The pod is a new concept introduced by Kubernetes. A pod is comprised of a group of related containers that represent a specific application. This is the most basic unit within Kubernetes; you don't have to keep thinking about containers because pods are what you should focus on here.
Let's consider an application called XYZ that stores its information in a database that exposes a REST API that is consumed by its UI, as shown in the following diagram:
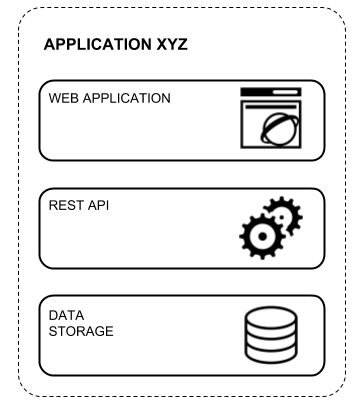
It's obvious that we need three separate services to make this application work. If we were dealing with Docker, we would say that we need three different containers, but from a Kubernetes perspective, all these three containers represent a single pod. This abstraction allows us to manage distributed applications more easily. In order to create a pod definition, you should create a .yaml file describing all the containers that are part of the pod. An example of the XYZ application that we mentioned earlier is described in the following code:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: application-xyz
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
- name: database
image: mysql
volumeMounts:
- name: mysql-data
mountPath: /path
- name: api
image: <your-api-image>
Once the file is created, you can execute the pod using the following Kubernetes command:
kubectl create -f <file-name.yaml>