 Index
Index 
 Index
Index 
Note: Page numbers in boldface refer to posture sequences.
abdominal breathing, 219
abduction, 142
absorption, 204
acetabulum, 138, 185
aches and pains, 135–201
hips, 184–86, 191–96
knees, 184–86, 197–201
muscular system, 139–43
neck and shoulders, 143–58
sacrum, 137–38, 184–90
skeletal system, 135–39
upper and lower back, 159–83
active reversal: inversion, 98–113
activity (vihāra), 130
adaptation, 6, 12–25
arm variations, 15–17
of the breath, 23–24
combining movement with holding, 22
combining postures, 22
for day-to-day changes, 12
direction of movement, 19–20
leg variations, 17–19
for long-term conditions, 12
movement into and out of a posture, 19–21
moving in stages, 21
origin of movement, 19
with props, 25
range of motion, 20
reasons for, 12–14
shifting attention in, 23
speed of movement, 21
using sound, 24
adduction, 142
adrenal glands, 257, 258, 304
adrenaline rush, 258
aerobic exercise, 216–17, 232, 252
aerobic respiration, 140
agni (heat), 131, 205
aham, 305
āhāra (diet), 130
AIDS, 246
allergies, 217, 218, 246–52
case study, 246–47
practice sequence for, 247–52
amygdala, 303, 304
anaerobic glycosis, 140
ānanda maya (spirituality), 130, 131
Ananta, 4
anemia, 232
anga bhanga sādhanā, 133
anger, 308
angina, 233
anna maya (physical body), 130
anxiety, 308–15
case study, 310
practice sequence for, 311–15
reduction of, 309
appendicular muscles, 142
appendicular skeleton, 136, 137–39
arm balances, 118–19
arms, movement of, 143
arm variations, 15–17
arrhythmia, cardiac, 232
arteries, 231, 233
arteriosclerosis, 232
arthritis, 138
articulate joints, 135–36
āsana practice:
adaptation in, 12–25
assessment of present condition for, 5
breath, movement, and spine brought together in, 6, 12
breath in, 7–12
commitment to, 132
effects of, 3–4
essential qualities of, 4
exhalation in, 10–12, 168
extension in, 85
form-function problem in, 5, 12
general principles in design of, 32–33
goals of, 4, 5, 85
inhalation in, 8–10, 160
key to, 4–5
movement patterns in, 5, 273
release valves in, 5
repetition vs. stay in, 5–6, 22
sequencing in, 26–34
āsanas, 3–6
actual functional value of, 5
adaptation of, 6
breath in, 4, 32
combinations of, 33–34
glossary of, 325–27
holding vs. repetition of, 5–6, 22
mind-body connection in, 4
objective criteria for, 3
release valves in, 5
assimilation, 204; see also digestion and assimilation
asthma, 217, 246, 273
case study, 220
exercises for, 219–20
practice sequence for, 221–24
treatment of, 218
atrophy, 140
ausadhi (medicine), 130
autoimmune diseases, 246
axial muscles, 141
axial skeleton, 136, 137
back, 159–83
hollow, 168
kyphosis, 138–39, 163
lordosis, 138–39, 159–60, 168
lower, 168–75, 184; practice sequence for, 170–75
postures on, 34
scoliosis, 138–39, 159, 176–83
upper, 160–67; practice sequence for, 163–67
see also spine
backward bends, 33, 49–60
arm balances with, 119
brahmana effect of, 131
inversion variations, 101–2
leg balances with, 117
and lower back, 168
practice sequence of, 56–60
primary and secondary intentions in, 49
release valves for, 50, 55
risks of, 55
technique, 49–51
thoraco-lumbar rhythm in, 49, 51
types of, 52–55
bala (volume), 24
balance, restoration of, 130–31, 359
balance postures, 114–25
arm, 118–19
leg, 115–17, 119
practice sequence of, 120–25
primary and secondary intentions in, 114
release valves, 119
risks of, 119
technique, 114–15
types of, 115–19
bhaya, 305
biomechanics of movement, 35–134
