- What does unsupervised learning mean?
- What is the major difference between unsupervised learning and supervised learning?
- How do we install the Python package sklearn?
- Discuss the relationship between distance and clustering classification.
- How do we define the distance between two objects?
- For non-numeric values, how do we define a distance between two members?
- For R, we could find a set of related packages related to unsupervised learning called cluster. Is there any task view, or similar super package, for Python?
- First, generate the following set of random numbers:
>set.seed(12345) >n=30 >nGroup=4 >x <- matrix(rnorm(n*nGroup),nrow =nGroup)
Then, based on the various definitions of distance, estimate the distances between those four groups.
- For the following set of data, estimate the minimum, maximum, and average distances:
> data <- rbind(c(180,20), c(160,5), c(60, 150), c(160,60), c(80,120))
- What is the usage of a dendrogram?
- Draw a dendrogram by using all wine data.
- Generate 20 random numbers with a mean of 1.2 and standard deviation of 2 from a normal distribution. Then draw a dendrogram.
- Using a five-year monthly historical price data for 30 stocks, estimate their annualized standard deviations and means. Classify them into different groups. The source of data is Yahoo!Finance (http://finance.yahoo.com). Note that the following formulae are used to calculate an annualized standard deviation:

Where σannual is the annualized standard deviation, σmonthly is the standard deviation based on monthly returns, 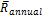 is the annualized mean return, and
is the annualized mean return, and  is the monthly mean return.
is the monthly mean return.
- For the R package called cluster, what is the meaning of the votes.repub dataset? Using that dataset, conduct a Cluster Analysis and draw a dendogram tree.
- Find more information about the linkage_tree() function contained in the sklearn.cluster submodule. (Python)
- For the rattle package, how do we save an R script?