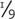 , and so on.
, and so on.A Aperture priority mode, as indicated by some camera manufacturers.
additive primary colors The three colors red, blue, and green, which can be combined to create any other color. When superimposed on each other they produce white.
algorithm Mathematical procedure that allows the step-by-step solution of a problem.
aliasing The jagged appearance of diagonal lines in an image, caused by the square shape of pixels.
anti-aliasing The smoothing of jagged edges on diagonal lines created in an imaging program, by giving intermediate values to pixels between the steps.
aperture The opening behind your lens that allows light to pass through it and reach the sensor.
aperture priority A camera setting that allows you to choose the aperture while the camera selects the appropriate shutter speed to ensure a good exposure. Some camera manufacturers indicate it with A, others with Av.
application (program) Software designed to make the computer perform a specific task. So, image-editing is an application, as is word-processing. System software, however, is not an application, as it controls the running of the computer.
artifact A flaw in a digital image.
aspect ratio The ratio of the height to the width of an image, screen, or page.
autofocus When the camera lens adjusts the focus to ensure a sharp image.
axis lighting Light aimed at the subject from close to the camera’s lens.
backlighting The result of shooting with a light source, natural or artificial, behind the subject to create a silhouette or rim-lighting effect.
backup A copy of either a file or a program, for safety reasons, in case the original becomes damaged or lost. The correct procedure for making backups is on a regular basis, while spending less time making each one than it would take to redo the work lost.
banding Unwanted effect in a tone or color gradient in which bands appear instead of a smooth transition. It can be corrected by higher resolution and more steps, and by adding noise to confuse that part of the image.
barrel distortion The effect when straight lines appear to curve, as if they’ve been stretched over a sphere or barrel, seen with wide-angle and fish-eye lenses.
Bézier curve A curve described by a mathematical formula. In practice, it is produced by manipulating control handles on a line that is partly held in place by anchor points.
bit (binary digit) The basic data unit of binary computing. See also byte
bit depth The number of bits-per-pixel (usually per channel, sometimes for all the channels combined), which determines the number of colors it can display. Eight bits-per-channel are needed for photographic-quality imaging.
bitmap (bitmapped image) Image composed of a pattern of pixels, as opposed to a mathematically defined object (an object-oriented image). The more pixels used for one image, the higher its resolution. This is the normal form of a scanned photograph.
BMP Image file format for bitmapped images used in Windows. Supports RGB, indexed color, grayscale and bitmap.
bracketing A method of ensuring a correctly exposed photograph by taking three shots; one with the supposed correct exposure, one slightly underexposed, and one slightly overexposed.
brightness The level of light intensity. One of the three dimensions of color. See also hue and saturation
buffer An area of temporary data storage, normally used to absorb differences in the speed of operation between devices. For instance, a file can usually be sent to an output device, such as a printer, faster than that device can work. A buffer stores the data so that the main program can continue operating.
byte Eight bits—the basic data unit of desktop computing. See also bit
cache An area of information storage set aside to keep frequently needed data readily available. This allocation speeds up operation.
calibration The process of adjusting a device, such as a monitor, so that it works consistently with others, such as scanners and film recorders.
CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) A tiny photocell used to convert light into an electronic signal. Used in densely packed arrays, CCDs are the recording medium in most digital cameras.
CGI (Computer-Generated Image) Electronic image created in the computer (as opposed to one that has been transferred from another medium, such as a photograph).
channel Part of an image as stored in the computer; similar to a layer. Commonly, a color image will have a channel allocated to each primary or process color, and sometimes one or more for a mask or other effect.
chiaroscuro Literally “light/dark,” the interplay of light and shadow to create an image.
clipboard Part of the memory used to store an item temporarily when being copied or moved. See also cut-and-paste
cloning In an image-editing program, the process of duplicating pixels from one part of an image to another.
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) An alternative sensor technology to the CCD, CMOS chips are used in ultra-high-resolution cameras from Canon and Kodak.
CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key) The four process colors used for printing, including black (key).
color depth See bit depth
color gamut The range of color that can be produced by an output device, such as a printer, a monitor, or a film recorder.
color model A system for describing the color gamut, such as RGB, CMYK, HSB, and lab.
color separation The process of separating an image into the process colors cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (CMYK), in preparation for printing.
color space A model for plotting the hue, brightness, and saturation of color.
color temperature A way of describing the color differences in light, measured in Kelvins and using a scale that ranges from dull red (1900 K), through orange, to yellow, white, and blue (10,000 K).
complementary color Colors that sit opposite each other on the color wheel, for example green and red.
compression Technique for reducing the amount of space that a file occupies, by removing redundant data. There are two kinds of compression: standard and lossy. While the first simply uses different, more processor-intensive routines to store data than the standard file formats (see LZW), the latter actually discards some data from the image. The best known lossy compression system is JPEG, which allows the user to choose how much data is lost as the file is saved.
contrast The range of tones across an image from highlight to shadow.
