 The inability to achieve and maintain an adequate erection for satisfactory sexual performance is extremely common and probably affects most men at some stage in their lives.
The inability to achieve and maintain an adequate erection for satisfactory sexual performance is extremely common and probably affects most men at some stage in their lives. The inability to achieve and maintain an adequate erection for satisfactory sexual performance is extremely common and probably affects most men at some stage in their lives.
The inability to achieve and maintain an adequate erection for satisfactory sexual performance is extremely common and probably affects most men at some stage in their lives.
This important men’s health issue is called erectile dysfunction (ED). The word ‘impotence’ is derived from the Latin for ‘loss of power’ and implies a complete inability to get an erection. The term ‘erectile dysfunction’ is preferred because there is a whole variety of erection-related problems. For some men this is only a temporary effect, perhaps when they are under stress, tired or have drunk too much alcohol; for others it can be a more long-lasting problem. However, ED can be an early sign of damage to the blood vessels elsewhere in the body, for example, the heart, the brain or the legs. It can have a significant impact on the quality of life for a man, his partner and their relationship.
What Is the Cause of Erectile Dysfunction?
There is no easy answer to this as there may be several different factors involved. We do know that many men still suffer needlessly in silence, as they either feel too embarrassed to raise the issue or they feel it is part of ‘normal ageing’. Fortunately, these types of issues are no longer taboo and have benefited from a great deal of media exposure in recent years. This has been helped enormously by the arrival of effective medical treatments for this condition, such as Viagra. As a result, men should have the confidence to discuss this important health issue with their family doctor and get appropriate help and treatment.
How Common Is Erectile Dysfunction?
It can occur at any age but is more common as a man gets older. About 50 per cent of all men aged between 40 and 70 and about 70 per cent of men aged over 70 are affected by erectile dysfunction issues.
How Normal Erections Work
Knowledge of how an erection works can be helpful in understanding the causes of erectile dysfunction (ED) as well as the treatment options. Normal erections require healthy arteries, veins and nerves, a mind that is ‘tuned in’, enough testosterone in the system and a chemical called nitric oxide. It is a complex process that starts with physical arousal or erotic thoughts. Penile erection is usually triggered by one of two main mechanisms: direct stimulation of the genitalia or stimuli coming from the brain (fantasy, smell, etc.). This causes messages in the form of chemicals (nitric oxide) to go from the brain down the spinal cord to the penis. The penis is an organ with spongy erectile tissue composed predominantly of muscle. These chemicals then cause the penis to enlarge by increasing its blood supply. This increased blood flow into and storage of blood within the spongy erectile tissue of the penis leads to an increase in its pressure and the development of rigidity (hardness). The increased pressure of blood in the penis helps to prevent blood from escaping out of the penis. Ongoing sexual arousal results in more chemicals going from the brain via the spinal cord into the nerve endings of the penis. Both of these processes help to maintain the erection.
The erection mechanism can be compared to blowing up a balloon. In this analogy the balloon is the penis, which needs a rapid increase in blood flow to become erect. The knot on the balloon represents the valve structure in the penis that keeps the penis erect. A firm balloon depends on being able to blow air quickly into it. A knot or pressure in place prevents the air from getting back out and keeps the balloon firm. If sexual stimulation ceases, then the balloon will lose its air and deflate. Alternatively, if stimulation continues, more and more air will enter the balloon until it eventually bursts (this represents orgasm).
When It Goes Wrong
Medical conditions such as heart disease or diabetes can physically damage the arteries and nerves involved in erections. They can do this by causing narrowing of the penile artery, which prevents proper blood flow, or scarring of the spongy erection tissue, which prevents proper trapping of blood. Psychological issues such as anxiety or depression can prevent the nitric oxide from reaching the level required to induce erection.
Physical Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction has an underlying physical cause in 80 per cent of men with the problem. Erectile dysfunction can cause anxiety, loss of self-esteem and loss of confidence, which can make the situation worse.
