CHAPTER 5
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNATIONAL SYSTEM OF UNITS (SI) – Conversion Factors for General Use (Unidirectional Alphabetical Conversion App Section)
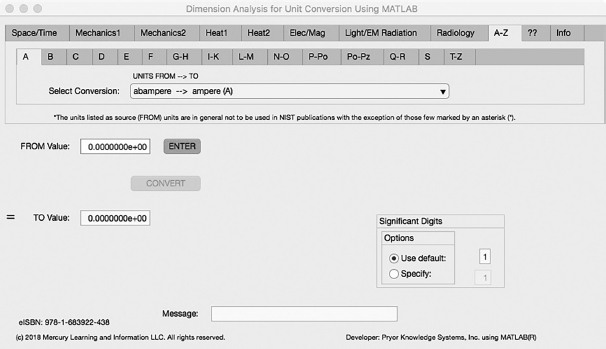
FIGURE 5-0 Unit Conversion MATLAB App Front Panel - A-Z Tab.
The NIST Special Publication 811{30} includes an alphabetical list of conversions to SI units. Conversion factors are the mathematical multiplier or divisor and associated units that allow any compatible measurements to be converted from one system of units to another system of units (e.g., inches to centimeters or vice versa). From-units listed, except those preceded by an asterisk, are not to be used in NIST publications.
Figure 5-0 shows the Unit Converter MATLAB App Front Panel with the A-Z Tab selected. Unidirectional matrices were created and installed within this app to allow the user the ability to easily select via pull-down menus the desired conversion pair. Each of the Tabs available in the App is explored herein.
5.1 A TAB
The first Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the A Tab (see Figure 5.1-1). This example demonstrates the conversion of ampere hour (A*h) to coulomb (C). In this example, the amplitude of ampere hours is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.1-1 {37}.
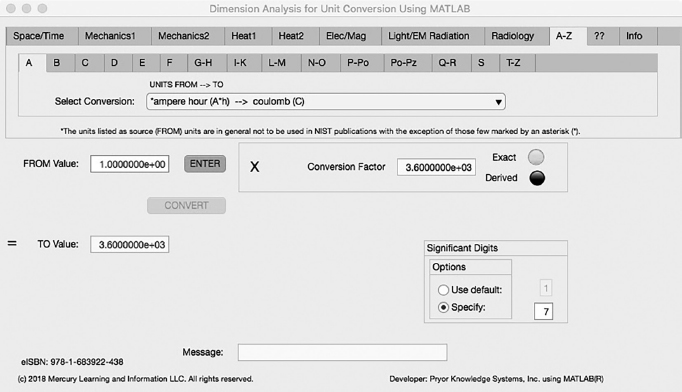
FIGURE 5.1-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - A Tab.
ampere hour (A*h) (=1.0) to coulomb (C) Example 5.1-1:
C | = | A * h * C/s * 1/A * s/min * min/h |
| = | A * h * 60 * 60 |
| = | A * h * 3.6E3 |
Where: C | = | the number of coulombs calculated |
A * h | = | the number of ampere hours to be converted (1.0) |
C/s * 1/A | = | the conversion factor from ampere to coulomb per second (1.0) |
s/min | = | the conversion factor from minute to second (60) |
min/h | = | the conversion factor from hour to minute (60) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
C = 1.0 * 3.6E3 = 3.6E3 coulomb | (5.1-1) |
The A-Z A Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / A | |
| abampere to ampere (A) |
| abcoulomb to coulomb (C) |
| abfarad to farad (F) |
| abhenry to henry (H) |
| abmho to siemens (S) |
| abohm to ohm (Ω) |
| abvolt to volt (V) |
| acceleration in free fall, standard (g) |
| to meter per second squared (m/s2) |
| acre (based on U.S. Survey foot) to square meter (m2) |
| acre foot (based on U.S. survey foot to cubic meter (m3) |
| *ampere hour (a * h) to coulomb (C) |
| angstrom (Å) to meter (m) |
| angstrom (Å) to nanometer (nm) |
| are (a) to square meter |
| *astronomical unit (ua) to meter (m) |
| atmosphere, standard (atm) to pascal (Pa) |
| atmosphere, standard (atm) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| atmosphere, technical (at) to pascal (Pa) |
| atmosphere, technical (at) to kilopascal (kPa) |
5.2 B TAB
The second Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the B Tab (see Figure 5.2-1). This example shows the conversion of bushel (bu) to cubic meter (m^3). In this example, the amplitude of bushel is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.2-1.
bushel (US) (bu) (=1.0) to cubic meter (m^3) Example 5.2-1:
m^3 = bu * m^3/ bu = bu * 3.523907E-2
Where: m^3 | = | the number of cubic meters calculated |
bu | = | the starting number of bushels (1.0) |
m^3/ bu | = | the conversion factor from bushel to cubic meter (3.523907E-2) |
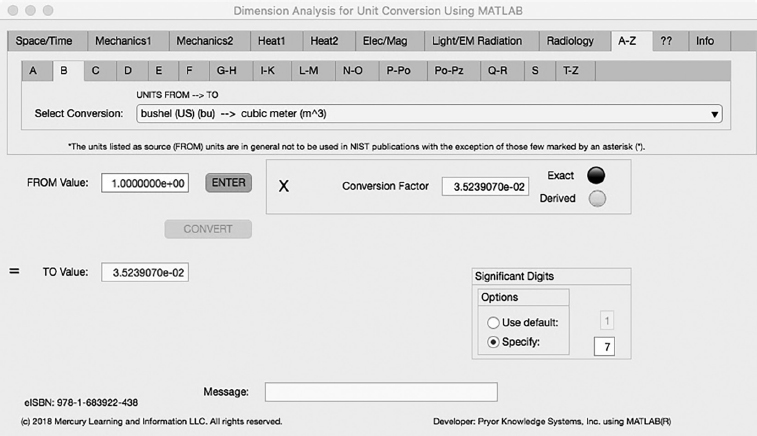
FIGURE 5.2-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - B Tab.