CPU (Central Processing Unit) The processing and control center of a computer.
cropping The process of removing unwanted areas of an image, leaving behind the most significant elements.
cursor Symbol with which the user selects and draws on-screen.
cut-and-paste Procedure in graphics for deleting part of one image and copying it into another.
default The standard setting or action used by a computer unless deliberately changed by the operator.
desktop The background area of the computer screen on which icons and windows appear.
desktop computer Computer small enough to fit on a normal desk. The two most common types are the PC and Macintosh.
depth of field The zone of sharpness in front of and behind the subject.
dialog box An on-screen window, part of a program, for entering settings to complete a procedure.
diffusion The scattering of light by a material, resulting in a softening of the light and of any shadows cast. Diffusion occurs in nature through mist and cloud cover, and can also be simulated using diffusion sheets and soft-boxes.
digital A way of representing data as a number of distinct units. A digital image needs a very large number of units so that it appears as a continuous-tone image to the eye; when it is displayed these are in the form of pixels.
digital zoom Many cheaper cameras offer a digital zoom function. This simply crops from the centre of the image and scales the image up using image processing algorithms (indeed the same effect can be achieved in an image editor later). Unlike a zoom lens, or optical zoom, the effective resolution is reduced as the zoom level increases; 2× digital zoom uses ¼ of the image sensor area, 3× uses 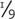 , and so on.
, and so on.
download Sending a data file from the computer to another device, such as a printer. More commonly, this has come to mean taking a file from the Internet or remote server and putting it onto the desktop computer. See also upload
dpi (dots-per-inch) A measure of resolution in halftone printing. See also ppi
drag Moving an icon or a selected image across the screen, normally by moving the mouse while keeping its button pressed.
drag-and-drop Moving an icon from one file to another by means of dragging and then dropping it at its destination by releasing the mouse button. See also drag
dynamic range The range of tones that an imaging device can distinguish, measured as the difference between its dmin and dmax. It is affected by the sensitivity of the hardware and by the bit depth.
edge lighting Light that hits the subject from behind and slightly to one side, creating flare or a bright “rim lighting” effect around the edges of the subject.
Ev Exposure Value, how the brightness of a scene is measured.
exposure How much light reaches a camera’s sensor.
f-stop The measurement of the variable opening in a lens (the aperture) that allows light to pass through it and reach the sensor or film. ƒ/1.4 is a large, or “fast” aperture; ƒ/22 is a small aperture.
fade-out The extent of any graduated effect, such as blur or feather. With an airbrush tool, for example, the fade-out is the softness of the edges as you spray.
feathering In image-editing, the fading of the edge of an image or selection.
file format The method of writing and storing a digital image. Formats commonly used for photographs include tiff, pict, bmp, and jpeg (the latter is also a means of compression).
fill flash A technique that uses the on-camera flash or an external flash in combination with natural or ambient light to reveal detail in the scene and reduce shadows.
fill light An additional light used to supplement the main light source. Fill can be provided by a separate unit or a reflector.
filter (1) A thin sheet of transparent material placed over a camera lens or light source to modify the quality or color of the light passing through.
(2) Imaging software included in an image-editing program that alters some image quality of a selected area. Some filters, such as Diffuse, produce the same effect as the optical filters used in photography after which they are named; others create effects unique to electronic imaging.
focal length The distance between the mid-point of the plane of the lens and the sensor or film in a camera.
focal point The center of interest in a photograph, the area where you focus your camera.
fringe In image-editing, an unwanted border effect to a selection, where the pixels combine some of the colors inside the selection and some from the background.
frontal light Light that hits the subject from behind the camera, creating bright, high-contrast images, but with flat shadows and less relief.
gamma A measure of the contrast of an image, expressed as the steepness of the characteristic curve of an image.
GB (GigaByte) Approximately one billion bytes (actually 1,073,741,824).
global correction Color correction applied to the entire image.
golden hour The period after dawn and before dusk that offers a soft, golden light ideal for dramatic photography.
gradation The smooth blending of one tone or color into another, or from transparent to colored in a tint. A graduated lens filter, for instance, might be dark on one side, fading to clear on the other.
grayscale An image made up of a sequential series of 256 gray tones, covering the entire gamut between black and white.
