Copyright © 2020 by
anonymous person
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written permission from the publisher, except in the case of brief quotations included in articles or critical reviews. Every effort has been made in preparing this book to ensure the accuracy of the information provided. However, the information in this book is sold without warranty, whether express or implied. Unsolved for an anonymous person Any damages caused or alleged by this book to have occurred directly or indirectly. An anonymous person sought to provide trademark information about all companies and products mentioned in this book through
appropriate use of capitals.
About
anonymous person
:
"I do not care about people's opinion of me or their criticisms ... Their words are nothing but jealousy ... a fatal emptiness ... a waste of their message and an internal reflection of their fears and unhappiness ... the only thing that interests me is my opinion of myself. By: anonymous person."
06
What is hacking?
Before you become a 1337 hax0r, first understand the basics PAGE
14
Why should you hack?
Because it’s cool. No, but seriously, there are many advantages PAGE
20
Why shouldn’t you hack?
The biggest fear is bricking your device, but there are worse things that PAGE
can happen. We are kidding of course.
26
Rooting and custom ROMs for Android
Get access to features such as overclocking, turning your phone into a PAGE
WiFi hotspot and more
38
Jailbreaking iOS
Install apps from anywhere and learn some cool customisations PAGE
49
Unlocking WindowsPhone
A decidedly rigid OS. Find out how to unlock your device and get the PAGE
most out of your OS
CONTENTS 3
57
Cracking Blackberry
Notaverycrack-friendlyplatform,butwestilltellyou
PAGE
aboutstuffhappeningintheworldofhacking
62
Flashing Symbian
The world’s most widely used platform has an
PAGE
equallymassive number of hacks
76
Custom firmware on PMPs
If you thought that cheap PMPs could simple not
PAGE
matchuptoa premiumone,thenyou’rewrong
82
Hacking Cameras
Features that cost a bomb, can be easily acuired. Read how...
PAGE
Vol ume 07 | Issue 07


Introduction
Don’t you just hate it when someone tells you what you can and can’t do?
W
hen you buy a device – whether a smartphone, tablet or evena camera–youbuyit touse itto the fullest; to squeeze out every little feature and last drop of performance from it. But not only do you buy a device, in most cases you
end up buying into an ideology and culture too. The manufacturer gives you access to its ecosystem and at the same time levies certain restrictions on what you can and can’t do with their device. These restrictions are more part of this ideology, than realistic reasons to limit access. Reasons cited can include security – “it’s for your own good; third party apps will give your
INTRODUCTION 5
device the heebie jeebies”; stability “if you get superuser access you might end up wrecking the device”; and many many more.
In this process manufacturers end up restricting many features, neutering the device by disabling hardware subsystemsand eventhe possibility of expanding functionality by way of addons. In fact, if you’ll notice in the first paragraph when we said their device, youdidn’t bat an eyelid.Shouldn’t it be your device once you’ve paid for it?
Of course warnings, disclaimers, and police tapes have never stopped the enterprising few from coming up with workarounds. This book is a compendium of all those workarounds that let you get the most out of your device. Jailbreaking iPhones, rooting Androids to get superuser access, installing custom firmware on MPSs and Cameras; we’ve covered it all.
6
Chapter #1
What is
hacking?
R
emember all those decades ago when computers were not a household entity, and we were updating our social lives as opposed to our online profiles? Neither do we. But there was suchatime- take our word forit.Over the years, astechnology
made computer-based devices first available and then mind-bogglingly capable, there was an almost expected by-product to the development the issue of power struggle. The power struggle between the the provider and the purchaser. Between the device makers and the device users. The corporations were always going to put a leash around powerful features. Maybe they do it for the safety of the device, or maybe it is to stamp their authority. That is a subjective debate. But the fact here is that there are many restrictions placed on stock firmware in the devices.
But that does not need to necessarily be the case. Thanks to jail-breaking, rootingandflashing (more on these later), youcan now makeyourdevice do
(even) more than ever thought possible. At a cost maybe(again, discussed later), but still, you get to become the king of your device, bar none. In fact, some people do it just for this purpose, to establish complete control over their devices. The hunger for power in mankind is almost astonishing. Narcissistic needs aside, there are more advantages, though. One immediate benefit is the ability to utilize software that may not necessarily be
approved by iTunes or Google Play. Various third party apps and themes exist, allowing total and radical customization of your phone. There are a number of people who also purchase their smart-phones from abroad and want to get them working in India. It even provides impetus for gaining the use of mobile devices not yet released in India. The best part?It’s also easily reversible (unlessyou’re crazy unlucky). Youcan experiment a bit and then revert to factory settings when/if you’ve had enough. Back up your data beforehand, and no harm, no foul, no hard feelings, mea culpa and whatnot.
All that being said, we must familiarize you with the game before we begin, right? So here is a beginner’s guide to hacking: an introduction to the tech jargon that you would encounter later in our journey to hackland.
What is Firmware?
Firmware is the data that is stored in a device’s ROM (Read Only Memory) area. Data contained within the ROM cannot be modified so it’s only used
to carry data that doesn’t need to be modified. The instructions carried on the ROM encompass the firmware, which provides an identity to the device and work closely with it’s associated hardware. ROM being non-volatile, firmware is an ‘ever-present’ data - it won’t be lost if the device is switched off or restarted. Hence the “firm”. Of course, it does much more than that. Firmware coordinates the various operations happening within the device (which is why, your OS can be called a firmware). There are three types of these when it comes to mobile devices: stock firmware, manufacturer branded firmware and custom firmware/ROM.
Google’s original Android can be considered a stock firmware, which sees its own set of updates from the OS manufacturer. Some examples of manufacturerbrandedfirmwareformobiledevicesincludeHTC’sSense, Samsung’s Touch Wiz, and many more. In these cases, the manufacturer hasoverlaid theirownuserinterfaceanddesignoverthedefaultAndroid architecture, giving it a unique flavour. Custom firmware, though, is fully designed by third party developers. It replaces the stock firmware, and while it may be Android, it provides an entirely new feel and usually, an upgraded set offeatures.
However, if it can’t be changed, what if one day, firmware becomes a limiting factor? For that matter, if you don’t keep your firmware up-to-date, there’s a chance you could face security lapses, and miss out on improvements to pre-existing features (because like PC software, no firmware is perfect at launch) or simply not take full advantage of the hardware in your hands.
That is where flashing comes in.
WhatisFlashing?
FlashingbasicallymeanssendingyourphonetoFlash,becausetheJustice Leaguedoesn’tprovideacompanyphonethesedays.AndmayGodbewith you if you can believe that.
When adding new features to existing data on ROM, manufacturers tend to overwrite certain modules . This is very much like spring cleaning: removing the old data to make way for the new. The entire process is known as“flashingfirmware” or simply flashing. This is usually done by connecting your mobile device to a PC via USB, and using the software provided by a manufacturer. You can also employ software like YourCellular, though instructions may vary for specific phones. It’s quite simple and the entire process takes about 15-20minutes.

The benefits of flashing are manifold. If a new component has been added to the system, flashing the firmware allows it to recognize said component and enable it’s proper working. In the case of smart phones, various firmware updates are constantly being provided by the manufacturer to extend functionality, address bugs and whatnot. It’s also been used by people who wish to switch carriers on their cellphones. However, say you could flash the firmware and add some features of your own? This opens up customization options beyond the typical updates. It also helps ensure people get the required updates for an OS.
One thing to be noted is that flashing the firmware of a device is not the same as jailbreaking or rooting it (or as Bill Shankly would’ve put it, “it is muchmoreseriousthanthat”).Jailbreakingsimplyallowsone to removeany restrictions the original manufacturer placed on the device, such as locking parts of the OS. Flashing is the complete replacement of the firmware on the phone, whether by custom ROMs, or even stock firmware. It will not only add new features to the current architecture– if saidfeatures are beyondthe capability of the available architecture, they won’t have any effect. Despite their differences, flashing and jail-breaking still fall under the realm of hacks. Apple still thumbs its nose at the same, but they’re thankfully not considered illegal anymore.
There’s also a danger of bricking one’s phone if the flashing is done incorrectly. A full battery is required for the complete process – a partial charge risks an incomplete flash process, hence, damaging one’s phone to the point of disuse.
What is Rooting?
When you talk about the iPhone, the term “jail-breaking” often comes up. Similarly, when it’s Android – or just about anything on a Linux/Unix architecture– the term thrown around is Rooting (akin to root access, i.e. superuser).Thinkaboutitasobtainingadministratoraccesstoyourown system,withthepowertochangeapps,howthey’llrun,replacingtheones youdon’t like and just moving past any restrictions that would be placed upon the user by the manufacturer.
So exactly what can you do with root access? Well, you can install custom themes, fool around with the performance for some added boosts, lower battery usage, install new features such as tethering and load custom ROMs
(detailed below). Its the epitome of true control – and given the amount of customization built into Android, the number of changes you can make is, lets just say that its a very large number. Read our Android coverage ahead to know more.
Take CyanogenMod for instance, which is meant to be a replacement firmware based on the Android architecture. Even though it’s more in line with a custom ROM, it allows app management permissions, and the ability to over-clock one’s CPU besides adding additional features such as WiFi support, tethering, FLAC support and more.
It’s important to note that though many developers and manufacturers aren’t exactly okay with jail-breaking and rooting, it’s no longer considered illegal. In fact, companies like Samsung and HTC are showing such support to third party developers like CyanogenMod that they intend to bring the superior firmware to their devices. Probably the best new feature of CyanogenMod is that it’s no longer rooted - you can simply install it and enable it as a feature. It also gives you several options for rooting and you can choose to disable it altogether. What does this mean? As repetitive as it sounds, the detailed coverage is still ahead.
It should be noted that rooting carries its own risks, depending on what you’re doing. System updates provided by Google may not work when applied. There’s also chance of bricking or boot looping if done incorrectly.
What are custom ROMs?
Custom ROMs are developed by third party developers as the core firmware of their targeted devices. Android being open source, is a logical choice for many such ROMs being released. Custom ROMs present their own set of advantages and disadvantages: you get a plethora of choices, all with their own themes and features, constantly being updated, and giving you options to exploit your device, doing whatever you want to do with it. However, they’re not perfect and are susceptible to bugs. All custom firmware aren’t free from bugs and still require exhaustive testing. So there’s a chance you may not quite get the performance boost you’re looking for, or even if you do, it might be a bumpy ride. ROMs also require your device to be rooted, and though no longer illegal, the risks are still the same.
Custom ROMs based off of Android often bring the advantage ofnewer OS versions to devices that might not otherwise receive them through proper vendors. Ice Cream Sandwich, anyone?. CyanogenMod isn’t the only custom firmware based on the Android architecture, although it is a sort of a torchbearer for the movement. Replicant is another one, built around the purpose of replacing the bundled hardware drivers with open source drivers. This was built with the intent of making it easier to share firmwares that actually work (since the drivers shipped with the phone are propriety and not free). It even has its own market called F-Droid for applications.
HowdoesonegoaboutexactlyinstallingacustomROMontheirmobile device? It usually varies for different manufacturers, but the basic steps arethesame.We’lltaketheexampleofCyanogenMod,butwhateveryou’re
using, you need to take a backup of your current ROM, including apps and data. The process is similar to flashing your firmware, with a few more steps.
Ω
First, replace your “recovery manager” with ClockworkMod Recovery. Ω
Then perform the process of flashing your firmware, selecting the ROM
you’d like to flash it with (in this case, CyanogenMod).
Ω
You have to download it, and will be informed to back up data since your
device will be doing a factory restart.
Ω
BackupyourdataandstockfirmwareusingClockworkModRecovery
before activating CyanogenMod.
You can also copy CyanogenMod and the required app files to an SD card’s root, which can then be installed using ClockworkMod Recovery.
There are many other custom ROMs, some of which maybe requiring root access. Always remember to go for the ROM that would best suit your needs. Read up on the different ROMs and freshen up on the flashing and installation process before trying any custom ROMs. Talking about reading up, you can just read on - you can find all the comprehensive coverage you need in this FastTrack itself!
how about hacking non-communication devices?
Behold, ye mortals! If we say we will give you a comprehensive coverage of device hacking, we will give you a comprehensive coverage of device hacking. That includes non-communicative devices like PMPs and even digital cameras? So be it.
Devices like these have only started receiving powerful hardware components recently, and it is for this reason that the interest in hacking these was a little late to develop. Still, now that it’s there, it is getting its due recognition. The hacks here are mostly performance enhancing ones, like maybe better media rendering for the PMPs, or producing RAW images for low and mid-range cameras. Not that it is limited to these upgrades, but these are the main motivations. More on this later.
14
Chapter#2
Why should
you hack?
H
acking, for a long time was thought to be a dark art. Only people with superhuman digital skills were thought to indulge in these practices. That time is almost as old as the dinosaurs. These days, hacking your devices is a piece of cake, maybe even
easier. A couple of straightforward clicks, and you’re good to go. Which is why, every regular Joe has flirted with the idea, and the little-less-regular Pete has done it. Hacking today puts everything from small, useful tweaks to a full blown overhaul of the experience, on the platter, and you can take your pick. One of the most most important advantages is that if you do manage to screw everything up, you can just flash almost any deviceback to its original firmware, and get back safely to the God fearing nation of non-hackers. These are the logical advantages that hacking offers in the modern day. Plus, it’s cool, you know. Useful, performance enhancing, so on and so forth, but it is also a badge of certified geekdom. Which is why we chart the promised land that device hacking offers.
The advantages of hacking, a device by device coverage:
android
Android is amongst the most hack-happyof systems. Considering that it was created on a Linux platform, it was practically built for hacking (rooting, as with the Linux ecosystem). Also, Google takes one of the most accepting stances in terms of rooting – it allows apps that specifically require root privileges to be listed on the Google Play, its app store. And finally, as with most other operating systems, you can, at any time, get your warranty back when you install the stock firmware. So here is a rundown of the treats that await you when you root your Android phone. First, there are the general ones - load custom themes, software, move around with your apps, create backups. Homely stuff. As for serious advantages, there’s perks like loading custom ROMs, overclocking your processor and upgrading your phone to newer OS releases before they’re released by your provider. Also, you can do as much as tweaking your network baseband for better signal reception. If you are sufficiently careful with yourrooting

softwareandothertoolsandoptionsthat you would use for rooting, you(r phone) can live a long, happy, more attractive and more productive life in hackland.
iPhone
Apple likes to be the all-encompassing overlord to all that carries the company logo. The Macs and the iPod-iTunes ecosystem are proof to

