supply-production-marketing chain which may lead to a critical undesirable deviation;
-

a subset of parameters used to identify the i-th incident (or its prediction);
-

a subset of all possible fuzzy (linguistic) values of the i-th incident;
-

a subset of actual values of the i-th incident at a certain time and space;
-

a subset of heuristic rules formed on the basis of fuzzy logic for each individual i-th incident;
-

the level of criticality of the undesirable deviation in the supply-production-marketing chain caused by the i-th incident.
Taking into account formula (2) and the information described in the work [1, p. 49], the level of undesirable deviation in the stress management system can be considered critical, provided that  where
where  is the average level of criticality of the undesirable deviation. Provided that
is the average level of criticality of the undesirable deviation. Provided that  (the low level of criticality of the undesirable deviation caused by the i-th incident in the supply-production-marketing chain), the enterprise may decide on the influence on it using conventional methods or ignoring it as not causing significant damage to the production and economic activity of the business entity.
(the low level of criticality of the undesirable deviation caused by the i-th incident in the supply-production-marketing chain), the enterprise may decide on the influence on it using conventional methods or ignoring it as not causing significant damage to the production and economic activity of the business entity.
 , it should be noted that such incidents are proposed to be considered within the supply, production, and marketing processes of each individual entity. Given this, the set of identifiers for i-th incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain with
, it should be noted that such incidents are proposed to be considered within the supply, production, and marketing processes of each individual entity. Given this, the set of identifiers for i-th incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain with  should be displayed as follows:
should be displayed as follows:
 are the identifiers of incident groups within the supply, production and marketing processes of the enterprise, respectively.
are the identifiers of incident groups within the supply, production and marketing processes of the enterprise, respectively. , it should be noted that this subset must include key parameters
, it should be noted that this subset must include key parameters  . Moreover, it is fair to assert that
. Moreover, it is fair to assert that  and
and
2.2 Parameters for Simulating the Impact of a Potential or Actual Incident on the Links of the Supply-Production-Marketing Chain
- 1.
Reliability of the supply chain
 . The parameter, based on the review and generalization of literary sources, is one of the key indicators in the supply logistics and, to some extent, generalizes its effectiveness. Taking into account the results of research by V. Ermoshyn [5, p. 56], it should be noted that the reliability parameter of the supply chain indicates the effectiveness of supplying “the right products to the right place, at the right time, in the right condition and packaging, with the right documentation”. In a way, this parameter allows identifying both the flexibility of supply systems, the time to respond to changes in factors of the internal and external environment, production necessity planning, procurement plans development, ensuring operational schedule of supply, acceptance of raw materials, materials and components, checking their quality at the enterprise, etc.
. The parameter, based on the review and generalization of literary sources, is one of the key indicators in the supply logistics and, to some extent, generalizes its effectiveness. Taking into account the results of research by V. Ermoshyn [5, p. 56], it should be noted that the reliability parameter of the supply chain indicates the effectiveness of supplying “the right products to the right place, at the right time, in the right condition and packaging, with the right documentation”. In a way, this parameter allows identifying both the flexibility of supply systems, the time to respond to changes in factors of the internal and external environment, production necessity planning, procurement plans development, ensuring operational schedule of supply, acceptance of raw materials, materials and components, checking their quality at the enterprise, etc.
- 2.
Inventory management system
 . The problems in the field of supply can be evidenced by the untenable and inefficient inventory management system at the enterprise. Its typical features may, in particular, include constant shortage of stocks, on the one hand, and their surplus—on the other. Thus, the stock shortages are known to cause interruptions in the production process, and, consequently, decrease in sales volumes and decrease in revenue from the sales of products. In turn, the surplus of stocks also leads to a number of problems such as increase in costs for the storage of raw materials, materials or components, physical and moral aging of the latter at the enterprise, etc.
