CHAPTER 4
GED® Science Test 1
This practice test is modeled on the format, content, and timing of the official GED® Science test and, like the official exam, presents a series of questions that focus on the fundamentals of scientific reasoning.
Work carefully, but do not spend too much time on any one question. Be sure you answer every question.
Set a timer for 90 minutes (1 hour and 30 minutes), and try to take this test uninterrupted, under quiet conditions.
Complete answer explanations for every test question follow the exam. Good luck!
PART I
35 total questions
90 minutes to complete
Please use the following to answer questions 1–3.
A non-predatory relationship between two organisms that benefits at least one of the organisms is called a symbiotic relationship. These relationships can be categorized further based on the effect of the relationship on the second organism. The table shows the three types of symbiotic relationships and their effects on each organism.

Veterinary clinics often treat pets with illnesses resulting from parasitism. Three common parasites diagnosed in dogs are the dog flea, the deer tick, and Cheyletiella mites.
Dog fleas and deer ticks both feed on the host animal’s (dog’s) blood and can transmit diseases to the host animal through their bites. Dog fleas lay their eggs on the host animal’s body and can survive on the host animal or on surfaces the animal comes in contact with, such as bedding. Deer ticks lay their eggs on the ground and attach to the host animal only while feeding.
Cheyletiella mites live within and feed on the keratin layer of the host animal’s skin. Cheyletiella mites reproduce on the host animal and can survive away from the host animal only for short periods of time.
1. Read the two descriptions of symbiotic relationships below, and select the correct term for each relationship from the following list. Write the correct answer in the box after each description.
commensalism
mutualism
parasitism
Mistletoe attaches to spruce trees. Using specialized structures, mistletoe penetrates into and extracts water and nutrients from the tree’s branches.
E. coli bacteria live within the intestinal tract of humans, obtaining nutrients from the food particles that pass through the intestines. Vitamin K produced by the E. coli is absorbed through the intestinal walls for use in the human body.
2. According to the passage, all of the dog parasites gain which benefit from their symbiotic relationships with the host dogs?
a. a habitat for living
b. a vector for disease
c. a source of nutrients
d. a site for reproduction
3. A veterinary technician is preparing to examine a dog suspected of having Cheyletiella mites. Based on the information in the passage, which precaution would most effectively prevent the transmission of mites to other animals in the clinic?
a. administering a vaccine to the infected dog
b. wearing disposable gloves while examining the dog
c. avoiding contact with open wounds on the dog
d. sterilizing the exam room before examining the dog
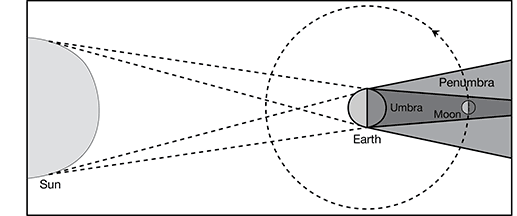
4. The passing of one object in space through the shadow of another object is called an eclipse. The orbits of the moon and Earth in relation to the sun cause both solar and lunar eclipses to occur. During a solar eclipse, the specific alignment of these three objects causes the moon to cast a shadow on the Earth. During a lunar eclipse, the alignment causes the Earth to cast a shadow on the moon.
The following diagram shows the alignment of the sun, Earth, and moon during a lunar eclipse. Draw an “X” in the correct spot to identify the location of the moon necessary to produce a solar eclipse.
5. The table below compares characteristics for four different groups of plants. A “1” indicates that the characteristic is present, and a “0” indicates that the characteristic is absent.
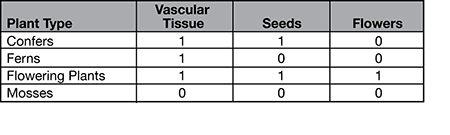
A cladogram illustrates the relatedness of organisms based on shared characteristics. Branches below a given characteristic represent organisms that do not exhibit that characteristic. Branches above a given characteristic represent organisms that do exhibit that characteristic. Each branch represents one plant type.
Use the information in the table to organize the four plant types onto the appropriate branches in the cladogram.
Write the correct plant type into each box. Select from the choices below.
conifers
ferns
flowering plants
mosses

Please use the following to answer questions 6–7.
The amount of oxygen gas dissolved in a body of water can provide information about the health of the aquatic ecosystem. In general, the closer the dissolved oxygen level to the maximum level, the more productive and less polluted the ecosystem can be assumed to be.
The table below shows the maximum amount of oxygen gas that can be dissolved in water at various temperatures.

6. The data in the table support which of the following statements about the relationship between water temperature and oxygen solubility?
a. Bodies of water with a lower average temperature can support a higher concentration of dissolved oxygen.
b. Bodies of water with an average temperature higher than 40°C contain no dissolved oxygen.
c. A 10°C increase in water temperature results in an approximately 3 mg/L change in oxygen solubility.
d. The oxygen solubility of a body of water is affected by many variables, including water temperature.
7. Researchers find that a body of freshwater with an average temperature of 21 °C has a dissolved oxygen concentration of 7.2 mg/L. What is a reasonable prediction of the water’s dissolved oxygen concentration after the population size of freshwater grasses doubles?
a. 6.3 mg/L
b. 7.2 mg/L
c. 8.5 mg/L
d. 14.4 mg/L
8. The chart below illustrates how the color of the light emitted by a star is dependent on the star’s temperature.
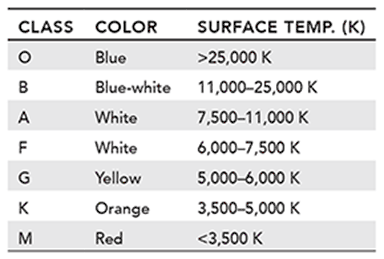
Which of the following statements is supported by the data in the table?
a. In general, white stars are hotter than blue-white stars.
b. A star with a surface temperature of 3,700 K produces red light.
c. Yellow light is produced by stars within the narrowest temperature range.
d. The highest known surface temperature of a star is 25,000 K.