Your ED is likely to be physical in cause if:
Narrowing of the Penile Artery
This is the most common physical cause. Narrowing of the blood vessel (artery) supplying the penis is due to fatty plaques sticking to the sides of the artery causing, in effect, the pipes to become furred up. This condition is known as atherosclerosis and can occur gradually over many years. It is responsible for heart disease, stroke and poor circulation to the legs as well as erectile dysfunction. So, developing erectile dysfunction may be the first sign of narrowings of blood vessels elsewhere in the body. The penile artery is 3 millimetres in diameter and the coronary artery supplying the heart is only 5 millimetres in diameter. Erectile dysfunction can be an early warning sign of potentially serious future health problems. Don’t ignore it.
The risk of developing atherosclerosis and erectile dysfunction is increased by these factors:
Obesity
Being obese is associated with an increased risk of ED, probably due to the effects of obesity on blood sugar levels and circulation.
Alcohol and Other Drugs
Alcohol is a good servant and a bad master. As we know, it is a depressant and certainly more than a few units of alcohol at any one time can impede performance. This has been described in medical circles as ‘brewer’s droop’, where one has an inability to maintain an erection after a few drinks. This, of course, can cause subsequent anxiety about performance on future occasions, even when alcohol has not been consumed.
Chronic alcohol abuse can cause liver damage, which raises the level of oestrogen (the female hormone) in the body, thereby causing impotence. However, alcohol in moderation can help protect against erectile dysfunction.
Other illegal drugs, including cocaine and marijuana, can cause sexual dysfunction. Just like chronic alcohol abuse, marijuana can raise the levels of oestrogen in the body, thereby causing impotence.
Diabetes
Erectile dysfunction is very commonly seen in men with diabetes. Diabetes can affect the nerve supply to the penis as well as narrowing the penile artery. If you have diabetes, it is extremely important, not just for your sexual health but for the general health of your blood vessels, to keep your blood sugar levels tightly controlled, not to smoke, to keep your blood pressure optimal, to take regular exercise and to keep your cholesterol and weight at acceptable levels.
Disorders of the Nervous System
As mentioned above, diabetes can affect the nerve supply to the penis, which can result in ED. Other conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, damage to the spinal cord, including spinal surgery, stroke and other forms of nerve damage can also cause impotence in this manner.
Cycling
Cycling, particularly long-distance cycling, has been associated with ED, probably due to a pressure effect of the saddle on the nerves that supply the penis.
Hormones
Hormonal causes of erectile dysfunction are uncommon and include testosterone deficiency. This is generally associated with loss of libido.
The Ageing Process
Erectile dysfunction becomes more common as we age. While our male testosterone levels do tend to reduce as we get older, they generally remain within the normal range, even for many elderly men. So, it is not the ageing process per se that causes erectile dysfunction, rather it is ageing of the blood vessels. This is caused by medical conditions such as diabetes or atherosclerosis, as discussed above. Also, as we get older there is a higher chance that we will be on medication for various conditions. The medication in itself maybe the culprit when it comes to erectile dysfunction. The classical example of erectile dysfunction caused by medication is the beta blocker, which has widely been used to treat high blood pressure and palpitations.
Medications That Can Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Psychological Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Many mental health issues can cause erectile dysfunction. These include stress, anxiety and depression, as well as relationship difficulties. Anxiety and depression can result from erectile dysfunction as well, so it can be a chicken-and-egg situation. A psychological cause for ED is more likely if:
Psychological causes of erectile dysfunction can occur when we are under excess stress or when we are feeling very anxious or indeed are suffering from depression. In all these situations our body and mind are out of balance. Erectile dysfunction may occur as a result. A classical example of this is performance anxiety, where the worry or fear of not being able to perform or maintain an erection causes such intense anxiety that the erection process is blocked or inhibited. Needless to say, there is a cause-and-effect process here also, in that erectile dysfunction from any cause can result in profound anxiety and a loss of confidence and self-esteem for many men.
It is normal for men to get night-time and early morning erections. If you still have these then it is likely your erectile dysfunction may have a psychological basis. The absence of night-time or early morning erections suggests a physical cause of erectile dysfunction.
What Can I Do if I Have ED?