backward bends, 49–60
balance, 114–25
extension, 85–97
forward bends, 35–48
inversion, 98–113
lateral bends, 72–84
twists, 61–71
bladder, 286
blood:
circulation process of, 231–32
functions of, 231
blood pressure, 231, 232, 258
high, 233–37
low, 238
blood sugar, 258–59
body:
anna maya, 130
control over functions of, 132
linked to mind, see mind-body connection
understanding of, 132
bone growth, 138
bone marrow, 138
bones (skeletal system), 135–39
brahmana (tonification), 131–32, 246
case study, 226
and depression, 316
practice sequence for, 226–30
simple exercises for, 225
brain:
limbic, 303–4, 306
motor cortex of, 273
and nervous system, 272–73
brain stem, 303
breastbone (sternum), 137
breath, 7–12
adapting, 23–24
aerobic, 140
allotment of, 216–17
in āsana sequences, 4, 32
exhalation of, 10–12
focus of attention in, 12, 132
inhalation of, 8–10
krama (in segments), 24, 210
mental control of, 12
mind-body connection in, 4, 132, 133
movement and spine integrated with, 6, 12
and oxygen intake, 216
prānāyāma, 306, 308
and respiratory system, 216–18
unconscious, 8
bronchitis, 217
bursitis, 137, 139
calcium, 138
candra (cooling), 131, 132
capillaries, 231
cardiac (heart) muscle, 139
cardiomyopathy, 232
cardiovascular system, 216, 231–44
functions of, 231
hypertension, 233–37; practice
sequence for, 234–37
hypotension, 238–44; practice
sequence for, 239–44
influences on, 232
and lymphatic system, 231
problems of, 232–33
and respiratory system, 216
cartilage, 137, 138
cerebellum, 303
cerebrum, 303, 304
cervical spine, 137
change (parināma), 129
chanting, 24
brahmana effect of, 131
langhana effect of, 131
chronic disease, 203–300
cardiovascular system, 231–44
digestion and assimilation, 203–15
endocrine system, 257–71
immunity, 245–46
lymphatic system, 245–56
nervous system, 272–85
reproductive system, 286–300
respiratory system, 216–30
urinary system, 286, 288, 289–300
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS), 246, 252, 281
case study, 253
practice sequence for, 254–56
cikitsa krama, 129
circulation:
meditation and, 306
in prāna pumps, 6
process of, 231–32
vocal sound and, 24
circulatory system, 231–33
circumduction, 142
clavicles (collarbones), 137
coccyx (tailbone), 136, 137, 138
colitis, 205
collagenous fibers, 135, 136
collarbones (clavicles), 137
concentric contraction, 140
connective tissues, 135
consonants (varna), 24
constipation, 210, 274
case study, 210
practice sequence for, 211–15
contractibility, 140
contraction, muscular, 140
cooling (candra), 131, 132
costae (ribs), 137
counterpose (pratikriyā), 30–31
coxa (hipbones), 137–38
cranium, 136
Crohn’s disease, 205
case study, 206
practice sequence for, 207–9
cumulative stress, in āsana sequences, 32
cystitis, 286
day/night cycle, 257
delivery, in respiration, 216
depression, 142, 307, 316–23
case study, 316–17
practice sequence for, 318–23
diabetes, 258–59
case study, 265
practice sequence for, 266–71
diaphragm:
control of, 218
and inhalation, 8
diarrhea, 205–6, 274
diet:
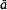 h
h ra, 130
ra, 130
and cardiovascular system, 232
digestion and assimilation, 203–15
fire (agni) image of, 205
and hormones, 257
hyper conditions of, 205–9; practice
sequence for, 207–9
hypo conditions of, 205, 210–15;
practice sequence for, 211–15
processes of, 203–4
and respiratory system, 218
and stress, 205, 273, 304
digestive system, 218
discs, 135, 137, 139
diseases, causes of, 131, 245, 304–5