And:
The resulting solution is:
m^3 = 1.0 * 3.523907E-2 = 3.523907E-2 cubic meter | (5.2-1) |
The A-Z B Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / B | |
| *bar (bar) to pascal (Pa) |
| *bar (bar) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| *barn (b) to square meter (m^2) |
| barrel [for petroleum, 42 gallons (US)] (bbl) |
| to cubic meter (m^3) |
| barrel [for petroleum, 42 gallons (US)] (bbl) to liter (L) |
| biot (Bi) to ampere (A) |
| British thermal unit IT (Btu IT) to joule (J) |
| British thermal unit th (Btu IT) to joule (J) |
| British thermal unit (mean) (Btu) to joule (J) |
| British thermal unit (39 degF) to joule (J) |
| British thermal unit (59 degF) (Btu) to joule (J) |
| British thermal unit (60 degF) (Btu) to joule (J) |
| Btu IT foot per hour square foot degree Fahrenheit [Btu IT*ft/(h*ft^2*degF)] |
| to watt per meter kelvin [W / (m * K)] |
| Btu th foot per hour square foot degree Fahrenheit [Btu IT*ft/(h*ft^2*degF)] |
| to watt per meter kelvin [W / (m * K)] |
| Btu IT inch per hour square foot degree Fahrenheit [Btu IT*in/(h*ft^2*degF)] |
| to watt per meter kelvin [W / (m * K)] |
| Btu th inch per hour square foot degree Fahrenheit [Btu th*in/(h*ft^2*degF)] |
| to watt per meter kelvin [W / (m * K)] |
| Btu IT inch per second square foot degree Fahrenheit [Btu IT*in/(s*ft^2*degF)] |
| to watt per meter kelvin [W / (m * K)] |
| Btu th inch per second square foot degree Fahrenheit [Btu th*in/(s*ft^2*degF)] |
| to watt per meter kelvin [W / (m * K)] |
| Btu IT per cubic foot (Btu IT/ft^3) |
| to joule per cubic meter (J / m^3) |
| Btu th per cubic foot (Btu th/ft^3) |
| to joule per cubic meter (J / m^3) |
| Btu IT per degree Fahrenheit (Btu IT/degF) |
| to joule per kelvin (J / K) |
| Btu th per degree Fahrenheit (Btu th/degF) |
| to joule per kelvin (J/K) |
| Btu IT per degree Rankine (Btu IT/degR) |
| to joule per kelvin (J/K) |
| Btu th per degree Rankine (Btu th/degR) |
| to joule per kelvin (J/K) |
| Btu IT per hour (Btu IT/h) to watt (W) |
| Btu th per hour (Btu th/h) to watt (W) |
| Btu IT per hour square foot degree Fahrenheit [Btu IT/(h*ft^2*degF)] |
| to watt per square meter kelvin [W/(m^2* K)] |
| Btu th per hour square foot degree Fahrenheit [Btu th/(h*ft^2*degF)] |
| to watt per square meter kelvin [W/(m^2* K)] |
| Btu th per minute (Btu th/min) to watt (W) |
| Btu IT per pound (Btu IT/lb) to joule per kilogram (J/kg) |
| Btu th per pound (Btu th/lb) to joule per kilogram (J/kg) |
| Btu IT per pound degree Fahrenheit [Btu IT/(lb*degF)] |
| to joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg*K)] |
| Btu th per pound degree Fahrenheit [Btu th/(lb*degF)] |
| to joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg*K)] |
| Btu IT per pound degree Rankine [Btu IT/(lb*degR)] |
| to joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg*K)] |
| Btu th per pound degree Rankine [Btu th/(lb*degR)] |
| to joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg*K)] |
| Btu IT per second (Btu IT/s) to watt (W) |
| Btu th per second (Btu th/s) to watt (W) |
| Btu IT per second square foot degree Fahrenheit [Btu IT/(s*ft^2*degF)] |
| to watt per square meter kelvin [W/(m^2*K)] |
| Btu th per second square foot degree Fahrenheit [Btu th/(s*ft^2*degF)] |
| to watt per square meter kelvin [W/(m^2*K)] |
| Btu IT per square foot [Btu IT/(ft^2)] |
| to joule per square meter [J/(m^2)] |
| Btu th per square foot [Btu th/(ft^2)] |
| to joule per square meter [J/(m^2)] |
| Btu IT per square foot hour [Btu IT/(ft^2*h)] |
| to watt per square meter [W/(m^2)] |
| Btu th per square foot hour [Btu th/(ft^2*h)] |
| to watt per square meter [W/(m^2)] |
| Btu th per square foot minute [Btu th/(ft^2*min)] |
| to watt per square meter [W/(m^2)] |
| Btu IT per square foot second [Btu IT/(ft^2*s)] |
| to watt per square meter [W/(m^2)] |
| Btu th per square foot second [Btu th/(ft^2*s)] |
| to watt per square meter [W/(m^2)] |
| Btu th per square inch second [Btu th/(in^2*s)] |
| to watt per square meter [W/(m^2)] |
| bushel (US) (bu) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| bushel (US) (bu) to liter (L) |
5.3 C TAB
The third Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the C Tab (see Figure 5.3-1). This example shows the conversion of cubic yard (yd^3) to cubic meter (m^3). In this example, the amplitude of cubic yard is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.3-1.
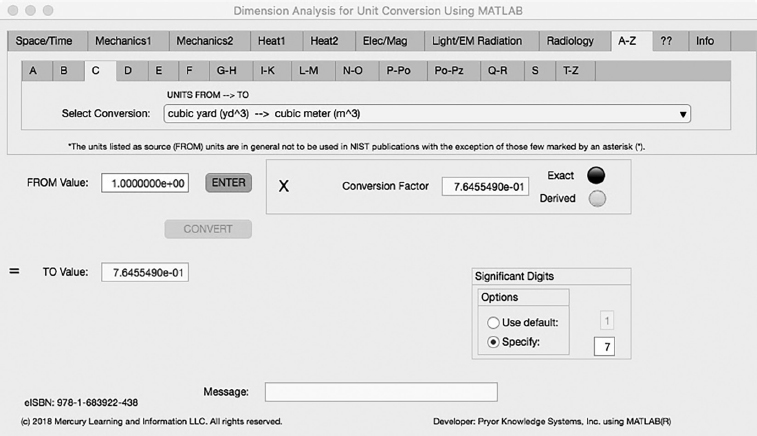
FIGURE 5.3-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - C Tab.