that much. Thus, it is only logical that hacking into an Apple device is as much a thing of pride for a hacker, as are the potential benefits that lie before him for the same. It is primarily for this reason that jailbreaking of an iPhone is so popular today. So, unless your only motive is to get one over the big corporations (not that it is not a valid motive), you can read on to know the benefits that lie in jailbreaking of the iPhone. First of all, and this is the most common (and important) of reasons is the plethora of apps that become available once you do it. Apple has a very stringent policy regarding uploads on its App Store, and the apps accepted by Apple are the only ones that are accessible to the general user. But jailbreaking ‘breaks’ those chains, and opens up limitless possibilities that you can harness. Also, there is the possibility of changes to the OS, and changing your entire experience with the device with theme overlays. You can also change the power management settings to improve the battery life (or, conversely the performance) of the phone. Pretty much all the tinkering that you would want to completely change your experience with the device.
Windows Phone
Windows phone is actually a very safe platform, in terms of hacking, and we wonder if this is an intentional step that Microsoft has taken. They allow developer to hack into devices with a special $100 license. There are not too many high level hacks known for Windows phones (except for the full blown custom ROMs), and mostly there are little tweak floating around, which will help you with specific parts of your experience while using Windows Phone. Maybe you want to play around with the interface. Or maybe you want that your messages be displayed in tiles instead of the default view. Or maybe you want some other nifty addition. There are hacks for them all. And with all changes being inherently reversible, there’s practically no reason why you would not want to hack your Windows device. Go on, child, go on, break them shiny Windows...
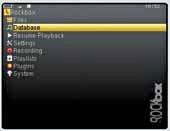
Blackberry
BlackBerry, until recently, was going very strong in the mobile space. Being the most popular smartphones, they were at the top of mostpeople’s prized possessions, and on top of the wishlist of the others. But with the sudden influx in the smartphone space, BlackBerry was probably the worst hit. And the resultisthatBlackBerry hasbecome somethinglikea‘oldie’ofthe mobile space-continuouslylosingground,bereftofideas,picking uprandomfights, blocking this or that service, and what not. Asalogicaleventuality,hacksweremade togiveyoua fulfillingBlackBerry experience.NowBlackBerrydevicesarenotthe most powerful ones on the market, and neither are the hacks very common. So you cannot expect radical changes here, but there will be sufficient ways to get you by, we would say. Find out more in our dedicatedBlackBerryhackingcoverage.

symbian
hacking the s40 platform:
Its still, there, you know. Symbian is not dead. In fact, that is what they now say on their logo, “Symbian: Not Dead Yet”. Well, if you say so, Nokia. So, the point is, the simple S40 devices actually carry a bit more punch than they are given credit for. The usual ‘Nokia’ carries enough in itself to perform tasks like multitasking and heavy (for its class) applications, like third-party media players and browsers. Sadly, Nokia does not allow multitasking on its devices, something that can be easily established by the simple flashing technique that we provide later. These are devices that definitely have latent power to harness!
hacking the Belle platform:
Nokia has never really been known for its OS expertise, and it shows. Belle (or for that matter, Anna) hacks are some of the easiest ones to implement. Quick fact (and this does not show Belle in a good light) - Belle was hacked a few hours after its release. The hacks are mostly straightforward, and offer you handy control to almost all sections of the device. Many online providers host third-party apps (some claim to hack in via Norton Security), and they promise the regular perks like using new apps, themes, and other tweaks. Straightforward, and more importantly, easy. Why shouldn’t you hack?
 PMP
PMP
PMPsare peculiardevices, really.They wereenvisionedashandheld devices that were supposed to play yourdigital entertainment media. Songs, videos, some games, maybe, but that’s it. Leave it to Apple, though to revolutionize an industry. In comes the iPod, out goes all perceptions of what a PMP is. Today, for all we know, a respectable PMP is a smartphone minus the calling
facility. Which makes us, sad, really, so don’t worry – we will tell you how to make a call through your WiFi enabled PMP, later. But, taking things one at a time, not all PMPs are suitably capable, as of today. They have the hardware, and hence the potential, for better performance. Which is what drives projects like RockBox, which aim to create better, more capable environment in even the less flashy of PMP devices. RockBox has been trying to give provide a powerful interface, along with the promise of better
audio and video rendering. Currently, a host of devices are supported, and while availability of many more are on the way.Head over towww.rockbox. org
to know more about the project. And be sure to read our chapter on hacking PMPs.
camera
Cameras of the modern day are criminally underestimated devices. In terms of hardware, they are being installed with pretty capable components, but for some bizarre reason, they seem to install software that does not make efficient use of all that is available to it. There are theories that it is a sales strategy, that if lower-end cameras carried full-blown features, then the high-end market would suffer. But if that is the case, then the companies should have been stringent with the hardware too. But they were not, and the result is that various hacking groups have been hard at work to develop custom firmware for these cameras, which harness the possibilities that the devices offer. One of the pioneers of this movement is the CHDK – the Canon Hack Development Kit, which is built to empower the low and midranged cameras from (surprise, surprise) Canon. It can give your camera professional (read: expensive) level features, and then some. Run-of-themill qualities such as shooting in RAW mode, manual control over the exposure, zebra mode, live histograms, grids, etc. are included, as are some fantastic ones such as controlling your camera with a remote, scripting to add your own requirements to the feature list, and many,many more - there are games too! There is another, slightly less popular hack called ‘Magic Lantern’ – again for Canon. Along with these two, there are many other firmware hacks available, while others are in some or the other levels of development, for various manufacturers. Expect to see some action in this field in the coming time.

20
Chapter#3
Why shouldn’t
youhack?
B
ecause you are not expected to. There – in half a line, the entire gist of the article. And because you are reading beyond that, we infer that you obviously want to know more. That shouldn’t be a problem – that’s exactly what we’re here for! What you need
to understand is that when you hack into your device, you are essentially bidding farewell to any form of warranty or authorized support you were entitled to; from now on, the service guys will only try to work their way around your problem, and at any point that they so desire, they may put their hands up and say that they cannot do anything about it. If they deem it so, the product will be declared ‘unusable’ and you might be stranded with a worthless brick of a device. In fact, there is a term for it ‘bricking’, where your phone’s software has been so badly damaged that it is as useful
an electronic device as a brick. And usually, this is the point of no return unless, of course, you are an expert at this and can flash your device with originalfirmwareagain(andthatmightevenwinyouyouroriginalwarranty back). This hazard applies to almost all devices, and is the main leverage the big corporations have to keep you from hacking into your device. But the most important thing is, do not hack if you’re not confident. You must be ready to face any problems that arise, along with the obvious perks that come with hacking into a mobiledevice.
the disadvantages of hacking, a device by device coverage:
1) android
Android, we know, is amongst the most hackhappy of systems. Still, as evidence suggests, Google is not really fond of the people who indulge in“rooting” their devices– as is evident by the fact that they recently blocked rooted devices from using the video rental service from Google Play. Not that this is relevant in India, we don’t even have legitimate access to the service!Apartfromthat,therearealsosome serious risks with respect to the functionality

of the device. With the popularity, and hence the market share, of Android devices increasing by the day, it was only a matter of time before malicious programsmadetheirwayinto the marketandasitstands,thereare manyout there now. There are many corrupt rooting software just lurking around the corner, waiting for you to give them a way into your device, giving yourself (and by extension, them) superuser privileges, and then leavingit to them to make your beloved device a brain-dead zombie. A security compromise is amongst the most dangerous possibilities in a smartphone, and with more and more services inclined on making your phone the ultimate all-purpose device, including a payment medium, you’d probably not want that. They say the known devil is better than the unknown one. But, given a choice, why not just stay away from them both?
2) iPhone
Apple is one company that likes to have utter and complete control over its devices, and it is only logical that it despises the people who jailbreak
their devices. To a point that it has been speculated (though never proved) that Apple puts in specific blocks of code in the iOS so that, if a jailbreak is detected, the device will slow down automatically, suffer periodic jitters, and the OS memory imprint is larger for practically no reason. There goes the whole ‘Apple experience’ out of the window. Also, once a device is jailbroken,youcannothavedirectandinstant accesstoupdatesthatareperiodically released bythe company–you will havetowaitforthe
hackers to crack the new update too, and then provide it for you. Not that there would be much delay in that; most of the new launches and their updates are cracked and distributed in a day or two, but the point to ponder is that you lose your direct link with the company. Then, there’s the ever- present issue of security breaches. It’s like, once you breach your own phone to jailbreak it, what is to say that others can’t do so remotely. The locked sections of the OS have already been broken into, and the veil of protection is too thin to stand a focussed attack. With iPhone being a powerful device, chances are that it might be storing some sensitive personal data for you, the compromise of which won’t be pleasing in the least. The seamlessness of the Apple environment, which is fast becoming the most important selling point forApple’sdevices, is compromised too, with constant reports ofbugs, and a generally discordant and unstable experience. Not what we want to pay such exorbitant prices for.
3) Windows Phone
Windows is really a pecu
liar platform in this regard,
considering that there are no
high-level hacks that you could
use.Sadly,therearenoreasons
then, for you to not hackyour
Windows phone. Sure, there are some nifty additions here and there, but nothing to really make you sit up and take notice. Like the messages being displayed in tiles, or changing the alarm sound - basic stuff. That just leaves you with the option to take up a developer’s license, which all the other companies provide too, and get tweaking in a way that is endorsed by the corporation. Dystopian scenario for a true hacker, we say.
4) Blackberry
BlackBerry hacks, to be honest, are not that popular. And that is precisely the reason that one should be very, very sure before hacking into their device
– you would practically be alone in the pursuit, and would not get much in the name of support, advice, and if needbe, troubleshootsaround–evenon the internet.BlackBerrydoesn’tofferthe most capable of devices anyway, and as we know, no hack can provide you a feature if the hardware cannot support it. Also, as BlackBerry recently announced, it does not condone the act of hacking into a BlackBerry, and along with the usual risks of bricking and voiding your warranty, there is a possibility that future support is denied to such devices. Also, it then becomes paramount to shell out a few bucks on getting a competent anti-virus software, because BlackBerry is a platform whose whole empire was built on secure communication, and that is something you’d not want compromised.


