Objects, classes and modules in Rubinius
In Chapter 2 I explained how Rubinius executes your code using a combination of Ruby and C++. We saw how Rubinius’s kernel contains pure Ruby implementations for all of the core classes, such as Array, String and Hash. For the portions of these core classes that cannot be implemented directly in Ruby, Rubinius uses native code written in a corresponding C++ class, compiled into the Rubinius VM.
This applies to the core classes behind Ruby’s object model as well. Here is how Rubinius represents Ruby objects internally:

On the left are three C++ classes: ObjectHeader, Object, and BasicObject. These are related using C++ class inheritance, indicated by the arrows. The Object and BasicObject C++ classes correspond to the Ruby core classes with the same name shown on the right. However, inside the Rubinius C++ VM, the Object class is the common base class for all Rubinius objects, while BasicObject is actually a subclass of Object. This is the opposite of what we have in Ruby, where BasicObject is the superclass of Object. The ObjectHeader class, similar to the RBasic structure in MRI, contains some basic technical information Rubinius keeps track of for every object:

header is an instance of the HeaderWord C++ class. This contains some technical flags Rubinius keeps track of for each object.
klass_ is a pointer to a C++ class called Class. This is the class of this Ruby object.
ivars_ is a pointer to a C++ object that contains a table of the instance variables stored in this object. Rubinius stores the variable names in this table also, like Ruby 1.8.
Since the Rubinius Object C++ class is a subclass of ObjectHeader, you can see it also meets our definition of a Ruby object:
Next let’s briefly look at how Rubinius implements classes and modules:
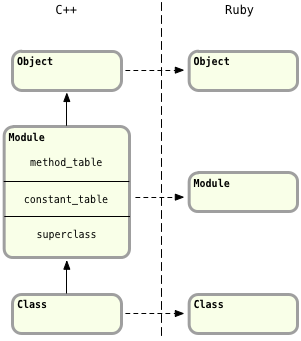
Again you can see a one to one correspondence between Ruby and C++ classes. This time the C++ class inheritance model reflects the Ruby object model; the Class class is a subclass of the Module class. Finally you can see Rubinius classes meet our previous definition since they contain all of the same information:
Rubinius stores the attribute names in the instance variable table, part of Object, and not in the Module object.