9. The diagram below illustrates the structure of an ocean wave.
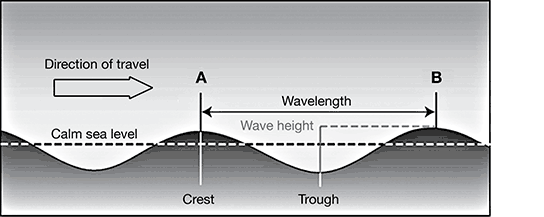
The period of a wave is the time required for the wave crest at point A to reach point B. The wave period can also be described as the amount of time required for a wave to do which of the following?
a. reach the shoreline
b. travel one wavelength
c. return to calm sea level
d. travel from crest to trough
Please use the following to answer questions 10–11.
The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) tracks the annual occurrence and effects of natural hazards in the United States. Based on its data, the USGS has calculated the probability of a natural hazard occurring in any given year that would cause 10 or more fatalities. The table below lists the probabilities for the four most commonly occurring natural hazards.
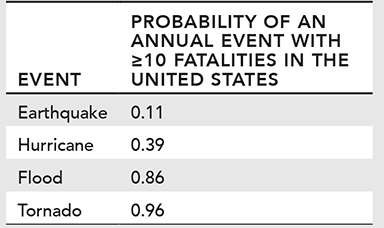
0 = no chance of occurring / 1 = 100% chance of occurring
10. What is the probability of a hurricane and a tornado, each with 10 or more fatalities, both occurring in the same year?
a. 0
b. 0.37
c. 0.96
d. 1.35
11. Write the appropriate natural hazard from the table in the box below.
A boundary between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates lies along the west coast of the continental United States. The probability of a(n) _____ with 10 or more fatalities is much higher in this region than the probability for the United States as a whole.
12. A marathon runner consumes foods with a high carbohydrate content before and during a race to prevent muscle fatigue. This practice, called carb loading, supports which of the following energy transformations within the runner’s body?
a. chemical to thermal
b. thermal to kinetic
c. kinetic to thermal
d. chemical to kinetic
Please use the following to answer questions 13–15.
Consumers in an ecosystem are classified by feeding level. Primary consumers feed on producers. Secondary consumers feed on primary consumers, and tertiary consumers feed on secondary consumers. Consumers in a food web are classified according to their highest feeding level.
A consumer’s population size is determined largely by the complex relationships that exist within the ecosystem’s food web. Population size is most obviously limited by the population size of the consumer’s food source(s). An increase or decrease in a food source population often leads to a similar change in the consumer population. The availability of a food source may be limited by other consumer populations competing for the same food source. An increase in a competitor population may lead to a decreased availability of the shared food source. Population size is also limited by the population size of the consumer’s predator(s). Predation by higher-level consumers keeps the lower consumer population from growing out of control and upsetting the ecosystem’s balance.
The food web for a woodland ecosystem bordering an area of farmland is shown below.

13. According to the passage, rabbits are considered primary consumers because they
a. feed on grasses and carrots
b. are consumed by foxes only
c. compete with grasshoppers only
d. are the only consumer of carrots
14. Which three organisms in the food web obtain energy directly or indirectly from grasshoppers?
a. owls, birds, and mice
b. owls, birds, and grains
c. foxes, rabbits, and mice
d. foxes, owls, and birds
15. A bacterial disease has destroyed most of the farm’s carrot crop for the past two seasons. As a result, the rabbit population has been forced to rely more heavily on grasses for a food source.
Explain how this disruption is likely to affect the rest of the ecosystem’s food web. Include multiple pieces of evidence from the text and discuss specific populations (other than carrots and rabbits) as examples to support your answer.
Write your response on the lines below. This task may take approximately 10 minutes to complete.
16. The table below illustrates the range of normal body temperatures in Fahrenheit for different age groups.
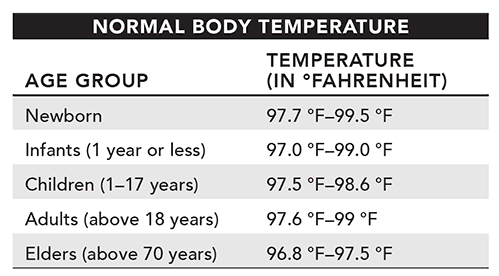
The formula for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is shown below.
(°F – 32) × 5/9 = °C
The normal body temperature range of a newborn baby is ____ °C to ____ °C. (You may use a calculator to answer this question.)
17. The process of meiosis is depicted in the diagram below.
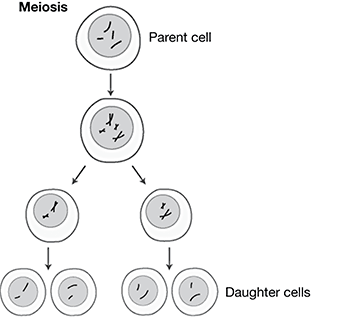
The daughter cells produced during meiosis are used for what purpose?
a. growth
b. tissue repair
c. differentiation
d. reproduction
18. A highway patrol officer is monitoring the speed of vehicles along a stretch of highway with a speed limit of 55 mph. The results are shown below.
Vehicle 1: 61 mphVehicle 2: 48 mph
Vehicle 3: 61 mph
Vehicle 4: 51 mph
Vehicle 5: 59 mph
What is the average speed of the five vehicles? (You may use a calculator to answer this question.)
a. 55 miles per hour
b. 56 miles per hour
c. 59 miles per hour
d. 61 miles per hour
19. Meiosis produces cells containing one chromosome from each chromosome pair. The diagram below shows the chromosome combinations that can be produced from a cell containing two pairs of chromosomes.
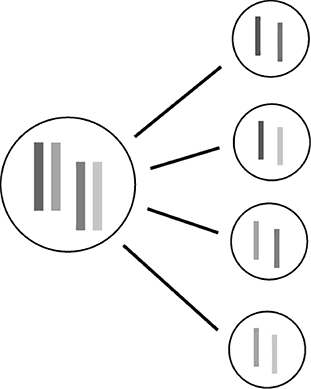
A barley plant has seven pairs of chromosomes. How many unique combinations of chromosomes can result from meiosis in barley?
a. 7
b. 14
c. 49
d. 128
Please use the following to answer questions 20–22.
Respiration is the cellular process used by living things to convert the chemical energy in food to a form that can be used by cells. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the high-energy molecule that all living things use to fuel cellular processes. During respiration, a molecule of glucose is converted to molecules of ATP to be used by the cell.