diverticulosis, 205
dizziness, 238
dysfunctional behavior, 305
dyspareunia, 287
eccentric contraction, 140
eczema, 274
efficiency, in āsana sequences, 32
elasticity, 140
elevation, 142
elimination, 204, 286
emotional health, 301–24
anger and anxiety, 308–15
depression, 316–23
healing insights, 305–6
limbic brain, 303–4, 306
mental illnesses, 307
mind-body connection in, 301, 303–5
prānāyāma, 306, 308
stress and disease, 304–5
three primary energies, 308
emphysema, 217
endocrine system, 257–71
balance in, 259
diabetes, 265–71; practice sequence for, 266–71
disorders of, 258–59
function of, 257, 272
hypometabolic conditions of, 259–64;
practice sequence for, 260–64
and immune system, 258
endurance, 140
energy:
and fuel, 140–41
prāna, 133
primary, 308
reserves of, 140–41
eversion, 142
excitability, 140
exercise, 143, 216–17, 232, 252
exhalation, 10–12
asthma and, 219–24
case study, 220
langhana effect of, 131
and lower back, 168
practice sequence for, 221–24
in prānāyāma, 306
and relaxation, 219
extensibility, 140
extension, 85–97, 142
inversion variations, 105
practice sequence for, 93–97
primary and secondary intentions in, 85–86
release valves for, 91
risks of, 92
technique, 86
types of postures, 87–90
faith, 131
femurs (thighbones), 138, 185
fibroelastic cartilage, 137
fibromyalgia, 246
fibrosis, 143
fight-or-flight response, 205, 258, 273, 304
flexion, 142
form-function problem, 5, 12
forward bends, 33, 35–48
exhalation and, 168
inversion variations, 100
langhana effect of, 131
leg balances with, 116–17
lumbar-pelvic rhythm in, 36–37, 44
positions for, 40
practice sequence of, 45–48
primary and secondary intentions in, 35–36
release valves for, 36, 38, 39, 44
risks of, 44
technique, 36–40
types of, 41–44
fuel, and energy, 140–41
genitals, 286
glucose, 258
glycosis, 140
gonads, 257, 258, 286–87
growth hormone, 257
gunas, 308
happiness, 308
Hatha Yoga, 3
hay fever, 246
head, mobility of, 143
headaches, 274
headstands, 34, 98–113
contraindications to, 107
langhana effect of, 131
risks of, 106–7
see also inversions
healing, foundation for, 132
healing insights, 305–6
health problems, causes of, 131, 245, 304–5
heart, 139, 231–44, 257
heart disease, 232–33
heart rate, 232, 273, 306
heat (agni), 131
hernias, 142
hipbones (coxa), 137–38
hippocampus, 303
hips, 184–86
case study, 191
practice sequence for, 192–96
holding vs. repetition, 5–6, 22
homeostasis, 257
hormones, 257–58, 304
humerus, 137
humming, 24, 131
hyperactivity:
case study, 274
practice sequence for, 275–80
hyperextension, 142
hypertension, 233–37
case study, 233–34
practice sequence for, 234–37
hypotension, 238–44
case study, 238
practice sequence for, 239–44
hypothalamus, 303, 304
IgA (immunoglobulin A), 308
iliopsoas, 168
ilium, 137–38
immortality (kaya kalpa), 130
immune system:
case study, 246–47
and endocrine system, 258
practice sequence for, 247–52
immunity, 217, 245–46, 308
immunodeficiency, 246, 252–56, 281
case study, 253
practice sequence for, 254–56
immunoglobulin A (IgA), 308
index of postures, 325–27
indigestion, 204
ingestion, 203
inhalation, 8–10, 160
brahmana effect of, 131, 225
case study, 226
practice sequence for, 226–30
in prānāyāma, 306
progression of, 10, 12
variations of, 10
insomnia, 274
intention, in āsana sequences, 32
intestines, 205, 210
inversion, 98–113, 142
contraindications to, 107
practice sequence of, 108–13
primary and secondary intentions in, 98
release valves, 106
