Review Questions
Select the ONE best answer.
-
Which layer of the heart is damaged in a heart attack?
- Epicardium
- Myocardium
- Endocardium
- All of the above
-
Your patient presents with chest pain and the above ECG. Which coronary artery most likely is occluded?
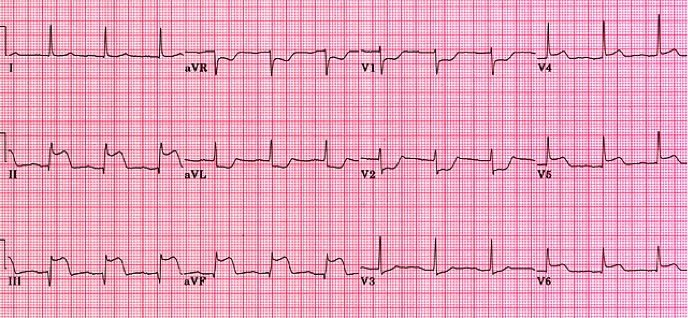
- LAD
- LCx
- LMCA
- RCA
-
Mitral valve regurgitation means that blood flows backward through the mitral valve. Into which of the following structures does blood flow during mitral valve regurgitation?
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
- Right atrium
- Right ventricle
-
During myocardial contraction, which of the following is true?
- Myocytes depolarize, and the cell potential becomes more negative.
- Myocytes depolarize, and the cell potential becomes more positive.
- Myocytes polarize, and the cell potential becomes more negative.
- Myocytes polarize, and the cell potential becomes more positive.
-
You notice an ECG of a patient has a PRI that is consistently 0.20 second long. There is a P wave for every QRS complex, but there is not a QRS complex for every P wave. Which of the following is most likely this patient’s rhythm?
- First-degree block
- Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type I
- Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type II
- Sinus arrest
-
During a successful intubation attempt of a patient in severe respiratory distress, you notice your patient’s heart rhythm is now marked sinus bradycardia at a rate of 34 when it was previously in the high 70s. The pulse oximetry remained in the high 90s throughout the attempt. What is the next most appropriate treatment?
- Begin CPR.
- Administer a 500 mL NSS bolus
- Administer 0.5–1 mg atropine intravenously.
- Administer 1 mg epinephrine 1:10,000 intravenously.
-
You arrive at a residence for a 50-year-old female complaining of dizziness after syncope. Her vital signs are HR: 190, BP: 84/36, RR: 24, SpO2: 99%. Her lead II tracing is above. What is the most appropriate treatment?
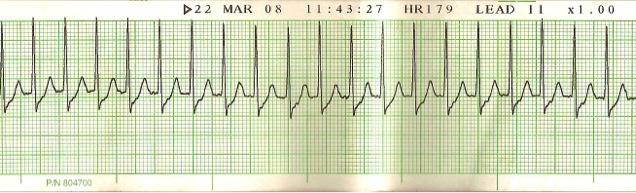
- Performing synchronized cardioversion at 100 J
- Performing synchronized cardioversion at 150 J
- Adminstering 6 mg adenosine followed with a 10 mL flush in a large vein
- Administering 12 mg adenosine followed with a 10 mL flush in a large vein
-
You have a 66-year-old patient found pulseless and apneic in his home. CPR was initiated by family members and is still continuing to produce a strong carotid pulse. The ECG shows the following rhythm, and you have started a 16-gauge intravenous line in the right EJ. Which medication is the best option for this patient?
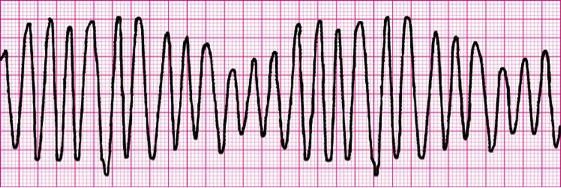
- 300 mg amiodarone
- 1 g calcium chloride
- 1 mg epinephrine 1:10,000
- 4 g magnesium sulfate
-
A 12-lead ECG reveals a QRS above the baseline in lead I and below the baseline in lead aVF. It also shows an RSRʹ pattern in lead V1. What is the most likely explanation for these findings?
- Left axis deviation and left bundle branch block
- Left axis deviation and right bundle branch block
- Right axis deviation and left bundle branch block
- Right axis deviation and right bundle branch block
-
Your patient is in cardiac arrest and the rhythm shows a pulseless 3rd-degree heart block at a rate of 30. All of the following are appropriate treatments for this patient EXCEPT:
- Continuous CPR.
- Treat the reversible causes (H’s and T’s).
- Pace the patient at a rate of 80 bpm.
- Epinephrine 1:10,000, 1 mg intravenous piggyback every 3–5 minutes.