Cloud computing systems for smart cities and homes
Abstract
To support this rapid change in information delivery and consumption, cloud computing has evolved from pure technical and narrow field applications to solve higher problem domains in the realms of smart homes and cities. Through standardized system architecture, communication and information exchange, cloud technologies rely on instrumentation and interconnection to provide intelligent feedback and to support new capacities such as digital convergence, energy management or safety and security. Smart homes and cities cannot thrive without data fusion, and mining. Managing, processing, and synthesizing mass flow of information in real time may only be accomplished with state of the art information systems architectures. Cloud computing technologies are a solid foundation to consolidate the physical infrastructure as well as to streamline service delivery platforms.
Keywords
1. Introduction
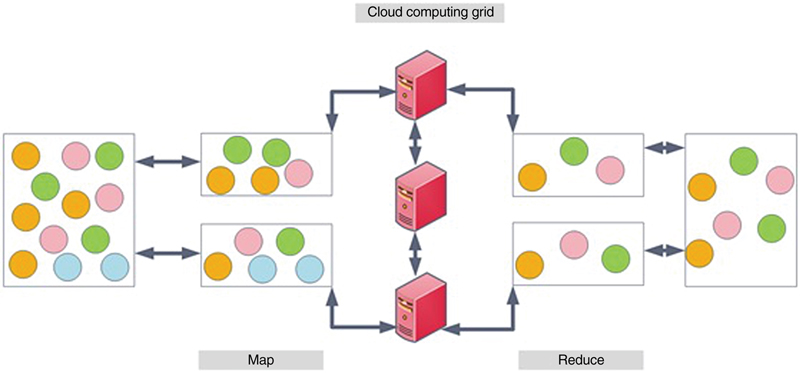
2. Cloud computing fundamentals
2.1. Cloud computing offerings
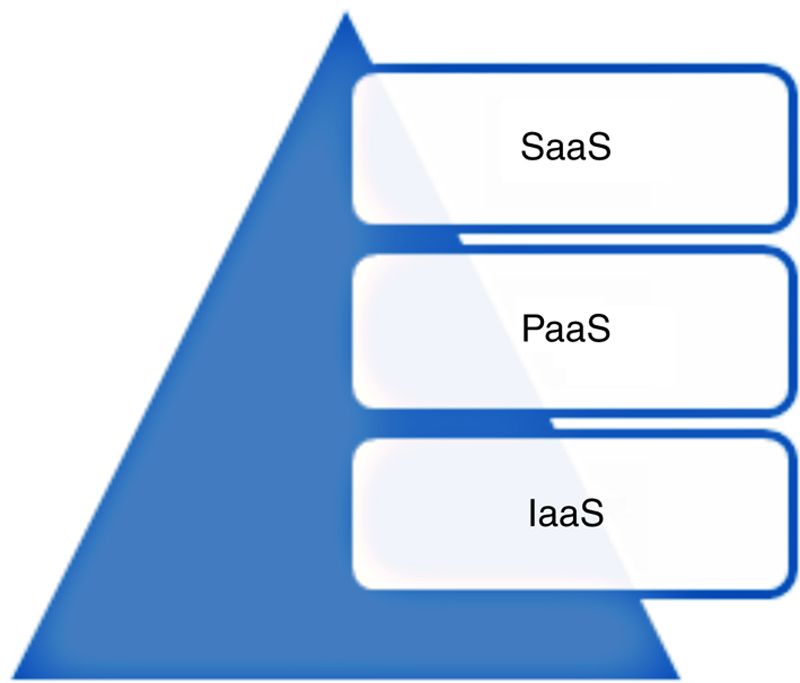
2.1.1. SaaS: Software as a Service
2.1.2. PaaS: Platform as a Service
2.1.3. IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service
2.2. Characteristics of cloud computing architecture
Table 12.1
Main Differentiating Characteristics Between Cloud Computing and Grid Computing
| Characteristic | Cloud Computing | Grid Computing |
| Service-oriented paradigm |