risks of, 106–7
techniques, 98–99
types of postures, 98–105
ischium, 137–38
isometric muscle work, 140
jaw, tension in, 143
jet lag, 257
joints, 135–36
knees, 138, 184–86
leverage and, 161
problems with, 186, 273
range of motion in, 135–36
weight-bearing, 186
kama, 305
kaya kalpa, science of immortality, 130
kidneys, 257, 286
kneecaps, 138
kneeling postures, 34
knees, 138, 184–86
case study, 197
practice sequence for, 197–201
krama breathing, 24, 210
Krishnamacharya, 133, 305
krodha, 305
kyphosis, 138–39, 159
case study, 163
practice sequence for, 163–67
lactation, 257
lactic acid, buildup of, 140–41, 309
langhana (purification), 130, 131, 206
allergies and, 246
depression and, 316
meditation and, 306
lateral bends, 33, 72–84
practice sequence of, 78–84
primary and secondary intentions in, 72
release valves, 73, 77
risks of, 77
technique, 73
types of, 74–76
learning, conditioned, 273
leg balances, 115–17, 119
legs, 184
leg variations, 17–19
lengthening the core: extension, 85–97
ligaments, 135, 136, 137, 138
limbic brain, 303–4, 306
limbic system, 303, 306
lipids, 138
liver, 257
lobha, 305
lordosis, 138–39, 159–60, 168
lower back, 168–75
case study, 170
pain in, 37, 159, 184
practice sequence for, 170–75
lumbar-pelvic rhythm, 36–37, 44
lumbar spine, 137, 138, 159, 168, 184
lumbar-thoraco rhythm, 49, 51
lungs, 216–17
lymphatic system, 245–56
autoimmune conditions of, 246–47;
practice sequence for, 247–52
and cardiovascular system, 231
function of, 245–46
and immunodeficiency diseases, 252, 253; practice sequence for, 254–56
lymph nodes, lymph glands, 245
lymphocytes, 245, 258
mada, 305
mama, 305
mano maya (mental faculties), 130
matsarya, 305
mayas, 130
medicine (ausadhi), 130
meditation:
brahmana effect of, 131
and hypertension, 233
langhana effect of, 131, 306
preparation for, 26
melatonin, 257
membranes, 135, 136
meniscus, 138
menopause, 287
menstrual cycle, 287
mental illnesses, 307
metabolic processes, 130, 140
metabolic rate, 258, 306
mind, states of, 302
mind-body connection:
in breath, 4, 132, 133
in emotional health, 301, 303–5
in Yoga cikitsa, 131, 133
moha, 305
motor cortex, 273
motor neurons, 273
movement:
biomechanics of, see biomechanics of movement
breath and spine integrated with, 6, 12
combined with holding, 22
into and out of a posture, 19–21
patterns of, 5, 273
range of motion, 20, 135–36, 142
multiple sclerosis (MS), 281–85
case study, 281
practice sequence for, 282–85
muscle atrophy, 140
muscle fatigue, 140–41
muscle fibers, 140
muscles, 139–43
activation of, 140
agonist-antagonist relationship of, 141
appendicular, 142
axial, 141
and brain, 273
and breath, 8, 10
contraction of, 140
exercise of, 143
intercostal, 8
structure of, 140
muscle tendons, 135
muscle tissue, 139–40
characteristics of, 140
deterioration of, 142
muscle tone, 140
muscular dystrophies, 142
muscular system, 139–43
myasthenia gravis, 142
myocardial infarction, 233
namama, 305
neck and shoulders, 143–58
case studies, 150, 156
developmental practice sequence for, 151–55
functional relationship of, 144
general procedures for, 144–49
musculoskeletal conditions of, 143
opposition principle of, 148
simple movement of, 147
stabilizing principle of, 148
therapeutic practice sequence for, 157–58
negative attitudes, 305
nervous system, 272–85
anatomical divisions of, 272–73
breathing and, 8
case study, 274
fight-or-flight response of, 205, 273
functional division of, 273
function of, 257, 272