Depending on the conditions, respiration occurs by two different pathways: aerobic and anaerobic. When a cell has a sufficient supply of oxygen, aerobic respiration occurs. This pathway uses oxygen as a reactant, along with glucose, to produce 36 to 38 molecules of ATP from each molecule of glucose. Aerobic respiration is the preferred pathway in most cells. The general equation for aerobic respiration is shown below.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O
When sufficient oxygen is not available, anaerobic respiration occurs. This pathway produces two molecules of ATP from each molecule of glucose. Anaerobic respiration sometimes occurs in human muscle cells. During exercise, muscle cells use energy faster than the oxygen supply can be replenished, causing the cells to switch temporarily to anaerobic respiration.
20. A student draws the model below to represent the process of aerobic respiration.
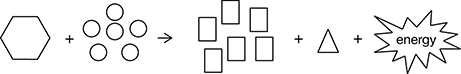
Which change would improve the accuracy of the student’s model?
a. connecting all of the circles to each other to show bonds
b. moving the energy symbol to the left side of the equation
c. adding five triangles to balance the right side of the equation
d. making the rectangles smaller to show relative molecular sizes
21. The energy produced by respiration is in what form?
a. ATP
b. oxygen
c. glucose
d. carbon dioxide
22. Explain the benefit of having two pathways for respiration in the human body.
Include multiple pieces of evidence from the text to support your answer.
Write your response on the lines on the following page. This task may take approximately 10 minutes to complete.
Please use the following to answer questions 23–24.
Matter exists in solid, liquid, and gas states. A substance may change between these three states. State changes can alter the physical properties of a substance, as depicted in the models below.

23. Which summary best explains the model of the states of matter?
a. Liquids have a fixed shape like solids but assume the volume of the container as gases do.
b. Liquids have a fixed volume and shape like solids. Gases assume the volume and shape of the container.
c. Liquids have a fixed volume like solids but assume the shape of the container as gases do.
d. Liquids assume the volume and shape of the container as gases do. Solids have a fixed volume and shape.
24. Based on the model, which state change increases the density of a substance?
a. gas to liquid
b. solid to gas
c. liquid to gas
d. solid to liquid
Please use the following to answer questions 25–26.
Information about five different fuel sources is listed in the table below.
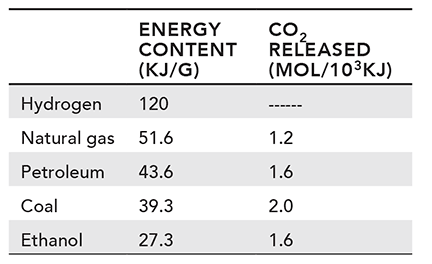
25. Which statement represents a fact supported by the data in the table?
a. All cars will be fueled by hydrogen cells in the future.
b. Petroleum is a better fuel source for cars than ethanol is.
c. Natural gas is too expensive to use as a fuel source for cars.
d. Ethanol fuel provides a car with less energy per gram than petroleum does.
26. Natural gas, petroleum, and coal are fossil fuels. Ethanol is derived from biomass.
Based on the data in the table, what is the best estimate of the energy content of fossil fuels?
a. 40 kJ/g
b. 42 kJ/g
c. 45 kJ/g
d. 50 kJ/g
27. The term exothermic describes a process in which energy is released, usually as thermal energy. The term endothermic describes a process in which thermal energy is absorbed.
Which of the following is an example of an exothermic process?
a. a candle burning
b. a snow bank melting
c. a loaf of bread baking
d. a plant making sugar
28. The graph below represents the motion of a remote-controlled car. The car’s acceleration, or change in velocity, is indicated by the slope of the graph.
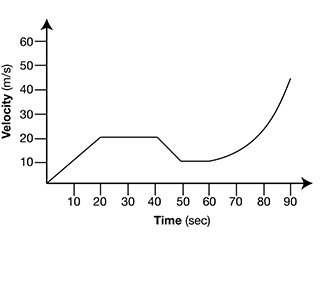
During which period did the car experience a constant positive acceleration?
a. between 0 and 20 seconds
b. between 20 and 40 seconds
c. between 40 and 50 seconds
d. between 50 and 90 seconds
Please use the following to answer questions 29–30.
The mechanical advantage (MA) of a machine is a measure of how much the machine multiplies the input force applied to it.
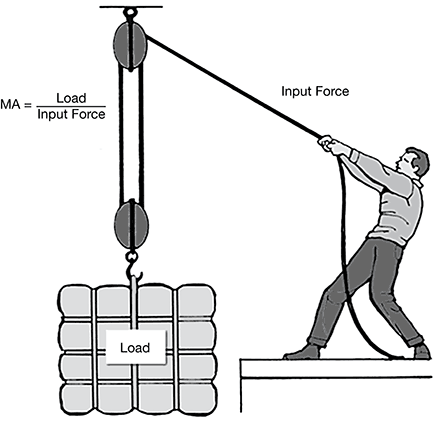
The table below shows the input force required to lift different loads using the pulley system shown above.
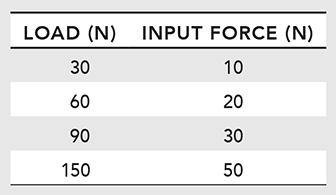
29. Based on the data in the table, what happens to the mechanical advantage of the pulley system as the load size increases?
a. The mechanical advantage increases at a constant rate.
b. The system’s mechanical advantage does not change.
c. The pulley system multiplies the mechanical advantage.
d. The mechanical advantage decreases at a constant rate.
30. A 1 Newton load has a mass of 10 grams. According to the table, what is the maximum mass that can be lifted by the pulley system using an input force of 50 Newtons?
a. 15 grams
b. 50 grams
c. 150 grams
d. 1,500 grams
31. Artificial selection is the process of breeding plants or animals to increase the occurrence of desired traits. Farmers use artificial selection to produce new crop species from existing plant species. The diagram below illustrates six crop species that have been derived from the common wild mustard plant.

Based on the information in the passage, how did farmers produce kale?
a. Farmers removed the stems and flowers from mustard plants as they grew.
b. Farmers allowed only wild mustard plants with large leaves to reproduce.
c. Farmers bred small-leafed plants with large-leafed plants to increase leaf size.
d. Farmers prevented wild mustard plants with large leaves from reproducing.
