1984
Surgical Robot
Geof Auchinleck (Dates Unavailable), Dr. Brian Day (b. 1947), James McEwan (Dates Unavailable)
Laparoscopic surgery is a complete reconceptualization of the surgical process that has many important benefits for the patient. But it is also a pain in the neck for the surgeon, who has given up his or her visual clarity and a lot of natural dexterity in return for these patient benefits. Is there any way for engineers to relieve some of the strain on the surgeon?
This is where the world’s first surgical robot, Heartthrob, comes in. Invented by a team lead by Dr. James McEwen, an engineering physics grad student, Geof Auchinleck, and physician Dr. Brian Day, the idea was to make a surgeon’s job much easier.
First, the robot provides a much better vision system. Two binocularly spaced high-definition cameras provide images from the surgical site, and the doctor controls these cameras. The surgeon rests her head in a cradle to look at the two screens, which creates a 3D view of the space. This step alone reduces fatigue and neck strain while providing a significantly better view of what is going on.
With her hands, the surgeon controls three manipulator arms. One arm is typically positioned and clamped to hold something stationary. Then the surgeon directly manipulates the other two with intricate hand controls providing seven degrees of freedom in the end effector. Because the surgeon is manipulating robot arms rather than working directly with tools (like scalpels and suture needles), the intermediary computer can do things like filtering out hand tremor and guarding against accidents.
The most interesting part of the whole procedure is that the surgeon’s station and the robotic arms are completely separate. Typically the surgeon is sitting just a few feet away from the patient, but with the separation, it is possible to imagine scenarios where the surgeon is many miles away from the patient. With a good communication link, remote surgery becomes a possibility. A doctor in a safe location could perform battlefield surgery, or a surgeon in India could perform surgery on a patient in another country.
SEE ALSO Laparoscopic Surgery (1910), Robot (1921).
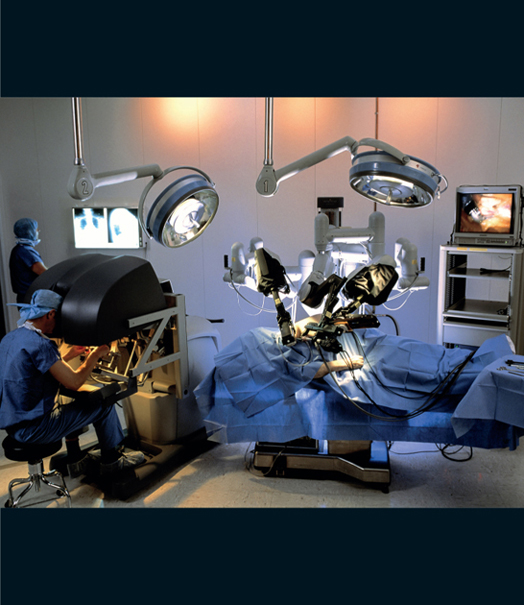
Surgeon (lower left) performing minimally invasive surgery (MIS) on a patient’s heart using a daVinci Si remotely-controlled robot surgeon (center right).