5) symbian
Hacking the S40 platform:
You thought we’d forgotten about this, didn’t you? Apparently, this is still among the most popular phone platforms in India. And it can be hacked. Which is why wemust tell you the hazards for the same. The main reason
that people hack their Symbian S40 devices is to break off some of the OS limitations discussed previously, but because S40 runs on low powered devices, it is essentially a case of trading features. Like, if you go in for a hack to avail multitasking, then you are essentially giving up the possibility of using resource
intensive apps like a 3rd party browser, or video playback, because a section of the memory is then reserved for multitasking support.
Hacking the Belle platform:
One of the most important reasons for not hacking could be that it wouldn’t be worth it. Belle (or for that matter, Anna its predecessor), as a platform,
hasn’t matured enough to be considered one for major usage, and frankly, does not capture the attention of major developers the way its adversaries do. Hence, the only reason for hacking into your Belle device would be if you wanted to use some unapproved apps. This in turn, carries the usual threat of
warranty getting void, and of security issues/bricking. Nothing out of line here. Whether the deal is worth it, is entirely up to you.
6) PMP
Traditionally PMPs were devices that most manufacturers did not build with the threat of hacking in mind. After all, they used to be simple music/ video playing devices – what more could you possibly get out of them! But then came the advent of iPods, and innovation after innovation led us to finally reach a stage where the proper PMPs of the day are basically smartphones minus the calling facility. And that is something that we actually cover – the possibility of making a call from a PMP over WiFi! While all these thoughts are fascinating, what must be considered here is that the support-stores network for PMPs is not as widespread as it is for other devices, and we again run the possibility of fighting the battle alone if a problemisencountered.Also,themain focus for a PMP manufacturer is that the rendering is as pleasing as it gets, and installing a different firmware to
the one the device was built for, is bound to throw up some teething problems. The danger of bricking is very, very real in thisregard.
7) camera
Withevenlowendcamerasbeingbuiltwithsufficientlypowerfulprocessors and good image processing capabilities, its a shame really, that manufacturers are not providing the software capable to harness all of the possibilities here. And it is for this reason that firmware ‘upgrades’ like Magic Lantern and CHDK (for Canon) and others,
are gaining popularity. But this again involves
all the risks that are stated above, in a more
grave capacity, if anything. Cameras are not
themosteasilyprogrammableofdevices,and
any steps you take with regards to firmware
tweaking should be done with extreme cau
tion, because the lack of support for this kind
of hacking means that you could end up with a worthless piece of mess, and have no place to go with it. That being said Canon Cameras are less risky when it comes to hacking.
26
Chapter#4
Rooting and
custom Roms
foRandRoid
A
ndroid is the underlying software that powers a major chunk of all smartphones in the world. Built from ground up by the Open Handset Alliance led by Google, Android was intended to bean open source operating systemformobile devices. This
open nature of the platform gave handset manufacturers almost limitless flexibility in the software and allowed them to differentiate their products from each other. Soon OEMs came up with their own take on the OS. (This is why devices from different manufacturers sport a very different look and feel, even though they all run Android). While this meant OEMs (and even carriers) could load the device with their own custom apps and interface tweaks, it also meant that OEMs could place several restrictions on the device, often to protect their own business interests.
This is where the openness of Android kicked in. Soon, developers and hackers were busy trying to circumvent the restrictions to fully utilize the potential of their smartphones. This led to a number of tweaks and aftermarket ‘firmwares’ being made available to Android, a feature very unique (and central) to the Android ecosystem. Soon regular users were able to tweak the software, it’s underlying components and even change the way the hardware worked using some relatively simple techniques. This led to concepts like ‘rooting a phone’ and installing a ‘Custom ROM’ - terms any Android enthusiast will be very familiar with. It is worth mentioning at this point that Android offers far more flexibility and customisability compared to rival platforms like iOS, Blackberry OS or Windows Phone. While other OSs only skim the surface in this regard, Android lets you alter the look and feel of the device without having to resort to a root or an alernative firmware. Themes, icon packs, home screen replacement apps and widgets for nearly every plausible feature will keep you in control of your device to a fair extent. Android also allows users to install apps not found in the official Google Play Store (called ‘sideloading’ apps), which many others like iOS and Windows Phonedon’t.
In this chapter, we give you lowdown on what it’s like to unleash the full powerof your Android device. While it’s nearly impossible to give a detailed guide for rooting or flashing a ROM for every device out there (due to the sheer number and variety of different /Android devices) we’ll cover some essentials concepts along with their benefits. Bear in mind though, that while they may unlock many new features on your device, they do involve some risk. At the very least you woudl be voiding your device’s warranty, or worst-case you might end up ‘bricking’ your phone, rendering it completey unusuable. On that note, let’s dive in to the wonderful world of Android!
Rooting your device
As discussed earlier, even though Android is supposed to be Open Source, users don’t always have access to all of the phone’s features or can’t modify the phone in an arbitrary way. One of the (if not the most) popular starting points for Android customization is to ‘root’ your phone. Rooting gives the useraccess to a plethora of tweaks andpowerful customizations include the ability to tether your phone’s internet connection via Wi-Fi, overclocking your phone’s CPU, backing up your apps or installing ad-blockers. But what exactly is rooting and what do you, as a user stand to gain from the process? Let’s find out!
What is rooting?
RootingaphoneisAndroid-speakforgainingadministrator-levelpriveleges to the phone. Typically, users don’t have access to a phone’s higher level
files and folders and can only deal with files and directories stored on the
phone’s external memory or SD card. The system critical files, processes
and applications like the dialer, messaging and camera apps reside in the
phone’s internal memory. Users can’t uninstall these apps, nor can they
directly make changes to the filesystem. This is where rooting comes in. By
rooting one’s phone, the user is granted elevated priveleges and can make
modificationstoanyfileorapplicationslocatedanywhereonthefilesystem. As a crude analogy, consider your desktop computer running Windows
– Your ‘Windows’ folder (typically located under C:\Windows) contains
system files which are critical to the system. Not having root priveleges
on an Android device is analogous to not being able to edit the contents of
this Windows folder. Rooting one’s device would be similar to ‘unlocking’
the contents of the Windows folder and being granted the ability to add,
remove or edit files at your will. While this may not seem like a big deal
(As most of us don’t interact directly with our Windows folders) there are
severa apps that can take advantage of this ability, resulting in greater functionality for your device. (This analogy has several inaccuracies, least of all
that Windows uses a very different filesystem structure than Android and
other UNIX-based systems, which use a top-down or tree-like hierarchy.) The term ‘root’ is a feature of UNIX and UNIX-based systems which use
a tree-like filesystem structure. The top level directory is designated with
a ‘/’ and is called root. Having access to files at this level of the hierarchy is
having ‘root’ access to the system, and a user having root access is a root
user (or superuser). Since Android uses a Linux kernel, and Linux itself is
derived from UNIX, the terminology carries on.
How does the rooting process work?
In order to understand how rooting occurs, we need some insight into the Android system.
Most devices, by default have their /system partition (found in the device’sinternalmemory)setto read-only,which meansappscannot modify thissacredfolder.Mountingthe /systempartitionwithread-writeaccess requires root priveleges. In an Android system, only a priveleged app (i.e. An app running as root) can invoke or start another priveleged app. Ordinaryappsthatarerunasusercannotstartappsthatneedpriveleged access. This is a security measure, for in its absence any app would have been able to invoke itself (essentially creating a copy itself) with elevated priveleges. Hence, for an app to run as root, it must request root priveleges from an external app, called the Superuser or simply ‘su’. The final aim of the rooting process is to install this Superuser app on the device’s internal memory as a system app. Any app that needs elevated priveleges (a.k.a. root access) can then request the same from the Superuser app, a request which is usually forwaded to theuser.
When an Android system boots up, the first piece of code that is executed is called the bootloader. This bootloader controls the boot process, hence access to the bootloader is required when installing a custom ROM or aftermarket firmware. Many devices, however, come with a ‘locked’ boot- loader and need to be worked upon (read: hacked into) before we can flash a custom ROM. However, if a device has an unlocked bootloader, rooting a phone becomes relatively easy. One can either find a custom ROM for your phone model that has already been rooted and flash it onto your phone, or you can simply pull the existing ROM from your device, add the Superuser. apk file to it and flash it back to your device.
Another nifty utility that Android provides is the Android Debug Bridge, betterknownasthe ADB. The ADB allows you to execute commands entered via a computer on your Android device, essentially allowing you to VNC into your device. Any command executed on the adb shell while the phone is connected to the computer will be exectued on the device. Some devices have a feature, where any command issue via the ADB is automaticaly given Superuser acess. In this case, installing the Superuser app permanently is as simple as plugging in the phone, starting the adb and issuing the commands to copy the file to the device. The ability to execute ADB shell commands as root depends on the value of a configuration key (analogous to a registry key in Windows) called ro.secure whose value can be either 1 or 0. A value of 0 implies that the system will execute all commands as root user, whereas a value of 1 means apps will run with unpriveleged rights. You can check the ability of your shell by entering getptop ro.secure into your device, either through a terminal emulator or the ADB.
Finally, in the event that both the bootloader and the ADB are locked, how does one go about rooting one’s phone? This is done using vulnerabilities in low level system processes that have root access in order to interact with the device’s hardware components. During the boot process, after the Linux kernel has been loaded into the memory, the init process is started
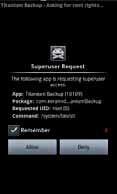
The Superuser app grants root permissions to apps
(‘spawned’) by it. This init process has root priveleges as it is required to start other priveleged processes and services that are critical to the functioning of the device. Thus, during normal operation of an Android device, there exist background processes running as root. The key lies in being able to trick these processes into executing some code that will mount the /system partition as writeable, as well as permanently install the Superuser application. Most popular rooting methods use this technique. After the device has been rooted, any app that claims to require root access will basically try to start other priveleged apps (often bundled within the same app) using
the su or Superuser app. When it tries to start su, the user is asked to grant or deny priveleged access to theapp.
How do i root my android device?
Android devices differ in many aspects, including the form factor, screen size, hardware features and most importantly, the build of Android they’re currently running. The sheer variety in the exploits used to root a phone means that no single method is applicable to all devices running Android. The rooting procedure itself is a very simple one, and most methods require to either connect the phone to the computer and use a tool, which, with the press of a single button will root your device for you. There also exist methods where users don’t need a computer, simply downloading an app and running the app should do the trick.
Some popular methods for rooting which apply to a large number of devices are Unlock Root, Gingerbreak, SuperOneClick and Universal Androot. However, if you wish to root your device, your best bet would be to look for a rooting method that has been tested to work on the same device running the same version of Android. This is because rooting methods differ from device to device and evenbetween differentversions of Android. There is really no ‘one size fits all’ technique for rooting.
One important thing to keep in mind is that rooting a phone qualifies as tampering with the phone’s internal software, and this will, in most cases nullify the warranty on your device. There is also a slight risk of something going wrong and the phone becoming unusable. This doesn’t usually happen, but to be on the safer side, it is highly recommended that you backup all of your phone’s data including your contacts, messages and applications (along with application data). Contacts are usually backed up by Google within your Gmail account, but if you want to be extra sure, you can export your contacts as a .vcffile to your SD card. This backup can be moved to a safe location and can be used to restore your contacts by importing your contacts from this file. Messages can be backed up using SMS Backup and Restore, which exports your messages along with their metadata to an .xml file on your SD card. Applications can be backed up using ES file explorer or Astro file manager.
Why should iroot my phone?
Asdiscussedbefore,rootingunleashesthefullpotentialofyourphonegiving you features from apps that were earlier unavailable. Apps can interact with much more advanced aspects of your phone, giving you almost limitless control over your device. As an example, we’ve listed the top 10 hacks you can use to gain control of your rooted phone. Naturally, all these hacks require you to be rooted with the Superuser binary installed.
1. control your cPu
Modern smartphones come with powerful CPUs with clock speeds in GHz and advanced frequency scaling features. Apps like SetCPU can change the scaling limits of your phone, allowing you to overclock it for better performance, or to underclock it to save battery life. Bear in mind though, that this is a highly risky task, and changing the parameters outside the device’s limits could be disastrous.
2. securelybackupapps/move apps to sd card
Apps like Titanium Backup / ROM Toolbox let you create secure backups of your apps
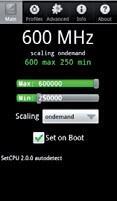
Overclock your CPU with SetCPU
along with their data to your SD card. Titanium Backup can even export your backups to the cloud via your Dropbox or Box account. These apps also let you forcibly move apps from the phone’s internal memory to the external (SD card) memory, a handy feature for lower-end devices. Titanium Backup has a few additional features like the ability to freeze apps or forcibly attach sideloaded apps to the Google Play Store.
3. useanad-blockertoblockads
Ever downloaded a really engaging app only to find that it displays annoying ads while you use it? The constant polling by theapphasbeenshowntoconsumealarge amount of battery. Ad-Away and Ad-Free are root apps that modify the hosts file located in /etc/hosts and block most (if not all) ads for you.
4. turn your phone into a portable Wi-fi hotspot
This is a handy feature for phones with a data plan. If you ever find yourself without an internet connection for your laptop/tabletandcan’tfinda datacable for your phone, you can tether your phone’s
internet connection by turning your phone into Wi-Fi hotpost. The network
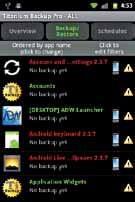
Titanium Backup can securely backup your apps and data
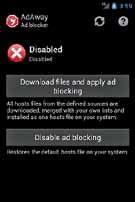
Block those annoying ads within your apps with Adaway

Wireless Tether can turn your rooted Android phone into a portable Wifi hotspot
will show up on your other Wi-Fi enabled devices like a regular wireless network.
5. Extendyourphone’sbatterylife
Smartphonesarenotoriousfortheirpoorbattery life and it’s not uncommon to have to charge your phone for a few hours everyday. Juice Defender can optimize yourphone’sbattery life by creating profiles and turning on/ off power-hungry settings when not in use. It can turn off your Wi-Fi/Cellular Data when the screen is turned off, or for a designated time of the day, or turn off the brightness and disable your GPS/Wifi radios whenyou’re phone is running low onbattery.
6. Backup or flash a
new Rom
This is one of the most compelling reasons to root one’s device, and ROM Manager is one of the most commonly used apps to manage your device’s firmware image or ‘ROM’. It can enable you to backup your complete system image and flash new custom versions of ROMs.
7. Browsethecontentsof your entire phone
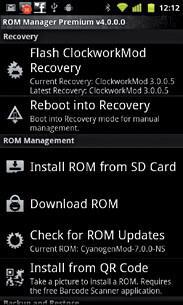
ROM Manager is an app that can install Clockworkmod recovery or flash a custom ROM for you
Root Explorer and ES File Manager are file managers that let you browse and edit the contents of your phone’s filesystem all the way down to the root level. You can move files around and even remove the bloatware that came pre-installed on yourphone.
8. set up a sambashare
If your and phone and computer are on the same wireless network, you can share your phone’s contents in the form of a Windows Share using Samba Share. Once set up, your phone will show up as a network device in Windows. Samba shares can also be set up on Linux/ OS X machines.
9. Enable region-specific apps from the google Play store
Many apps on the Play store are region specific and aren’t available to users from other regions. The Google Play Store is not available in many countries, which puts them at a huge disadvantage. The Market-Enabler is an app that can mask your phone’s location and make available to you the hundreds of thousands of apps that populate the Play Store.
10. use virtual buttons/swipe gestures for back/menu/home
Ifyourphonehashardwarebuttonsforhome/ menu and back, chances are these buttons might wear out over time and eventually stop functioning. Button Saviour, Virtual button Bar and Zmooth Root are apps that allow you to use on-screen equivalents of your phone’s hardware buttons and also ads some intuitive swipe gestures for back/menu andhome.
Whyshouldn’t iroot
my phone?
Like we’ve said before, rooting will almost certainly void your device’s warranty, and any damage that might occur to your phone during or after the rooting process will not be covered under the warranty. This is purely a statutory warning though, most modern rooting methods are quite safe and cases of phones being‘bricked’
Note
YoudoNOTneedto be rootedin order to sideload applications on your Android device.Just check the‘InstallfromUnknown Sources’ op- tion under Settings > Applications. Any application in the form of avalid.apk file can beinstalledonyour device by copying the file into your phone’s external storage, navigating to the file using a file manager and selectingthe .apk file.
while rooting are highly rare. Nevertheless, rooting is not for the faint at heart, and some root applications like SetCPU if misused, can wreck havoc on yourphone’sinternals and cause irreparable damage to the device. There is, however, some consolation in the fact that one can usually reverse the process and un-root a device, making it almost impossible to detect if it had been rooted earlier.
custom Roms in android
While rooting certainly extends your device’s capabilities to a large extent, your device is capable of a lot more. Instead of simply accessorizing your phone, why not give it a completely new wardrobe? For Android geeks, flashing a new firmware onto their devices is the ultimate exercise in customizing one’s Android experience. So just what is a custom ROM, why would one want to install (or ‘flash’) a new ROM onto his device and how does one go about the process? We’re here to show you.
In computer technology, a ROM stands for Read Only Memory, a section of memory that cannot be written into, and stores important firmware that is read from during the boot process. However, in the Android community, the meaning of a ROM is quite different, and the term is used to refer to the image of the OS that your phone runs. These ‘images’ are all based on the original (or‘stock’) Android system provided and open sourced by Google. Different developers add (or sometimes remove) components to tweak the performance of the device running Android. Android ROMs are treasured by the community as they unlock features previously locked down by the manufacturer (or at times, the wireless carrier),

Cyanogenmod lets you easily tweak your phone
remove crapware installed by OEMs and provide significant performance enhancements, giving a new lease of life to older devices. The process of installing an Android ROM is called ‘flashing’, and will in most cases void your warranty. Needless to say, one needs to exercise caution in attempting to flash a ROM. If done correctly though, a custom ROM can make using your device a joyride.
Custom ROMs for Android, as you might’ve guessed are a dime a dozen. There existliterally hundreds ofROMs, each boasting ofa particular feature suchas a lowersystem footprint, added featuresandapps, betteraesthetics in the UI, or a mixture of all three. These are analogous to Linux distributions, where the ability to openly modify and redistribute the source code has resulted in a number of flavours of Linux. Two of the most popular ROMs are Cyanogenmod and MIUI, where the former focuses on speed and featured, the latter sports a gorgeous interface and some beautiful stock apps.
Due to the wide range of devices with different internal hardware and screen sizes, there is no universal firmware when it comes to Android. ROMs are always catered to specific device models, and you can seri