. The problems in the field of supply can be evidenced by the untenable and inefficient inventory management system at the enterprise. Its typical features may, in particular, include constant shortage of stocks, on the one hand, and their surplus—on the other. Thus, the stock shortages are known to cause interruptions in the production process, and, consequently, decrease in sales volumes and decrease in revenue from the sales of products. In turn, the surplus of stocks also leads to a number of problems such as increase in costs for the storage of raw materials, materials or components, physical and moral aging of the latter at the enterprise, etc.
- 3.
Negative reaction from external sales stakeholders
 This parameter is suitable primarily for simulating the impact of incidents in the field of sales. As the study of theory and practice suggests, a significant indicator of the future crisis at an enterprise may include negative reaction to cooperation with the company under review primarily on the part of sales intermediaries and end users (however, potential negative issues can also be evidenced by negative assessments from intermediaries, creditors, financial institutions, shareholders, etc.). This negative reaction may be due to various reasons (e.g., deterioration in product quality, default by the company on its contractual obligations, regular changes in strategy, objectives and policies, frequent conflicts with business entities, etc.). In any case, negative reaction from external sales stakeholders means problems in the field of product sales, in particular, a significant decrease in its volumes, and thus a decrease in the revenue from the sales of products, increase in inventory balances, deterioration of turnover, etc. Within the scope of the study, we will consider the level of negative reaction as a measure of this negative reaction parameter on the part of external sales stakeholders; it is proposed to be calculated as the ratio of the number of external sales stakeholders that negatively assesses the cooperation with the enterprise-producer to the total number of such stakeholders.
This parameter is suitable primarily for simulating the impact of incidents in the field of sales. As the study of theory and practice suggests, a significant indicator of the future crisis at an enterprise may include negative reaction to cooperation with the company under review primarily on the part of sales intermediaries and end users (however, potential negative issues can also be evidenced by negative assessments from intermediaries, creditors, financial institutions, shareholders, etc.). This negative reaction may be due to various reasons (e.g., deterioration in product quality, default by the company on its contractual obligations, regular changes in strategy, objectives and policies, frequent conflicts with business entities, etc.). In any case, negative reaction from external sales stakeholders means problems in the field of product sales, in particular, a significant decrease in its volumes, and thus a decrease in the revenue from the sales of products, increase in inventory balances, deterioration of turnover, etc. Within the scope of the study, we will consider the level of negative reaction as a measure of this negative reaction parameter on the part of external sales stakeholders; it is proposed to be calculated as the ratio of the number of external sales stakeholders that negatively assesses the cooperation with the enterprise-producer to the total number of such stakeholders. - 4.
Competitiveness of the marketing mix
 . Identification of incidents in the field of sales can be done by identifying problems with the false forecast of demand for products, ineffective positioning of products in the market, inappropriate pricing policies, negative changes in the structure of the orders portfolio, imbalances in marketing policies, inadequate sales promotion, etc. The above should be generalized in the competitiveness parameter of the marketing mix.
. Identification of incidents in the field of sales can be done by identifying problems with the false forecast of demand for products, ineffective positioning of products in the market, inappropriate pricing policies, negative changes in the structure of the orders portfolio, imbalances in marketing policies, inadequate sales promotion, etc. The above should be generalized in the competitiveness parameter of the marketing mix.
- 5.
Production process quality
 . This parameter should also be considered generalized during the simulation of the impact of incidents in the industrial sphere of the enterprise. Thus, problems can arise in case of inefficient production technology, deficit or surplus of resources taking into account anticipated expected production volumes, inappropriate level of production capacity, low level of control over individual parts of the production process, inappropriate priorities in the spheres of research and development, etc. It is proposed to consider the above in general within the parameters of the production process quality. Low quality of the production process can result, for example, in the failure of planned production volumes, inappropriate energy consumption, increase in equipment downtime, etc. The measure of this parameter, as in the previous case, should be such quality level, which is also proposed to be established in an organization using an expert method.