32.
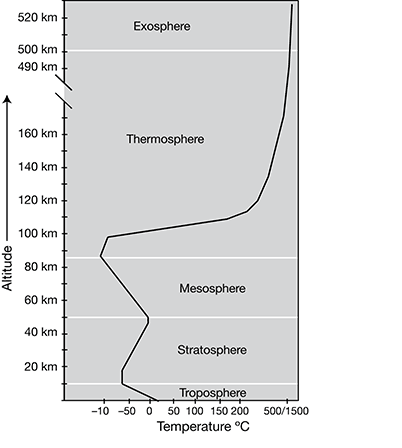
According to the graph, in which atmospheric layers does temperature decrease as altitude increases?
a. mesosphere and exosphere
b. troposphere and thermosphere
c. stratosphere and thermosphere
d. troposphere and mesosphere
33. Surface currents in the ocean are classified as warm or cold currents. In general, warm currents tend to travel from the equator toward the poles along the eastern coast of continents. Cold currents tend to travel from the poles toward the equator along the western coast of continents.
The map below shows the major surface ocean currents of the world.

Based on the passage, which of the following statements about the Alaska current is true?
a. The Alaska current is a typical cold current because it travels along the western coast of the continent.
b. The Alaska current is not a true surface current because it does not follow the general pattern of surface currents.
c. The Alaska current is an exception to the general pattern because warm currents typically travel along the eastern coast of continents.
d. The Alaska current transports water from the north pole toward the equator because it travels along the western coast of the continent.
34. Every person has two copies, or alleles, of the ABO blood type gene. A person’s ABO blood type is determined by his or her specific combination of alleles. The table below shows the allele combinations that cause the four different ABO blood types.

Suppose that a mother’s allele combination is IAi, and a father’s allele combination is IAIB. Which of the following statements is true about the blood type of their first child?
a. The child will have the same blood type as the mother.
b. The child cannot have the father’s blood type.
c. The child will have a blood type different from both parents’.
d. The child cannot have blood type O.
35. Blood glucose levels are tightly regulated in the human body by the hormones insulin and glucagon. When glucose levels become too high or low, the pancreas produces the appropriate hormone to return the body to homeostasis. The diagram below shows the feedback mechanism for regulating blood glucose levels.
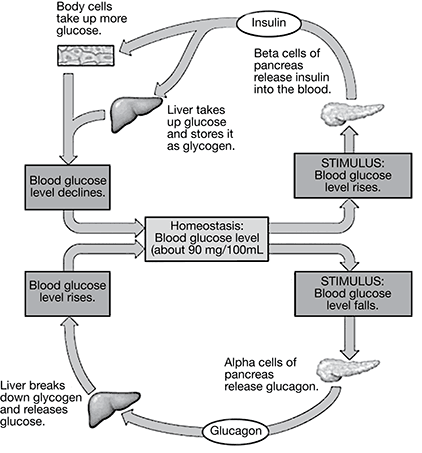
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which the pancreas is unable to produce the insulin needed to regulate blood glucose levels. What result would occur from providing an insulin injection to a diabetic person with high blood sugar?
a. The insulin travels to the liver, where it binds to and destroys excess glucose in the bloodstream.
b. The insulin signals the pancreas to produce glucagon, which increases the level of glucose in the bloodstream.
c. The insulin causes the liver to convert glucose to glycogen, removing excess glucose from the bloodstream.
d. The insulin breaks down glycogen into glucose, releasing stored glucose into the bloodstream.
Answers and Explanations
1. The symbiotic relationship exhibited by mistletoe and spruce trees is parasitism. The mistletoe receives a benefit in the form of a source of nutrients and water. The spruce tree is harmed because it loses nutrients and water, which can eventually lead to the death of the tree. The table indicates that parasitism is occurring when one organism benefits (mistletoe) and the other organism is harmed (spruce tree).
The symbiotic relationship exhibited by E. coli and humans is mutualism. The E. coli receive a benefit in the form of nutrients and a habitat in which to live. The human also receives a benefit because the E. coli produce vitamin K, which is then used within the human body. The table indicates that mutualism is occurring when both organisms benefit.
Commensalism is not demonstrated in either of these relationships. The table indicates that commensalism occurs when one organism benefits, but the other organism is neither helped nor harmed.
2. Choice c is correct. The fleas and ticks obtain nutrients from the host animal’s blood, and the mites obtain nutrients from the host animal’s skin.
Choice a is incorrect. Though the fleas and mites may live on the host animal’s body, the ticks do not.
Choice b is incorrect. Parasites can transmit diseases to the host animal, but this does not provide a benefit to the parasite.
Choice d is incorrect. Though the fleas and mites reproduce on the host animal’s body, the ticks do not.
3. Choice b is correct. The passage states that Cheyletiella mites live within the outermost layer of the dog’s skin and have difficulty surviving away from the host animal’s body. A technician wearing gloves during examination of the dog and disposing of them afterward helps to prevent mites that may be on the technician’s hands from being transmitted to other animals in the clinic.
Choice a is incorrect. Vaccines can be administered to uninfected individuals to prevent the transmission of diseases caused by viruses. Mites are arthropods that live on the host animal’s body and cannot be eliminated with a vaccine.
Choice c is incorrect. Avoiding contact with open wounds would help prevent the transmission of blood-borne pathogens, such as those transmitted by fleas and ticks.
Choice d is incorrect. Sterilizing the exam room after, not before, examination of the infected dog could help prevent the transmission of mites to other animals in the clinic.
4. In order for an eclipse to occur, the sun, Earth, and moon must be aligned in a particular way. When the Earth is positioned between the sun and the moon, the Earth will prevent sunlight from reaching the moon. This is a lunar eclipse. When the moon is positioned between the sun and the Earth, the moon will prevent sunlight from reaching a portion of the Earth. This is a solar eclipse.
