CHAPTER XVI
THE FALL OF THE CITY
Now, when the Khalifa Abdullah saw that the last army that remained to him was broken, that all his attacks had failed, and that thousands of his bravest warriors were slain, he rode from the field of battle in haste, and, regaining the city, proceeded like a brave and stubborn soldier to make preparations for its defence, and, like a prudent man, to arrange for his own flight should further resistance be impossible. He ordered his great war-drum to be beaten and the ombya to be blown, and for the last time those dismal notes boomed through the streets of Omdurman. They were not heeded. The Arabs had had enough fighting. They recognised that all was lost. Besides, to return to the city was difficult and dangerous.
The charge of the 21st Lancers had been costly, but it was not ineffective. The consequent retirement of the Dervish brigade protecting the extreme right exposed their line of retreat. The cavalry were resolved to take full advantage of the position they had paid so much to gain, and while the second attack was at its height we were already trotting over the plain towards the long lines of fugitives who streamed across it. With the experience of the past hour in our minds, and with the great numbers of the enemy in our front, it seemed to many that a bloody day lay before us. But we had not gone far when individual Dervishes began to walk towards the advancing squadrons, throwing down their weapons, holding up their hands, and imploring mercy.
As soon as it was apparent that the surrender of individuals was accepted, the Dervishes began to come in and lay down their arms—at first by twos and threes, then by dozens, and finally by scores. Meanwhile those who were still intent on flight made a wide détour to avoid the cavalry, and streamed past our front at a mile’s distance in uninterrupted succession. The disarming and escorting of the prisoners delayed our advance, and many thousands of Dervishes escaped from the field. But the position of the cavalry and the pressure they exerted shouldered the routed army out into the desert, so that retiring they missed the city of Omdurman altogether, and, disregarding the Khalifa’s summons to defend it and the orders of their Emirs, continued their flight to the south. To harry and annoy the fugitives a few troops were dismounted with carbines, and a constant fire was made on such as did not attempt to come in and surrender. Yet the crowds continued to run the gauntlet, and at least 20,000 men made good their escape. Many of these were still vicious, and replied to our fire with bullets, fortunately at very long range. It would have been madness for 300 Lancers to gallop in among such masses, and we had to be content with the results of the carbine fire.
While all this had been going on, the advance of the army on Omdurman was continuing. Nor was it long before we saw the imposing array of infantry topping the sandhills near Surgham and flooding out into the plain which lay between them and the city. High over the centre brigade flew the Black Flag of the Khalifa, and underneath a smaller flash of red marked the position of the Headquarters Staff. The black masses of men continued to move slowly across the open ground while we fired at the flying Arabs, and at twelve o’clock we saw them halt near the river about three miles from the city. Orders now reached us to join them, and as the sun was hot, the day dragged, all were tired and hungry, and the horses needed water, we were not long in complying, and the remnants of the Dervish army made good their retreat unmolested.
We marched back to the Nile. The whole force had halted to drink, to eat, and to rest at Khor Shambat. The scene was striking. Imagine a six hundred yards stretch of the Suez Canal. Both banks are crowded with brown- or chocolate-clad figures. The northern side is completely covered with the swarming infantry of the British division. Thousands of animals—the horses of the cavalry, the artillery mules, the transport camels—fill the spaces and the foreground. Multitudes of khaki-clad men are sitting in rows on the slopes. Hundreds are standing by the brim or actually in the red muddy water. All are drinking deeply. Two or three carcasses, lying in the shallows, show that the soldiers are thirsty rather than particular. On all sides water-bottles are being filled from the welcome Nile, which has come into the desert to refresh the weary animals and men.