|

|
| System loose coupling |

|

|
| System fault tolerance |

|

|
| Networking: TCP/IP stack |

|

|
| Infrastructure virtualization |

|

|
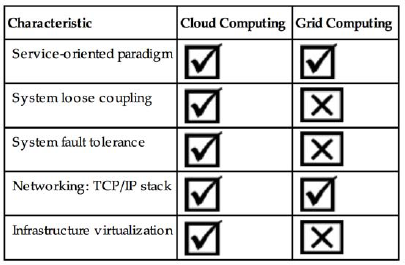
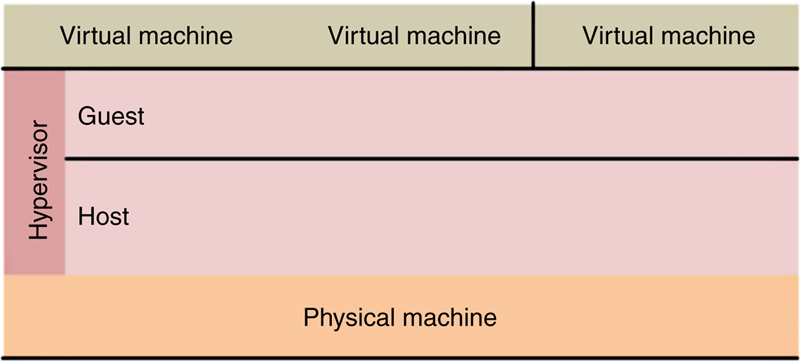
Table 12.2
Cloud Computing Fault Tolerance Model
| Error Source | Description |
| Provider inner | In this scenario, the fault is fixed by substituting the failed part or by using redundancy mechanism. |
| Provider across | In this scenario, when different providers are aggregated to provide a service, the system attempts to redirect to healthy nodes or service providers in order to provide seamless runtime to clients. This can also be achieved using load balancing. |
2.3. Cloud computing models

