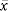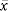Index
absolute risk reduction see risk difference
abstracts
accuracy, diagnostic
ACP Journal Club
alpha (α)
American Journal of Epidemiology
American Journal of Physiology
American Journal of Public Health
analysis of covariance
analysis of variance
Annals of Internal Medicine
area under receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC)
association
attributable risk (AR)
authors
instructions to
statistical checklists
statistical guidelines
baseline differences
benefit per 1000 patients
bias
binary variables
clinical trials
meta-analysis
regression analysis
Binomial distribution
table for confidence intervals
blinding techniques
Bonferroni correction
bootstrap methods
bias corrected and accelerated method
bias corrected method
parametric
percentile method
software
brackets (…)
British Heart Journal
British Medical Journal (BMJ)
misuse of confidence intervals
policies
statistical checklists
use of confidence intervals
case–control study
matched
more than two levels of exposure
unmatched
causality
censored observations
checklists, statistical
chi squared (x2) test
CIA software see Confidence Interval Analysis (CIA) software
clinically worthwhile difference, smallest
clinical trials
adjusting for other variables
arguments against confidence intervals
benefit per 1000 patients
cluster
crossover trials see crossover trials guidelines for authors
interpretation
multiple groups
number needed to treat
parallel groups
presentation of results
results section
software
statistical checklists
subgroups
Clopper–Pearson method
cluster randomised trials
complex analyses, guidelines for authors
Confidence Interval Analysis (CIA) software
Data Editor window
help
Method window
options
outline of program
Output window
updates and bug fixes
confidence intervals
degree
in non-parametric methods
dissenting voices
exact
guidelines for authors
link to P values
in medical journals see journals, medical
method of calculation
null values and
presentation of results
rationale
suggested use
use
us P values
us standard errors
width
sample size estimation from
confidence limits
CONSORT statement
checklist
patient flow diagram
continuous variables clinical trials
diagnostic problem
meta-analysis
non-Normal
regression analysis
summary statistics
control group
correlated variables, hypothesis tests
correlation
coefficient
guidelines for authors
matrix
technical details
cost-effectiveness ratio
Cox regression
in clinical trials
in time to event studies
crossover trials
binary outcome
continuous outcome
data
description
presentation see presentation of results
tied
decimal places, number of
degrees of freedom
design, study
Diabetic Medicine
diagnostic tests
area under ROC curve
classification
into more than two groups
clinical cutpoints
interpretation
kappa statistic
likelihood ratios
measurement-based
positive/negative predictive values
sensitivity
specificity
difference, smallest clinically worthwhile
discussion section
distribution-free methods see nonparametric methods
distribution of data
economics, health
editorials, in medical journals
editorial staff, statistical checklists
epidemiological studies
Epidemiology
error bars
errors in journal articles
estimates, sample study
imprecision
presentation
Evidence-Based Medicine
ex
exact confidence intervals
medians
proportions
software
extrapolation
false-negative results
false-positive results
figures
Fisher’s exact test
flow diagram
follow-up studies see also time to event studies
forest plot
Geigy scientific tables
graphical presentation
guidelines, statistical
discussion section
methods section
results section
hazard
ratio
histograms
hypergeometric distribution
hypothesis tests see also P values
dependent (correlated) data
guidelines for authors
interpretation
medical journal policies
multiple
overemphasis
presentation of results
sample size determination
two-sided
vs confidence intervals
incidence
rates
ratio, standardised see standardised incidence ratio
study
use of term
individuals
data presentation
repeated measurements
as units of analysis
instructions to authors
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors
interquartile range
Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA)
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
journals, medical
editorials and expository articles
instructions to authors
misuse of confidence intervals
policies
secondary publication
statistical checklists
statistical guidelines
surveys of use
Kaplan–Meier survival curves
kappa statistic
The Lancet
life tables
likelihood ratios (LR)
log method
score method
logarithmic transformation
likelihood ratio
means/differences
in meta-analysis
relative risk
loge x
logistic regression
in clinical trials
multiple
logit method
logistic regression
pooled estimate of odds ratio
logrank test
McNemar’s test
Mann–Whitney U test
Mantel–Haenszel method
in meta-analysis
masking see blinding techniques
mean
difference (two samples)
geometric
guidelines for authors
notation
sampling distribution
single sample
two-group comparison, sample size
variability, sample size estimation
median
definition
difference (two samples)
tables for confidence intervals
unpaired data
exact method
guidelines for authors
sampling distribution
single sample
survival time
table for confidence intervals
technical note
Medical Journal of Australia
meta-analysis
analysis methods
binary outcome
continuous outcome
fixed effects approach
interpretation
presentation of results
random effects approach
time to event outcome
methods section, guidelines for authors
mid-P confidence interval
MINITAB
misuse, of confidence intervals
mortality
ratio, standardised see standardised mortality ratio
studies
multiple comparisons
multiple regression
in clinical trials
guidelines for authors
multivariate techniques
Newcombe’s method
paired proportions
unpaired proportions
non-Normal data
means/differences
medians/differences
non-parametric methods
presentation of results
terminology
non-significant results
Normal distribution
area under ROC curve (AUC)
assumption, guidelines
correlation analysis
logit method
means/differences
notation