GUI (Graphic User Interface) Screen display that uses icons and other graphic means to simplify using a computer. The Macintosh GUI was one of the reasons for Apple’s original success in desktop computing.
hard disk, hard drive A sealed storage unit composed of one or more rigid disks that are coated with a magnetically sensitive surface, with the heads needed to read them. This can be installed inside the computer’s housing (internal), or in a separate unit linked by a bus (external).
haze The scattering of light by particles in the atmosphere, usually caused by fine dust, high humidity, or pollution. Haze makes a scene paler with distance, and softens the hard edges of sunlight.
HDRI (High Dynamic Range Imaging) A method of combining digital images taken at different exposures to draw detail from areas which would traditionally have been over or under exposed. This effect is typically achieved using a Photoshop plugin, and HDRI images can contain significantly more information than can be rendered on screen or even percieved by the human eye.
high-key Low-contrast images that have a feeling of light airiness and positivity.
highlights Technically, the pure white parts of an image, but often it refers to the lightest areas of an image.
histogram A map of the distribution of tones in an image, arranged as a graph. The horizontal axis is in 256 steps from solid to empty, and the vertical axis is the number of pixels.
HMI (Hydrargyrum Medium-arc Iodide) A lighting technology known as “daylight” since it provides light with a color temperature of around 5600 K.
honeycomb grid In lighting, a grid can be placed over a light to prevent light straying. The light can either travel through the grid in the correct direction, or will be absorbed by the walls of each cell in the honeycomb.
hot-shoe An accessory fitting found on most digital and film SLR cameras and some high-end compact models, normally used to control an external flash unit. Depending on the model of camera, information to lighting attachments might be passed via the metal contacts of the shoe.
HSB (Hue, Saturation and Brightness) The three dimensions of color. One kind of color model.
hue A color defined by its spectral position; what is generally meant by “color” in lay terms.
icon A symbol that appears on-screen to represent a tool, file, or some other unit of software.
image compression A digital procedure in which the file size of an image is reduced by discarding less important data.
image-editing program Software that makes it possible to enhance and alter a scanned image.
image file format The form in which an image is handled and stored electronically. There are many such formats, each developed by different manufacturers and with different advantages according to the type of image and how it is intended to be used. Some are more suitable than others for high-resolution images, or for object-oriented images, and so on.
incandescent lighting This strictly means light created by burning, referring to traditional filament bulbs. They are also know as hotlights, since they remain on and become very hot.
incident meter A standalone light-measuring instrument, distinct from the metering systems built into many cameras. These are used by hand to measure the light falling at a particular place, rather than (as the camera does) the light reflected off of a particular subject.
interface Circuit that enables two hardware devices to communicate. Also used for the screen display that allows the user to communicate with the computer. See also GUI
interpolation Bitmapping procedure used in resizing an image to maintain resolution. When the number of pixels is increased, interpolation fills in the gaps by comparing the values of adjacent pixels.
ISO An international standard rating for film speed, with the film getting faster as the rating increases. ISO 400 film is twice as fast as ISO 200, and will produce a correct exposure with less light and/or a shorter exposure. However, higher-speed film tends to produce more grain in the exposure, too.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) Pronounced “jay-peg,” a system for compressing images, developed as an industry standard by the International Standards Organization. Compression ratios are typically between 10:1 and 20:1, although lossy (but not necessarily noticeable to the eye).
KB (KiloByte) Approximately one thousand bytes (actually 1,024).
kelvin Scientific measure of temperature based on absolute zero (simply take 273.15 from any temperature in Celsius to convert to kelvin). In photography measurements in kelvin refer to color temperature. Unlike other measures of temperature, the degrees symbol in not used.
lasso A selection tool used to draw an outline around an area of the image.
layer One level of an image file, separate from the rest, allowing different elements to be edited separately.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Flat screen display used in digital cameras and some monitors. A liquid-crystal solution held between two clear polarizing sheets is subject to an electrical current, which alters the alignment of the crystals so that they either pass or block the light.
leading line A line in an image that draws the eye to the subject.
lossless Type of image compression in which no information is lost, and so most effective in images that have consistent areas of color and tone. For this reason, not so useful with a typical photograph.
lossy Type of image compression that involves loss of data, and therefore of image quality. The more compressed the image, the greater the loss.
low-key High-contrast photographs, usually very dark in tone, that have a feeling of brooding.
luminaires A complete light unit, comprising an internal focusing mechanism and a fresnel lens. An example would be a focusing spot light. The name luminaires derives from the French, but is used by professional photographers across the world.
luminosity Brightness of color. This does not affect the hue or color saturation.
lux A scale for measuring illumination, derived from lumens. It is defined as one lumen per square meter, or the amount of light falling from a light source of one candela one metre from the subject.
macro A single command, usually a combination of keystrokes, that sets in motion a string of operations. Used for convenience when the operations are run frequently.
mask A grayscale template that hides part of an image. One of the most important tools in editing an image, it is used to make changes to a limited area. A mask is created by using one of the several selection tools in an image-editing program; these isolate a picture element from its surroundings, and this selection can then be moved or altered independently.