Table 12.3
Description of Cloud Computing Types
| Cloud Type | Characteristics |
| Public | Offers pay as you go billing model Supports multiple tenants Services are either shared of dedicated Externally managed Externally designed |
| Private | Self-hosted Self-managed |
| Hybrid | Partner hosted Dedicated environment |
2.4. Cloud computing security
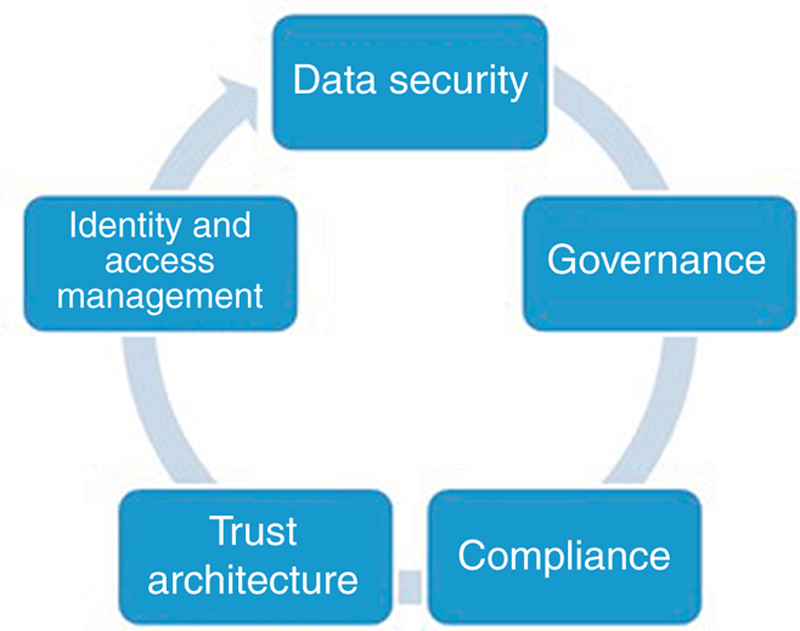
2.4.1. Effectively manage identities
2.5. Key concerns about cloud computing
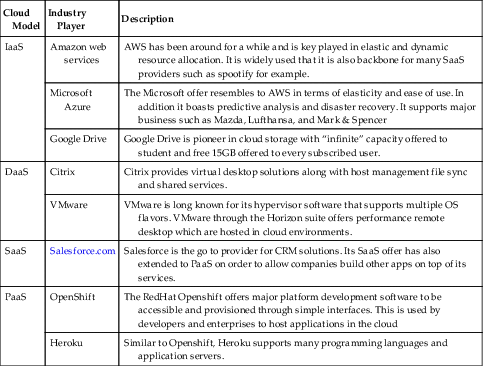
2.6. Major industry players
Table 12.4
Cloud Computing Major Industry Players
| Cloud Model | Industry Player | Description |
| IaaS | Amazon web services | AWS has been around for a while and is key played in elastic and dynamic resource allocation. It is widely used that it is also backbone for many SaaS providers such as spootify for example. |
| Microsoft Azure | The Microsoft offer resembles to AWS in terms of elasticity and ease of use. In addition it boasts predictive analysis and disaster recovery. It supports major business such as Mazda, Lufthansa, and Mark & Spencer | |
| Google Drive | Google Drive is pioneer in cloud storage with “infinite” capacity offered to student and free 15GB offered to every subscribed user. | |
| DaaS | Citrix | Citrix provides virtual desktop solutions along with host management file sync and shared services. |
| VMware | VMware is long known for its hypervisor software that supports multiple OS flavors. VMware through the Horizon suite offers performance remote desktop which are hosted in cloud environments. | |
| SaaS | Salesforce.com | Salesforce is the go to provider for CRM solutions. Its SaaS offer has also extended to PaaS on order to allow companies build other apps on top of its services. |
| PaaS | OpenShift | The RedHat Openshift offers major platform development software to be accessible and provisioned through simple interfaces. This is used by developers and enterprises to host applications in the cloud |
| Heroku | Similar to Openshift, Heroku supports many programming languages and application servers. |
3. Cloud computing applications
3.1. Big Data as an enabling technology for Smart homes and cities
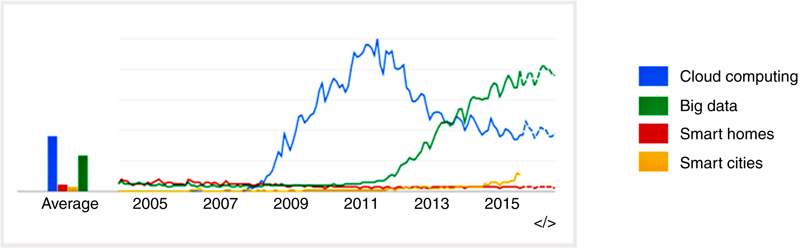
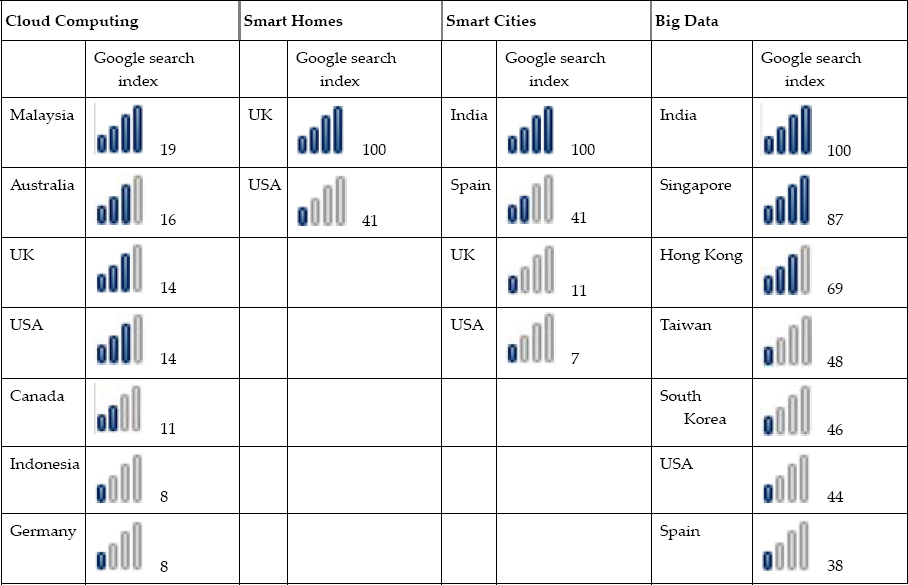
Table 12.5
Google Trends Search Index Weight for the Key Words: Cloud Computing, Smart Homes, Smart Cities and Big Data per Region of Interest
| Cloud Computing | Smart Homes | Smart Cities | Big Data | ||||
| Google search index | Google search index | Google search index | Google search index | ||||
| Malaysia |
 19 19 |
UK |
 100 100 |
India |
 100 100 |
India |
 100 100 |
| Australia |
 16 16 |
USA |
 41 41 |
Spain |
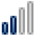 41 41 |
Singapore |
 87 87 |
| UK |
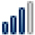 14 14 |
UK |
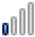 11 11 |
Hong Kong |
 69 69 |
||
| USA |
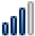 14 14 |
USA |
 7 7 |
Taiwan |
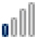 48 48 |
||
| Canada |
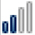 11 11 |
South Korea |
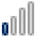 46 46 |
||||
| Indonesia |
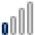 8 8 |
USA |
 44 44 |
||||
| Germany |
 8 8 |
Spain |
 38 38 |
||||
3.1.1. Big data, data fusion, and data analytics
3.1.2. Trends in big data as an enabling technology
3.2. Smart cities
3.2.1. Smart city concept