. This parameter should also be considered generalized during the simulation of the impact of incidents in the industrial sphere of the enterprise. Thus, problems can arise in case of inefficient production technology, deficit or surplus of resources taking into account anticipated expected production volumes, inappropriate level of production capacity, low level of control over individual parts of the production process, inappropriate priorities in the spheres of research and development, etc. It is proposed to consider the above in general within the parameters of the production process quality. Low quality of the production process can result, for example, in the failure of planned production volumes, inappropriate energy consumption, increase in equipment downtime, etc. The measure of this parameter, as in the previous case, should be such quality level, which is also proposed to be established in an organization using an expert method. - 6.
Production process flexibility
 . As theory and practice suggest, production process flexibility is important under the conditions of dynamic environment of the enterprise. It is considered from different aspects in the literature, while most authors hold an opinion that the flexibility indicates the ability of the production process to be promptly readjusted to manufacture new or modified products as a result of changing market requirements. Such a reorganization may include solving various problems, in particular, reequipping of technological processes, changes in the structure of production process or integrating new elements into it, introducing parallel technological channels, etc. It is obvious that the measure of the production process flexibility parameter should be the time to adjust it for the manufacture of a new or improved product (expert estimates should apply).
. As theory and practice suggest, production process flexibility is important under the conditions of dynamic environment of the enterprise. It is considered from different aspects in the literature, while most authors hold an opinion that the flexibility indicates the ability of the production process to be promptly readjusted to manufacture new or modified products as a result of changing market requirements. Such a reorganization may include solving various problems, in particular, reequipping of technological processes, changes in the structure of production process or integrating new elements into it, introducing parallel technological channels, etc. It is obvious that the measure of the production process flexibility parameter should be the time to adjust it for the manufacture of a new or improved product (expert estimates should apply). - 7.
The level of planned processes violation
 This parameter is suitable for simulating the impact of incidents in the field of supply, as well as in the field of production and marketing. Any deviation from the planned parameters may be promptly eliminated and significantly violate the established rules, mechanisms, policies, regulations, etc. The higher the level of violations, the higher the negative effects of crisis phenomena. This parameter must be both a measure and assessed by an expert method at the enterprise.
This parameter is suitable for simulating the impact of incidents in the field of supply, as well as in the field of production and marketing. Any deviation from the planned parameters may be promptly eliminated and significantly violate the established rules, mechanisms, policies, regulations, etc. The higher the level of violations, the higher the negative effects of crisis phenomena. This parameter must be both a measure and assessed by an expert method at the enterprise.
Each of the abovementioned parameters characterizes certain side of the incidents impact simulation in the supply-production-marketing chain. Obviously, under certain conditions, such parameters can complement each other and thereby increase the negative effect. Understanding how these parameters affect the entity’s activities allows you to identify potential problems, make predictions, take preventive measures, etc.
Each business entity has its priority in the identification of incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain within the framework of stress management systems. In many respects, such priority is determined by the activity of the enterprise, its stage of the life cycle, management parameters, etc. On the other hand, it should be borne in mind that different companies will react differently to existing or potential problems in the supply-production-marketing chain.
2.3 Justification of Feasibility of Using the Fuzzy Sets Theory for Diagnosing the Undesirable Deviation Criticality Level
In terms of their content the absolute majority of parameters for simulating the impact of a potential or actual incident that causes undesirable deviation for each link in the supply-production-marketing chain are fuzzy, it is feasible and necessary to use fuzzy set tools for further research. Based on the review and generalization of literary sources [6–10], the theory of fuzzy sets is widely used in solving various economic problems.
 should be formed on the basis of a set of parameters
should be formed on the basis of a set of parameters  , while:
, while:

-

is the number of potential incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain;
-

the number of parameters within the stress management systems associated with the i-th incident.
 within the framework of stress management systems, we obtain the following:
within the framework of stress management systems, we obtain the following:  Thus, formula (7) will be as follows:
Thus, formula (7) will be as follows:
-

appropriate parameters for identifying incidents within the supply section
 ;
;-

appropriate parameters for identifying incidents within the production section;
-

appropriate parameters for identifying incidents within the marketing section.
Parameters for diagnosing incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain
Parameters | Sections | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Supply section | Production section | Marketing section | |
Reliability of the supply chain | X | ||
Inventory management system | X | ||
Negative reaction on the part of external sales stakeholders | X | ||
Competitiveness of the marketing mix | X | ||
Production process quality | X | ||
Production process flexibility | X | ||
The level of planned processes violation | X | X | X |
2.4 Description from the Position of Fuzzy Sets of a Subset of All Possible Fuzzy (Linguistic) Values of Incidents
Then, it is necessary to describe a subset of all possible fuzzy (linguistic) values of the i-th incident, as well as a subset of heuristic rules formed on the basis of fuzzy logistics for each such incident from the position of fuzzy sets. This will eventually identify the level of undesirable deviation in the supply-production-marketing chain caused by the i-th incident.
 functions (Fig. 1).
functions (Fig. 1).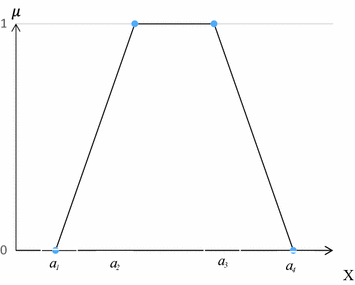

 —are the numerical parameters (actual values) of the trapezoidal
—are the numerical parameters (actual values) of the trapezoidal  function, in turn
function, in turn  ;
;  —are the left zero value of the function;
—are the left zero value of the function;  —right zero value of the function;
—right zero value of the function;  —points where the value of the membership function is maximum (trapezium vertex) (i.e. the certainty of the allegation of affiliation to a certain term-set).
—points where the value of the membership function is maximum (trapezium vertex) (i.e. the certainty of the allegation of affiliation to a certain term-set).Taking into account the peculiarities of the tasks solved in the context of simulating critical undesirable deviations in the supply-production-marketing chain, we should stress the appropriateness of using the following approach to the reflection of linguistic variables within the limits given in Fig. 1 of the trapezoidal membership function, i.e.:  —pessimistic assessment;
—pessimistic assessment;  —optimistic assessment;
—optimistic assessment;  —the most realistic assessment.
—the most realistic assessment.
Trapezoidal scale of all possible fuzzy (linguistic) values of the diagnosis of the i-th incident within the framework of stress management systems
Linguistic variables | Very low | Low | Average | High | Very high |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Trapezoidal scales of assessments | (0; 0; 0.1; 0.3) | (0.1; 0.3; 0.3; 0.5) | (0.3; 0.5; 0.5; 0.7) | (0.5; 0.7; 0.7; 0.9) | (0.7; 0.9; 1.0; 1.0) |
 , it should be noted that for each such rule the following expression is true:
, it should be noted that for each such rule the following expression is true:
-

is p-th rule for the diagnosis of a potential i-th incident within stress management systems;
-

a unique state identifier for each i-th incident (and this state takes into account the number of diagnostic parameters of the i-th incident and the number of terms);
-