MB (MegaByte) Approximately one million bytes (actually 1,048,576).
megapixel (1 million pixels) A rating of resolution for a digital camera, directly related to the number of pixels forming or output by the CMOS or CCD sensor. The higher the megapixel rating, the higher the resolution of images created by the camera. However, megapixel count alone is not a defining factor of image quality.
menu An on-screen list of choices available to the user.
mid-tone The parts of an image that are approximately average in tone, midway between the highlights and shadows.
mode One of a number of alternative operating conditions for a program. For instance, in an image-editing program, color and grayscale are two possible modes.
modeling light A small light built into studio flash units that remains on continuously. It can be used to position the flash, approximating the light that will be cast by the flash.
monobloc An all-in-one flash unit with the controls and power supply built-in. Monoblocs can be synchronized together to create more elaborate lighting setups.
negative space Areas of a photograph that do not contain any subject matter.
neutral density filter A neutral color filter that absorbs light from different wavelengths without altering the overall color of an image, permitting longer exposures or wider apertures when there is too much available light.
noise Random pattern of small spots on a digital image that are generally unwanted, caused by non-image-forming electrical signals.
object-oriented (image, program) Software technology using mathematical equations rather than pixels to describe an image element. Scalable, in contrast to bitmapped elements.
open flash The technique of leaving the shutter open and triggering the flash one or more times, perhaps from different positions in the scene.
overexposure What happens when too much light reaches the sensor or film and a photograph is too bright with too many pure-white areas in the frame.
P Program mode, an autoexposure mode in which the camera chooses both the aperture and shutter speed, but you can manually change the relationship between these variables, and all other camera settings remain available for you to adjust.
panning A photographic technique in which you move the camera in time with a subject in motion to create a image where the subject is sharp and the background is blurred.
paste Placing a copied image or digital element into an open file. In image-editing programs, this normally takes place in a new layer.
PDF (Portable Document Format) An industry standard file type for page layouts including images. Can be compressed for Internet viewing or retain full press quality; in either case the software to view the files—Adobe Reader—is free.
peripheral An additional hardware device connected to and operated by the computer, such as a drive or printer.
photo-composition The traditional, non-electronic method of combining different picture elements into a single, new image, generally using physical film masks.
pixel (PICture ELement) The smallest unit of a digitized image—the square screen dots that make up a bitmapped picture. Each pixel carries a specific tone and color.
plug-in module Software produced by a third party and intended to supplement a program’s performance.
ppi (pixels-per-inch) A measure of resolution for a bitmapped image.
prime lens A lens with a fixed focal length.
processor A silicon chip containing millions of micro-switches, designed for performing specific functions in a computer or digital camera (in which it converts the information captured by the sensor into an editable, viewable image file).
program A list of coded instructions that makes the computer perform a specific task. See also software
Raw files A digital image format, known sometimes as the “digital negative,” which preserves higher levels of color depth than traditional 8 bits per channel images. The image can then be adjusted in software—potentially by three stops—without loss of quality. The file also stores camera data including meter readings, aperture settings, and more. In fact each camera model creates its own kind of Raw file, though leading models are supported by software like Adobe Photoshop.
real-time The appearance of instant reaction on the screen to the commands that the user makes—that is, no appreciable time-lag in operations. This is particularly important when carrying out bitmap image-editing, such as when using a paint or clone tool.
reflector An object or material used to bounce light onto the subject, often softening and dispersing the light for a more attractive result.
resampling Changing the resolution of an image either by removing pixels (lowering resolution) or adding them by interpolation (increasing resolution).
resolution The level of detail in an image, measured in pixels (e.g. 1024 by 768 pixels), lines-per-inch (on a monitor) or dots-per-inch (in the halftone pattern produced by a printer, e.g. 1200 dpi).
RFS (Radio Frequency System) A technology used to control lights where control signals are passed by radio rather than cable. It has the advantage of not requiring line-of-sight between the transceiver and device.