3.2.2. Smarter grid
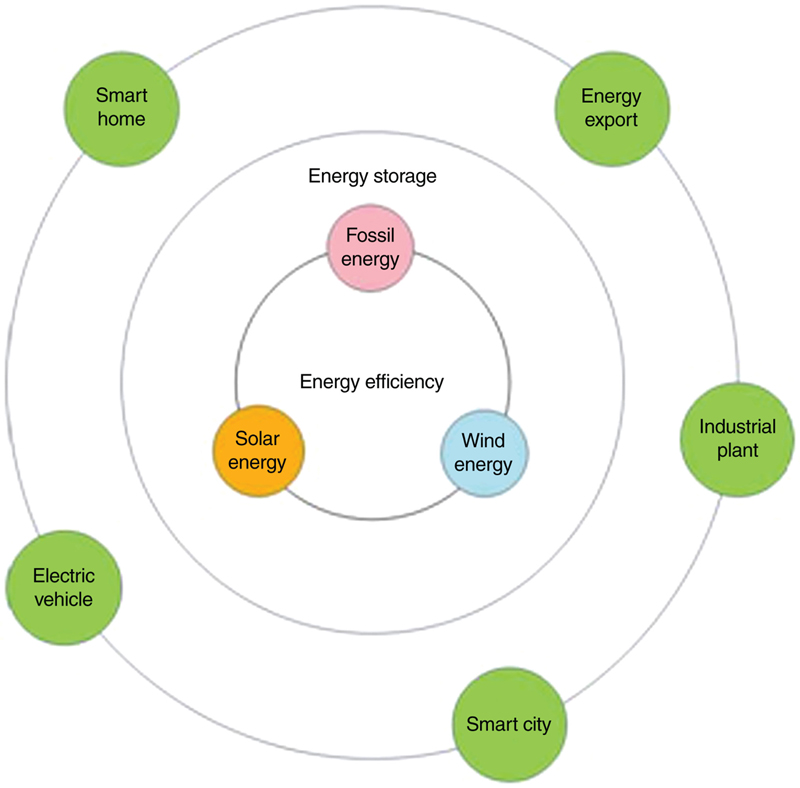
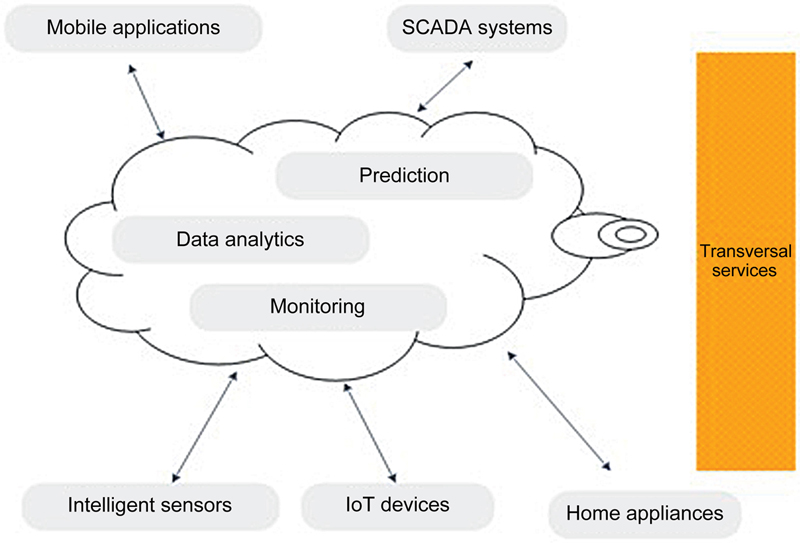
3.3. Smart home
3.3.1. Concept
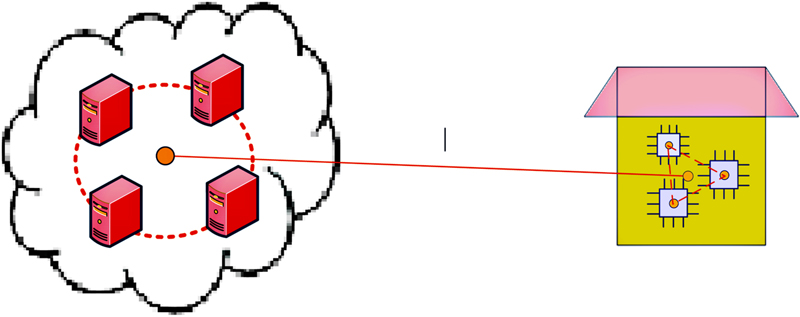
Table 12.6
Example of Smart Devices
| Home Device | Description in a Smart Home Context |
| Home energy distributer | On the basis of the activities in the home and the surrounding building, energy usage by other home appliances will be adaptive to optimize the cost of the KWH as well as the load of the grid. This adaptive information is extracted through continuous sensor data collection from the home as well as continuous behavior analysis and comparison with other relevant data from the cloud |
| TV set | Propose programs and content on the basis of user watch list history Propose targeted ads on the basis of content |
| Refrigerator | Adjust the thermostat on the basis of the volume of the food items it contains |
| Washer and dryer | Determine the water temperature in the wash/rinse/dry cycle on the basis of the load volume, dirt level, etc. |