cubic yard (yd^3) (=1.0) to cubic meter (m^3) Example 5.3-1:
m^3 = yd^3 * m^3/yd^3 = yd^3 * 7.645549E-1
Where: m^3 | = | the number of cubic meters calculated |
yd^3 | = | the number of cubic yards to be converted (1.0) |
m^3/yd^3 | = | the conversion factor from cubic yard to cubic meter (7.645549E-1) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
m^3 = 1.0 * 7.645549E-1 = 7.645549E-1 cubic meter | (5.3-1) |
The A-Z / C Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / C | |
| calorieIT (calIT) to joule (J) |
| calorieth (calth) to joule (J) |
| calorie (cal) (mean) to joule (J) |
| calorie (15 ˚C) (cal) to joule (J) |
| calorie (20 ˚C) (cal) to joule (J) |
| calorieIT, kilogram (nutrition) to joule (J) |
| calorieth, kilogram (nutrition) to joule (J) |
| calorie (mean), kilogram (nutrition) to joule (J) |
| calorieth per centimeter second degree Celsius [calth/(cm*s*˚C)] |
| to watt per meter kelvin [W/(m*K)] |
| calorieIT per gram (calIT/g) to joule per kilogram (J/kg) |
| calorieth per gram (calth/g) to joule per kilogram (J/kg) |
| calorieIT per gram degree Celsius [calIT/(g*˚C)] |
| to joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg*K)] |
| calorieth per gram degree Celsius [calth/(g*˚C)] |
| to joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg*K)] |
| calorieIT per gram kelvin [calIT/(g*K)] |
| to joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg*K)] |
| calorieth per gram kelvin [calth/(g*K)] |
| to joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg*K)] |
| calorieth per minute (calth/min) to watt (W) |
| calorieth per second (calth/s) to watt (W) |
| calorieth per square centimeter (calth / cm^2) |
| to joule per square meter (J / m^2) |
| calorieth per square centimeter minute [calth/(cm^2*min)] |
| to watt per square meter (watt / m^2) |
| calorieth per square centimeter second [calth / (cm^2 * s)] |
| to watt per square meter (watt / m^2) |
| candela per square inch (cd / in^2) |
| to candela per square meter (cd / m^2) |
| carat, metric to kilogram (kg) |
| carat, metric to gram (g) |
| centimeter of mercury (0 degC) to pascal (Pa) |
| centimeter of mercury (0 degC) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| centimeter of mercury, conventional (cmHg) to pascal (Pa) |
| centimeter of mercury, conventional (cmHg) |
| to kilopascal (kPa) |
| centimeter of water (4 degC) to pascal (Pa) |
| centimeter of water, conventional (cmH2O) to pascal (Pa) |
| centipoise (cP) to pascal second (Pa * s) |
| centistokes (cSt) to meter squared per second (m^2 / s) |
| chain (based on US survey foot) (ch) to meter (m) |
| circular mil to square meter (m^2) |
| circular mil to square millimeter (mm^2) |
| clo to square meter kelvin per watt (m^2 * K / W) |
| cord (128 ft^3) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| cubic foot (ft^3) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| cubic foot per minute (ft^3 / min) |
| to cubic meter per second (m^3 / s) |
| cubic foot per minute (ft^3 / min) to liter per second (L / s) |
| cubic foot per second (ft^3 / s) |
| to cubic meter per second (m^3/s) |
| cubic inch (in^3) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| cubic inch per minute (in^3/min) |
| to cubic meter per second (m^3/s) |
| cubic mile (mi^3) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| cubic yard (yd^3) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| cubic yard per minute (yd^3/min) |
| to cubic meter per second (m^3/s) |
| cup (US) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| cup (US) to liter (L) |
| cup (US) to milliliter (mL) |
| *Curie (Ci) to becquerel (Bq) |
5.4 D TAB
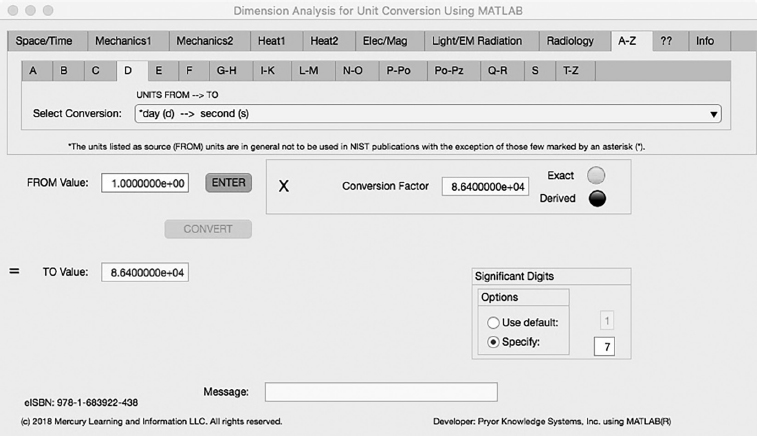
FIGURE 5.4-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - D Tab.
The fourth Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the D Tab (see Figure 5.4-1). This example shows the conversion of day (d) to second (s). In this example, the amplitude of day is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.4-4.
day (d) (=1.0) to seconds (s) Example 5.4-4:
s | = | d * h/d * min/h * s/min |
| = | d * 24 * 60 * 60 |
| = | d * 8.64E4 |
Where: s | = | the number of second calculated |
d | = | the number of day to be converted (1.0) |
h/d | = | the conversion factor from day to hour (24) |
min/h | = | the conversion factor from hour to minute (60) |
s/min | = | the conversion factor from minute to second (60) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
s = 1.0 * 8.64E4 = 8.64E4 seconds | (5.4-1) |
The A-Z D Tab allows the bidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / D | |
| darcy to meter squared (m^2) |
| *day (d) to second (s) |
| day (sidereal) to second (s) |
| debye (D) to coulomb meter (C * m) |
| *degree (angle) to radian (rad) |
| *degree Celsius (temperature interval) (degC) to kelvin (K) |
| degree centigrade (temperature interval) |
| to degree Celsius (degC) |
| degree Fahrenheit (temperature interval) (degF) |
| to degree Celsius (degC) |
| degree Fahrenheit (temperature interval) (degF) |
| to kelvin (K) |
| degree Fahrenheit hour per British thermal unit IT (degF * h/Btu IT) |
| to kelvin per watt (K/W) |
| degree Fahrenheit hour per British thermal unit th (degF * h/Btu th) |
| to kelvin per watt (K / W) |
| degree Fahrenheit hour square foot per Btu IT (degF*h*ft^2/Btu IT) |
| to square meter kelvin per watt (m^2*K/W) |
| degree Fahrenheit hour square foot per Btu th (degF*h*ft^2/Btu th) |
| to square meter kelvin per watt (m^2*K/W) |
| degree Fahrenheit hour square foot per Btu IT inch (degF*h*ft^2/Btu IT*in) |
| to meter kelvin per watt (m*K/W) |
| degree Fahrenheit hour square foot per Btu th inch (degF*h*ft^2/Btu th*in) |
| to meter kelvin per watt (m*K/W) |
| degree Fahrenheit second per Btu IT (degF*s/Btu IT) |
| to kelvin per watt (K/W) |
| degree Fahrenheit second per Btu th (degF*s/Btu th) |
| to kelvin per watt (K/W) |
| degree Rankine (temperature interval) (degR) to kelvin (K) |
| denier to kilogram per meter (kg/m) |
| denier to gram per meter (g/m) |
| dyne (dyn) to newton (N) |
| dyne centimeter (dyn-cm) to newton meter (N * m) |
| dyne per square centimeter (dyn/cm^2) to pascal (Pa) |
5.5 E TAB
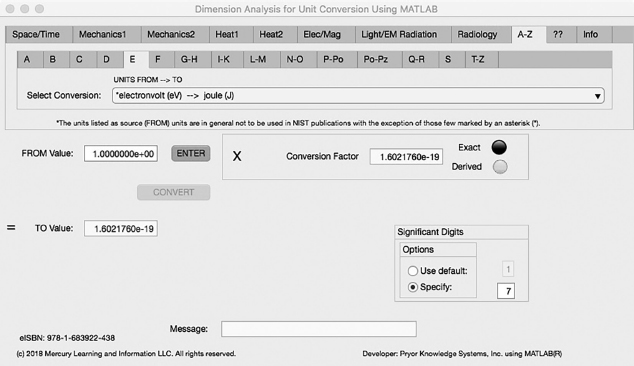
FIGURE 5.5-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - E Tab.