MIUI ROM focuses on aesthetics, and is one ofthe most beatifulROMS around
ously damage your phone if you try to flash a ROM that isn’t tar- geted for your device. Having said that, the vast community support that Android enjoys means nearly every device out there has a alternative firmware for it, but if there isn’t one available for your device, you can request your favourite ROM’s developer for a port. While the exact procedure for flashing ROM varies from one ROM to another and even between devices, the generic method is somewhatlike:
DISCLAIMER: These steps are genericandareonlymeanttobeindicative in nature, to give readers an idea ofwhat theflashing process islike. They are by no means a complete guide on how to go about installing a new ROM for your device. For installation guides, pleaserefertothewikifor eachROM’s
website. All popular ROMs will provide elaborate installation guides for all supported devices, as the process varies from device to device. It is infeasible to give a detailed guide covering every device and ROM out there.
1. Backup your apps, contacts, settings andmessages.
2. Obtain the ROM’s firmware in a .zip file and store it in the root of your SD card.
3. Use ROM Manager, an app from the Google Play Store to flash Clockworkmod recovery, an alternative ‘recovery’ for your device. (The recovery partition has been discussed in an earlier section). Your phone needs to be rooted in order to do this.
4. Reboot your phone into recovery mode using the option in ROM Manager. Devices also come with a specific key combination for this purpose, but if you’re unsure (and don’t want to risk damaging your phone’s hardware buttons) we recommend you use this option.
5. Choose the ‘update from zip file’ option and select the firmware file that you had earlier copied into the SD card.
Somephones(likeHTC’snewerdevices) come with locked bootloaders than prevent you from installing a third-party firmware. There are tools available (HTC provides an official tool to unlock the bootloader) to circumvent this issue, though the process may not always be straightforward. Find out if your phone comes with any such restrictions before you begin the flashing process. If you’re running a rooted Android device, make sure you take a complete backup of your ROM using Clockworkmod’s Backup and Restore feature. Furthermore, devel
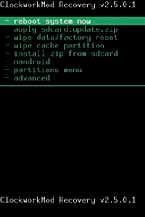
Clockworkmod is a powerful recovery image for your phone
opers usually make a list of all the fully working features as well as bugs in the build, read it and make sure that the ROM is stable enough for everyday use.
Android is truly a hacker’s dream, for it provides almost endless potential to tweak and mod your device to your heart’s content. You can improve existing features, add new ones or remove ones you don’t need, and truly customize your mobile experience provided you know what you’re getting into. Having said that, hacking into one’s Android device is not a necessity
– Android is a highly advanced platform with plenty of features right out of the box, along with a plethora of apps to try out from the Google Play Store. However if you’re someone who’s not content with ‘good-enough’ and is looking to extend your phone’s functionality, Android should be your platform of choice.
38
Chapter#5
Jailbreaking
iOS
A
pple’s mobile operating system, iOS, powers more than 300 million devices all over the globe and yet you’d rarely hear about any major security threat, malware or virus for the platform in the wild, nor would you have ever heard about an
anti-virus software for the iPhone.
The reason iOS has been safe from all sorts of malware and viruses is becauseAppledesignedtheplatformwithsecurityatitscore,leavingbehind baggagefromthetraditionaldesktopparadigmofcomputing.BecauseApple had the opportunity to start from scratch with iOS, it abandoned a lot of desktop metaphors people were familiar with. This move did attract the ire of the tech community, but made things a lot easier for the average user.
One of the trade offs Apple made is that it disallowed any unapproved software to run on iOS. This was a concept unheard of in the decades of the personal computing era that preceded the iPhone, but Apple pulled it off
by creating a vibrant iOS developer community, and a centralized, curated repository of applications that spanned across almost all categories. Apple called this repository the “App Store,” which presently hosts more than 6,50,000 applications.
Apple requires all apps on the App Store to follow a certain set of guidelines. These guidelines include the obvious “your app can’t steal private data,” “install backdoors into the user’s device” and other similar security measures. But these guidelines also include clauses that prevent certain kinds of applications to appear on the App Store at all. Apps that customize the look of iOS, replicate functionality provided by Apple, allow command line access to the OS, provide ways to tweak the system are all disallowed into the App Store which means that users don’t get access to these apps.
Well, most of them anyway. While Apple’s controlled ecosystem works really well for most average users, power users find this to be a dealbreaker. Fortunately, there’s a way for these power users to work around Apple’s
restrictions and gain complete access into their devices to do absolutely whatever they want. This is established by a method called “jailbreaking.” JailbreakingdatesbacktotheintroductionofthefirstgenerationiPhone. Back then, the App Store didn’t even exist and the only apps that you could run on your iPhone were the ones that shipped with it. Hackers found ways to getaccess to the operating system and allow the installation of third party apps, providing a glimpse into the future of the iOS ecosystem.
Technically, jailbreak software exploits certain holes in iOS to gain “root” access into the system. Once “root” access is established, the OS is opened up and there are no restrictions at all.
Jailbreaking also has a closely related process, unlocking. Apple generally partners with carriers to sell the iPhone, and in many cases the device is locked to the carrier’s network. Unlocking, as the names suggests, lets the iPhone run on any carrier’s network as long as the carrier’s bands are supported by the hardware.
So let’s dive in, and help you unlock the full potential of your iPhone! Jailbreaking, although meantfor powerusers, isa really easy process. The tools required for jailbreaking are easy to use and pretty quick. They vary depending on the version of iOS that your phone runs though. Some jailbreak tools even require you to connect your iPhone to your PC/Mac every time you boot up. These are called “tethered” jailbreaks, and as you can imagine, introduce a bit of difficulty when you’re away from your computers for a few days.
We’ll detail the process for jailbreaking the latest release of iOS -- iOS 5.1.1. Fortunately, this jailbreak is untethered, which means you would not have to run to your nearest PC to restart or switch on your iPhone.
The tool required to jailbreak an iOS 5.1.1 device is called “Absinthe,”and is available for the PC, Mac and Linux. Although the screenshots show a Windows version of the tool running, instructions for Mac and Linux are the same.
Before proceeding to the actual jailbreak instructions please make sure you are on iOS 5.1.1. You can do this by opening the Settings app, navigating to General>About and seeing the value in the “Version” field. In case you are not on iOS 5.1.1, fire up iTunes and upgrade your iPhone or better still, update iOS over-the-air by navigating to General>Software Update in the Settings app.
Once you’re done with that, as a measure of precaution, back up your iPhone to iTunes or iCloud depending on what preferences you have set. During the whole process, make sure that your iPhone remains plugged in to your Mac or PC. Also fair warning, as you might have guessed, Apple isn’tvery fond of jailbreaking, and if you take a jailbroken device to its stores they might refuse to address your problem. You might void your warranty. But once you remove all traces of a jailbreak by a clean restore, your phone should be the same as anyone else’s. We’ll also give you instructions on how to “clean restore” your iPhone.
Step one:
Download Absinthe from the following URLs, depending on your OS. Windows : http://dgit.in/KRASYb
Mac : http://dgit.in/MK2lZj
Linux : http://dgit.in/LbnQOI
Step two:
Once you’re done downloading the file, install it at your favourite location. Windows users, unzip the file, navigate to the unzipped location and
simply click on the Absinthe executable file. It should pop up a command
line window with lots of text scrolling. Let it do its thing, and terminate by
itself. Once it’s done, you’ll notice another folder in the same directory as
the executable. Go into thisfolder.
Step three:
Launch the Absinthe executable file, and you should be presented with a screen that looks something like this.
Note: Windows users should run Absinthe withadministratorprivileges. Right click the file, switch to the “Compat- ibility” tab from the top and enable the “Run this program as an administrator” check box. Additionally, check the “Run this program in compat
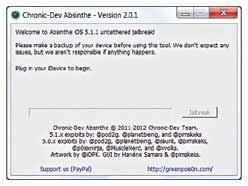
The Absinthe tool allows you toJailbreak your iOS 5.1.1 device.
ibility mode” box and select Windows XP from the drop down.
Step four:
Connect your iPhone to your PC/Mac via USB and make sure you don’t have passcode lock enabled. If you do, you can temporarily disable it, and enable it again once you’re done with the jailbreak process. Absinthe should detect your iPhone and display the firmwareit’s on. Tobe double sure, check that the firmware is 5.1.1.
Step five:
It’s a pretty easy ride if you’ve made it till here (not that the earlier steps were too difficult). Hit the “Jailbreak” button. Absinthe should now start the jailbreaking process, updating the progress bar and taking you through the various stages of the process. Here are the stages:
1. “Beginning jailbreak, this may take awhile”
2. “Sending initial jailbreak data. This may also take a while” 3. “Sending initial jailbreak data. Your device will appear to be restoring
a backup, this may take a while”
4. “Waiting for reboot...not done yet, don’t unplug your deviceyet!”
5. “Waiting for process to complete”
6. And finally when the whole thing is done “Done, Enjoy!” Once the last message appears, you can safely unplug your device.
Step six:
Although your iPhone has been jailbroken, there’s one more thing you need to do on your device. Open up “Cydia” on your iPhone (if you can’t find it on your homescreen, search for it) and let it complete its processing. It’ll also ask you if you’re a “User”, “Hacker” or “Developer.” If you don’t know what to choose, then you should choose “User,” besides you could always change this in the settings. If you’re connected to WiFi or 3G Cydia should present a screen like this.
Cydia is the App Store of the jailbreak world. Unlike Apple’s App Store, Cydia doesn’t have any restrictions, and you can install all sorts of
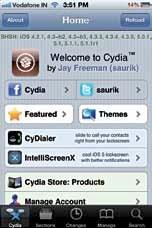
The Cydia storefor jailbroken devices
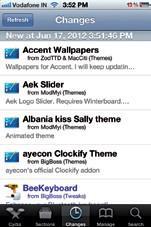
The‘Changes’taboftheCydiaapp
apps, tweaks and themes that wouldn’t have made it to the App Store due to guideline violations.
Tapon the “Changes” tabatthe bottom, and hit “Refresh” at the top if you don’t see a list like this. If you see any “Essential upgrades” dialog, hit the upgrade button and proceed as Cydia says.
The “Sections” tab categorizes allthat’s available on Cydia into various sections for easier discovery. The “Changes” tab is a list of all tweaks arranged in reverse chronological order depending on when they were added or updated. The “Manage” tab lets you manage installed software and also add “Sources.” Sources are places on the web where this software is hosted. Youdon’t need to worry about this much since Cydia already has a number of sources added by default. “Search” is of course to find by name. Many tweaks, afterinstallation,mightpresentabuttonto “respring”orrestartyouriPhone.Thisisto ensurethattheinstallationgetscompleted without any problems.
Also note that unlike apps on the App Store, many installations from Cydia mightnotaddanicontoyourhomescreen. When youstartlookingatthelist,you will very likely be overwhelmed by the sheer quantity of apps you could install, which is why we tell you some of the best ones you should install below.
best apps and tweaks on Cydia
Jailbreaking is all about taking control of your device, which is why many of the apps listed below are focused more on changing the way iOS behaves and l rather than isolated applications you would find on the App Store.
SbSettings
If you’ve used an Android phone, you’d know how annoyingly long it takes to toggle settings in iOS. As opposed to Android, where the toggles are present right on the home screen, in iOS they’re buried inside the Settings app. SBSettings solves this problem by making these toggles just a swipe away in a nice customizable window. The way you bring up the window on your screen is by swiping horizontally across the status bar at the top. It comes preinstalled with a few themes, but you can always install more by searching for “SBSettings themes” on Cydia. You can also remove or add more toggles from the
 SBSettings allows easy access to Settings
SBSettings allows easy access to Settings
“more” icon in the SBSettings window. As an added bonus, the toggles are added to Notification Center as well, which means you can pull down the Notification Center as you would normally and disable/enable WiFi, Bluetooth, 3G from right there. (You can enable this behaviour by hitting the “more” icon) Pretty handy,right?
Winterboard
Many iPhone users, fond of customising their devices, have gotten bored of the same look and feel of iOS throughout the years. Fortunately, in Jailbreakland, you’re free to customize each and every part of iOS. WinterBoard is an application that helps you change the look and feel of iOS entirely, right from homescreen icons, lock screen, system sounds to fonts, the dock and a lot more. A few themes come bundled with WinterBoard, and there are a lot of them on Cydia, both free and paid.
iFile
One thing missing from iOS is filesystem access. iOS intentionally tries to abstract away the file metaphor, which means that in many cases
iFileisahandy FileManager foriOS
F.lux
when you do want file access, you’d be left crippled.
iFile is an excellent file manager app
(like explorer.exe in Windows or Finder on Mac) that gives you full control over your filesystem, letting you copy, move, and open almost all files residing on your device’s storage. It also has a lightweight webserver built in, which lets you wirelessly transfer files from your PC or Mac via a web browser. The app is shareware, which means that a few features are not available in the free version. You can pay $4 to buy or use the free version with restrictions.
If you have ever used your iPhone in the middle of the night, in a dark room, you know how uncomfortable the bright light is to your eyes. F.lux, a name you might be familiar with from the desktop, adapts your iPhone’s display by changing its colour as per the time of the day.
activator
Activator is a tweak that gives you full control over the behaviour of hardware buttons and gestures throughout the OS. You can assign actions to various input methods like double tapping on the status bar, slide-in gesture from the edgeof the screen, volume buttonpress, mute button toggle, device shake and a lot more. The actions include showing music controls, locking the device, toggling settings, bringing up the Tweet dialog, or even simulate the press of any hardware button.
If your home button is unresponsive (a common problem with iPhones), you could define any button you don’t use commonly, like the volume down button, to act as the home button. Another handy one is to tell Activator to bring up the multitask app switcher when you slide your finger up from the bottom of your phone’sscreen.
Five icon Dock
Squeezes in five app icons in the dock, instead of the regular four. There are complementary Five Icon Switcher, and Five Icon folder which do the same thing on other elements of the homescreen. There’s also a tweak called “FiveIRows” that adds an extra row to the 4x4 grid of icons on the homescreen.
SpringFlash
In many situations, the iPhone might also double up as a torch. While there exist apps on the App Store solely for this purpose, it takes a lot of time to find the app on the homescreen and wait for it to launch. SpringFlash lets you assign a physical button that turns up your iPhone’s camera LED when you press it.
infinifolder, infiniboard
These are two separate tweaks, costing $1.99, that enable infinite scrolling, one in folders while the other on the homescreen. This removes the limit to the number of icons a homescreen or a folder can have.
Zephyr
iPads on iOS 5 have multitouch gestures enabled, so that you can pinch with four fingers to close apps and return to your homescreen, swipe left and right with four fingers to switch between apps. Apple didn’t choose to add this to the iPhone, presumably due to the lack of screen real estate. Thanks to a jailbreak tweak named “Zephyr” you can easily multitask with gestures on your iPhone. It’s available for$4.99.
intelliScreenX
TheiPhone’slockscreenisreallystatic,andyoucan’treallydomuchfrom it. It was only in iOS 5 that the Notification Center was introduced, and although it did improve the situation a bit, it still didn’t fare very well in terms of functionality.
IntelliScreenXisajailbreaktweakthatsuperchargesyourlockscreen, sothatyoucouldgetavariety ofthingsdonewithoutevenunlockingyour phone.HereareafewscreenshotsofthetweakrunningonaniPhone,and as you see it adds tons of information including weather, Twitter, Facebook, mail and RSS feeds. It also gives you the ability to message your friends right from the lockscreen.
Intel li Screen XletsyouputallofyourimportantfeedsrightonyouriOSdevice’slock screen
The tweak can be downloaded as a free 3 day trial, and if you like it (you will) you can purchase it for $9.99 (a bit expensive, but worth it considering the time you’ll save).
FaceTime over 3g
Although FaceTime is pretty awesome, it works only on WiFi which means you always have to be within the active range of a WiFi router to video call someone. With “My3G” you can remove this restriction and FaceTime anyone as long as you have an active 3G connection. Apple’s added FaceTime over cellular in the upcoming iOS 6 release, but it’s only for iPhone 4S and iPad 2 and higher, which means iPhone 4 users would still be relying on this tweak. It’s available as a free trial and can be purchased for $3.99.
OpenSSH
If you’re a Linux fan, you’ll love this. You can install an SSH server in your iPhone, letting you remotely gain access to the entire iOS filesystem as well as getting a full blown Unix shell. Note that you won’t see any visible changes right on your device, you’ll have to install an SSH client on your desktop. To login as “root” your password would be “alpine,” make sure you change it using the “pwd” command to avoid others remotely logging into your device. Also, gaining root access comes with a lot of responsibility, don’t go messing around with system files or you’d end up with an unusable iPhone.
There are of course a lot more tweaks and apps that you can install from Cydia, but be carefulbecausea few might conflict with tweaks you’ve already install or refuse to work at all with the current version of iOS.
Veency
Veency is a VNC server for your iPhone. In case you don’t know what that means, it lets youcontrol your iPhone’s screen, feed it inputs right from the comfort of your Mac or PC.It’snotreallyanessential feature, but you never know when you might need it. You’ll, of course, havetoinstallaVNCclient