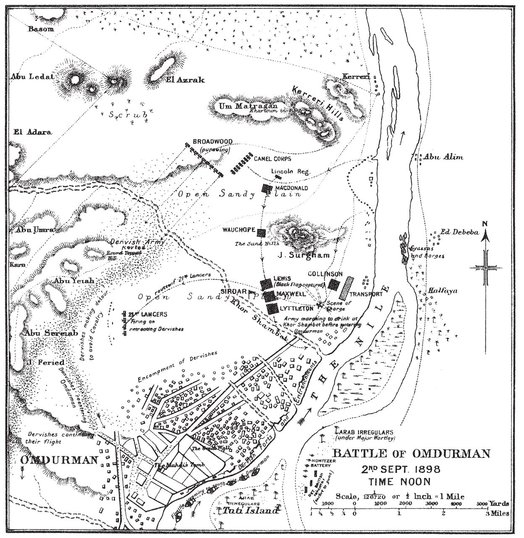
During the attack on MacDonald’s brigade the Egyptian cavalry had watched from their position on the southern slopes of the Kerreri Hills, ready to intervene, if necessary, and support the infantry by a charge. As soon as the Dervish onsets had ended and the whole mass had begun to retreat, Broadwood’s cavalry brigade formed in two lines, of four and of five squadrons respectively, and advanced in pursuit—first west for two miles, and then south-west for three miles more towards the Round-topped Hill. Like the 21st Lancers, they were delayed by many Dervishes. who threw down their arms and surrendered, and whom it was necessary to escort to the river. But as they drew nearer the mass of the routed army, it became apparent that the spirit of the enemy was by no means broken. Stubborn men fired continually as they lay wounded, refusing to ask for quarter—doubting, perhaps, that it would be granted. Under every bush that gave protection from the lances of the horsemen little groups collected to make a desperate stand. Solitary spearmen awaited unflinching the charge of a whole squadron. Men who had feigned death sprang up to fire an unexpected shot. The cavalry began to suffer occasional casualties. In proportion as they advanced the resistance of the enemy increased. The direct pursuit had soon to be abandoned, but in the hope of intercepting some part of the retreating mob Major Le Gallais, who commanded the three leading squadrons, changed direction towards the river, and, galloping nearly parallel to Khor Shambat, charged and cut into the tail of the enemy’s disordered array. The Arabs, however, stood their ground, and, firing their rifles wildly in all directions, killed and wounded a good many horses and men, so that the squadrons were content to bring up their right still more, and finally to ride out of the hornet swarm, into which they had plunged, towards Surgham Hill. The pursuit was then suspended, and the Egyptian cavalry joined the rest of the army by the Nile.
It was not until four o’clock that the cavalry received orders to ride round the outside of the city and harry such as should seek to escape. The Egyptian squadrons and the 21st Lancers started forthwith, and, keeping about a mile from the houses of the suburbs, proceeded to make the circle of the town. The infantry had already entered it, as was evident from a continual patter of shots and an occasional rattle of the Maxim guns. The leading Soudanese brigade—Maxwell’s —had moved from Khor Shambat at 2.30, formed in line of company columns and in the following order:—
Direction of Advance
The Sirdar, attended by his whole Staff, with the Black Flag of the Khalifa carried behind him and accompanied by the band of the XIth Soudanese, rode in front of the XIVth battalion. The regiments were soon enveloped by the numberless houses of the suburbs and divided by the twisting streets; but the whole brigade pressed forward on a broad front. Behind followed the rest of the army—battalion after battalion, brigade after brigade—until all, swallowed up by the maze of mud houses, were filling the open spaces and blocking and choking the streets and alleys with solid masses of armed men, who marched or pushed their way up to the great wall.
For two miles the progress through the suburbs continued, and the General, hurrying on with his Staff, soon found himself, with the band, the Maxims, and the artillery, at the foot of the great wall. Several hundred Dervishes had gathered for its defence; but the fact that no banquette had been made on which they could stand to fire prevented their resistance from being effective. A few ill-aimed shots were, however, fired, to which the Maxim guns replied with vigour. In a quarter of an hour the wall was cleared. The Sirdar then posted two guns of the 32nd Field Battery at its northern angle, and then, accompanied by the remaining four guns and the XIVth Soudanese, turned eastwards and rode along the foot of the wall towards the river, seeking some means of entry into the inner city. The breach made by the gunboats was found temporarily blocked by wooden doors, but the main gate was open, and through this the General passed into the heart of Omdurman. Within the wall the scenes were more terrible than in the suburbs. The effects of the bombardment were evident on every side. Women and children lay frightfully mangled in the roadway. At one place a whole family had been crushed by a projectile. Dead Dervishes, already in the fierce heat beginning to decompose, dotted the ground. The houses were crammed with wounded. Hundreds of decaying carcasses of animals filled the air with a sickening smell. Here, as without the wall, the anxious inhabitants renewed their protestations of loyalty and welcome; and interpreters, riding down the narrow alleys, proclaimed the merciful conditions of the conquerors and called on the people to lay down their arms. Great piles of surrendered weapons rose in the streets, guarded by Soudanese soldiers. Many Arabs sought clemency; but there were others who disdained it; and the whirring of the Maxims, the crashes of the volleys, and a continual dropping fire attested that there was fighting in all parts of the city into which the columns had penetrated. All Dervishes who did not immediately surrender were shot or bayoneted, and bullets whistled at random along or across the streets. But while women crowded round his horse, while sullen men fired carefully from houses, while beaten warriors cast their spears on the ground and others, still resisting, were despatched in corners, the Sirdar rode steadily onward through the confusion, the stench, and the danger, until he reached the Mahdi’s Tomb.