The fifth Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the E Tab (see Figure 5.5-1). This example shows the conversion of electron volt (eV) to joule (J). In this example, the amplitude of electron volt (eV) is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.5-1.
electronvolt (eV) (=1.0) to joule (J) Example 5.5-1:
J | = | eV * J/eV |
| = | eV * 1.602176E-19 |
Where: J | = | the number of joule calculated |
eV | = | the number of electronvolt to be converted (1.0) |
J/eV | = | the conversion factor from electronvolt to joule (1.602176E-19) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
J = 1.0 * 1.602176E-19 = 1.602176E-19 joules | (5.5-1) |
The A-Z E Tab allows the bidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / E | |
| *electronvolt (eV) to joule (J) |
| EMU of capacitance (abfarad) to farad (F) |
| EMU of current (abampere) to ampere (A) |
| EMU of Electric potential (abvolt) to volt (V) |
| EMU of inductance (abhenry) to henry (H) |
| EMU of resistance (abohm) to ohm |
| erg (erg) to joule (J) |
| erg per second (erg / s) to watt (W) |
| erg per square centimeter second [erg / (cm^2 * s)] |
| to watt per square meter (W / m^2) |
| ESU of capacitance (statfarad) to farad (F) |
| ESU of current (statampere) to ampere (A) |
| ESU of Electric potential (statvolt) to volt (V) |
| ESU of inductance (stathenry) to henry (H) |
| ESU of resistance (statohm) to ohm |
5.6 F TAB
The sixth Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the F Tab (see Figure 5.6-1). This example shows the conversion of foot per minute (ft/min) to meter per second (m/s). In this example, the amplitude of foot per minute is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.6-1.
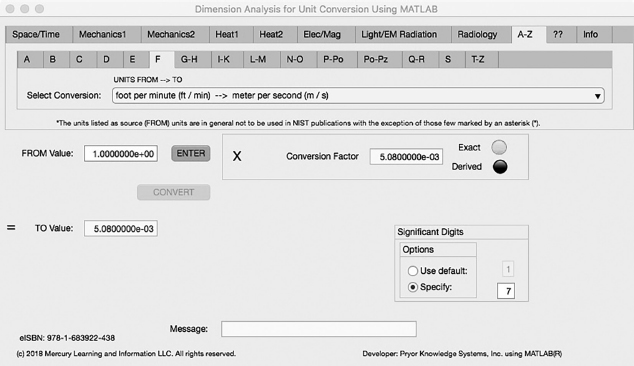
FIGURE 5.6-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - F Tab.
foot per minute (ft/min) (=1.0) to meter per second (m/s) Example 5.6-1:
m/s | = | ft/min * m/ft * min/s |
| = | ft/min * 0.3048 * 1/60 |
| = | ft/min * 5.08E-3 |
Where: m/s | = | the number of meter per second calculated |
ft/min | = | the number of foot per minute to be converted (1.0) |
m/ft | = | the conversion factor from foot to meter (0.3048) |
min/s | = | the conversion factor from second to minute (1/60) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
m/s = 1.0 * 0.3048 * 1/60 = 5.08E-3 meter per second | (5.6-1) |
The A-Z F Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / F | |
| faraday (based on carbon 12) to coulomb (C) |
| fathom (based on US survey foot) to meter (m)) |
| fermi to meter (m) |
| fermi to femtometer (fm) |
| fluid ounce (US) (fl oz) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| fluid ounce (US) (fl oz) to milliliter (mL) |
| foot (ft) to meter (m) |
| foot (US Survey) (ft) to meter (m) |
| footcandle to lux (lx) |
| footlambert to candela per square meter (cd / m^2) |
| foot of mercury, conventional (ftHg) to pascal (Pa) |
| foot of mercury, conventional (ftHg) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| foot of water (39.2 degF) to pascal (Pa) |
| foot of water (39.2 degF) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| foot of water, conventional (ftH2O) to pascal (Pa) |
| foot of water, conventional (ftH2O) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| foot per hour (ft / h) to meter per second (m / s) |
| foot per minute (ft / min) to meter per second (m / s) |
| foot per second (ft / s) to meter per second (m / s) |
| foot per second squared (ft / s^2) |
| to meter per second squared (m / s^2) |
| foot poundal to joule (J) |
| foot pound-force (ft * lbf) to joule (J) |
| foot pound-force per hour (ft * lbf / h) to watt (W) |
| foot pound-force per minute (ft * lbf / min) to watt (W) |
| foot pound-force per second (ft * lbf / s) to watt (W) |
| foot to the fourth power (ft^4) |
| to meter to the fourth power (m^4) |
| franklin (Fr) to coulomb (C) |
5.7 G-H TAB
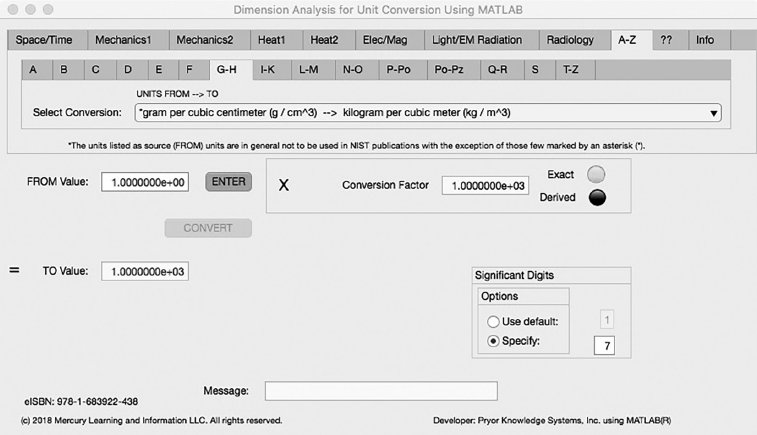
FIGURE 5.7-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - G-H Tab.
The seventh Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the G-H Tab (see Figure 5.7-1). This example shows the conversion of gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm3) to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3). In this example, the amplitude of gram per cubic centimeter is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.7-1.
gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm^3) (=1.0) to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) Example 5.7-1:
kg/m^3 | = | g/cm^3 * kg/g * cm^3/m^3 |
| = | g/cm^3 * 1.0E-3 * 100^3/1.0^3 |
| = | g/cm^3 * 1.0E-3 * 1.0E6 |
| = | g/cm^3 * 1.0E3 |
Where: kg/m^3 | = | the number of kilogram per cubic meter calculated |
g/cm^3 | = | the number of grams per cubic centimeter to be converted (1.0) |
kg/g | = | the conversion factor from gram to kilogram (1.0E-3) |
cm^3/m^3 | = | the conversion factor from cubic meter to cubic centimeter (100^3/1.0^3) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
kg/m^3 | = | g/cm^3 * 1.0E3 = 1.0 * 1.0E3 | |
| = | 1.0E3 kilogram per cubic meter | (5.7-1) |
The A-Z G-H Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / G-H | |
| gal (Gal) to meter per second squared (m / s^2) |
| gallon [Canadian and U.K. (Imperial)] (gal) |
| to cubic meter (m^3) |
| gallon [Canadian and U.K. (Imperial)] (gal) to liter (L) |
| gallon (US) (gal) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| gallon (US) (gal) to liter (L) |
| gallon (US) per day (gal / d) |
| to cubic meter per second (m^3 / s) |
| gallon (US) per day (gal / d) to liter per second (L / s) |
| gallon (US) per horsepower hour [gal/(hp * h)] |
| to cubic meter per joule (m^3/J) |
| gallon (US) per horsepower hour [gal/(hp * h)] |
| to liter per joule (L/J) |
| gallon (US) per minute (gpm) (gal/min) |
| to cubic meter per second (m^3/s) |
| gallon (US) per minute (gpm) (gal/min) |
| to liter per second (L/s) |
| gamma to tesla (T) |
| gauss (Gs, G) to tesla (T) |
| gilbert (Gi) to ampere (A) |
| gill [Canadian and U.K. (Imperial)] (gi) |
| to cubic meter (m^3) |
| gill [Canadian and U.K. (Imperial)] (gi) to liter (L) |
| gill (US) (gi) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| gill (US) (gi) to liter (L) |
| gon (also called grade) (gon) to radian (rad) |
| gon (also called grade) (gon) to degree (angle) |
| grain (gr) to kilogram (kg) |
| grain (gr) to milligram (mg) |
| grain per gallon (US) (gr/gal) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| grain per gallon (US) (gr/gal) |
| to milligram per liter (mg/L) |
| gram-force per square centimeter (gf/cm^2) to pascal (Pa) |
| *gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm^3) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| *hectare (ha) to square meter (m^2) |
| horsepower (550 ft * lbf / s) (hp) to watt (W) |
| horsepower (boiler) to watt (W) |
| horsepower (electric) to watt (W) |
| horsepower (metric) to watt (W) |
| horsepower (U.K.) to watt (W) |
| horsepower (water) to watt (W) |
| *hour to second (s) |
| hour (sidereal) to second (s) |
| hundredweight (long, 112 lb) to kilogram (kg) |
| hundredweight (short, 100 lb) to kilogram (kg) |
5.8 I-K TAB
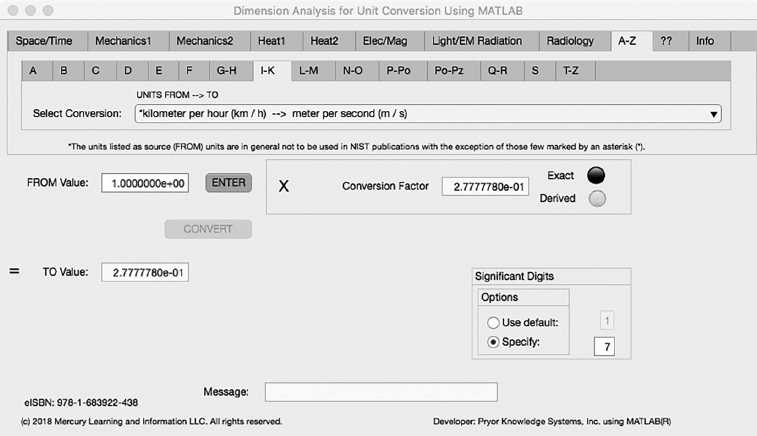
FIGURE 5.8-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - I-K Tab.
The eighth Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the I-K Tab (see Figure 5.8-1). This example shows the conversion of kilometer per hour (km/h) to meter per second (m/s). In this example, the amplitude of kilometer per hour (km/h) is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.8-1.
kilometer per hour (km/h) (=1.0) to meter per second (m/s) Example 5.8-1:
m/s | = | km/h * h/min * min/s* m/km |
| = | km/h * 1/60 * 1/60 * 1.0E3 |
| = | km/h * 2.777778E-1 |
Where: m/s | = | the number of meter per second calculated |
km/h | = | the number of kilometer per hour to be converted (1.0) |
h/min | = | the conversion factor from minutes to hour (1/60) |
min/s | = | the conversion factor from seconds to minutes (1/60) |
m/km | = | the conversion factor from kilometers to meters (1.0E3) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
| m/s | = | km/h * 2.777778E-1 | |
| | = | 1.0 * 2.777778E-1 kilometers per hour | | (5.8-1) |
The A-Z I-K Tab allows the bidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / I-K | |
| inch (in) to meter (m) |
| inch (in) to centimeter (cm) |
| inch of mercury (32 degF) to pascal (Pa) |
| inch of mercury (32 degF) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| inch of mercury (60 degF) to pascal (Pa) |
| inch of mercury (60 degF) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| inch of mercury, conventional (inHg) to pascal (Pa) |
| inch of mercury, conventional (inHg) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| inch of water (39.2 degF) to pascal (Pa) |
| inch of water (60 degF) to pascal (Pa) |
| inch of water, conventional (inH2O) to pascal (Pa) |
| inch per second (in/s) to meter per second (m/s) |
| inch per second squared (in/s^2) |
| to meter per second squared (m/s^2) |
| inch to the fourth power (in^4) |
| to meter to the fourth power (m^4) |
| kayser (K) to reciprocal meter (m^-1) |
| kilocalorie IT (kcal IT) to joule (J) |
| kilocalorie th (kcal th) to joule (J) |
| kilocalorie (mean) (kcal) to joule (J) |
| kilocalorie th per minute (kcal th/min) to watt (W) |
| kilocalorie th per second (kcal th/s) to watt (W) |
| kilogram-force (kgf) to newton (N) |
| kilogram-force meter (kgf * m) to newton meter (N * m) |
| kilogram-force per square centimeter (kgf/cm^2) |
| to pascal (Pa) |
| kilogram-force per square centimeter (kgf/cm^2) |
| to kilopascal (kPa) |
| kilogram-force per square meter (kgf/m^2) to pascal (Pa) |
| kilogram-force per square millimeter (kgf/mm^2) |
| to pascal (Pa) |
| kilogram-force per square millimeter (kgf/mm^2) |
| to megapascal (Pa) |
| kilogram-force second squared per meter (kgf * s^2/m) |
| to kilogram (kg) |
| *kilometer per hour (km/h) to meter per second (m/s) |
| kilopond (kilogram-force) (kp) to newton (N) |
| *kilowatt hour (kW * h) to joule (J) |
| *kilowatt hour (kW * h) to megajoule (MJ) |
| kip (1 kip = 1 000 lbf) to newton (N) |
| kip (1 kip = 1 000 lbf) to kilonewton (kN) |
| kip per square inch (ksi) (kip/in^2) to pascal (Pa) |
| kip per square inch (ksi) (kip/in^2) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| *knot (nautical mile per hour) to meter per second (m/s) |
5.9 L-M TAB
The ninth Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the L-M Tab (see Figure 5.9-1). This example demonstrates the conversion of mile (mi) to meter (m). In this example, the amplitude of mile is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.9-1.
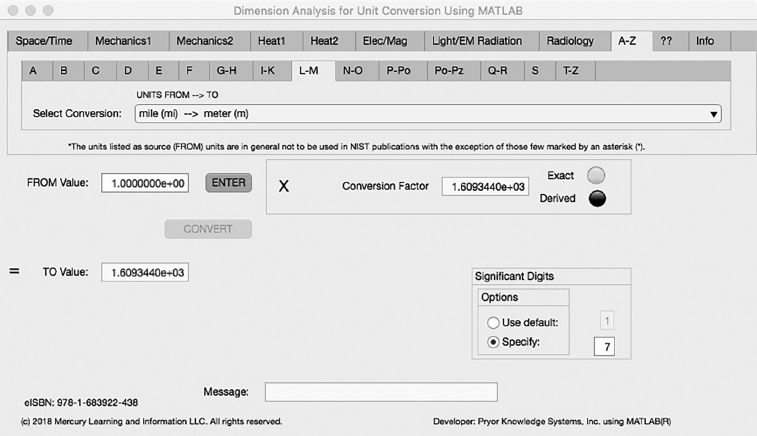
FIGURE 5.9-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - L-M Tab.