Your doctor can make an informed decision about the likely causes of your erectile dysfunction from a good chat with you and an appropriate assessment, which may include a physical examination and blood tests. Don’t let embarrassment or fear prevent you from taking action and seeking help. If you have any concerns or questions about your sexual health, ask. Your doctor is there to help you but don’t leave it up to your doctor to raise these important issues.
Tests for Erectile Dysfunction
Tests carried out may include:
Most men presenting with erectile dysfunction do not require any further tests, but a minority may benefit from more specialised tests with a urologist.
Treatment of ED
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of ED. Key areas that can help include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, looking after your mental health, examining your current medication, pelvic floor exercises, drug therapy, injection therapy, urethral suppositories, vacuum devices and surgery.
Healthy Lifestyle
There is good evidence that following a healthy lifestyle can really help with erectile dysfunction. A heart-healthy diet, taking plenty of exercise and watching your stress levels can all help keep you in good shape. It is important to keep your weight down and avoid tobacco products.
A regular medical check-up will help ensure your blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels are well controlled. While taking a tablet like Viagra can help cure erectile dysfunction it won’t necessarily address the underlying health issues. It is no substitute for the healthy foundations we all need for good long-term health.
Mental Health
It is important to optimise your mental well-being. This includes recognising and treating any underlying depression or anxiety and moderating your alcohol intake. Assess your level of stress. Do you cope well under pressure? Have you enough down time? Counselling can be helpful, particularly if there are relationship issues. Sex therapy can sometimes play an important role. This works best when the patient is well motivated and has the time to invest in the process.
Reviewing Your Medication
It can be useful to review your medication carefully with your doctor or pharmacist. If your doctor thinks some of your medications may be the culprit he may decide to stop one medication at a time for a few weeks to see what benefit it has. It is important not to stop medication without consulting your doctor as this may have health consequences. It’s okay to be a good detective but not your own doctor. Talk to your doctor, he or she is there to help you.
Pelvic Floor Exercises
These are exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor and can sometimes help with ED. They involve the muscles you use to stop yourself from passing wind and also those muscles used to stop the flow of urine. A physiotherapist would be able to give you a leaflet to help with this.
Medical Treatment
This has been revolutionised over the past ten years or so since the arrival of drugs like Viagra. The impact of these drugs has been massive, not just because they work but also because they have done so much to increase awareness of ED as a health issue. Early media coverage generated massive worldwide demand for this medication. Prescribing drugs like Viagra is now mainstream medical practice and there is no need to be embarrassed or shy about asking your doctor if you might benefit. At least it gives you an opportunity for this important health issue to be discussed in a sensitive and confidential manner.
There are three different types of drug available at present:
How Do They Work?
They all work slightly differently but all affect hormonal chemicals that come from the brain during sexual arousal. These drugs work by increasing the amount of nitric oxide produced. This chemical does two important things: it causes the nerve connections between the brain and the penis to become more fine-tuned; and it also increases the blood supply to the penis and causes the blood vessels in the penis to widen, causing an erection. These drugs in themselves do not create erections but they make an erection much more likely after sexual arousal. Ideally they should be taken about an hour before sexual activity and the effects can last several hours.
Do They Work?
Yes, in the majority of cases (about 70–80 per cent) these drugs can produce a good erection. Some men may find that one drug works and another doesn’t so it can be a trial-and-error process. Also, the dosage may vary. However, these medications can produce a good erection even when the blood supply to the penis is narrowed, as in cases of atherosclerosis and nerve damage, for example.
Do They Have any Side Effects?
Like all medicine there is a potential risk of side effects. Discuss this with your doctor. Common side effects include headache, facial flushing, nasal congestion and stomach upset. About 3 per cent of men who take Viagra get visual disturbances, most commonly affecting colour vision. This is often described as a bluish tinge.
It is felt that Viagra is generally safe to take for men with heart disease, provided their condition is stable and well-controlled. Discuss this further with your doctor if you have concerns.
Do They Interact with Other Medicines?
There is a risk of severe interaction with nitrates (used in patients with heart disease and angina) and for this reason drugs like Viagra cannot be taken if you are on nitrates. Check with your doctor or pharmacist about other potential interactions. The effectiveness of some of these drugs is affected if taken after a fatty meal – another good reason to watch your diet.