Veency running on aJailbroken iPhone
on your Mac or PC to talk control see your iPhone’s screen and control it.
recovering from a bad tweak
It’s not impossible to mess up your phone by installing a bad tweak. What’s worse is, since many of these tweaks mess with OS internals, they might not let you go beyond the lockscreen. Fortunately there’s a way you can gain access to Cydia and uninstall the broken tweak or app.
While rebooting your iPhone, hold down the volume up button, and your iPhone goes into “Safe mode” where all jailbreak tweaks are disabled. You can now open up Cydia, and remove the app from the “Changes” tab at the bottom.
restoring to Stock OS
This is required if you’ve inflicted damage upon your iPhone and want to take it for repairs to your nearest Apple Store employee, who of course frowns upon the idea ofjailbreaking.
It’s not really that difficult to “unjail- break” and get back to stock iOS. You just have to download the latest firmware for your iPhone, links of which you could find at http://www.felixbruns.de/iPod/ firmware/.
The update weighs in at around 700MB, after which can fire up iTunes and restore your phone. You do this by pressing the “Shift” key and clicking on the “Restore” button, after which a file dialog should pop up. Point iTunes to the .ipsw file you downloaded, and your iPhone should start restoring to stock iOS. Make sure you keep your iPhone plugged in to your PC throughout the process, and that you don’t restore from backup, since it might contain a few remnants from the jailbreak.
The jailbreak community is an active one, with developers creating awesome new apps and tweaks on a daily basis. While this guide is in no way exhaustive, it should help you enter the world of jailbreaking and unlock the true potential of your iPhone.
Common
jailbreak
jargon:
Stock oS:
A clean non-jailbroken OS
jailbreak:
Theprocessoffreeingup your iOS device from the restrictions imposed by Apple
Unlocking:
Making your carrier locked iPhone run on other networks via software tools
Cydia:
AnAppStoreforjail
break apps and tweaks
mobileSubstrate:
Aframeworkthatworks behind the scene to make allsystemtweakswork.
Chapter#6
49
Unlocking
WindoWs Phone
T
he latest version of Microsoft’s mobile OS is kind of a mixed bag. Though it got rave reviews for its interface, the platform itself hasn’t been very popular. Even in terms of “hacking” or “jailbreaking”theplatform,theresultsarefarfromsatisfactory.
Depending on your device, your jailbreaking experience can be a walk in the park or a painful, almost impossible experience.
Why bother?
What are the advantages? For starters, you get to side-load apps that are not (or will not be) available in the Windows Phone Marketplace. These include Instant Messaging clients, file managers, screen capture utili
ties and the like. You will also be able to download apps from other OEM marketplaces (such as apps available only on Nokia devices on a Samsung device). One of the biggest advantages of course, is custom ROMs. Why use a custom ROM? While Microsoft conscientiously releases updates to device manufacturers, the manufacturers (or the notorious wireless carriers) themselves are not so considerate and have been known to take almost a year (AT&T for example), to release updates to their devices. Custom ROMs usually include these official updates and are available to you right after they have been officially released by Microsoft. They can also add extra functionality such as replacing the default Bing! search with Google, or address common issues such as the lack of a comprehensive task manager, instant messaging client etc.
identify your device
As it stands, yourWindowsPhone device will fall into three main categories: Ω
First generation devices which are fully updated: Unlocking these devices is a bit difficult, but can be managed if you’re careful and follow the right instructions. These devices are usually not as powerful as the second generation devices and the best indicator is the presence of a 1GHz processor.
Ω
Second generation devices:Most of these devices are currently impossible to jailbreak. You can get a developer unlock code from Microsoft by paying$99though.Allofthesedevicesusuallyruna1.4GHzprocessor with 512MB RAM and include all current generation devices such as the Nokia Lumia series or Samsung Omnia W onwards.
Ω
Windows Phone Tango devices: These devices are an under-powered variantofthesecondgeneration devicesandalsocannotbecracked at this time. Microsoft has announced a Tango update for all Windows Phone devices though, and custom ROMs featuring this update are already available.
To check which version of Windows Phone you’re running, go to
Settings->about->more info and check your OS version. The current, hackable version is 7.10.8107.XX which you should be running if you’ve updated your device. If you’re running 7.0.7008.XX or earlier, you have a first generation device that is not upgraded. it’s recommended that you upgrade to the latest version if you are not completely dedicated to messing with your phone. Before we begin hacking though, some important notes.
important notes:
Ω
There is no fixed method to unlock your Windows Phone device, and methods vary from device to device, given the myriad of different Windows Phone devices currently available. Wewon’t cover all the unlocking methods individually, but will cover only the most popular techniques that should work on most, but not all Windows Phone devices.
Ω
Read all the instructions carefully and only proceed when you have thoroughly understood them.
Ω
Check your phone’s OS version, in fact, double-check it. Trying to unlock the wrong version can result in your device getting bricked.
Ω
When downloading a custom ROM, ensure that the ROM supports your phone, otherwise your device can be bricked.
Ω
Make sure that all the required software has been downloaded beforehand and have been installed asspecified.
Ω
If you have frequent power-cuts in your area, make sure you have a UPS, or are unlocking your device using a laptop, or are doing this at a time when you know you have uninterrupted power.
Ω
Make sure your phone’s battery is fullycharged.
Ω
Take a complete backup of all the data on the phone as some of these hacks involve a complete format of the phone’s memory.
Ω
Most importantly, ensure that you are wide awake and in your senses.
What you need
Here is a list of prerequisite software that you need to have installed. Ω
Microsoft Zune desktop software (http://dgit.in/MLxQPj)
Ω
Windows Phone SDK(http://dgit.in/NP2IUn)
Ω
Chevron WP7 hack and certificate (on the Omega DVD)
Ω
A custom ROM of your choice. (if you want to indulge in some modding action)
In general, there are two methods of unlocking your device. The first
method is the “interop” unlock, which will allow you to side -load apps without the penalty of having to mess with your ROM and risking a bricked device. The second method is a true jailbreak, but only meant for those who are brave of heart and don’t mind risking their devices.
The actual process of jailbreaking is nearly identical for all devices. We will provide step-by-step instructions for Jailbreaking a Samsung Focus v1.3 device here, which is applicable to almost all jailbreak ready Samsung devices. The jailbreaking of HTC devices is much more complicated though.
Jailbreaking samsung devices
For this tutorial, we will show you how to jailbreak an upgraded, first generation Samsung device. This includes the SamsungFocus(v1.4orearlier)andthe Samsung Omnia 7.
Window Break (interop or developerunlock)
The simplest hack, specifically for Samsung devices, is the “Window- Break” project. To do this,
Ω
Set your browser’s Website preferences to “Mobile Version”. To do this open your browser, open settings and select “Mobile version”.
Ω
Head over to http://windowsphonehacker.com/windowbreak
Ω
Tap on“WindowBreakMe”, a new page will open.
Ω
Tap on windowbreak.xml, you will be greeted with a blank page.
Ω
Open the diagnosis window by dialing ##634# in the dialer.
Ω
Enter #9908# in the app that opens, this will run the GPRS manager.
Ω
Tap the dropdown menu and tap “windowbreak” and hit“save”.
Ω
Wait a few seconds till you see a message in the text box below.
Ω
Restart the phone.
Ω
Your phone is now developer unlocked!
TheSamsungFocuscanbeunlocked using theinterop method shown here.
The true jailbreak
Time for some advanced stuff. To hack your Samsung Focus, you need to first determine the “HW Version” number of your device. The process for the Samsung Omnia 7 is similar. You need to do this because there are different ROMs for different versions so please check before proceeding. To do that:
Ω
Dial ##634# in the dialer.
Ω
Enter #32489# in the “Diagnosis” menu that pops up.
Ω
Press the on screen “back” button 4
times till you see a “Main Menu” Ω
Type“2”to select“VersionInformation” Ω
Type “2” to select “HW Version” Ω
Type “1” to select “Read HW Version”
Ω
You will now see a message on screen saying something like “HW Version: Rev 1.X” where X is your version number.
Before you begin your jailbreak, download the following software:
Ω
DFT SammyRainbow.zip from http://
dgit.in/M7nNZC
Ω
A custom ROM from http://dgit.in/
MhkDim.
The entire page is in Chinese so remember to translate it into
English (unless you speak Chinese of
course) and make sure the default language for the ROM is English. Read
carefully what each ROM has to say
about itself and you can then decide
for yourself which ROM will best suit
your needs.
Ω
Download and install ActiveSyncfrom
http://dgit.in/MuLSXf
Now that you have everything and have made sure you read and understood everything in “Important Notes”, you may proceed.
Ω
Extract the files from the DFTSammyRainbow.zip file that
you downloaded.
Ω
Run the DFT MAGLDR installer. Ω
Put the phone in “Download” mode.
To do that:
• Turn off yourphone.
• Press the Volume up, camera and power buttons simultaneously.

Diagnosis menu
The recovery screen on the
Samsung Focus
Ω
Connect your device to the computer via USB.
Ω
Select your device from the DFT MAGLDR installer screen. it’s paramount that you select the right device, there is a very good chance of rendering your device completely unusable otherwise.
Ω
Proceed with the installation.
Ω
When the installation is successful, disconnect your phone from the computer.
Ω
Put your phone into “recovery” modeby:
• Turning off your phone and then pressing the Volume down, Camera and power buttons simultaneously.
Ω
Press the back arrow on your phone at the screen that follows. Pressing the Windows key will format the device so be careful.
Ω
Select the custom ROM that you decided on, extract the files and run the DFT installer for that ROM.
Ω
Check the device and its version again (at the install screen) and ensure that it’s the same as that of your phone’s.
Ω
Make sure ActiveSync isinstalled.
Ω
Connect your phone to the PC while still in recovery mode.
Ω
Allow the MAGLDR device driver to install.
Ω
The installation might fail at this point but do not worry, just restart the installation again. This happens if when the MAGLDR driver fails to install on time but is only a minor issue.
Ω
You should see an installation bar on your phone, if you don’t, start over.
Ω
When the installation is completed, reboot your phone by removing the battery and reinserting it, if it doesn’t happen automatically.
Ω
Restart the phone and put it back into recovery mode.
Ω
When prompted, press the Windows logo on your phone to formatit.
Ω
Thephone willrebootaftertheformatting processandwillbeinitsinitial factory state. Reset all your settings, verify that the phone is working and you’re good to go. You are now the proud owner of a properly rooted, jailbroken, windows phone device.
Ω
Note that the final rebooting process might take a while so don’t panic if it’s taking too long or if the screen appears to be frozen. If it stays like that for half an hour or more however, well, you can at least claim that you have an unusual taste inpaper-weights!
You can now freely side-load apps, follow this link to get more information and some free apps http://dgit.in/KUsxhw
and/orparticipate in the app
development process.
 Jailbreaking hTc devices
Jailbreaking hTc devices
When it comes to HTC devices, they have what is probably the most versatile device currently available, the HTC HD2. This phone can run Android, Windows Phone Mango, Windows Mobile 6.5 and even variants of Ubuntu and Meego. If you’ve got this phone, you’ve hit the jackpot as far as rooting and custom ROMs go.
HTC also manufactures the only second generation Windows Phone devices to be jailbroken so far, the Radar and Titan.
The rooting of HTC devices is far more complicated than that of Samsung devices and is in fact, beyond the scope of this book, probably requiringafast-trackofitsown.ThebasicpointstorememberaboutHTC devices are theses:

The HTCHD2 is one of the most hacker-friendly phones around
Ω
HTC devices are extremely sensitive to the jailbreak process.
Ω
Each device has a specific MID, which must be noted before you proceed.
The method is different for each series of MIDs.
Ω
The reason behind the importance of MIDs is that each device has a
different Secondary Program Loader (SPL) that controls the bootloader.
This SPL must be replaced with a cracked SPL, which, if not done correctly, will result in a completely bricked and un-recoverable device. So,
proceed with caution.
Ω
Custom ROMs are available at the DFT site mentioned earlier. (http://
dgit.in/MhkDim)
Ω
Detailed instructions can be found at http://dgit.in/MyMNno.
Make sure
that you read the instructions carefully to avoid bricking your device.
Chapter#7
57
CraCking
BlaCkBerry
A
lthough BlackBerry is generally regarded as a very secure platform (and your company’s IT department’s platform of choise), there are ways to crack the security measures built into BlackBerry devices and gain control of the device, or as
Unix geeks would say, gain “root” access.
Hacking the BlackBerry isn’t as popular as, say, jailbreaking an iPhone is, presumably due to the large corporate user base of these phones. Hopefully the upcoming BlackBerry 10 OS might just ignite the interest of the hacker community, since it’s largely based on the same OS as the PlayBook, which has already been scrutinized and rooted by hackers.
Most operating systems are based on the Unix architecture, which have a superuser named “root” who has the liberty to do literally anything in the OS while other users that have limited privileges. Manufacturers generally
do not allow users to login as “root” as a safety precaution, but people who want complete control over their device can figure a way out.
DingleBerry
Oddly named “DingleBerry” this tool lets users gain root access into their PlayBooks. This process is also called “jailbreaking” at times.
While this might sound like a trivial task to ordinary users, the techniques to gain root access into mobile devices is quite complicated, mainly
due to the security measures put in place by manufacturers.
DingleBerry has been around since late 2011, and has sincethen undergone 3 major updates, with a fourth one due very soon. As of now the tool doesn’t support the latest version of PlayBook OS, which is what the fourth major release would probably address.
The tool makes the rooting processreallysimple,requiringjusta few clicks from the user’s end to gain unfettered rootaccess to a PlayBook.
Afterthetoolcompletesexploiting vulnerabilities in the PlayBook OS in order to gain root access, it opens up an SSH port on the PlayBook and enables remote “root” login.
Gaining root access opens up a wide array of possibilities, like adding support for USB devices, adding support for services that were blocked on the PlayBook , customizing the interface and a lot more.
Adding support for USB thumb drives is particularly handy, due to the ease of transfer, and, of course, the extra storage. (only works in the US though).
Since rooting exposes the entire filesystem, adventurous users also got hold of the locations used by the system to fetch icons and other resources such as fonts, and managed to alter the resources and implement a crude way of theming the PlayBook OS.
Of course if rooting doesn’t bring any big changes for the end user, it’s not useful enough. So how about installing the whole Android Market (now called Google Play) onto the device?
A BlackBerry Playbook might not be the greatest tablet in town, with the limited number of apps available on AppWorld, but it turns out that the device can easily access the thousands and thousands of apps available on the Android Market.
While RIM did add the ability to run Android apps on the BlackBerry PlayBook with the 2.0 update, it still requires developers to manually upload their apps to the BlackBerry AppWorld, only after which users can install these apps. The extra steps required didn’t enthuse developers much, and only a fraction of the apps on the Android Market have made it to the BlackBerry AppWorld.
What’s better than that? Having the whole Android Market on your device, of course.
Strictly speaking, BlackBerry devices are very prickly when it comes to hacking. Extreme care is required, for instance, the Android Market installation process was something like this:
Ω
On the PlayBook OS 2.0, install any Android app specially packaged
for the PlayBook.
Ω
DownloadCyanogenMod’s Google Apps package, and copy a bunch of
files from that package (which includes the Android Market) to a system
folderonthePlayBook.ThewholethingisdoneviaanSCPclient,which
remotely logs in as root into the device.
Ω
Launch the Android app installed in the first step, delete a few files, kill
a few processes and run a particular script.
Ω
One should then be able to launch the Android Market, after which app
installs become a breeze.
Since the process involved messing around with system files, it wasn’t too hard to alter the wrong files and have a broken OS, which could only be fixed via a restore.
There’s another way to install Android apps on your PlayBook, but for that you need to have the .apk file as well as a few other tools installed on your PC. The .apk file needs to be repackaged into .bar, and also needs to be signed after which it can be side loaded into a PlayBook in developer mode. It’s a fairly involved process, much more complicated than simply installing Android Market.
If the vast amount of Android apps weren’t enough, a developer even foundawaytoruniOSappsonaPlayBook.Thedeveloper,whogoesbythe name of“Businesscat2000” on Crackberry.com
Forums managed to provide the frameworks that iOSnormally provided and got these apps running.
As forthe technical details, this is what “Businesscat2000” had to say:
“The CPU isn’t emulated on Playbook (though it is on Windows). It works verysimilarlytohowWINEworkstorunWindowsapplicationsonLinux. Theappbinaryismappedintomemoryandimportsareresolvedtopoint to my own implementation of the various APIs needed. iOS actually uses afewopen APIsalready,which Playbooksupports justaswell([Open]GL ES, and OpenAL). The bulk of the work has been in implementing all of theobjectiveCclassesthatarerequired.TheARMcodeoftheapplications run as-is - the armv6/v7 support on PB/iDevices are pretty much identical, and the code is designed to run in USR mode. No SWIs, GPIO accesses or any of that kind of shenanigans.”
HepostedavideoofiOSappslikeSuperMonkeyBall,TinyTower,Sushi Cat, Galcon, iFart and a few others running on his PlayBook.
Since the task of getting iOS apps to run on a PlayBook is really hard to believe, other users questioned the legitimacy of the software and raised doubts. But after running a variety of iOS apps, including some that were exclusive to the platform, people were finally convinced.
Although the iconsdon’t showup on the PlayBook homescreen, the emulation software is capable of loading up to 10 iOS apps at once. Also the apps have a resolution of only 480-by-360-pixels. Presently “Businesscat2000” says that the software isn’t fit for public consumption, and would only be released after it is polishedenough.
DOS and Windows
It turns out that DOS, Windows 3.11, Windows 95 and 98 are also quite simple to run on the BlackBerry Playbook. Not going into details of why one would want the ancient Windows 95 running on their cutting edge PlayBook hardware. To do this, the DOSBox emulator needs to be installed, which lets the user run these Operating Systems on the PlayBook with the help of a Bluetooth keyboard.
Once DOSBox, a well known DOS emulator, is installed on your PlayBook, you can run old school games like The Lion King
and Prince of Persia.
The emulator also gives you access to a DOS shell on which you can run your favourite DOS commands and access thefilesystem.
Once DOSBox is installed, a Windows 95 image can easily be mounted and loaded into the system. Once Windows 95 is booted up, you have access to the familiar, albeit old, Minesweeper, Solitaire and other Windows 95 goodness.
Dingleberry, the origin of all these hacks, hasn’t made RIM very happy, as you would expect. In a statement on its official blog, RIM discouraged the use of these tools, and said that jailbreaking your PlayBook would void its warranty.
62
Chapter#8
Flashing
symbian
C
onsidering the fact that symbian has by far not made it into any peculiar list, be that of cool apps and games or developing apps for your OS, you probably might be surprised to see it here. But all’s not lost for this ‘endangered’ OS. You can hack your phone
and override the permissions provided by Nokia by either ‘flashing’ your phone, or by using ‘Norton Hack’ method. Besides helping you install loads of apps and games, you can flash or hack your Symbian Belle device to get cool widgets, custom icons, plenty of awesome theme effects and other such things which for reasons known only to Nokia, have not been included their default firmware, or are availablein limited numbers on their Store. So if you guys are tired of being jealous of your ‘Android’ or ‘Apple’ friends showing off their customization options, read on to know how you can compete with them, if not beat them.
advantages
That’s an obvious question for users who are not much into flashing their devices and hence, run the risk of bricking it. The answer is quite simple- exploring your phone to maximum possibilities. Flashing is basically ‘replacing’ your firmware files with those which have better utilisation of your phone’s resources. This gives following important advantages
Ω
Increase your phone memory– The most common problem on Symbian Belle devices today, especially Nokia N8, is its low phone memory. Though, unlike Android, you can install your apps on memory card, but the browser cache, i.e. every time you use your default browser, it stores browsing information on phone memory and some data files from apps and games that you install on your phone, hogs up your internal memory. This in turn makes your phone slow. Flashing is a good way to free up all device memory and make it faster and smoother. Also, mods (modifications) are available through which we can change the browser cache memory to external memory card and thereby save space.
Ω
Theme Effects– Symbian has got wide range of theme effects, but unfortunately, not by default. A third party software named ThemeFX lets you change them with just a restart. But, you need to hack your phone to install that software. Another way to do this is flash your phone with a Customised Firmware (CFW). There are many available on net. The makers of these firmware have either preinstalled fancy effects or they let you choose your own. Theme effects are instantly noticed and appreciated when you or your friends use your phone. It certainly helps improve your phone’s UI.
Ω
New widgets– Symbian has got very limited number of widgets when compared to Android. Also, the customization options, i.e. skins,size etc of these widgets cannot be changed. But there are plenty of widgets outside the Nokia store which gives your phone a completely new look. These include widgets of clock, mail, RSS reader, weather and many more.
Ω
Startup sound and logo– If you are tired of those Nokia hands you’ve been seeing from time immemorial, and are eager to get your own startup sound, then with hacking, that is easily possible. If you are planning on gifting a mobile to someone, personalizing startup sound of your phone will surely add spice to your gift.
symbian hacking
Tools you’ll need
There are a wide assortment of tools available for modifying or “cooking” your Symbian firmware. Here are some of the most popular ones. You’ll only need to use a few tools out of these depending upon the task to be accomplished.
Ω
NaviFirm+
The very first thing you’ll need is your firmware if you wish to “cook” it and NaviFirm gets it for you. It has an extensive database and you’ll find the latest firmware for your phone as and when released. Also it downloads all the files from official Nokiaservers.
Ω
Notepad++ along with the Hex Editor plugin A Hex editor allows you to modify binary files and since Notepad++ happens to have a plugin for one, one might as well go in for it. If you wish to use a separate tool then any Hex editor like XVI32, HxD, Hex Workshop etc. can get the job done.
Ω
Nokia Cooker
It allowsyou to modify the contentsof yourfirmware to help create a custom firmware. It can modify UDA, CORE (only ROFS1 data), ROFS and ROFx data. One can add/remove content from the firmware using this tool. The safest option is to modify the UDA data, the rest are a bit risky given that the likelihood of bricking your phone increases unless done properly on CORE, ROFS and ROFx(ROF2, ROF3, ROF4, etc.).
Ω
Phoenix Service Software
Nokia’s very own software that is used to “flash” or write the firmware onto the EEPROM(flash memory). It requires a dongle to authenticate the software though everywhere we looked we found the cracked version of the software being used, so use with caution. It is feature rich and frequently updated as and when Nokia releases new phones.
OR
Ω
J.A.F. by Odeon
Just Another Flasher is one of the many third party tools available for flashing DCT3, DCT4, BB5 phones. Though now defunct, it still works great, though newer phone models are not supported and you’ll still have touse Phoenix Service Software for that. And if you are using 64-bit Windows then get the proper 64-bit drivers, otherwise do not attempt flashing using this software.
Ω
Symbian SDK
Needless to say the SDK allows you to write your own applications that you can install on your phone. Though programming is the hardest way of getting into your phone it is also the most fulfilling.
Ω
Carbide.ui
Not a hacking tool but one that allows you to build your own theme and UI for all Nokia Symbian devices.
Ω
Nokia Firmware Editor
Another software to modify ROFS2 and UDA firmware files. Pretty useful for removing the built-in applications.
Ω
Sis Contents/SIS Explorer/SISware
Nifty tools to extract and create SIS packages for different Symbian versions.
Ω
Petran GUI
Included as part of Symbian SDK to convert PE (Portable Executable - Windows executable format .dll & .exe) files to Symbian OS executable format.
Ω
Mediabar Editor
A tool specifically for editing the Mediabar present in phones like Nokia 5800.
Ω
File format convertors
You’ll need a host of file format converters like SVG to SVGB / SVG to DAT / SVG to SVG-T / (PNG, JPG, JPEG, GIF to MIF) / Bitmap(BMP) to Multibitmap(MBM) etc.
Though software like Adobe Illustrator and Photoshop will get most of the job done, these command line tools get the job done much quicker.
Ω
ROFS2 Language Tool
Allows you to skip editing the resource/bootdata/languages.txt manually. Just point to the ROFS2 file and select which language you want removed.
Ω
Nokia QWERTY keyboard editor
This nifty tool allows you to edit the qwerty keyboard on S^1,S^3 symbian devices.
Ω
Theme Icon switcher
Youcan use this to switch icons in your themes to suit your needs. Or one can open the theme in Carbide.ui and edit it there.
Ω
RSC Editor
Allows you to edit the .rsc file which stores all the visible text in the program. Quite useful if you wish to translate a program or add a new language in an application altogether.
Ω
PPMod
One can modify core files of S40 firmware (.ppm files) using this software.
haCKs
installing Unsigned applications
Often wecome across errors regarding application certificates being invalid andsubsequentlyapplicationscannotbeinstalledontoyoursymbiandevice. There a couple of workarounds for this, some involve hacking your phone and then again one could take the easy wayout by getting those applications signed using your own custom certificate. We’ll go through bothmethods.
Get a Custom Certificate
This method involves getting your own developer certificate which when used to sign an application will grant it all rights on your phone and you’ll be able to utilise all features of that phone. More and more developers now provide unsigned applications and using your own certificate goes a long way in reducing restrictions as they are bound to the IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity). Here is how you can obtain Dev 17 certificate (17 capabilities developer certificate) for your phone.
1. Goto http://www.s60certkey.com
and register an account. 2. Once done you’ll be able to obtain three S60 certificates for free. For
more certificates one can make a new account or get in touch with the site admin who’ll grant more requests for a small donation.
3. Enter the IMEI number of the S60v3 or S60v5 device on which the applications are to be installed. The IMEI number can be easily obtained by keying in the code #06# or by checking the battery compartment or by checking the device packaging.
4. It’ll take upto 24 hours to obtain your certificate, you’ll be notified by email when your certificate is ready.
5.
Once you have obtained the certificate, download SignTools 2.2 from theirforums http://www.s60certificatekey.com/forum/index.php.
6. You’ll obtain a .cert file and a .key file from the website, use them to sign your application using SignTool.
7. You now have a signed application which will install on your device without any problems.
This method needs to be repeated for each new application that you install, alternatively you can use HelloOX2 from http://helloox2.com/
HelloOX2
Get the unsigned HelloOX2.v2.03.sis and repeat the above steps to sign and install the application on your mobile device. Once installed, run the program and it will automatically do the following..
Ω
Map C:\sys\bin\ to a virtual drive
Ω
Unpack hacking files to the virtual drive
Ω
Activate the file system
Ω
Unmapvirtual drive
Ω
Install
root certificate
Ω
Install ROMPatcher
Ω
Optional Install
Modo (an unlimited
access file manager)
ROMPatcher has
multiple patches which
can be enabled or your
ROM can be “patched”
to enable certain fea
tures. There are a few
variants available, the
Original by Z0Rn and
another at Symbian-Toolsare equally good. Plenty of documentation has been provided about creating your own patches to enable extra features on your phone, all depending on your programming skills. All patches are applied
using a memory hack, that is, the ROM is mapped to certain sections of the RAM and all modifications are made in the mapped RAM. This is reflected in the ROM virtually and the hack is enabled. Thus, these hacks are not permanent and you do not risk messing up your phone. Just reset your phone and it will be returned to its prior state. Any extra patches which you wish to apply must have an .rpm extension and should be placed in the patches folder.
Apply the InstallServer patch to allow unsigned applications to be installed on your phone without going through the hassle of signing each and every application.
All modifications that HelloOX2 makes to your phone can be enabled disabled via the application as and when you need to.
Norton Hack
If you don’t want to get into flashing and risk your phone getting bricked, you can opt for a simple method known as ‘Norton Hack’. Follow thisprocedure, and you can install whatever you want. (We have tested on Nokia 701 but it is compatible with all s60v3,v5 and Symbian^3 devices) 1. Download Norton Antivirus and RomPatcher package. 2. Installtheapplication. Ignore the‘Applicationnotcompatibleerror’ifany,
while installing. Now launch the application. It should look something like this
3. Now go to Options-Quarantine list.
4. Now again go to Options-Restore all. Confirm it
5. Now install the other file in the package, RomPatcherPlus_3.1_LiteVersion. Launch the application
6. You will see an open4all patch. Apply this patch. After this, you can access all the system folders of your phone through file manager.
7. Another patch in the download package is Install Server1.7RP+.rmp You need to extract this file in E:/Patches (create the folder if it doesn’t exist) of your phone’s external memory. Apply this patch in the same way as before and there won’t be any kind of certificate errors while installing apps and games. YourRompatcher screen will look like this after patches are applied. There are many patches available on net as you can see in the screenshot above. They are self-explanatory in terms of the functions they perform. Like the ‘saveclipboardafterreboot’ patch saves stuff you copied even after you reboot your phone and ‘savelogsafterchangingsim’ saves your call logs even after change of sim card. You can find more of them on the internet.
Cross Flashing
Sometimes all you need to do to enable new features is to flash the device with the firmware of a similar model. Now, the word ‘similar’ in this con- text means they must have the same hardware, only minor differences are allowed. Example - The 6300b which is the North American version using the 850/1800/1900 MHz band whereas the 6300 uses the 900/1800/1900. These locked phones can be used in other countries after cross flashing the 6300b phone with a 6300 firmware. This only unlocks the 1800/1900 bands as the 850-900 band is actually limited via hardware, so for a full conversion you’ll need to modify the hardware a bit too.
Sometimes firmwares are region specific and newer firmwares are released in only select regions, so you can flash your phone with those firmware but that isn’t cross-flashing in its true definition. Just ensurethe RM-xxx number is the same to avoid anyissues.
Flashing your symbian Device using Phoenix
As we already mentioned, flashing is basically replacing your firmware files with modded ones.
Download the firmware for your device using Navifirm
Rememberto performflashing on a fully charged battery only! And stay clear from flashing SL3(Simlock3) phones with custom firmware for now atleast, google to figure out what your phoneis. There isavery lowrateof success. Now, follow these steps 1. You will need your original
firmware files first. You can
Select your firmware file
download that from Navifirm (
http://dgit.in/L9qPvy).
Once you install Navifirm, you will see list of Nokia devices.
2. Check RM type, software version and product code of your firmware in your phone (you can do that by pressing #0000#; keep the screen open). Scroll down in Navifirm and select your device model with corresponding RM type. In our case, it is Nokia 701 (RM-774).
3. Next is the software release. Select the one which corresponds to your phone.
4. Now you will get list of variants available for your phone. Search for the one which matches your product code. The final screen should look somewhat like this.
5. The files you need will be of this format core, rofs2, rofs3, uda, dcp, vpl, bin(signature). Download these files anywhere on your computer. Size will be around 400mb.
6.
Now you need Nokia Cooker to calibrate the core file. You can downloadthatfrom here. http:// dgit.in/LR3jV7.
7. Download, and open Nokia Cooker.exe in the zip file.
8. NowselectOpenFirmware.
9. Browse to the place where you
Select your RM-number
have downloaded your firmware files and select .core file. 10. It will take a while before you can access all the icons, have patience. You
need to select ‘Unlock ROFS’ there.
11. Once you do that, a dialogue box will open. There will be three parameters ROFS1, ROFS2, ROFS3. By default, they will be assigned value ‘2B’. You need to
change them to ‘2C’. Press ok.
12. Next you need to do is press ‘Extend
ROFS’. You’ll see that the size will
increase to around163MB.
13. Now press ‘Save Firmware’. This will
take time too. Do not worry.
14. You’ll see a file named ‘RM-
774_112.010.1404_79u_prd.core_
BACKUP_.fpsx’ will be created at the
location of your firmware files.
15. Download and installPhoenix 16. Before using phoenix, create a folder in
C:\ProgramFiles\Nokia\Phoenix\Products and name it according to your RM version. For example, RM-774
as in our case. Phoenix will look up here while flashing.
17. Copy all the firmware files you downloaded from Navifirm, here. Do not
copy the ‘.core_BACKUP_.fpsx’ file. Also, do not cut-paste the original
firmwarefiles. Ifsomething goes wrong, youneed touse your original
firmware files to get your phone back.
18. Now, for CFW, you will need modified core,uda,rofs2 and rofs3 files.
Head over to http://dgit.in/NDcOaP
(or you can google them) to get a
list of CFWs. Select the one which suits your need according to your
phone model. Different developers add different mods and pack
their FW.
19. They will either provide all the FW files, or the four above mentioned
files. If they have provided all the firmware files, download and extract
them in RM-XX folder which you created. Replace the files which you
pasted earlier.
20. If they provide only those four files, copy them to RM-XX folder and
replace it with your original firmwarefiles.
21. Now your firmware is ready to be flashed with Phoenix.
22. Open Phoenix- Open product- Scroll down to your RM version and select
it. No screen will open. That’sok
23. Now select Flashing-Firmware Update press ‘...’ as shown in
the screenshot
24. Scroll down to your product code and press ok.
Select your variant
25. Now tick ‘Dead Phone USB flashing’. Make sure your phone is not connected at this point.
26. Press Options-you will get list of five files, one of which will be red in color. Select that file and delete-confirm ‘yes’ and press OK.
27. Now switch off your mobile phone. Don’t connect it as yet. Make sure battery level is minimum 50%. There are high chances of bricking your phone if battery drains out in the middle of the flashing procedure
28. Press Refurbish. Once you get this screen, connect your phone in switched off mode via usb, and then turn it on
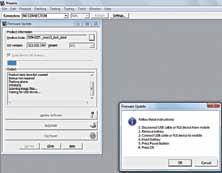
The flashing begins
by pressing the power button for about three seconds and then press Ok. Flashing will begin.
29. Once flashing is complete, you will need to sync your data back to your phone.
Here are some screenshots of the phone.
Diy – Create your own FbUs adapter
Fbus (for “Fast Bus”) is an ANSI/IEEE data bus oriented towards back- planes and cell phones. It is used by Phoenix and J.A.F. to connect to your phone. Flashing can be accomplished by USB but testing out all features via Phoenix requires you to make use of the FBUS adaptor. Buying a new adaptor can throw you back by upwards of Rs. 3000/- for a multi pin configuration universal cable. Or you could make one for a few hundred rupees. Here’s how
Once you’ve built your own FBUS cable all
you have to do is figure out your phone’s
pinout diagram which is a google search
pinout diagram which is a google search
5 brass contacts clumped together behind
the battery compartment.
Here is a chart for your reference, always
confirm first before connecting your device via
FBUS as FBUS operates on a higher voltage
and will fry your device if connected to the
wrong pins.
Once your phone is hacked, you will be
able to install all the mod files on your phone
which will help you change your theme
effects, start-up sound and logo and improve
customization features. But to improve the
performanceofyourphone,flashingisabetter
option. Also, the above method will retain
hack only as long as your phone is formatted.
Once you restore your default settings, your
phone will be un-hacked the way it was. To
get it permanently hacked, flashing is recommended. Also, if you guys are facing ‘Component builtin’ error in Belle FP1, there is no other way to remove it besides flashing.
But before you flash your phone, don’t forget to backup your data on phone memory. This will include contacts,messages, notes, calendar events and tasks and bookmarks and feeds. Nokia PC suite is quite handy to sync your data with computer and take a backup. But if you have an older version of Nokia PC Suite, you can even copy-paste your contents to PC if you find that easier.
Components
Symbol Pcs Component U1 1 MAX232 Equivalent**
Other manufacturer’s
equivalent substitute (possiblyall“232”chips are not equivalent with MAX232)
Emergency solution*** MAX3232, requires
pull-up to pin 10, smaller capacitors and zener diode.V+must notexceed 7 volts.
1 16 pin IC socket D1,D4 2 1N5819
D3 1 4.7V 400mW zener
C1,C2,C3 3 1µF 16V Any schottky diode Any 4,7 volt zener with higher power rating Any 1µF capacitor with higher voltage rating 1N4148
78L05-based linear regulator circuit
R1 1 47 ohm J1 1 DB9 female DB25 female (different pin arrangement, see chapter 2.3)
J2 1 Phone connector Copper-striped circuit board 11 x 10 holes
Your data on memory card is safe, but since you are backing up your phone memory, it will be safer to spend few extra minutes taking backup of your memory card as well, just in case you need it later. Also, it is recommended to delete system folders (sys, private, resource) from your memory card by connecting your phone in ‘Mass Storage’ mode. Though we went ahead without doing it, it may or may not cause bugs after new firmware is installed. Once you’ve backed up your data, you are ready to flash your phone without risk of losing itpermanently.
Flashing … 5% … 25% … bRiCKED!!!!
Ifyoudo manage tobrickyourphone, don’tworry getyourhandson Phoenix and flash your phone while keeping in mind the following.
1. Remove the USB cable and turn your phone off. Remove and insert the
battery if necessary.
2. Run Phoenix Service Software and Select “NO CONNECTION” as
connection type.
3. Select “Open Product” option in “File” menu. Then select the RM-xxx
number of your mobilephone.
4. Select “Firmware Update” option in “Flashing” menu. Then click on “...” in the top-right corner and select the product code which is a 7 digit number which often starts with 05. Example 0524529. Select your language pack and
tick “Dead Phone Flashing”.
9. Press “Update Software”. If the phone
fails to turn on then retry and choose
“Refurbish” this time. Then follow whatever instructions that proceed. You may
be prompted to press the powerbutton
after connecting the USB cable.
The phone will begin flashing and should get completed successfully. If not then try again till it does. Swapping the USB ports does help sometimes.
Reference websites
Ω
http://www.cpkb.org/wiki/Main_Page
Ω
http://forum.dailymobile.se
Ω
http://www.developer.nokia.com/
Ω
http://www.ipmart-forum.com/forum.php
Ω
http://www.symbian-toys.com/
Ω
http://www.symbian-freak.com
Ω
http://forum.gsmhosting.com/vbb/
76
Chapter#9
Custom
firmware on
PmPs
P
ortable Media Players come in a lot of form factors and each with its own setoffeatures, some of which are unique to it. Now,custom firmware allows you to get an ordinary PMP and unleash its hidden potential. It can best be defined as something that levels
the playing field. If you thought that your PMP was limited to just the few features it came with out of the box then here are some nifty options foryou.
advantages
Why exactly would one turn towards custom firmware when whatthey have rightnowispretty decent?That’sbecause gettingtheextra capability ofyour device is always enticing. Here is what you stand to gain by going custom.
more codecs supported
There are a lot of codecs available in the market but each have their own licensing fee, so making more codecs available subsequently leads to a rise in the price. This is one of the primary reasons for many variants of PMPs existing with the same hardware but with varying support for codecs. Open source codecs on the other hand are capable of playing all of the various file formats but some tend to take a hit when it comes to sound quality. However, certain open source codes do better than the proprietary ones. As an example, Dirac an open source video codec developed by BBC turned out to be better than H.264 which is a proprietary codec.
themes
Making your own theme hasbecomeanintegralpart of custom firmware. Getting more features wasn’t enough so making stuff seem groovier by adding a personal touch had quite
the appeal.
Rockbox themes
Plugins
There are plugins for everything, One can get a new interface altogether, get more applications (DOOM, the game runs well on most implementations of Rockbox). Then there are apps being developed for the popular custom firmware.
Greater control over your device
Now we all know how irritating it is when you need to use a particular software to get the job done. Moreover, these software come with their own quirks which include wiping out your entire collection if the device is connected to a new computer.
it’s economical
Sometimes if you do your research well, you’ll come across a method of making your humble PMP sound like its awesome counterpart by flashing itwiththelatter’sfirmware.Thisdrasticallyalterstheprice-to-performance ratio of the device.
Rockbox has plenty of plugins
multi-tasking
Customfirmware has been known to enable multitasking on devices like iPod 2G which have long stopped getting OS updates from Apple.
and more …
While each custom firmware comes with its own set of features, here is a list of things which are common across various custom firmware projects high-resolution volume control, equalisers with more parameters than the average person can differentiate between, the ability to turn off irritating features, support for copy-paste, crossfading, greater gain control, emulate applications which would otherwise not becompatible.
Disadvantages
The downside of going custom is pretty much the same for most devices, there is the loss of any claim for warranty. All manufacturers like to put this little clause in their warranty statements which are accompanied by tamper proof seals placed all over the device. Nowsome of these seals can be peeled off and then affixed back on again after the deed is done. All you need are a hair dryer and some waxed paper. However, there are other ways in which companies can figure out if you’ve been fiddling around with your device.
Then comes the chance of “bricking” your device. At the end of the day, you’ll be programming an EEPROM( Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) chip and there are a ton of things that can go wrong, which include frying your device. There is no coming back from such situations, however, good brands always have redundancies and performing a “dead-flash” (flashing a bricked device) repairs whatever damage might have been caused on a softwarelevel.
the offerings out there.
rockbox
Rockbox has been kicking since 2001 and so far has proved to be a much better firmware than most stock firmware that devices come with these days. Rockbox offers support for over 30 codes, features gapless playback, volume normalisation, support of a variety of games and other applications.Italsofeatures a multi-lingual interfaceconsistingofmore than 30 languages.
What is the best part? The equaliser. The sheer level at which the equaliser can be adjusted makes audiophiles weak in the knees.
Since it has been around for a little over 11 years now, Rockbox supports a wide variety of players and new firmware are constantly being developed for PMPs as and when they hit the market.
freemyipod
A custom firmware solution for iPods
without iOS. The project started
where others like iPodLinux and
Linux4Nano left off. The project is
about reverse-engineering iPods so
that developers can figure out a wayto
port custom firmware onto the PMPs.
whited00r
Also a custom firmware for iPod devices happens to be one of the most popular iOS modding communities. It is because whited00r is a jailbroken version of the latest iOS but for older generation devices which are no longer supported.
So if you have an iPod Touch 1st gen or 2nd gen which are limited to iOS 3.1.3and4.2.1oriPhone 1st gen / 2ndgen theninstalling Whited00ronyour device gets you features of iOS 5. Be it simple things like the new ringtones that come in iOS 5oruseful features like multitasking where the background appsarestillrunningandnotpausedwhenyouswitchbetweenapplications. This project is not just limited to older gen apple devices, red00r, a variant of Whited00r based on iOS 4 is still under development. Also, the folks who came out with whited00r have recently released the first beta of yellowd00r which brings OS X Lion to 3rd/4th Generation macs.
Lesser known firmwarefor lesser known devices
There are various tools availableon the internet for modifying the firmware of lesser known devices. All you have to figure out is whether your device is based on the same SOC chip as they tool.
There is the Rockchip UI Editor for all PMPs based on the Rockchip RK27 and there is a tool for Gemei’s HD8800 chip. Most of these devices are termed as knock-offs of more popular brands, however, once laden with custom firmware, these devices are as good as if not better than the real thing.
Given the fact that these are cheap SOCs major brands often haveandroid devices powered by these chips which brings out the aspect of having android onto these players. However, companies don’t bring out these products with Android on them as the licensing fees would raise the price and subsequently hurt sales. Hence, they take the easy way out by developing their own firmware in-house. Android can then be ported onto these devices provided the hardware is goodenough.
Conclusion
There are plenty of options in the market that you can go in for. Various brands like Cowon, Apple, Archos, iriver, MPIO, Onda, Olympus etc. offer a variety of PMPs, however, like all major brands, these products are segregated into various categories based on price and often they share the same hardware across various price brackets, all that makes them different are the goodies that they come with and the firmware. So can you buy a budgetfriendly PMP and make it sound like one of the more expensive ones? Well, to a certain extent, yes.
Cross-flashing is one of the most common solutions to bypassing firmware limitations, however, when there are even minor hardware changes between different models then comes the risk of bricking your device. So be careful while pimping your newest purchase with custom firmware, a little reading always helps as there are people out on the Internet who have tried doing so before you and have tasted success or bitter failure.
Links
Ω
http://www.whited00r.com/
Ω
http://www.freemyipod.org/wiki/Main_Page
Ω
http://www.rockbox.org/
Ω
http://www.mp4nation.net
82
Chapter #10
Hack your
cameras
A
camera, whether it’s a Point And Shoot or dSLR, is able to take pictures thanks to the combination of hardware and software bundled into the system. When we talk of hardware on a camera it can include a whole bunch of things. The body, the
lens, the sensor, the battery and many other things constitute the hardware side. The software part of this system relates to the code that enables you to fiddle around with settings such as exposure, whitebalance, aperture size etc. Right from the user interface to the algorithms that process the image that the sensor captures is the software. This software layeris not technically an operating system but it does communicate with the underlying hardware. In the case of cameras and otherembedded systems its called the Firmware and enables the user to interact with the hardware modules of the camera.
Often changing this firmware can greatly enhance the feature-set of the camera. How is that possible? There are a couple of reasons. Camera
manufacturers come out with a lot of models to appropriately segment the market. Attimes they may use the same hardware but disable certain modulesorparts -maybeaGPSunitforinstance.Inthis casereplacingthe firmware mayallow you to activate that disabled hardware unit, thereby enhancing your lower model camera to a higher model.
Apart from unlocking hardware modules, certain
DsLr v/s Point-and-shoot
Cameras are broadly divided into two categories: Point-and-Shoot(PnS), and DSLR(Digital Single-Lens Reflex). The consumer grade PnS cameras are used by amateurs professionals alike. They are compact, lightweight and designed for simple operation. PnS cameras come with auto-focus, built in flash units and automatically set the exposure options. However, most new models from all major brands can somewhat hold their own against DSLRs. These are single lens cameras that let you view directly through the lens and see exactly what will be captured, unlike the viewfinder in point
and-shoot cameras where the image that the photographer sees is not what passes through the primary lens of the camera. DSLRs offer manual control over camera settings, but are usually heavier andexpensive.
What we mean by hacking?
Your camera contains a tiny computer. The firmware of your camera tells the computer how to run different functions on your camera. When we say hack your camera, we mean firmware enhancement. This is similar to hacking any other device. Installing a custom firmware in your camera will improve its functionality; give you features which the stock firmware that came with your camera would not provide.
cHDk for your canon point-and-shoot
Enhancing your Canon point-andshoot camera’s firmware will give it DSLR like features. The Canon Hack Development Kit(CHDK) is a firmware enhancement that operates on an array of Canon PowerShot compact cameras. It adds to your camera’s functionality beyond that provided by the stock firmware. It gives you more manual options and features like RAW shooting mode, motion detection and time-lapse on your point-and-shoot.