mile (mi) (=1.0) to meter (m) Example 5.9-1:
m | = | mi * km/mi * m/km |
| = | mi * 1.609344 * 1000 |
| = | mi * 1.609344E3 |
Where: m | = | the number of meters calculated |
mi | = | the number of miles to be converted (1.0) |
km/mi | = | the conversion factor from mile to kilometer (1.609344) |
m/km | = | the conversion factor from kilometer to meter (1000) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
m = 1.0 * 1.609344E3 = 1.609344E3 meter | (5.9-1) |
The A-Z L-M Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / L-M | |
| lambert to candela per square meter (cd/m^2) |
| langley (cal th/cm^2) to joule per square meter (J/m^2) |
| light year (l.y.) to meter (m) |
| *liter (L) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| lumen per square foot (lm/ft^2) to lux (lx) |
| maxwell (Mx) to weber (Wb) |
| mho to siemens (S) |
| microinch to meter (m) |
| microinch to micrometer (um) |
| micron (u) to meter (m) |
| micron (u) to micrometer (um) |
| mil (0.001 in) to meter (m) |
| mil (0.001 in) to millimeter (mm) |
| mil (angle) to radian (rad) |
| mil (angle) to degree, mile (mi) to meter (m) |
| mile (mi) to kilometer (km) |
| mile (based on US survey foot) (mi) to meter (m) |
| mile (based on US survey foot) (mi) to kilometer (km) |
| *mile, nautical to meter (m) |
| mile per gallon (US) (mpg) (mi/gal) |
| to meter per cubic meter (m/m^3) |
| mile per gallon (US) (mpg) (mi/gal) |
| to kilometer per liter (km / L) |
| mile per hour (mi/h) to meter per second (m/s) |
| mile per hour (mi/h) to kilometer per hour (km/h) |
| mile per minute (mi/min) to meter per second (m/s) |
| mile per second (mi/s) to meter per second (m/s) |
| millibar (mbar) to pascal (Pa) |
| millibar (mbar) to kilopascal (kPa) |
| *millimeter of mercury, conventional (mmHg) |
| to pascal (Pa) |
| millimeter of water, conventional (mmH2O) to pascal (Pa) |
| *minute (angle) (‘) to radian (rad) |
| minute (min) to second (s) |
| minute (sidereal) to second (s) |
5.10 N-O TAB
The tenth Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the N-O Tab (see Figure 5.10-1). This example demonstrates the conversion of ounce (avoirdupois) per cubic inch (oz/in^3) to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3). In this example, the amplitude of ounce per cubic inch is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.10-1.
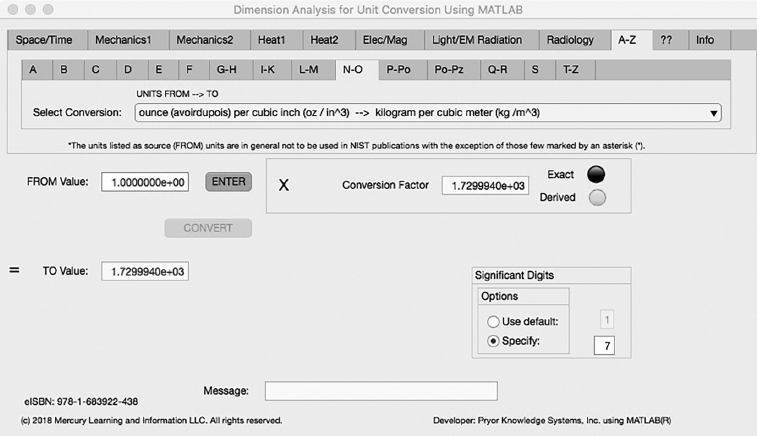
FIGURE 5.10-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - N-O Tab.
ounce (avoirdupois) per cubic inch (oz/in^3) to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) Example 5.10-1:
| kg/m^3 | = | oz/in^3 * in^3/cm^3 * cm^3/m^3 * g/oz * kg/g |
| | = | oz/in^3 *6.1023744E-2 * 1.0E6 * 2.834952E1 * 1.0E-3 |
| | = | oz/in^3 * 1.7299939E3 |
Where: kg/m^3 | = | the number of kilogram per cubic meter calculated |
oz/in^3 | = | the number of ounces per cubic inch to be converted (1.0) |
in^3/cm^3 | = | the conversion factor from cubic centimeter to cubic inch (6.1023744E-2) |
cm^3/m^3 | = | the conversion factor from cubic meter to cubic centimeter (1.0E6) |
g/oz | = | the conversion factor from ounce to gram (2.834952E1) |
kg/g | = | the conversion factor from gram to kilogram (1.0e-3) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
| kg/m^3 | = | 1.0 * 1.7299939E3 | |
| | = | 1.7299939E3 kilogram per cubic meter | | (5.10-1) |
The A-Z N-O Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / N-O | |
| oersted (Oe) to ampere per meter (A/m) |
| *ohm centimeter (ohm * cm) to ohm meter (ohm * m) |
| ohm circular-mil per foot to ohm meter (ohm * m) |
| ohm circular-mil per foot |
| to ohm square millimeter per meter (ohm * mm^2/m) |
| ounce (avoirdupois) (oz) to kilogram (kg) |
| ounce (avoirdupois) (oz) to gram (g) |
| ounce (troy or apothecary) (oz) to kilogram (kg) |
| ounce (troy or apothecary) (oz) to gram (g) |
| ounce [Canadian and U.K. fluid (Imperial)] (fl oz) |
| to cubic meter (m^3) |
| ounce [Canadian and U.K. fluid (Imperial)] (fl oz) |
| to milliliter (mL) |
| ounce (U.S. fluid) (fl oz) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| ounce (U.S. fluid) (fl oz) to milliliter (mL) |
| ounce (avoirdupois)-force (ozf) to newton (N) |
| ounce (avoirdupois)-force inch (ozf * in) |
| to newton meter (N * m) |
| ounce (avoirdupois)-force inch (ozf * in) |
| to millinewton meter (mN * m) |
| ounce (avoirdupois) per cubic inch (oz / in^3) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| ounce (avoirdupois) per gallon [Canadian and U.K. (Imperial)] (oz/gal) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| ounce (avoirdupois) per gallon [Canadian and U.K. (Imperial)] (oz/gal) |
| to gram per liter (g/L) |
| ounce (avoirdupois) per gallon (U.S.) (oz/gal) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| ounce (avoirdupois) per gallon (U.S.) (oz/gal) |
| to gram per liter (g/L) |
| ounce (avoirdupois) per square foot (oz/ft^2) |
| to kilogram per square meter (kg/m^2) |
| ounce (avoirdupois) per square inch (oz/in^2) |
| to kilogram per square meter (kg/m^2) |
| ounce (avoirdupois) per square yard (oz/yd^2) |
| to kilogram per square meter (kg/m^2) |
5.11 P-PO TAB
The eleventh Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the P-Po Tab (see Figure 5.11-1). This example demonstrates the conversion of pica (computer) (1/6 in) to meter (m). In this example, the amplitude of pica (computer) (1/6 in) is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.11-1.