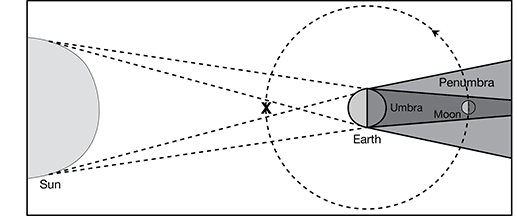
On the diagram, the moon has reached the position in its orbit that is in Earth’s shadow, resulting in a lunar eclipse. From its current position on the diagram, the moon would need to travel 180° (or halfway) around its orbit to produce a solar eclipse. In this new position, the moon would cast a shadow on the Earth.
5. In a cladogram, the group that exhibits the fewest characteristics is listed on the bottom left branch, and the group exhibiting the most characteristics is listed on the top right branch.
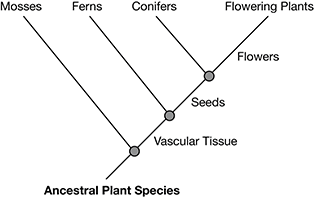
Mosses are placed on the first (lower left) branch because they exhibited none of the characteristics listed in the table. Ferns contain vascular tissue, so are listed on the second branch. Confers are the third branch because they contain vascular tissue and produce seeds. Flowering plants exhibit all three characteristics listed in the table, so are the fourth (highest) branch.
6. Choice a is correct. Describing the pattern in the data allows for the relationship between water temperature and oxygen solubility to be identified. As you look down the table, water temperature increases and maximum oxygen solubility decreases. This shows that water temperature and dissolved oxygen concentration have an inverse relationship, with highest dissolved oxygen concentrations occurring at the lowest temperatures.
Choice b is incorrect. According to the table, bodies of water with an average temperature of 40°C have a maximum oxygen solubility of 6.4 mg/L, and bodies of water with an average temperature of 100°C contain no dissolved oxygen. Temperatures between these two should support oxygen concentrations between 6.4 and 0 mg/L.
Choice c is incorrect. Though an increase from 0 to 10°C results in a 3 mg/L increase in oxygen solubility, oxygen solubility does not continue to increase by the same increment with each additional 10°C increase in temperature.
Choice d is incorrect. Though many variables can affect oxygen solubility, the table focuses only on the relationship between oxygen solubility and water temperature.
7. Choice c is correct. Grasses release oxygen into the environment as a byproduct of photosynthesis. Using this reasoning, it can be predicted that an increase in freshwater grasses will increase the dissolved oxygen concentration. Based on the data in the table, an increase to 8.5 mg/L brings the dissolved oxygen concentration closer to the maximum oxygen solubility for a body of water with an average temperature of 21°C.
Choice a is incorrect. Aquatic plants like freshwater grasses release oxygen into the environment. A dissolved oxygen concentration of 6.3 mg/L would result from an event that decreases the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water.
Choice b is incorrect. A dissolved oxygen concentration of 7.2 mg/L would indicate no change in the ecosystem. A change in the freshwater grass population would alter the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water.
Choice d is incorrect. A doubling of the freshwater grass population would cause an increase in dissolved oxygen concentration but not a doubling. According to the table, a dissolved oxygen concentration of 14.4 mg/L far exceeds the maximum oxygen solubility for a body of water with an average temperature of 21°C.
8. Choice c is correct. Range can be determined by calculating the difference between the lowest and highest values in a data set. The table shows that the temperature of a yellow star is between 5,000 K and 6,000 K. This is a range of 1,000 K, which is the smallest (or narrowest) range listed in the table.
Choice a is incorrect. White stars have a maximum temperature of 11,000 K. The minimum temperature of blue-white stars is 11,000 K.
Choice b is incorrect. Red stars have a maximum temperature of 3,500 K. A star with a temperature of 3,700 K would be within the range of an orange star.
Choice d is incorrect. The table does not provide information about the highest surface temperature recorded for a star. The minimum temperature of a blue star is shown to be 25,000 K. This indicates that blue stars can have temperatures higher than 25,000 K.
9. Choice b is correct. In the context of this ocean wave diagram, a wavelength is the horizontal distance between two crests (A and B). Using the given definition of wave period, it can be determined that the wave period is the amount of time required to travel one wavelength.
Choice a is incorrect. A shoreline is not shown or mentioned in the diagram.
Choice c is incorrect. Wave period relates to the horizontal movement of a wave, while calm sea level is a reference point used to measure the vertical movement of a wave.
Choice d is incorrect. In the diagram, points A and B used to measure wave period are both crests. The time required to travel from crest to trough would be half of a wave period.
10. Choice b is correct. A hurricane and tornado occurring in the same year would be considered a compound event because two events are occurring together. The probability of a compound event can be determined by multiplying the probabilities of each event occurring individually. The probability of a hurricane (0.39) multiplied by the probability of a tornado (0.96) provides a compound probability of 0.3744.
Choice a is incorrect. A probability of 0 indicates that there is no chance of an event occurring. Since there is a possibility of a hurricane and a possibility of a tornado occurring individually, there is also a possibility of both events occurring in the same year.
Choice c is incorrect. This is the probability of a tornado alone occurring during any given year. The probability of both a tornado and a hurricane occurring in the same year would be much lower because the probability of a hurricane is much lower (0.39) than the probability of a tornado (0.96).
Choice d is incorrect. A probability greater than 1 indicates that an event is guaranteed to occur. Since the individual probabilities of a hurricane or tornado occurring are both less than 1, the probability of both events occurring in the same year would also be less than 1.
11. The natural hazard that best completes this statement is earthquake. The Earth’s crust is made up of tectonic plates. The location where two or more tectonic plates meet is called a plate boundary. When the pressure built up at a plate boundary becomes too great, energy is released in the form of an earthquake.
Earthquakes can be expected to occur most frequently along plate boundaries. Since the west coast of the continental United States lies on a plate boundary, the probability of an earthquake occurring in this region can be predicted to be much higher than the probability for the United States as a whole, most of which does not lie on plate boundaries.
The occurrence of hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes is not specifically tied to the activity of tectonic plates. An increase in the probability of any of these natural hazards along a plate boundary as compared to the United States as a whole is not a reasonable prediction.
12. Choice d is correct. The runner takes in chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. This chemical energy is transformed into kinetic energy as the runner’s muscles contract and relax, causing the runner to move. Runners carb load to ensure that their bodies have enough chemical energy to be transformed into the kinetic energy required to run a marathon.