hyper conditions of, 273, 274–80; practice sequence for, 275–80
hypo conditions of, 273, 281–85; practice sequence for, 282–85
neuromodulators, 272
neuroses, 307
neurotransmitters, 257, 272, 307
niralāmba (without support), 99
olfactory lobe, 306
ossification, 135
osteoarthritis, 138
osteoporosis, 138
overtraining, 232
oxygen, 216, 304
pancreas, 257, 258, 259
parathyroid gland, 257
parināma (change), 129
Patañjali, 4, 217, 302, 304, 305, 316
patella (kneecap), 138
pathogens, 245–46
patterns (samskāras), 129, 130
pelvic girdle, 136, 137, 184
pelvic-lumbar rhythm, 36–37, 44, 186
pelvis, 138, 168, 184–85
pericardium, 231
peristalsis, 210
perspiration, 141
phagocytes, 245
pineal gland, 257
pitch (svara), 24
pituitary gland, 257–58, 304
pleural membranes, 216
PMS, 287
case study, 296
practice sequence for, 297–300
posture:
erect, 138
poor, effects of, 139
postures:
index of, 325–27
see also āsana practice; āsanas
prāna (vital energy), 133
prāna maya (metabolic functions), 130
prāna pumps, 6
prānāyāma, 306, 308
adaptations of, 14
antah kumbhaka, 315
anuloma krama, 226, 244, 284, 323
preparation for, 26
sītalī, 264, 300
viloma krama, 215, 224, 280, 295
pratikriyā (counterpose), 30–31
pregnancy, 257, 287
preparation (vinyāsa), 26–29
props, adaptations with, 25
prostate, 286, 288
case study, 289
practice sequence for, 289–95
psychoneuroimmunology, 305
pubis, 137–38
pronunciation guide, 325
purification (langhana), 130, 131, 206, 246, 306, 316
quadriceps femoris, 138
rajasic energies, 308, 309
range of motion, 20, 135–36, 142
rashes, skin, 246, 274
reduction (langhana) therapy, 131
relationships, and trust, 130, 131
relaxation:
and cardiovascular system, 233
and digestive system, 205
exhalation and, 219
and homeostatic balance, 246
and lymphatic system, 246
and nervous system, 273
for reproductive and urinary systems, 296
and respiratory system, 218
release valves, 5
repetition vs. holding, 5–6, 22
reproductive system, 286–300
functions of, 286, 287
gonads, 258, 286–87
pregnancy and, 287
problems of, 287
soothing of, 296; practice sequence for, 297–300
stimulation of, 288; practice sequence for, 289–95
respiratory muscles, 141
respiratory system, 216–30
and breathing, 216–18
and cardiovascular system, 216
causes of problems in, 217, 218
and digestive system, 218
exhalation, 219–24; practice sequence for, 221–24
function of, 216
inhalation, 225–30; practice sequence for, 226–30
process of, 216
rest, in āsana sequences, 33
rest-and-repose system, 273
reversal, active (inversion), 98–113
revolving: twists, 61–71
rheumatoid arthritis, 138, 246
rib cage, 137
ribs (costae), 137
right association (sat sangha), 131
risk, in āsana sequences, 33
rotation, 142
sacrum, 137–38, 184–90
case study, 186–87
practice sequence for, 187–90
SAD (Seasonal Affective Disorder), 257
samskāras (patterns), 129, 130
samyoga (linking), 130, 301
sat sangha (right association), 131
sattva guna, 308
sattvic quality of mind, 308
scapulae (shoulder blades), 137
schizophrenia, 307
sciatic nerves, 184
scoliosis, 138–39, 159, 176–83
case study, 177
practice sequence for, 177–83
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), 257
self-awareness, 132, 133
self-healing, 130
sense organs, 272
sequencing, 26–34
design principles for, 32–33
in posture combinations, 33–34
pratikrya (counterpose), 30–31
vinyāsa (preparation), 26–29
sexual drive, 287–88
shoulder blades (scapulae), 137
shoulder girdle, 136, 137