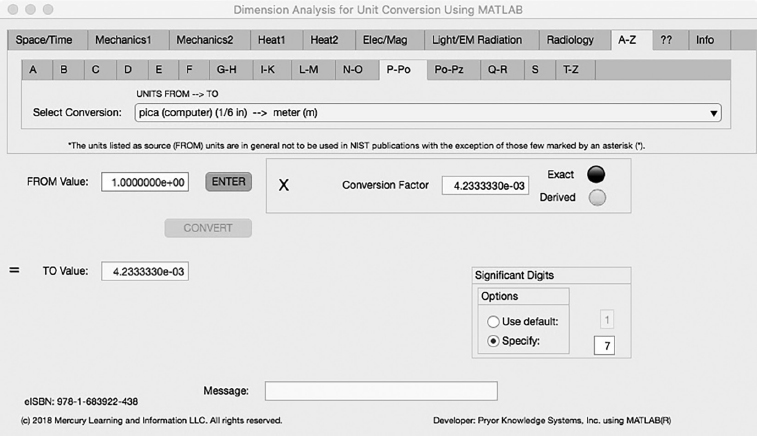
FIGURE 5.11-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - P-Po Tab.
pica (computer) (1/6 in) to meter (m) Example 5.11-1:
| m | = | pica (computer) * in/pica (computer) * cm/in * m/cm |
| | = | pica (computer) * 1/6 * 2.54 * 1.0E-2 |
| | = | pica (computer) * 4.2333333E-3 |
Where: m | = | the number of meter calculated |
pica (computer) | = | the number of pica to be converted (1.0) |
in/pica (computer) | = | the conversion factor from pica to inch (1/6) |
cm/in | = | the conversion factor from inch to centimeter (2.54) |
m/cm | = | the conversion factor from centimeter to meter (1.0E-2) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
m = 1.0 * 4.2333333E-3 = 4.2333333E-3 meter | (5.11-1) |
The A-Z P-Po Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / P-Po | |
| parsec (pc) to meter (m) |
| peck (U.S.) (pk) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| peck (U.S.) (pk) to liter (L) |
| pennyweight (dwt) to kilogram (kg) |
| pennyweight (dwt) to gram (g) |
| perm (0 degC) to kilogram per pascal second square meter [kg / (Pa * s * m^2)] |
| perm (23 degC) to kilogram per pascal second square meter [kg / (Pa * s * m^2)] |
| perm inch (0 degC) to kilogram per pascal second meter [kg / (Pa * s * m)] |
| perm inch (23 degC) to kilogram per pascal second meter [kg / (Pa * s * m)] |
| phot (ph) to lux (lx) |
| pica (computer) (1/6 in) to meter (m) |
| pica (computer) (1/6 in) to millimeter (mm) |
| pica (printers) to meter (m) |
| pica (printers) to millimeter (mm) |
| pint (U.S. dry) (dry pt) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| pint (U.S. dry) (dry pt) to liter (L) |
| pint (U.S. liquid) (liq pt) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| pint (U.S. liquid) (liq pt) to liter (L) |
| point (computer) (1/72 in) to meter (m) |
| point (computer) (1/72 in) to millimeter (mm) |
| point (printers) to meter (m) |
| point (printers) to millimeter (mm) |
| poise (P) to pascal second (Pa * s) |
| pound (avoirdupois) (lb) to kilogram (kg) |
| pound (troy or apothecary) (lb) to kilogram (kg) |
| poundal to newton (N) |
| poundal per square foot to pascal (Pa) |
| poundal second per square foot to pascal second (Pa * s) |
| pound foot squared (lb * ft^2) |
| to kilogram meter squared (kg * m^2) |
| pound-force (lbf) to newton (N) |
| pound-force foot (lbf * ft) to newton meter (N * m) |
| pound-force foot per inch (lbf * ft/in) |
| to newton meter per meter (N * m/m) |
5.12 PO-PZ TAB
The twelfth Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the Po-Pz Tab (see Figure 5.12-1). This example demonstrates the conversion of pound per gallon (U.S.) (lb/gal) to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3). In this example, the amplitude of pound per gallon (U.S.) (lb/gal) is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.12-1.
FIGURE 5.12-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - Po-Pz Tab.
pound per gallon (U.S.) (lb/gal) (=1.0) to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) Example 5.12-1:
| kg/m^3 | = | lb/gal * kg/lb * gal/L * L/m^3 |
| | = | lb/gal * 4.5359237E-1 * 2.6417204E-1 * 1.0E3 |
| | = | lb/gal * 1.1982642E2 |
Where: kg/m^3 | = | the number of kilograms per cubic meter calculated |
lb/gal | = | the number of pounds per gallon to be converted (1.0) |
kg/lb | = | the conversion factor from pound to kilogram (4.5359237E-1) |
gal/L | = | the conversion factor from liters to gallon (2.6417204E-1) |
L/m^3 | = | the conversion factor from cubic meters to liter (1.0E3) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
m | = | 1.0 * 1.1982642E2 | |
| = | 1.1982642E2 kilograms per cubic meter | (5.12-1) |
The A-Z Po-Pz Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / Po-Pz | |
| pound-force inch (lbf * in) to newton meter (N * m) |
| pound-force inch per inch (lbf * in/in) |
| to newton meter per meter (N * m/m) |
| pound-force per foot (lbf/ft) to newton per meter (N/m) |
| pound-force per inch (lbf/in) to newton per meter (N/m) |
| pound-force per pound (lbf/lb) (thrust to mass ratio) |
| to newton per kilogram (N/kg) |
| pound-force per square foot (lbf/ft^2) to pascal (Pa) |
| pound-force per square inch (psi) (lbf/in^2) to pascal (Pa) |
| pound-force per square inch (psi) (lbf/in^2) |
| to kilopascal (kPa) |
| pound-force second per square foot (lbf * s/ft^2) |
| to pascal second (Pa * s) |
| pound-force second per square inch (lbf * s/in^2) |
| to pascal second (Pa * s) |
| pound inch squared (lb * in^2) |
| to kilogram meter squared (kg * m^2) |
| pound per cubic foot (lb/ft^3) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| pound per cubic inch (lb/in^3) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| pound per cubic yard (lb/yd^3) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| pound per foot (lb/ft) to kilogram per meter (kg/m) |
| pound per foot hour [lb/(ft * h)] to pascal second (Pa * s) |
| pound per foot second [lb/(ft * s)] to pascal second (Pa * s) |
| pound per gallon [Canadian and U.K. (Imperial)] (lb/gal) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| pound per gallon [Canadian and U.K. (Imperial)] (lb/gal) |
| to kilogram per liter (kg/L) |
| pound per gallon (U.S.) (lb/gal) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| pound per gallon (U.S.) (lb/gal) |
| to kilogram per liter (kg/L) |
| pound per horsepower hour [lb/(hp * h)] |
| to kilogram per joule (kg/J) |
| pound per hour (lb/h) to kilogram per second (kg/s) |
| pound per inch (lb/in) to kilogram per meter (kg/m) |
| pound per minute (lb/min) to kilogram per second (kg/s) |
| pound per second (lb/s) to kilogram per second (kg/s) |
| pound per square foot (lb/ft^2) |
| to kilogram per square meter (kg/m^2) |
| pound per square inch (NOT pound-force) (lb/ft^2) |
| to kilogram per square meter (kg/m^2) |
| pound per yard (lb/yd) to kilogram per meter (kg/m) |
| psi (pound-force per square inch) (lbf/in^2) to pascal (Pa) |
| psi (pound-force per square inch) (lbf/in^2) |
| to kilopascal (kPa) |
5.13 Q-R TAB
The thirteenth Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the Q-R Tab (see Figure 5.13-1). This example demonstrates the conversion of quart (U.S. liquid) (liq qt) (=1.0) to cubic meter (m^3). In this example, the amplitude of quart is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.13-1.
