Eyes

EXAMINATION
Ask patient to sit or stand.
| Technique | Findings |
| Visual Testing | |
| Measure visual acuity in each eye separately | |
| EXPECTED: Vision 20/20 with or without lenses with near and far vision in each eye. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Myopia, amblyopia, or presbyopia. | |
| EXPECTED: Vision 20/20. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Limited fields of vision temporally, 50 degrees superiorly, 70 degrees inferiorly. | |
 |
|
| External Examination | |
| Inspect eyebrows | |
| EXPECTED: Unusually thin if plucked. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Ending short of temporal canthus. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Coarse. | |
| Inspect orbital area | |
| UNEXPECTED: Edema, puffiness not related to aging, or sagging tissue below orbit. Xanthelasma. | |
| Inspect eyelids | |
| UNEXPECTED: Ectropion or entropion. | |
| EXPECTED: Superior eyelid covering a portion of iris when open. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Fasciculations when lightly closed. Ptosis. Lagophthalmos. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Flakiness, redness, or swelling. Hordeola. | |
| EXPECTED: Present on both lids. Turned outward. | |
| Palpate eyelids | |
| UNEXPECTED: Nodules. | |
| Palpate eye | |
| EXPECTED: Can be gently pushed into orbit without discomfort. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Firm and resists palpation. | |
| Pull down lower lids and inspect conjunctivae and sclerae | |
| EXPECTED: Conjunctivae clear and inapparent. Sclerae white and visible above irides only when eyelids are wide open. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Conjunctivae with erythema. Sclerae yellow or green. Sclerae with dark, rust-colored pigment anterior to insertion of medial rectus muscle. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Exudate. Pterygium. Corneal arcus senilis or opacities. | |
| Inspect lacrimal gland region | |
| EXPECTED: Slight elevations with central depression on both upper and lower lid margins. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Enlarged glands. Dry eyes. | |
| Test corneal sensitivity | |
| Touch wisp of cotton to cornea. | EXPECTED: Bilateral blink reflex. |
| Inspect external eyes | |
| UNEXPECTED: Blood vessels present. | |
| EXPECTED: Clearly visible pattern. Similar color. | |
| EXPECTED: Round, regular, equal in size. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Miosis, mydriasis, anisocoria, or coloboma. | |
| EXPECTED: Constricting with consensual response of opposite pupil. | |
| EXPECTED: Constricting when pupils focus on near object or dilating when focus changes from near to distant object. | |
| EXPECTED: The pupil toward which the light is moving dilates and then constricts as the light shines onto it. | |
| UNEXPECTED: The pupil continues to dilate when the light shines into it. | |
| Extraocular Eye Muscles | |
| Evaluate muscle balance and movement of eyes | |
| EXPECTED: A few horizontal nystagmic beats. Smooth, full, coordinated movement of eyes. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Sustained or jerking nystagmus. Exposure of sclera from lid lag. Inability of eye to move in all directions. | |
 |
|
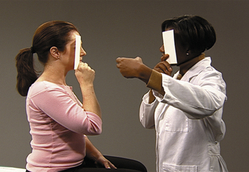
| EXPECTED: Light reflected symmetrically from both eyes. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Movement of covered or uncovered eye. | |
| Ophthalmoscopic Examination | |
| Inspect internal eye | |
| UNEXPECTED: Cloudiness or opacity. Shallow chamber. If observed, avoid mydriatics. | |
 |
|
| UNEXPECTED: Opacities. | |
 |
EXPECTED: Yellow or pink background, depending on race. Possible crescents or dots of pigment at disc margin, usually temporally. |
| UNEXPECTED: Discrete areas of pigmentation away from disc. Lesions. Drusen bodies. Hemorrhages. | |
| EXPECTED: Possible venous pulsations (should be documented). Arteriole/venule ratio 3:5 or 2:3. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Nicking, tortuosity. | |
 |
|
| EXPECTED: Yellow to creamy pink, varying by race. Sharp, well-defined margin, especially in temporal region; 1.5-mm diameter. | |
| UNEXPECTED: Myelinated nerve fibers. Papilledema. Glaucomatous cupping. | |
| EXPECTED: Yellow dot surrounded by deep pink. | |



AIDS TO DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
| Subjective Data | Objective Data |
| Strabismus (paralytic and nonparalytic) | |
| Eyes cannot focus simultaneously. Can focus separately in nonparalytic type. | Eye movement on the cover-uncover test, strabismic eye will fixate on the object after the “straight” eye is covered. |
| Episcleritis | |
| Acute onset of mild to moderate discomfort or photophobia. Painless injection and/or watery discharge. | Injection of the bulbar conjunctiva purplish elevation of a few millimeters. |
| Cataracts | |
| Cloudy or blurry vision, faded colors; halo may appear around lights. | Opacity of lens, generally central, occasionally peripheral. |
| Diabetic Retinopathy (background or nonproliferative) | |
| Initially asymptomatic. Blurred vision, distortion, or visual acuity loss in more advanced stages. | Dot hemorrhages, microaneurysms, hard exudates. |
| Diabetic Retinopathy (proliferative) | |
| Generally asymptomatic, floaters, blurred vision, or progressive visual acuity loss in advanced stages. | New vessel formation; extension out of the retina, hemorrhage. |
PEDIATRIC VARIATIONS
EXAMINATION
| Technique | Findings |
| Visual Testing | |
| Measure visual acuity | |
| EXPECTED: Infants should be able to focus on and track a face or light through 60 degrees. Age 3-5 years: 20/40 or better. Age 6: 20/30 or better. |
|
| Visual acuity is tested, when child is cooperative, with Lea cards, Landolt C, or HOTV chart, usually at about 3 years of age. | |
| Extraocular Eye Muscles | |
| Evaluate muscle balance and movement of eyes | |
| Evaluation of six cardinal fields of gaze is performed as with adults. You may, however, need to hold child’s head still. | |
Sample Documentation
Eyes
Near vision 20/40 in each eye uncorrected, corrected to 20/20 with glasses. Distant vision 20/20 by Snellen. Visual fields full by confrontation. Extraocular movements intact and full, no nystagmus. Corneal light reflex equal.
Lids and globes symmetric. No ptosis. Eyebrows full, no edema or lesions evident.
Conjunctivae pink, sclerae white. No discharge evident. Cornea clear, corneal reflex intact. Irides brown; pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation.
Ophthalmoscopic examination reveals red reflex. Discs cream colored, borders well defined with temporal pigmentation in both eyes. No venous pulsations evident at disc. Arteriole/venule ratio 3:5; no nicking or crossing changes, hemorrhages, or exudates noted. Maculae are yellow in each eye.