Choice a is incorrect. The runner does take in chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. Though some of this chemical energy is transformed into thermal energy in the form of body heat, the purpose of carb loading is to improve muscle performance, not increase body heat.
Choice b is incorrect. The purpose of carb loading is to increase the amount of energy available for transformation into kinetic energy (motion). Carb loading increases the availability of chemical energy, though, not thermal energy. Carbohydrates contain energy stored in their chemical bonds, not as heat.
Choice c is incorrect. The goal of carb loading is to improve muscle performance (motion), not increase body heat. Muscle performance is improved by increasing the chemical energy available for transformation into kinetic energy.
13. Choice a is correct. A primary-level consumer feeds on producers. Producers, such as plants, make their own food using energy from sunlight. Rabbits feed on two producers, carrots and grasses, making rabbits a primary-level consumer.
Choice b is incorrect. An organism’s feeding level is determined by how it obtains its food, not by the organisms that it provides food for. Though the rabbits in the food web are consumed by foxes, this does not determine the rabbits’ feeding level.
Choice c is incorrect. Competition with other organisms does not affect how an organism’s feeding level is classified.
Choice d is incorrect. The presence of other organisms that consume the same food source does not affect how an organism’s feeding level is classified.
14. Choice d is correct. An organism provides energy to all organisms above it in the food web. In this food web, the grasshoppers provide energy to the birds, owls, and foxes. The birds and owls obtain energy directly when they consume the grasshoppers. The foxes obtain energy indirectly when they consume birds that previously consumed grasshoppers.
Choice a is incorrect. Although owls and birds obtain energy from grasshoppers, mice do not obtain energy from grasshoppers.
Choice b is incorrect. Grains provide energy to grasshoppers but do not obtain energy from grasshoppers.
Choice c is incorrect. Rabbits and mice do not obtain energy from grasshoppers either directly or indirectly.
15. The highest number of points you can earn on this short-response essay is 3.
A 3-point essay contains:
• a clear and well-developed explanation of how a change in one population effects change in other populations within the food web
• well-developed examples from the given food web describing the likely effects of change in the rabbit population on other specific populations
• complete support from the passage
Sample 3-point response:
The interrelatedness of populations in the food web makes it likely that all populations will be affected in some way by the shift in the rabbits’ feeding habits. The rabbits’ increased reliance on grasses will cause a domino effect on the availability of food for all primary consumers. Since grasshoppers directly compete with rabbits for grasses, the availability of grasses for grasshoppers may be limited. As a result, grasshoppers would likely increase their dependence on grains, decreasing the availability of this food source for birds and mice. The overall increase in competition among primary consumers may cause some decreases in population sizes, which would also limit the population sizes of higher-level consumers.
A 2-point essay contains:
• an adequate or partially articulated explanation of how a change in one population effects change in other populations within the food web
• partial examples from the given food web describing the likely effects of change in the rabbit population on other specific populations
• partial support from the passage
Sample 2-point response:
When the rabbits start eating more grasses, the grasshoppers will have less food because they eat grasses too. This means that the grasshopper population might get smaller, so the owls and birds would have less food. Foxes eat birds, so they would have less food too.
A 1-point essay contains:
• a minimal or implied explanation of how a change in one population effects change in other populations within the food web
• one or incomplete examples from the given food web describing the likely effects of change in the rabbit population on other specific populations
• minimal or implied support from the passage
Sample 1-point response:
The rabbits will eat more grass. Grasshoppers will not have as much grass to eat. Some grasshoppers will die because they don’t have enough food.
A 0-point essay contains:
• no explanation of how a change in one population effects change in other populations within the food web
• no examples from the given food web describing the likely effects of change in the rabbit population on other specific populations
• no support from the passage
16.
Blank 1:
The appropriate value to complete this statement is 36.5.
The formula for converting temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius is given as (°F – 32) × 5/9 = °C. Replacing the lower variable °F with 97.7 and solving gives (97.7 – 32) × 5/9 = 36.5.
Blank 2:
The appropriate value to complete this statement is 37.5.
The formula for converting temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius is given as (°F – 32) × 5/9 = °C. Replacing the lower variable °F with 99.5 and solving gives (99.5 – 32) × 5/9 = 37.5.
17. Choice d is correct. As indicated in the diagram, the daughter cells produced during meiosis each have half the total number of chromosomes as the parent cell does. These daughter cells, called gametes, are used for reproduction. When reproduction occurs, two gametes (egg and sperm) unite to create a cell with a full set of chromosomes.
Choice a is incorrect. To allow an organism to grow larger, the daughter cells produced must be identical to the parent cell. Cells used for growth are produced by the process of mitosis.
Choice b is incorrect. To allow an organism to repair tissues, the daughter cells produced must be identical to the parent cell. The cells used for tissue repair are produced by the process of mitosis.
Choice c is incorrect. Cell differentiation occurs when a single, non-specialized cell is converted to a specialized cell type, like a blood cell or skin cell. No daughter cells are produced during the differentiation process.
18. Choice b is correct. The average speed can be determined by adding the individual vehicle speeds and dividing by the total number of vehicles. This is calculated as 61 + 48 + 61 + 51 + 59/5 = 56 mph.
Choice a is incorrect. This is the speed limit for the highway, not the average speed of the five vehicles listed.
Choice c is incorrect. This is the median speed of the five vehicles, not the average (mean) speed.
Choice d is incorrect. This is the mode for the speed of the five vehicles, not the average (mean) speed.
19. Choice d is correct. Each new cell created by meiosis must contain one chromosome from each of the seven chromosome pairs. As illustrated in the diagram, these single chromosomes can be combined in multiple ways. To determine the total number of unique chromosome combinations, the number of chromosomes in each set (pair) must be multiplied. Seven sets of two chromosomes each means that seven 2’s must be multiplied (2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 128) to determine the total number of unique chromosome combinations possible.
Choice a is incorrect. There are seven total chromosomes in a cell produced by meiosis, but the specific chromosome present from each chromosome pair can vary.
Choice b is incorrect. Two chromosomes in each of seven pairs provides a total of 14 chromosomes, but the specific chromosome present from each pair can vary.
Choice c is incorrect. Multiplying 7 × 7 does not provide the total number of chromosome combinations possible. To determine this, the number of chromosomes in each pair must be multiplied by the number of chromosomes in each other pair.