element of the set of linguistic variables of the i-th incident.
 can acquire the values “very low”, “low”, “average”, “high” and “very high”, and also denoting the value of the output parameters as H—low, C—average, B—high and D—very high, we give a set of heuristic rules
can acquire the values “very low”, “low”, “average”, “high” and “very high”, and also denoting the value of the output parameters as H—low, C—average, B—high and D—very high, we give a set of heuristic rules  for the diagnosis of incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain (Table 3).
for the diagnosis of incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain (Table 3).A set of heuristic rules  for diagnosing incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain
for diagnosing incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain
Rule number | Indicators in the supply-production-marketing chain | Result | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| ||
1 | VL | VL | VL | H |
2 | VL | VL | LW | H |
3 | VL | VL | AR | H |
4 | VL | VL | HG | C |
5 | VL | VL | VH | C |
6 | VL | LW | VL | H |
7 | VL | LW | LW | H |
8 | VL | LW | AR | H |
9 | VL | LW | HG | C |
10 | VL | LW | VH | C |
11 | VL | AR | VL | H |
12 | VL | AR | LW | H |
13 | VL | AR | AR | C |
14 | VL | AR | HG | C |
15 | VL | AR | VH | C |
16 | VL | HG | VL | C |
17 | VL | HG | LW | C |
18 | VL | HG | AR | C |
19 | VL | HG | HG | B |
20 | VL | HG | VH | B |
21 | VL | VH | VL | C |
22 | VL | VH | LW | C |
23 | VL | VH | AR | C |
24 | VL | VH | HG | B |
25 | VL | VH | VH | B |
26 | LW | VL | VL | H |
27 | LW | VL | LW | H |
28 | LW | VL | AR | C |
29 | LW | VL | HG | C |
30 | LW | VL | VH | C |
31 | LW | LW | VL | H |
32 | LW | LW | LW | H |
33 | LW | LW | AR | H |
34 | LW | LW | HG | C |
35 | LW | LW | VH | C |
36 | LW | AR | VL | H |
37 | LW | AR | LW | H |
38 | LW | AR | AR | C |
39 | LW | AR | HG | C |
40 | LW | AR | VH | C |
41 | LW | HG | VL | H |
42 | LW | HG | LW | H |
43 | LW | HG | AR | C |
44 | LW | HG | HG | C |
45 | LW | HG | VH | B |
46 | LW | VH | VL | C |
47 | LW | VH | LW | C |
48 | LW | VH | AR | C |
49 | LW | VH | HG | B |
50 | LW | VH | VH | B |
51 | AR | VL | VL | H |
52 | AR | VL | LW | H |
53 | AR | VL | AR | C |
54 | AR | VL | HG | C |
55 | AR | VL | VH | C |
56 | AR | LW | VL | H |
57 | AR | LW | LW | H |
58 | AR | LW | AR | C |
59 | AR | LW | HG | C |
60 | AR | LW | VH | C |
61 | AR | AR | VL | C |
62 | AR | AR | LW | C |
63 | AR | AR | AR | C |
64 | AR | AR | HG | C |
65 | AR | AR | VH | B |
66 | AR | HG | VL | C |
67 | AR | HG | LW | C |
68 | AR | HG | AR | C |
69 | AR | HG | HG | B |
70 | AR | HG | VH | B |
71 | AR | VH | VL | C |
72 | AR | VH | LW | C |
73 | AR | VH | AR | C |
74 | AR | VH | HG | B |
75 | AR | VH | VH | D |
76 | HG | VL | VL | H |
77 | HG | VL | LW | H |
78 | HG | VL | AR | C |
79 | HG | VL | HG | C |
80 | HG | VL | VH | B |
81 | HG | LW | VL | H |
82 | HG | LW | LW | H |
83 | HG | LW | AR | C |
84 | HG | LW | HG | B |
85 | HG | LW | VH | B |
86 | HG | AR | VL | C |
87 | HG | AR | LW | C |
88 | HG | AR | AR | C |
89 | HG | AR | HG | B |
90 | HG | AR | VH | B |
91 | HG | HG | VL | C |
92 | HG | HG | LW | B |
93 | HG | HG | AR | B |
94 | HG | HG | HG | B |
95 | HG | HG | VH | B |
96 | HG | VH | VL | B |
97 | HG | VH | LW | B |
98 | HG | VH | AR | B |
99 | HG | VH | HG | B |
100 | HG | VH | VH | D |
101 | VH | VL | VL | H |
102 | VH | VL | LW | H |
103 | VH | VL | AR | C |
104 | VH | VL | HG | C |
105 | VH | VL | VH | B |
106 | VH | LW | VL | H |
107 | VH | LW | LW | H |
108 | VH | LW | AR | C |
109 | VH | LW | HG | B |
110 | VH | LW | VH | B |
111 | VH | AR | VL | C |
112 | VH | AR | LW | C |
113 | VH | AR | AR | C |
114 | VH | AR | HG | B |
115 | VH | AR | VH | D |
116 | VH | HG | VL | B |
117 | VH | HG | LW | B |
118 | VH | HG | AR | B |
119 | VH | HG | HG | B |
120 | VH | HG | VH | D |
121 | VH | VH | VL | B |
122 | VH | VH | LW | B |
123 | VH | VH | AR | D |
124 | VH | VH | HG | D |
125 | VH | VH | VH | D |
Moreover, it should be noted that due to the same number of diagnostic parameters of these incidents, as well as the same formed set  (“very low”, “low”, “average”, “high” and “very high”) and the same approach to displaying the output parameters (H—low, C—average, B—high and D—very high), the number and contents of the heuristic rules
(“very low”, “low”, “average”, “high” and “very high”) and the same approach to displaying the output parameters (H—low, C—average, B—high and D—very high), the number and contents of the heuristic rules  for the diagnosis of incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain will be the same irrespective of the elements of this chain, which somehow simplifies further calculations in this area within of stress management systems at the enterprise.
for the diagnosis of incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain will be the same irrespective of the elements of this chain, which somehow simplifies further calculations in this area within of stress management systems at the enterprise.
As shown in information in Table 3, in the analyzed context, we should mention the existence of 125 heuristic rules  for the diagnosis of incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain.
for the diagnosis of incidents in the supply-production-marketing chain.
2.5 Integrated Models for Incident Groups in the Supply-Production-Marketing Chain