shoulders and neck, see neck and shoulders
shoulder stands, 34, 98–113
brahmana effect of, 131
contraindications to, 107
risks of, 106
see also inversion
skeletal system, 135–39
appendicular skeleton, 136, 137–39
axial skeleton, 136, 137
functions of, 138
growth of, 258
injuries to, 139
joints in, 135–36
muscles in, 140–41
skin rashes, 246, 274
sound, 24, 131,216,296
spinal cord, 106, 137, 272–73
spine, 159–83
awareness focused on, 12, 132
breath and movement integrated with, 6, 12
cervical, 137
curvatures of, 138–39, 159–60
function of, 137
lumbar, 137, 138, 159, 168, 184
movement patterns and, 5
sacral, 137
segments of, 137
as structural core of the body, 5, 12
thoracic, 137, 138, 159
vertebrae of, 137
vertical axis of, 136, 137
see also back
spirituality (ānanda maya), 130, 131
spleen, 245, 304
standing postures, 34
stay vs. repetition, 5–6, 22
sternum (breastbone), 137
sthira, 4
stomach, 205, 210
stools, examination of, 204–5
stress:
and cardiovascular system, 232
chronic, 131
cumulative, 32
and digestion, 205, 273, 304
and disease, 304–5
and endocrine system, 258
fight-or-flight response to, 205, 258, 273, 304
and immune system, 246
and nervous system, 273, 274
and respiratory system, 218
and skeletal system, 139
stretching the east: backward bends, 49–60
stretching the west: forward bends, 35–48
striated (skeletal) muscle, 140
sukha, 4
survival, 304
svara (pitch), 24
synapses, 272
synergists, 141
synovial fluid (bursae), 137
synovial joints, 136, 138
synovial membranes, 136
tachycardia, 232
tailbone (coccyx), 136, 137, 138
tamasic energies, 308, 316
teacher, importance of, 131, 132, 133, 134
tendinitis, 139
tendons, 139, 140
thalamus, 303, 304
therapy, see Yoga cikitsa
thighbones (femurs), 138, 185
thighs, 184
thoracic spine, 137, 138, 159
thoraco-lumbar joints, 138
thoraco-lumbar rhythm, 49, 51
thymus, 245, 257, 258
thyroid gland, 257, 258
case study, 259–60
practice sequence for, 260–64
tonification (brahmana), 131–32
transition, in āsana sequences, 32
trochanter, greater, 185
twists, 33, 61–71
inversion variations, 102–3
langhana effect of, lw31
practice sequence of, 67–71
primary and secondary intentions in 61
release valves, 62, 66
risks, 66–67
technique, 61–62
types of, 63–66
upper back, 160–67
case study, 163
pain in, 159
practice sequence for, 163–67
ureters, 286
urethra, 286
urethritis, 286
urinary system, 286
soothing of, 296; practice sequence for, 297–300
stimulation of, 288; practice sequence for, 289–95
uterus, 287
utilization of oxygen, 216
vaccines, 246
varna (consonants), 24
veins, 231
ventilation, 216
vertebrae, 137
vertebral canal, 106
vihāra (activity), 130
vijñãna maya (intuitive capacity), 130, 131
vināsa (preparation), 26–29
viparīta karanī (active reversal), 98–113
visceral (smooth) muscle, 139
visualization:
brahmana effect of, 131
langhana effect of, 131
vital energy (prāna), 133
viyoga (separation), 130, 301
vocal sound, 24, 131, 216, 296
Yoga, goals of, 301
Yoga cikitsa (therapy), 129–34
balance restored in, 130–31
basic principle of, 130
brahmana (tonification) therapy in, 131–32
commitment to, 132
and interconnectedness, 132, 133
kaya kalpa (immortality) in, 130
langhana (reduction) therapy in, 131
mind-body connection in, 131, 133
prāna (vital energy) increased in, 133
samyoga in, 130
self-awareness in, 132, 133
self-healing in, 130
starting point of, 133
teacher required for, 131, 132, 133, 134
viyoga in, 130
Yoga Sūtras (Patañjali), 4