
If you live in an area where the soil is quite wet (preventing a good vegetable garden from growing the spring), or find it difficult to bend over to plant and cultivate your vegetables or flowers, or if you just want a different look to your backyard garden, you should consider building a raised bed.
A raised bed is an interesting and affordable way to garden. It creates an ideal environment for growing vegetables, since the soil concentration can be closely monitored and, as it is raised above the ground, it reduces the compaction of plants from people walking on the soil.
Raised beds are typically 2 to 6 feet wide and as long as needed. In most cases, a raised bed consists of a “frame” that is filled in with nutrient-rich soil (including compost or organic fertilizers) and is then planted with a variety of vegetables or flowers, depending on the gardener’s preference. By controlling the bed’s construction and the soil mixture that goes into the bed, a gardener can effectively reduce the amount of weeds that will grow in the garden.
When planting seeds or young sprouts in a raised bed, it is best to space the plants equally from each other on all sides. This will ensure that the leaves will be touching once the plant is mature, thus saving space and reducing the soil’s moisture loss.
How to Make a Raised Bed
Things You’ll Need
• Forms for your raised bed (consider using 4 x 4-inch posts cut to 24 inches in height for corners, and 2 x 12-inch boards for the sides)
• Nails or screws
• Hammer or screwdriver
• Plastic liner (to act as a weed barrier at the bottom of your bed)
• Shovel
• Compost or composted manure
• Soil (either potting soil or soil from another part of your yard)
• Rake (to smooth out the soil once in the bed)
• Seeds or young plants
• Optional: PVC piping and greenhouse plastic (to convert your raised bed to a greenhouse)
1. Plan Out Your Raised Bed
1. Think about how you’d like your raised bed to look, and then design the shape. A raised bed is not extremely complicated, and all you need to do is build an open-top and open-bottom box (if you are ambitious, you can create a raised bed in the shape of a circle, hexagon, or star). The main purpose of this box is to hold soil.
2. Make a drawing of your raised bed, measure your available garden space, and add those measurements to your drawing. This will allow you to determine how much material is needed. Generally, your bed should be at least 24 inches in height.
3. Decide what kind of material you want to use for your raised bed. You can use lumber, plastic, synthetic wood, railroad ties, bricks, rocks, or a number of other items to hold the dirt. Using lumber is the easiest and most efficient method.
4. Gather your supplies.
2. Build Your Raised Bed
1. Make sure your bed will be situated in a place that gets plenty of sunlight. Carefully assess your placement, as your raised bed will be fairly permanent.
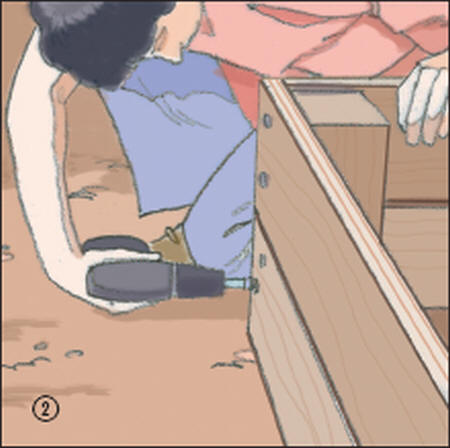
2. Connect the sides of your bed together (with either screws or nails) to form the desired shape of your bed. If you are using lumber, you can use 4 x 4-inch posts to serve as the corners of your bed, and then nail or screw the sides to these corner posts. By doing so, you will increase strength of the structure and ensure that the dirt will stay inside.
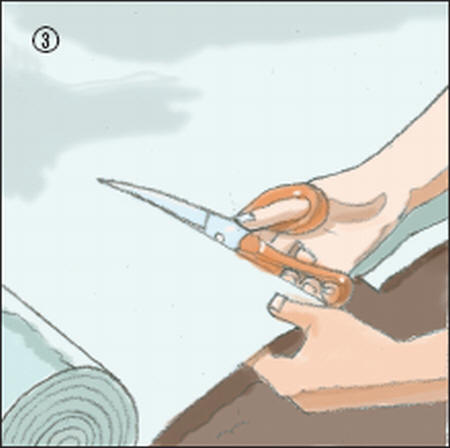
3. Cut a piece of gardening plastic to fit inside your raised bed. This will significantly reduce the amount of weeds growing in your garden. Lay it out in the appropriate location.
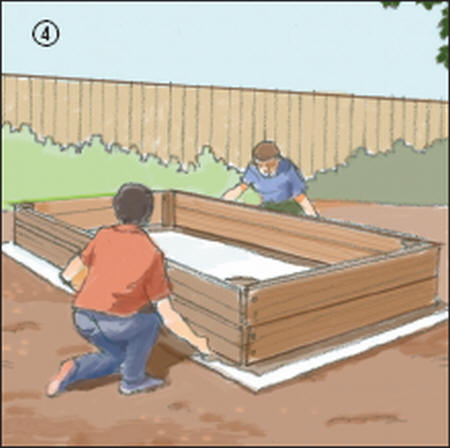
4. Place your frame over the gardening plastic (this might take two people).

3. Start Planting
1. Add some compost into the bottom of the bed and then layer potting soil on top of the compost. If you have soil from other parts of your yard, feel free to use that in addition to the compost and potting soil. Plan on filling at least ⅓ of your raised bed with compost or composted manure (available from nurseries or garden centers in 40-pound bags).
2. Mix in dry organic fertilizers (like wood ash, bone meal, and blood meal) while building your bed. Follow the package instructions for how best to mix it in.
3. Decide what you want to plant. Some people like to grow flowers in their raised beds; others prefer to grow vegetables. If you do want to grow food, raised beds are excellent choices for salad greens, carrots, onions, radishes, beets, and other root crops.
Things to Consider
1. To save money, you can dig up and use soil from your yard. Potting soil can be expensive, and yard soil is just as effective when mixed with compost. However, removing grass and weeds from the soil before filling your raised beds can be time-consuming.
2. Be creative when building your raised planting bed. You can construct a great raised bed out of recycled goods or old lumber.
3. You can convert your raised bed into a greenhouse. Just add hoops to your bed by bending and connecting PVC pipe over the bed. Then clip greenhouse plastic to the PVC pipes, and you have your own greenhouse.
4. Make sure to water your raised bed often. Because it is above ground, your raised bed will not retain water as well as the soil in the ground. If you keep your bed narrow, it will help conserve water.
5. Decorate or illuminate your raised bed to make it a focal point in your yard.
6. If you use lumber to construct your raised bed, keep a watch out for termites.
7. Beware of old pressure-treated lumber, as it may contain arsenic and could potentially leak into the root systems of any vegetables you might grow in your raised bed. Newer pressure-treated lumber should not contain these toxic chemicals.