Results of diagnosing criticality of some actual incidents at PJSC “Lviv Locomotive Repair Plant” in Q4 2017
Links of the supply-production-marketing chain | Incidents | Fuzzy (linguistic) values of influence | Level of criticality (identified by a set of heuristic rules | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Supply | Delays in the supply of brake equipment | Reliability of the supply chain | Inventory management system | The level of planned processes violation | High |
High | High | High | |||
Noncompliance with the standards of purchased contactors of the MK series | Reliability of the supply chain | Inventory management system | The level of planned processes violation | Average | |
Average | Average | High | |||
Marketing | Different decrease in demand for the thermal treatment of shafts by external customers | Negative reaction on the part of external sales stakeholders | Competitiveness of the marketing mix | The level of planned processes violation | Low |
Low | Average | Low | |||
Negative feedback on the quality of wheeled pairs repair | Negative reaction on the part of external sales stakeholders | Competitiveness of the marketing mix | The level of planned processes violation | High | |
High | High | Average | |||
Thus, the results of diagnosing the criticality of certain actual incidents at PJSC “Lviv Locomotive Repair Plant” in Q4 2017 make it possible to conclude that it is expedient to interpret delays in the supply of brake equipment, as well as negative feedback on the quality of wheel pairs repair as critical. The foregoing suggests the possibility of practical use of the proposed method for diagnosing the level of criticality of undesirable deviation in the supply-production-marketing chain.
It should be noted that PJSC “Lviv Locomotive Repair Plant” is one of the leading enterprises of Ukrainian railway, and this justifies its selection as an object for diagnosing the possibility of implementation the method of undesirable deviation criticality level diagnostic in the supply-production-marketing chain. Today, this is one of the leading enterprise in Ukraine in repairing locomotives. The Company is equipped with the current techniques and the breakthrough technologies are being widely used. The plant carries out the medium repairs and overhaul of the trunk electric locomotives, both direct and alternating current, repairs of industrial railway transport and the quarry electric locomotives traction units, as well as repairs the traction motors, auxiliary electrical machines, wheel sets, etc.
PJSC “Lviv Locomotive Repair Plant” is a successful modern enterprise, which is developing dynamically and efficiently provides its services in the rolling stock repairs and modernization of the whole post-Soviet area railways. For the consistently high quality and benefits achieved in the Ukrainian business of the repair and maintenance of the railway rolling stock, the plant was repeatedly awarded with the “Star of Quality” and as the “Enterprise of the Year” of the National Rating of Goods and Services Quality of Ukraine, as well as with the International Economic Rating “League of the Bests”. In recent years, the plant won the winner’s fame of the “Face of the City” contest in the category “Lviv Industrial”.
At PJSC “Lviv Locomotive Repair Plant”, the certification center TUV SUD Management Service GmbH has realized the certified audit of the quality management system for compliance with the requirements of ISO 9001:2015. Based on the audit results (report number 707084328), a positive decision according the certificate issue has been taken. The Certificate is in force from 01/05/2018 to 01/04/2021.
the market conditions change;
failure to provide the plant activities with the sufficient amount of raw materials, materials and energy;
a lack in training the plant employees to produce new types of competitive products;
deterioration of the general economic situation in Ukraine, the tax law instability.