RGB (Red, Green, Blue) The primary colors of the additive model, used in monitors and image-editing programs.
rim-lighting Light from the side and behind a subject which falls on the edge (hence rim) of the subject.
ring-flash A lighting device with a hole in the center so that the lens can be placed through it, resulting in shadow-free images.
rubber-stamp A paint tool in an image-editing program that is used to clone one selected area of the picture onto another. It allows painting with a texture rather than a single tone/color, and is particularly useful for extending complex textures such as vegetation, stone, and brickwork.
S Shutter priority mode as indicated by some camera manufacturers.
saturation The purity of a color, going from the lightest tint to the deepest, most saturated tone.
scrim A light, open-weave fabric, used to cover softboxes.
selection A part of the on-screen image that is chosen and defined by a border, in preparation for making changes to it or moving it.
shutter The device inside a conventional camera that controls the length of time during which the film is exposed to light. Many digital cameras don’t have a shutter, but the term is still used as shorthand to describe the electronic mechanism that controls the length of exposure for the CCD.
shutter priority A camera setting that allows you to control shutter speed, while the camera determines aperture to ensure a good exposure.
shutter speed The period of time for which the shutter remains open and allows light to reach the sensor or film.
side-lighting Light that hits the subject from the side, as opposed to the front or back.
SLR (Single Lens Reflex) A camera which transmits the same image via a mirror to the film and viewfinder.
slow sync The technique of firing the flash in conjunction with a slow shutter speed (as in rear-curtain sync).
snoot A tapered barrel attached to a lamp in order to concentrate the light emitted into a spotlight.
soft-box A studio lighting accessory consisting of a flexible box that attaches to a light source at one end and has an adjustable diffusion screen at the other, softening the light and any shadows cast by the subject.
software Programs that enable a computer to perform tasks, from its operating system to job-specific applications such as image-editing programs and third-party filters.
spot meter A specialized light meter, or function of the camera light meter, that takes an exposure reading for a precise area of a scene.
stop An increment of the measurement of aperture.
stylus Penlike device used for drawing and selecting, instead of a mouse. Used with a graphics tablet.
sync cord The electronic cable used to connect camera and flash.
telephoto A photographic lens with a long focal length that enables distant objects to be enlarged. The drawbacks include a limited depth of field and angle of view.
thumbnail Miniature on-screen representation of an image file.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) A file format for bitmapped images. It supports CMYK, RGB, and grayscale files with alpha channels, and lab, indexed-color, and it can use LZW lossless compression. It is now the most widely used standard for good-resolution digital photographic images.
tool A program specifically designed to produce a particular effect on-screen, activated by choosing an icon and using it as the cursor. In image-editing, many tools are the equivalents of traditional graphic ones, such as a paintbrush, pencil, or airbrush.
toolbox A set of programs available for the computer user, called tools, each of which creates a particular on-screen effect. See also tool
trackball An alternative input device to a mouse, used to move the cursor on-screen. Mechanically, it works as an upside-down mouse, with a ball embedded in a case or the keyboard.
TTL (Through The Lens) Describes metering systems that use the light passing through the lens to evaluate exposure details.
tungsten A metallic element, used as the filament for lightbulbs, hence tungsten lighting.
Tv “Time value,” the term used to indicate shutter priority mode on some cameras.
umbrella In photographic lighting umbrellas with reflective surfaces are used in conjunction with a light to diffuse the beam.
underexposure When too little light reaches the sensor or film and a photograph is too dark.
upgrade Either a new version of a program or an enhancement of hardware by addition.
upload To send computer files, images, etc. to another computer. See also download
USB (Universal Serial Bus) In recent years this has become the standard interface for attaching devices to the computer, from mice and keyboards to printers and cameras. It allows “hot-swapping,” in that devices can be plugged and unplugged while the computer is still switched on.
USM (Unsharp Mask) A sharpening technique achieved by combining a slightly blurred negative version of an image with its original positive.
vapour discharge lamp A lighting technology common in stores and street lighting. It tends to produce color casts.
virtual memory The use of free space on a hard drive to act as temporary (but slow-to-access) memory.
white balance A digital camera control used to balance exposure and color settings for artificial lighting types.
WiFi A wireless connectivity standard, commonly used to connect computers to the Internet via a wireless modem or router.
window light A softbox, typically rectangular (in the shape of a window) and suitably diffused.
workstation A computer, monitor, and its peripherals dedicated to a single use.
zoom A camera lens with an adjustable focal length, giving, in effect, a range of lenses in one. Drawbacks include a smaller maximum aperture and increased distortion over a prime lens (one with a fixed focal length).