| Water heater | Water heater that turns on to heat the water when the cost of energy is cheap and let the water cool off when this water is not needed |
| Air conditioner | It will consume and match usage and climate patterns, power cost and grid state in order to provide the most optimal temperature in the home at an optimal cost |
3.3.2. Smart homes enabled by the cloud
3.3.3. Home cloud service delivery platform
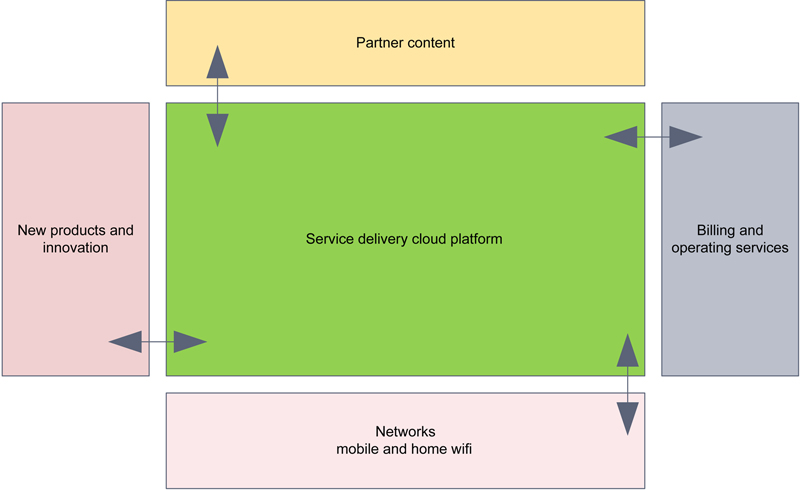
3.3.4. Emerging protocols for smart homes
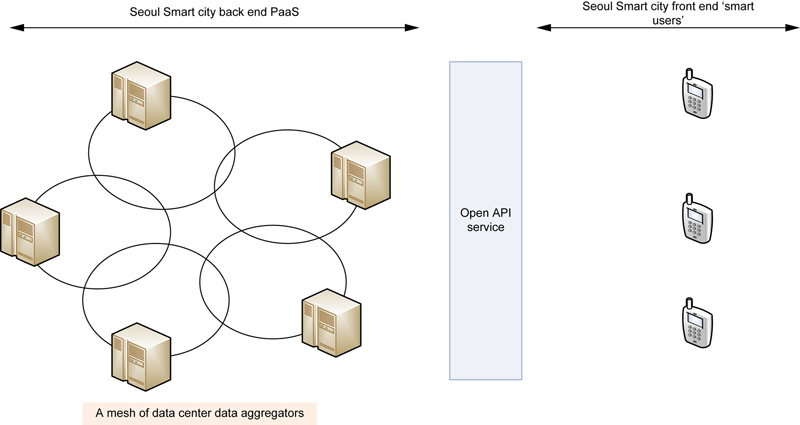
4. Case study: Seoul smart city
4.1. Presentation
4.2. Cloud based ICT infrastructure
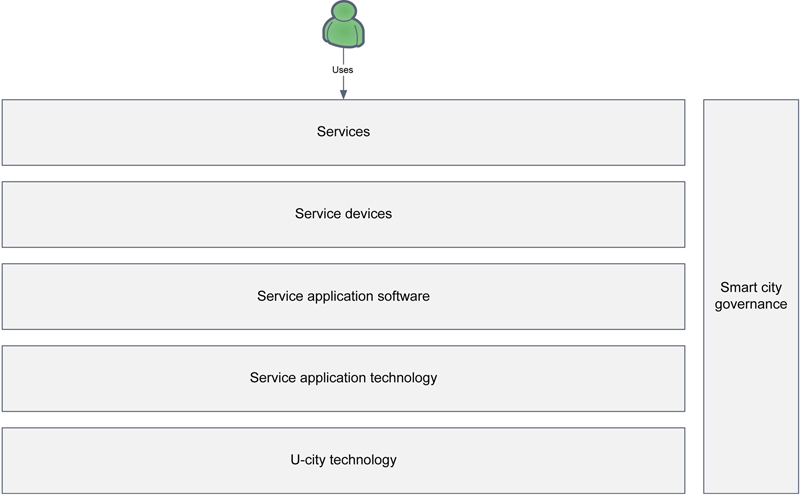
4.3. Data and service delivery
4.4. Open Application Programming Interface (API) and Open Data
Table 12.7
Evolution of Data Sources in Seoul’s Smart City Cloud Infrastructure
| Classification | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 |
| Accumulated number of databases | 20 | 60 | 100 | 150 |
| Proportion of total (target of 150 DBs at full system scale) | 15% | 40% | 70% | 100% |