substitution method and
table for confidence intervals
notation
null value
confidence intervals including
sample size estimation and
number needed to harm (NNH)
number needed to treat (NNT)
for benefit (NNTB)
for harm (NNTH)
meta-analysis
observational studies
odds ratio (OR)
clinical trials
homogeneity test
logistic regression
logit method
logit pooled estimate
Mantel–Haenszel method
matched case–control studies
meta-analysis
more than two levels of exposure
relative odds reduction
stratified analysis
unmatched case–control studies
one-sided test
outliers
p
P see P values
paired data
in clinical trials
means
medians
presentation
proportions
parameter
parametric bootstrap
parametric methods
Pearson’s product moment correlation coefficient
percentages
presentation
sample size estimation and
percentile
method, bootstrapping
range
person-years at risk
πx
planning, study
± sign
Poisson distribution
table for confidence intervals
power, study
sample size estimation
precision
presented results
sample study estimates
prediction
diagnostic tests and
intervals, in regression analysis
predictive values
negative
positive
prevalence-adjusted
presentation of results clinical trials
confidence intervals
guidelines for authors
limitations of P values
meta-analysis
summary statistics
in tables
textual
prevalence
predictive values and
studies
probability
posterior
prior
values see P values
proportional hazards regression analysis see Cox regression
proportions
difference see also proportions, two samples
notation
single sample
recommended (Wilson’s) method
software
survival
technical note
two-group comparison, sample size
two samples, paired data
recommended (Newcombe’s) method
two samples, unpaired data
recommended (Newcombe’s) method
very low/high
zero (no observed events)
P values see also hypothesis tests; mid-P values
Bonferroni correction
cut-off points
exact
interpretation
limitations
link to confidence intervals
medical journal policies
presentation
suggested use
vs confidence intervals
quality of life studies
quantiles see also median
QUOROM statement
random allocation
randomised controlled trials see also clinical trials
statistical checklists
receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, area under (AUC)
referees, statistical checklists
reference interval
regression
Cox see Cox regression guidelines for authors
interpretation
line(s)
difference between slopes of two
mean value of y for any given value of x
vertical distance between two
linear
logistic see logistic regression more than two samples
multiple see multiple regression
prediction intervals
residuals
single sample
technical details
two samples
relative risk (risk ratio)
clinical trials
incidence study
matched case–control study
meta-analysis
reduction
unmatched case–control study
repeated measurements
replicate readings
Resampling Stats
residuals, regression analysis
response rates
results, presentation of see presentation of results
results section
presentation of results
statistical analysis
risk difference (absolute risk reduction, ARR)
meta-analysis
number needed to treat and
risk ratio see relative risk
risk reduction
absolute (ARR) see risk difference relative
rounding up/down, numbers
sample size
confidence interval approach
confidence interval width and
effective
hypothesis test-based approach
hypothesis test interpretation and
notation
sampling distribution and
small
statistical checklists
sample study estimates see estimates, sample study
sampling distribution
sampling variation
scatter plots
screening tests
SD see standard deviation
SE see standard error sensitivity
serial measurements
σ
significance
clinical
levels see also P values sample size estimation
statistical
tests see hypothesis tests
skewed data see non-Normal data
smallest clinically worthwhile difference
small samples
software, computer
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient
specificity
SPlus
standard deviation (SD)
assumptions involving
confidence interval width and
notation
± sign notation
pooled estimate
pooled residual, two regression lines
prediction interval for individuals
residual, regression line
standard error (SE)
area under ROC curve (AUC)
confidence interval calculation
difference between independent estimates
kappa statistic
mean
median survival times
notation
odds ratio (log)
± sign notation
presentation
proportions
regression line, predicted values
relative risk (log)
standardised rate
survival proportions
vs confidence intervals
standardisation
direct method
indirect method
standardised incidence ratio (SIR)
ratio of two
standardised mortality ratio (SMR)
ratio of two
sampling distribution
standardised rates
standardised ratios
ratio of two
Stata
statistical analysis
checklists
methods section
results section
statistical checklists
general papers
other types of study
randomised controlled trials
statistical guidelines see guidelines, statistical statisticians
advice from
assessment of medical papers
views on confidence intervals
StatXact software
stratified analysis
bootstrap method
odds ratio
subgroups
in clinical trials
in correlation analysis
in regression analysis
substitution method
summary statistics
presentation
standard error
surveys
response rates
survival
analysis see also time to event studies
curves, Kaplan–Meier
proportions
time
median see median, survival time regression
tables
t distribution
table for confidence intervals
t test
test statistics, suggested use
tied data
time to event studies
in clinical trials
Cox regression
hazard ratio
meta-analysis
number needed to treat
single sample
two samples
“to”, in range of confidence intervals
transformation, data, see also logarithmic transformation
guidelines for authors
uncertainty, standard error as measure
units of analysis
Vancouver guidelines
variability
confidence interval width and
in sample size estimation
standard deviation as measure
weaknesses, in discussion section
Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank sum distribution
Wilcoxon one sample test
Wilcoxon test, paired
Wilcoxon two sample rank sum distribution
Wilson’s method, single proportions
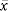
Z1–α/2 value
Zα/2 value