CHDK is a non-destructive and a temporary firmware upgrade, so you can always remove it. It leaves your stock firmware untouched. After you delete the software from your memory card, the camera functions normally. So it does not void your camera’s warranty, but who knows! We’re not giving any legal opinion. Log on to http://dgit.in/MskIAf
to get a list of camera models and firmware versions that are currently supported by CHDK. Check your camera’s model and firmware version before you go on installing it(http:// dgit.in/KSIa9g).
A different version of CHDK works for different firmware versions even of the same cameramodel.
Download and install cHDk
CHDK has two builds: 1.0.0 and 1.1.0. The 1.0.0 build has a more stable code, whereas the 1.1.0 build is called a development trunk where new code is introduced.Downloadthecorrectbuildforyourcamerafromhttp://dgit.in/ NQj8NA.
Installing it involves copying the required CHDK program files to yourcamera’s memory card. Itgets loadedinto yourcamera’s memory upon boot up (either manually or automatically). For loading it manually every time you turn on your camera, use the Firmware Update method where you use the camera’s built-in ‘Firmware Update’ menu item to load CHDK. If you want it to load automatically when you turn on your camera, use the Bootable SD card method. Follow the instructions in the following link and then lock your card by sliding the LOCK switch on its side. You will see the CHDK logo flash on the screen when you turn on the camera.