At the mosque two fanatics charged the Soudanese escort, and each killed or badly wounded a soldier before he was shot. The day was now far spent, and it was dusk when the prison was reached. The General was the first to enter that foul and gloomy den. Charles Neufeld and some thirty heavily shackled prisoners were released. Neufeld, who was placed on a pony, seemed nearly mad with delight, and talked and gesticulated with queer animation. ‘Thirteen years,’ he said to his rescuer, ‘have I waited for this day.’ From the prison, as it was now dark, the Sirdar rode to the great square in front of the mosque, in which his headquarters were established, and where both British brigades were already bivouacking. The rest of the army settled down along the roadways through the suburbs, and only Maxwell’s brigade remained in the city to complete the establishment of law and order—a business which was fortunately hidden by the shades of night.
While the Sirdar with the infantry of the army was taking possession of Omdurman, the British and Egyptian cavalry had moved round to the west of the city. There for nearly two hours we waited, listening to the dropping fusillade which could be heard within the great wall and wondering what was happening. Large numbers of Dervishes and Arabs, who, laying aside their jibbas, had ceased to be Dervishes, appeared among the houses at the edge of the suburbs. Several hundreds of these, with two or three Emirs, came out to make their submission; and we were presently so loaded with spears and swords that it was impossible to carry them, and many interesting trophies had to be destroyed. It was just getting dark when suddenly Colonel Slatin galloped up. The Khalifa had fled! The Egyptian cavalry were at once to pursue him. The 21st Lancers must await further orders. Slatin appeared very much in earnest. He talked with animated manner to Colonel Broadwood, questioned two of the surrendered Emirs closely, and hurried off into the dusk, while the Egyptian squadrons, mounting, also rode away at a trot.
It was not for some hours after he had left the field of battle that Abdullah realised that his army had not obeyed his summons, but were continuing their retreat, and that only a few hundred Dervishes remained for the defence of the city. He seems, if we judge from the accounts of his personal servant, an Abyssinian boy, to have faced the disasters that had overtaken him with singular composure. He rested until two o‘clock, when he ate some food. Thereafter he repaired to the Tomb, and in that ruined shrine, amid the wreckage of the shell-fire, the defeated sovereign appealed to the spirit of Mohammed Ahmed to help him in his sore distress. It was the last prayer ever offered over the Mahdi’s grave. The celestial counsels seem to have been in accord with the dictates of common-sense, and at four o’clock the Khalifa, hearing that the Sirdar was already entering the city, and that the English cavalry were on the parade ground to the west, mounted a small donkey, and, accompanied by his principal wife, a Greek nun as a hostage, and a few attendants, rode leisurely off towards the south. Eight miles from Omdurman a score of swift camels awaited him, and on these he soon reached the main body of his routed army. Here he found many disheartened friends; but the fact that, in this evil plight, he found any friends at all must be recorded in his favour and in that of his subjects. When he arrived he had no escort—was, indeed, unarmed. The fugitives had good reason to be savage. Their leaders had led them only to their ruin. To cut the throat of this one man who was the cause of all their sufferings was as easy as they would have thought it innocent. Yet none assailed him. The tyrant, the oppressor, the scourge of the Soudan, the hypocrite, the abominated Khalifa; the embodiment, as he has been depicted to European eyes, of all the vices; the object, as he was believed in England, of his people’s bitter hatred, found safety and welcome among his flying soldiers. The surviving Emirs hurried to his side. Many had gone down on the fatal plain. Osman Azrak, the valiant Bishara, Yakub, and scores whose strange names have not obscured these pages, but who were, nevertheless, great men of war, lay staring up at the stars. Yet those who remained never wavered in their allegiance. Ali-Wad-Helu, whose leg had been shattered by a shell splinter, was senseless with pain; but the Sneikh-ed-Din, the astute Osman Digna, Ibrahim Khalil, who withstood the charge of the 21st Lancers, and others of less note rallied to the side of the appointed successor of Mohammed Ahmed, and did not, even in this extremity, abandon his cause. And so all hurried on through the gathering darkness, a confused and miserable multitude—dejected warriors still preserving their trashy rifles, and wounded men hobbling pitifully along; camels and donkeys laden with household goods; women crying, panting, dragging little children; all in thousands—nearly 30,000 altogether; with little food and less water to sustain them; the desert before them. the gunboats on the Nile, and behind the rumours of pursuit and a broad trail of dead and dying to mark the path of flight.