20. Choice c is correct. The products of respiration are six molecules of carbon dioxide, six molecules of water, and energy. On the right side of the model, six rectangles are present but only one triangle. To accurately represent a balanced equation, all molecules must be represented in the model.
Choice a is incorrect. The circles represent the six molecules of the reactant oxygen. Connecting the circles would not improve the model’s accuracy because separate molecules are not bound to each other.
Choice b is incorrect. Energy is a product of the respiration reaction and is therefore appropriately placed on the right side of the equation. Moving the energy symbol to the left side of the equation would indicate that energy is a reactant.
Choice d is incorrect. Reducing the size of the rectangles is not the most needed change, since the other molecules are not represented to scale.
21. Choice a is correct. The purpose of respiration is to convert energy into a form that is useable by cells. Respiration produces ATP, a high-energy molecule, which the cell can use to carry out cellular functions.
Choice b is incorrect. Oxygen is a reactant—not a product—of aerobic respiration and does not provide energy for the cell.
Choice c is incorrect. Respiration uses the glucose in food to produce ATP. Respiration does not produce glucose.
Choice d is incorrect. Though respiration does produce carbon dioxide, this molecule does not provide energy for the cell.
22. The highest number of points you can earn on this short-response essay is 3.
A 3-point essay contains:
• a clear and well-developed explanation of the benefits of the aerobic respiration pathway in the human body
• a clear and well-developed explanation of the benefits of the anaerobic respiration pathway in the human body
• complete support from the passage
Sample 3-point response:
The human body may use two different pathways to carry out respiration. The presence of two different pathways is valuable because it allows a cell to choose the pathway that best meets its current energy needs. Aerobic respiration produces the greatest amount of ATP per glucose molecule. Under normal conditions with adequate oxygen, this pathway provides the greatest possible amount of energy to the cell. Anaerobic respiration produces much less ATP per glucose molecule but does not require oxygen. Under strenuous conditions when the cell demands energy faster than the oxygen supply can be replenished, this pathway provides enough energy to maintain cell functions. The ability to switch between aerobic and anaerobic pathways allows the human body to function properly under varying conditions.
A 2-point essay contains:
• an adequate or partially articulated explanation of the benefits of the aerobic respiration pathway in the human body
• an adequate or partially articulated explanation of the benefits of the anaerobic respiration pathway in the human body
• partial support from the passage
Sample 2-point response:
Aerobic respiration produces the most ATP, but requires oxygen. Anaerobic respiration produces much less ATP, but does not require oxygen. Having two pathways is important because sometimes oxygen is available, and sometimes it is not.
A 1-point essay contains:
• a minimal or implied explanation of the benefits of the aerobic respiration pathway in the human body
• a minimal or implied explanation of the benefits of the anaerobic respiration pathway in the human body
• minimal or implied support from the passage
Sample 1-point response:
Cells use aerobic respiration most of the time. Muscle cells use anaerobic respiration when a person is exercising. Both types of respiration are important.
A 0-point essay contains:
• no explanation of the benefits of the aerobic respiration pathway in the human body
• no explanation of the benefits of the anaerobic respiration pathway in the human body
• no support from the passage
23. Choice c is correct. As shown in the model, a solid has a fixed volume and shape. A liquid has a fixed volume but assumes the shape of the container. A gas assumes the volume and shape of the container. A liquid has one property in common with solids, and one property in common with gases.
Choice a is incorrect. In this summary, the properties of a liquid are reversed. Liquids have a fixed volume and assume the shape of the container.
Choice b is incorrect. Liquids have a fixed volume as solids do, but not a fixed shape.
Choice d is incorrect. Liquids assume the shape of the container as gases do, but not the volume.
24. Choice a is correct. The density of a substance describes how tightly packed the substance’s molecules are. As shown in the model, a substance’s molecules are most spread out when in the gas state. This means that a substance’s density is lowest when in the gas state. The substance’s density increases when going from gas to liquid state because the molecules become more tightly packed.
Choice b is incorrect. A substance’s molecules become more spread out when changing from solid to gas state. This causes the substance’s density to decrease.
Choice c is incorrect. A substance’s molecules become more spread out when changing from liquid to gas state. This causes the substance’s density to decrease.
Choice d is incorrect. A substance’s molecules may become slightly more spread out, or less dense, when changing from solid to liquid state. However, the density of a substance does not change much during this state change.
25. Choice d is correct. Based on the data in the table, this statement can be identified as a fact. The energy content of ethanol is 27.3 kJ/g, about 16 kJ/g less than the energy content of petroleum (43.6 kJ/g).
Choice a is incorrect. This statement is speculation based on data from the table. According to the table, hydrogen has the greatest energy content and releases no carbon dioxide. Although this data supports the speculation that cars may be fueled by hydrogen cells in the future, this statement is no guarantee.
Choice b is incorrect. This statement is a judgment based on data from the table. According to the table, petroleum has a higher energy content than ethanol. Although this data can be used to support the judgment that petroleum is the better fuel source, this statement is an opinion rather than a fact.
Choice c is incorrect. This statement is speculation based on data from the table. Although the data in the table suggests that natural gas is a relatively efficient and clean fuel source, the statement is speculation because no information is provided about the cost of natural gas.
26. Choice c is correct. The passage identifies natural gas, petroleum, and coal as fossil fuels, because each is derived from the fossil remains of organisms. The energy content of each fossil fuel can be approximated to 50 kJ/g, 45 kJ/g, and 40 kJ/g, respectively. This provides an estimated average energy content of 45 kJ/g.
Choice a is incorrect. This would be an appropriate estimate for the energy content of coal, not for the energy content of all three fossil fuels.
Choice b is incorrect. This would be an appropriate estimate for the energy content of petroleum and coal, but natural gas is also a fossil fuel.
Choice d is incorrect. This would be an appropriate estimate for the energy content of natural gas, not for the energy content of all three fossil fuels.
27. Choice a is correct. Burning a candle is an exothermic process because thermal energy, or heat, is released as a result of the process.
Choice b is incorrect. Melting a snow bank is an endothermic process because the input of heat is required to melt the snow. This means that thermal energy is absorbed during the process, not released.