Injection Therapy
An injection of a drug called Caverject with a very fine needle is made into the penis, which usually causes an erection to occur within about 15 minutes that can last up to an hour. While this can sound scary, most men can learn the technique. The erection occurs even if you are not sexually aroused (unlike medication).
Side effects can include penile pain and discomfort. A rarer side effect of this injection is a prolonged painful erection, which is known as priapism. This condition needs emergency treatment to prevent long-term damage to the penis.
Injection treatment is less popular now that oral medication is available, for obvious reasons.
Urethral Pellet
An urethral suppository (brand name Muse) is a pellet, the size of a grain of rice, that is placed in the tip of the urethra. An erection usually occurs within 10 minutes and can last up to 60 minutes, though this can vary from person to person. This treatment is based on the finding that the urethra (the tube in the penis through which urine and semen flow) can absorb certain medications into the surrounding tissues, creating an erection. Muse urethral suppositories use the same medication as is used in injection therapy.
Vacuum Devices
The penis is put into an airtight plastic container and a hand-held pump is then used to pump air out of the container to create a vacuum. This causes blood to flow into the penis, leading to an erection in about 80 per cent of men within a few minutes. A special band is then put around the base of the erect penis to keep the blood in the penis until after intercourse. The band is then removed and the penis becomes limp. Side effects can include penile pain and bruising.
Penile Surgery
This can be an option for some men in which a surgeon inserts a rod or prosthesis permanently into the penis. There are two types of device. A rigid one uses a silicone rod that can be bent up and down; it keeps the penis erect at all times. There is also an inflatable option, which has an inbuilt pump to cause an erection.
Aphrodisiacs
These are substances that are reputed to improve virility. For many years various foods and herbs have been promoted as having sexual vitality properties. Examples include oysters, ginger and chocolate. Whether or not they work is certainly very difficult, if not impossible, to prove scientifically. However the placebo effect can have a strong influence on us. If we believe something is going to work then there is a good chance it just might. It is best to be cautious about taking any herbs or supplements. Make sure to discuss this first with your doctor, especially if you are already on prescribed medication.
Self-Assessment Questionnaire
The following self-assessment questionnaire on erectile dysfunction can help in terms of defining the nature of the problem. It has been designed as an easy-to-use diagnostic tool to help the assessment of both the presence and severity of ED. Each question has five possible responses. Circle the number that best describes your own situation. Select only one answer to each question.
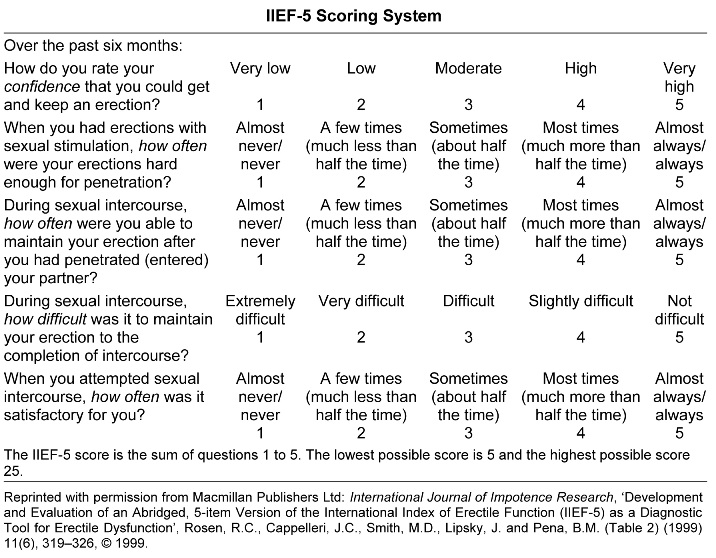
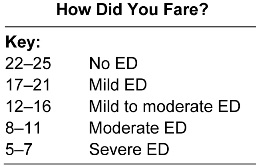
If a man scores 21 or less, then his chance of truly having erectile dysfunction rises to about 93 per cent. If he scores 22 or more, then it falls to 2 per cent or less.
Key Points