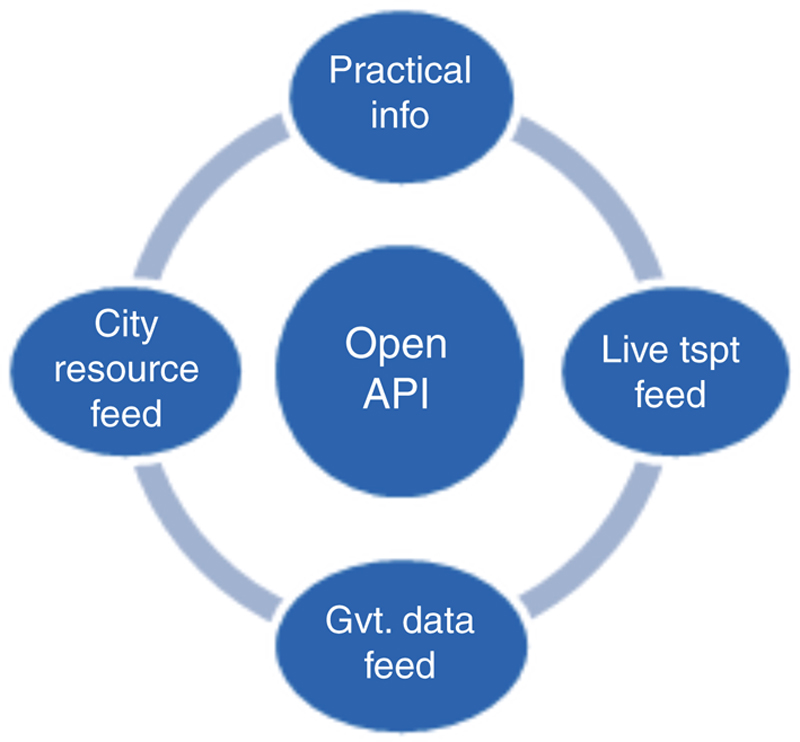
4.5. PaaS mobile application data access