Choice c is incorrect. Baking a loaf of bread is an endothermic process because the input of heat is required to convert the ingredients to bread. This means that thermal energy is absorbed during the process, not released.
Choice d is incorrect. Photosynthesis is an endothermic process because the input of energy (sunlight) is required for plants to make sugar. This means that energy is absorbed during the process, not released.
28. Choice a is correct. The car has a constant positive acceleration when the car’s velocity is increasing at a steady, or constant, rate. Between 0 and 20 seconds, the graph moves upward in a straight diagonal line, indicating that the velocity is increasing at a constant rate.
Choice b is incorrect. Between 20 and 40 seconds, the car is maintaining a constant velocity of 20 m/s. Since the velocity is constant within this time period, the car is not accelerating (has an acceleration of 0 m/s2).
Choice c is incorrect. Between 40 and 50 seconds, the car’s velocity is decreasing at a constant rate. This indicates a constant negative acceleration.
Choice d is incorrect. Between 50 and 90 seconds, the car’s velocity is increasing but not at a constant rate. The graph moves upward in a curved line within this time period, indicating that the velocity is increasing at a variable rate.
29. Choice b is correct. The mechanical advantage of a pulley system does not change with the load. Mechanical advantage is calculated as load divided by input force. In the data table, dividing each load by its corresponding input force produces a mechanical advantage of three.
Choice a is incorrect. As the load size increases, the input force required to lift the load increases at a constant rate. The mechanical advantage of the pulley system does not change.
Choice c is incorrect. A pulley system multiplies the input force, not the mechanical advantage, applied to a load.
Choice d is incorrect. No decrease in mechanical advantage occurs with an increase in load. The mechanical advantage of a pulley system is constant regardless of the size of the load.
30. Choice d is correct. According to the table, an input force of 50 N can lift a 150 N load. If a 1 N load has a mass of 10 grams, the mass of a load can be determined by multiplying the force of the load by 10. A 150 N load therefore has a mass of 1,500 grams.
Choice a is incorrect. This value is the result of dividing the force of the load (150 N) by 10. The mass of the load is determined by multiplying, not dividing, the force of the load by 10.
Choice b is incorrect. This is the value of the input force, not the mass of the load.
Choice c is incorrect. This is the value of the force of the load in Newtons, not the mass of the load in grams.
31. Choice b is correct. Kale is a leafy crop species. According to the diagram, wild mustard plants were selected for leaves to produce kale. This means that wild mustard plants that had large leaves were specifically bred together to increase leaf size. This selective breeding over multiple generations led to a new species (kale) characterized by large leaves.
Choice a is incorrect. Plants with desired characteristics (large leaves for kale) must be bred together to produce offspring plants with those characteristics. Removing stems and flowers from existing mustard plants will not increase leaf size in subsequent generations.
Choice c is incorrect. Breeding small-leafed plants and large-leafed plants allows the possibility that offspring will have either small or large leaves. To ensure offspring have the best chances of large leaves, large-leafed plants should be bred together.
Choice d is incorrect. Preventing plants with large leaves from growing works to remove the large-leaf trait from subsequent generations rather than increase its appearance.
32. Choice d is correct. In the graph, temperature increases to the right and altitude increases upward. Any portion of the graph that has a negative slope, or slopes to the left, indicates a decrease in temperature. The graph has a negative slope in the troposphere and mesosphere layers.
Choice a is incorrect. The graph has a negative slope within the mesosphere but a slight positive slope in the exosphere. This means that temperature decreases as altitude increases in the mesosphere but increases with altitude in the exosphere.
Choice b is incorrect. The graph has a negative slope within the troposphere but a positive slope in the thermosphere. Even though the slope is not constant within the thermosphere, the slope remains positive within this layer. This means that temperature decreases in the troposphere but increases in the thermosphere.
Choice c is incorrect. The graph has a positive slope within both the stratosphere and the thermosphere. This means that temperature increases with altitude in both layers.
33. Choice c is correct. The Alaska current is a warm current. The passage states that warm currents typically travel along the eastern coast of continents, but the Alaska current travels along the western coast of North America.
Choice a is incorrect. Although the Alaska current does travel along the western coast of the continent, the map key indicates that it is a warm current.
Choice b is incorrect. The Alaska current does not follow the typical pattern for a warm current but is identified as a surface current on the map.
Choice d is incorrect. The map key identifies the Alaska current as a warm current. Warm currents transport warm water originating near the equator toward the poles.
34. Choice d is correct. The blood type O can be produced only by the allele combination ii. A child receives one allele from each parent. Since the mother has an i but the father does not, the allele combination ii is not possible for their children.
Choice a is incorrect. Based on the table, the mother’s blood type is A. The child can receive IA or i from the mother and IA from the father, resulting in type A blood caused by the possible allele combinations IAIA or IAi. However, the child could receive IB from the father, which would result in a blood type different from the mother’s.
Choice b is incorrect. Based on the table, the father has blood type AB. The child can receive IA from the mother and IB from the father, resulting in the possible allele combination IAIB. This allele combination will produce the same blood type as the father’s.
Choice c is incorrect. Based on the table, the mother’s blood type is A, and the father’s is AB. The child can receive IA or i from the mother and IA from the father, resulting in type A blood caused by the possible allele combinations IAIA or IAi. The child can receive IA from the mother and IB from the father, resulting in the blood type AB caused by the possible allele combination IAIB. This means it is possible for the child to have the same blood type as one of the parents’.
35. Choice c is correct. According to the diagram, when a person’s blood glucose level rises, the pancreas secretes insulin. The insulin signals body cells to absorb glucose from the blood and signals the liver to convert excess glucose into the storage molecule glycogen. These processes remove excess glucose from the blood, returning the blood glucose level to homeostasis. Insulin injected into a diabetic person initiates the same pathway as insulin produced in the pancreas of a healthy person.
Choice a is incorrect. Insulin signals the liver to convert and store excess glucose to glycogen, not to destroy the glucose.
Choice b is incorrect. Insulin and glucagon do not signal each other but perform opposite functions. Insulin works to decrease blood glucose levels, while glucagon works to increase these levels.
Choice d is incorrect. Glucagon signals the breakdown of glycogen into glucose when blood glucose levels are low. Insulin signals the conversion of glucose to glycogen when blood glucose levels are high.