Full nodes can autonomously verify transactions without external reference. They use a bottom-up verification approach. This means that they can track each and every coin from the moment of its creation through all transactions it's been involved in. In doing so, they start from the genesis block and go up the chain of blocks to get to the current transaction that needs to be verified. This can be better visualized using the following diagram:
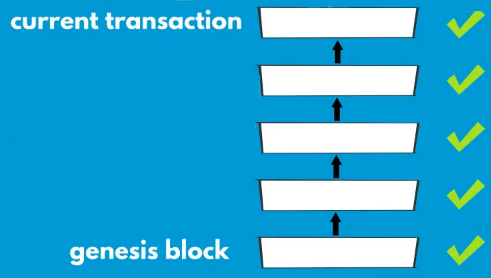
In this way, they know which coins have been spent and when, and who is the rightful owner of each coin at all times. Maintaining a full node comes with its own resource requirements in terms of storage capacity, as the size of the Bitcoin blockchain currently stands at 160 gigabytes.