Uninstalling CHDK from the file system requires you to delete those files from the memory card. Since CHDK is loaded onto the RAM, no permanent changes are made to your ROM or filesystem. For more details read on http://dgit.in/Msn6Ha.
What new features cHDk brings to your camera?
CHDK is a continuously evolving software, and developers from all around the world are continuously working towards improvising its features for different camera models. Some of the enhancements that it brings to your simple cameras are:
Ω
Enhanced Image Capture:CHDK adds support for two RAWformats - DNG
and CHDK RAW. DNGis a popular industry standard whereas CHDK RAW isa dumpoftheentiresensordata,soitvariesfromcameratocamera.Longer recording time or length for videos (up to 1 hour or 2GBs), and several new compression options are also offerings that CHDK brings along.
Ω
Modify the user interface: Using CHDK, your camera’s UI can be modifiedto your liking. Features include numeric battery life meter,a detailedlivehistogram, multi-lingualinterfacewith22languages etc.
Ω
Additional Settings:If your hardware can support it, then CHDK tries to make it happen CHDK expands the capabilities of your camera like greater control over exposure timings with flash-sync(2048 seconds to 1/60,000th of a second), motion detection sensitive enough to capture lightning, faster shutter speeds (1/25,000 sec or faster), automatic bracketing of your photos, andmore.
Ω
Support for Small Programs/Scripts: If you can script in ubasic or lua then you pretty much have unprecedented control over your camera’s capabilities. You can toy around with all its features by making use of the many user contributed scripts already available on the forums and hobbyist web sites.
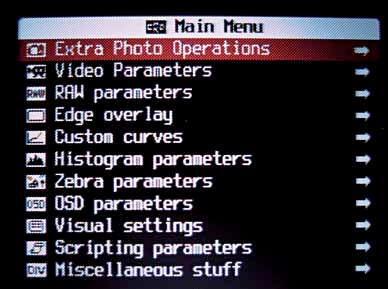
CHDK Parameters

CHDK does a lot more to your camera. Visit the following link to read the full list of features
http://dgit.in/MvpniP.
magic Lantern for your canon DsLr
Magic Lantern is also an enhancement on top of your video-capable Canon DSLR’s firmware which gives it professional video camera like features. It isn’t a firmware upgrade, but basically a software that runs alongside your stock firmware. Initially it was developed for independent filmmakers and tailored to enhance video capabilities of Canon 5D Mark II. With time it attracted developers interested in both still photography and DSLR videography. Magic Lantern was then ported to smaller cameras like 550D, 50D, 60D, 600D and 500D.
The installation process is similar to CHDK. To install it on your camera, read the instructions guide here http://dgit.in/NhACjs.
What will it do for you?
Magic Lantern allows greater control over audio settings and lets you program a mechanical rack focus which is quite essential when it comes to shooting videos. Also, it allows you to adjust within a greater scope when it comes to frame rates.
Other features include Ω
On-screenaudio meters which
is a great indicator for positioning your microphone. Ω
Manual gain control with negligible pestering by the
AGC(Automatic Gain Control) Ω
Setting up crop marks
according to your preference,
be it 16:9 or 4:3 or a custom
crop mark
Ω
Zebra stripes (video peaking) which gives you a live histogram stating
which areas of the frame are over or underexposed.
Because its an open framework, extensions can be developed for the existing versions of the software to add more features.
 Will it wreck your camera?
Will it wreck your camera?
It does not write to the ROM, so it’s fairly safe. But Magic Lantern comes with no warranty or guarantee that it would work. No bricking has been reported yet, but there are chances of damage when you fiddle with the hardware. The software goes through beta testing before it reaches you, and by that time it has been used by thousands of users. So, the chances of it wrecking your camera are pretty low. Most of the risk is borne by the developers who experiment with their DSLRs while probing the camera’s firmware to extract more and more features. If you want to remove it, all you need to do is format your memory card and reboot into the stock Canon firmware.
Why should you need these enhancements?
CHDK for your Canon point-and-shoot, and Magic Lantern for your Canon DSLR. These are custom firmwares which might void your camera’s war- ranty, but give you additional features. So if you’re on a tight budget but still want professional capabilities from your camera, make sure you’re ready to get out of the comfort zone that the warranty gives you.
For cameras other thancanon
If you own a Canon point-and-shoot or DSLR, then you’re being served on a silver platter. For all of you who own a Nikon, Panasonic or Sony good news seem a little distant. The hacking kit that we explained above works only on Canon, one of the most popular brand. Currently, research projects are underway for Nikon (http://dgit.in/KLSV1O),
Pentax (http://dgit.in/MswHhf),
Panasonic (http://dgit.in/NhDSvk),
Sony and other brands. These are open forums. So if you think you know about software/hardware/firmware hack to supercharge your camera, then you can always contribute.


















 PMP
PMP












 The Superuser app grants root permissions to apps
The Superuser app grants root permissions to apps Overclock your CPU with SetCPU
Overclock your CPU with SetCPU Titanium Backup can securely backup your apps and data
Titanium Backup can securely backup your apps and data Block those annoying ads within your apps with Adaway
Block those annoying ads within your apps with Adaway

 Cyanogenmod lets you easily tweak your phone
Cyanogenmod lets you easily tweak your phone MIUI ROM focuses on aesthetics, and is one ofthe most beatifulROMS around
MIUI ROM focuses on aesthetics, and is one ofthe most beatifulROMS around Clockworkmod is a powerful recovery image for your phone
Clockworkmod is a powerful recovery image for your phone

 The Absinthe tool allows you toJailbreak your iOS 5.1.1 device.
The Absinthe tool allows you toJailbreak your iOS 5.1.1 device. The Cydia storefor jailbroken devices
The Cydia storefor jailbroken devices The‘Changes’taboftheCydiaapp
The‘Changes’taboftheCydiaapp SBSettings allows easy access to Settings
SBSettings allows easy access to Settings
 iFileisahandy FileManager foriOS
iFileisahandy FileManager foriOS Intel li Screen XletsyouputallofyourimportantfeedsrightonyouriOSdevice’slock screen
Intel li Screen XletsyouputallofyourimportantfeedsrightonyouriOSdevice’slock screen Veency running on aJailbroken iPhone
Veency running on aJailbroken iPhone

 TheSamsungFocuscanbeunlocked using theinterop method shown here.
TheSamsungFocuscanbeunlocked using theinterop method shown here. Diagnosis menu
Diagnosis menu The recovery screen on the
The recovery screen on the Jailbreaking hTc devices
Jailbreaking hTc devices
 The HTCHD2 is one of the most hacker-friendly phones around
The HTCHD2 is one of the most hacker-friendly phones around







 Download the firmware for your device using Navifirm
Download the firmware for your device using Navifirm Select your firmware file
Select your firmware file Select your RM-number
Select your RM-number Select your variant
Select your variant
 The flashing begins
The flashing begins


 Rockbox themes
Rockbox themes Rockbox has plenty of plugins
Rockbox has plenty of plugins
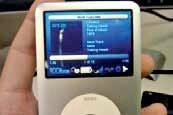





 CHDK Parameters
CHDK Parameters CHDK does a lot more to your camera. Visit the following link to read the full list of features http://dgit.in/MvpniP.
CHDK does a lot more to your camera. Visit the following link to read the full list of features http://dgit.in/MvpniP.
 Will it wreck your camera?
Will it wreck your camera?