Key problems that make a significant influence on the PJSC “Lviv Locomotive Repair Plant” activities from the position of critical undesirable deviations are the problems of political, economic and production-technological character. In particular, the political instability in the country and management change of the branch made a negative impact on the stability and sustainability of production due to the insufficient planning and financing the orders volumes of Ukrzaliznytsia. Too harsh pricing policy of the monopolist-customer has a harmful impact on the production and solvency; because of the lack of working capital, the timely manufacture kitting-up gets broken, the time schedules and technologies of repairs works deform, and this leads to quality deterioration and the production costs increase. Besides, in such conditions the company is not able to renew the fixed assets according the plan and fully, to absorb new technologies and new types of overhaul and modernization. The financial plan of PJSC “Lviv Locomotive Repair Plant” has proposed a complex of measures for reducing possible risks, which would allow to minimize these risks, as the financial plan is based on the calculations and on the company’s abilities to improve the financial, organization and production situation. At this stage the Company requires the support of the Government of Ukraine in matters of the plant reconstruction by supporting the potential investors.
At the same time, it should be mentioned that the production and services in electric locomotives overhaul at PJSC “Lviv Locomotive Repair Plant” is profitable and have perspectives of the further demand growth on the market of Ukraine and CIS countries. Business operations financing is realized according to the principle of planned self-financing. The funds receipted from the sold production are being allocated by the enterprise on its own to cover the items of production costs, wage fund, taxes, contributions to the social security funds, losses, etc. The Company, in accordance with the agreements terms, must receive cash for the performed products (services) within a period not exceeding 10 days after the works are completed. Most often it happens that the customers postpone their payments. That is why the Issuer is making every effort to replenish the working capital in order to provide payments of wages, taxes, compulsory payments, and so on. To do this, the Issuer uses the banking services to get the short-term credits. It is also provided for the Company to use the funds to purchase the fixed assets, intangible assets and for the other purposes that contribute to the production development, improve social conditions of the Company’s employees and their material welfare. Renovation of the production fixed assets, implementation of the new breakthrough technologies, mastering the new types of repairs require the commitment of significant financial resources in the form of profitable investment projects. The separate investment projects of production diversification by means of electric locomotives modernization development are promising.
Information about the product sales of PJSC “Lviv Locomotive Repair Plant” in the 1st quarter of 2018
# | The main types of the enterprise products | Output volume | Sales volume | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In monetary terms, thousand UAH | In percent to the total output (%) | In monetary terms, thousand UAH | In percent to the total sales volume (%) | ||
1 | Services in the rolling stock repair and modernization | 14,397 | 54.13 | 20,475 | 67.69 |
2 | Services in the wheel sets repair | 8234 | 30.96 | 7275 | 24.05 |
3 | Services in the traction motors repair | 2549 | 9.58 | 1674 | 5.53 |
4 | Other services | 1218 | 4.58 | 824 | 2.72 |
3 Conclusion
The proposed method for diagnosing the level of criticality of an undesirable deviation in the supply-production-marketing chain enables the analysts to simulate the impact of a potential or actual incident that causes such a deviation on each link in the chain using a number of representative parameters (reliability of the supply chain, inventory management system, negative response from external marketing stakeholders, competitiveness of the marketing complex, quality of the production process, flexibility of the production process, level of planned processes violation). Simulation of stress management systems in the supply-production-marketing chain enables us to identify the level of influence of potential incidents on each of these areas. If necessary, it is also possible to determine the level of influence of these incidents on the chain as a whole.
