FIGURE 5.13-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - Q-R Tab.
quart (U.S. liquid) (liq qt) (=1.0) to cubic meter (m^3) Example 5.13-1:
m^3 | = | liq qt * L/liq qt * m^3/L |
| = | liq qt * = liq qt * 9.463529E-1 * 1.0E-3 |
| = | liq qt * 9.463529E-4 |
Where: m^3 | = | the number of cubic meters calculated |
liq qt | = | the number of liquid quarts to be converted (1.0) |
L/liq qt | = | the conversion factor from liquid quart to liter (9.463529E-1) |
m^3/L | = | the conversion factor from liter to cubic meter (1.0E-3) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
m^3 = 1.0 * 9.463529E-4 = 9.463529E-4 cubic meter | (5.13-1) |
The A-Z Q-R Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / Q-R | |
| quad (10^15 Btu IT) to joule (J) |
| quart (U.S. dry) (dry qt) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| quart (U.S. dry) (dry qt) to liter (L) |
| quart (U.S. liquid) (liq qt) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| quart (U.S. liquid) (liq qt) to liter (L) |
| *rad (absorbed dose) (rad) to gray (Gy) |
| *rem (rem) to sievert (Sv) |
| revolution (r) to radian (rad) |
| revolution per minute (rpm) (r / min) |
| to radian per second (rad / s) |
| rhe to reciprocal pascal second (Pa * s)^-1 |
| rod (based on U.S. survey foot) (rd) to meter (m) |
| *roentgen (R) to coulomb per kilogram (C / kg) |
| rpm (revolution per minute) (r / min) |
| to radian per second (rad / s) |
5.14 S TAB
The fourteenth Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the S Tab (see Figure 5.14-1). This example demonstrates the conversion of square mile (mi^2) (=1.0) to square meter (m^2). In this example, the amplitude of square mile is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.14-1.
FIGURE 5.14-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - S Tab.
square mile (mi^2) (=1.0) to square meter (m^2) Example 5.14-1:
m^2 | = | mi^2 * km^2/mi^2 * m^2/km^2 |
| = | mi^2 * 2.589988 * 1.0E6 |
| = | mi^2 * 2.589988E6 |
Where: m^2 | = | the number of square meters calculated |
mi^2 | = | the number of square miles to be converted (1.0) |
km^2/mi^2 | = | the conversion factor from square mile to square kilometer (2.589988) |
m^2/km^2 | = | the conversion factor from square kilometer to square meter (1.0E6) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
m^2 = 1.0 * 2.589988E6 = 2.589988E6 square meter | (5.14-1) |
The A-Z S Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / S | |
| *second (angle) (“) to radian (rad) |
| second (sidereal) to second (s) |
| shake to second (s) |
| shake to nanosecond (ns) |
| slug (slug) to kilogram (kg) |
| slug per cubic foot (slug/ft^3) |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| slug per foot second (slug/(ft * s) |
| to pascal second (Pa * s) |
| square foot (ft^2) to square meter (m^2) |
| square foot per hour (ft^2/h) |
| to square meter per second (m^2/s) |
| square foot per second (ft^2/s) |
| to square meter per second (m^2/s) |
| square inch (in^2) to square meter (m^2) |
| square inch (in^2) to square centimeter (cm^2) |
| square mile (mi^2) to square meter (m^2) |
| square mile (mi^2) to square kilometer (km^2) |
| square mile (based on U.S. survey foot) (mi^2) |
| to square meter (m^2) |
| square mile (based on U.S. survey foot) (mi^2) |
| to square kilometer (km^2) |
| square yard (yd^2) to square meter (m^2) |
| statampere to ampere (A) |
| statcoulomb to coulomb (C) |
| statfarad to farad (F) |
| stathenry to henry (H) |
| statmho to siemens (S) |
| statohm to ohm (ohm) |
| statvolt to volt (V) |
| stere (st) to cubic meter (m^3) |
| stilb (sb) to candela per square meter (cd / m^2) |
| stokes (St) to meter squared per second (m^2 / s) |
5.15 T-Z TAB
The fifteenth Minor Tab under the A-Z Major Tab is the T-Z Tab (see Figure 5.15-1). This example demonstrates the conversion of year (365 days) (=1.0) to second (s). In this example, the amplitude of year is set equal to one (1.0). The conversion equation is shown in Example 5.15-1 {37}.
FIGURE 5.15-1 Unit Converter Using MATLAB App A-Z - T-Z Tab.
year (365 days) (=1.0) to second (s) Example 5.15-1:
| s | = | year (365 days) * d/year (365 days) * h/d * min/h * s/min |
| | = | 1.0 * 365 * 24 * 60 * 60 = 3.1536E7 |
Where: s | = | the number of seconds calculated |
year | = | the number of years to be converted (1.0) |
d/year | = | the conversion factor from year to day (365) |
h/d | = | the conversion factor from day to hour (24) |
min/h | = | the conversion factor from hour to minute (60) |
s/min | = | the conversion factor from minute to second (60) |
And:
The resulting solution is:
s = 1.0 * 3.1536E7 = 3.1536E7 second per 365 day year | (5.15-1) |
The A-Z T-Z Tab allows the unidirectional selection of the following dimensions:
| Major/Minor-Tab | From/To Units on Pull-Down |
| A-Z / T-Z | |
| tablespoon to cubic meter (m^3) |
| tablespoon to milliliter (mL) |
| teaspoon to cubic meter (m^3) |
| teaspoon to milliliter (mL) |
| tex to kilogram per meter (kg/m) |
| therm (EC) to joule (J) |
| therm (U.S.) to joule (J) |
| ton, assay (AT) to kilogram (kg) |
| ton, assay (AT) to gram (g) |
| ton-force (2000 lbf) to newton (N) |
| ton-force (2000 lbf) to kilonewton (kN) |
| ton, long (2240 lb) to kilogram (kg) |
| ton, long, per cubic yard |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| *ton, metric to kilogram (kg) |
| tonne (called metric ton in U.S.) (t) to kilogram (kg) |
| ton of refrigeration (12 000 Btu IT / h) to watt (W) |
| ton of TNT (energy equivalent) to joule (J) |
| ton, register to cubic meter (m^3) |
| ton, short (2000 lb) to kilogram (kg) |
| ton, short, per cubic yard |
| to kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m^3) |
| ton, short, per hour to kilogram per second (kg/s) |
| torr (Torr) to pascal (Pa) |
| unit pole to weber (Wb) |
| *watt hour (W * h) to joule (J) |
| *watt per square centimeter (W/cm^2) |
| to watt per square meter (W/m^2) |
| watt per square inch (W/in^2) |
| to watt per square meter (W/m^2) |
| *watt second (W * s) to joule (J) |
| yard (yd) to meter (m) |
| *year (365 days) to second (s) |
| year (sidereal) to second (s) |
| year (tropical) to second (s) |