Meanwhile the Egyptian cavalry had already started on their fruitless errand. The squadrons were greatly reduced in numbers. The men carried food to suffice till morning, the horses barely enough to last till noon. To supplement this slender provision a steamer had been ordered up the river to meet them the next day with fresh supplies. The road by the Nile was choked with armed Dervishes, and to avoid these dangerous fugitives the column struck inland and marched southward towards some hills whose dark outline showed against the sky. The unknown ground was difficult and swampy. At times the horses floundered to their girths in wet sand; at others rocky khors obstructed the march; horses and camels blundered and fell. The darkness complicated the confusion. At about ten o’clock Colonel Broadwood decided to go no further till there was more light. He therefore drew off the column towards the desert, and halted on a comparatively dry spot. Some muddy pools, which were luckily discovered, enabled the bottles to be filled and the horses to be watered. Then, having posted many sentries, the exhausted pursuers slept, waking from time to time to listen to the intermittent firing which was still audible, both from the direction of Omdurman and from that in which the Dervish army was flying.
At 3 A.M. on the 3rd Colonel Broadwood’s force moved on again. Men and horses seemed refreshed, and by the aid of a bright moon the ground was covered at a good pace. By seven o‘clock the squadrons approached the point on the river which had been fixed for meeting the steamer. She had already arrived, and the sight of the funnel in the distance and the anticipation of a good meal cheered everyone, for they had scarcely had anything to eat since the night before the battle. But as the troopers drew nearer it became evident that 300 yards of shallow water and deep swamp intervened between them and the vessel. Closer approach was prevented. There was no means of landing the stores. In the hopes of finding a suitable spot further up the stream the march was resumed. The steamer kept pace along the river. The boggy ground delayed the columns, but by two o’clock seven more miles had been covered. Only the flag at the masthead was now visible, and an impassable morass separated the force from the river bank. It was impossible to obtain supplies. Without food it was out of the question to go on. Indeed, great privations must, as it was, accompany the return march. The necessity was emphasised by the reports of captured fugitives, who all told the same tale. The Khalifa had pushed on swiftly, and was trying to reorganise his army. Colonel Broadwood thereupon rested his horses till the heat of the day was over, and then began the homeward march. It was not until eleven o’clock on the 4th of September that the worn-out and famished cavalry reached their camp near Omdurman.
Such was the pursuit as conducted by the regular troops. Abdel-Azim, with 750 Arabs, persisted still further in the chase. Lightly equipped, and acquainted with the country, they reached Shegeig, nearly a hundred miles south of Khartoum, on the 7th. Here they obtained definite information. The Khalifa had two days’ start, plenty of food and water, and many camels. He had organised a bodyguard of 500 Jehadia, and was, besides, surrounded by a large force of Arabs of various tribes. With this numerous and powerful following he was travelling day and night towards El Obeid, which town was held by an unbeaten Dervish garrison of nearly 3,000 men. On hearing these things the friendly Arabs determined—not unwisely—to abandon the pursuit, and came boastfully back to Omdurman
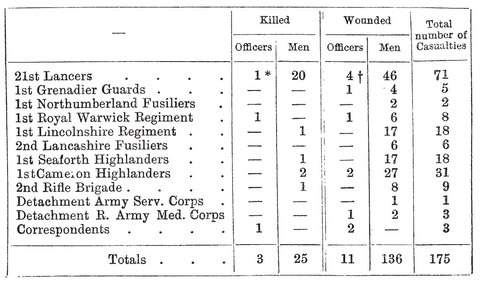
In the battle and capture of Omdurman the losses of the Expeditionary Force were as follows:
BRITISH DIVISION
Officers Killed (3)
Capt. G. Caldecott, 1st Royal Warwickshire Regiment.
Lieut. R. G. Grenfell, 12th Royal Lancers, attached 21st Lancers.
Hon. H. Howard, correspondent of the TIMES.
Officers Wounded (11)
Col. F. Rhodes, D.S.O., correspondent of the TIMES
Lieut.-Col. Sloggett, R.A.M.C.
Capt. Hon. W. L. Bagot, 1st Grenadier Guards
Capt. S. S. S. Clarke, 1st Cameron Highlanders
Lieut. and Adj. A. M. Pirie, 21st t Lancers
Lieut. J. C. Brinton, 2nd Life Guards, attached 21st Lancers
Lieut. C. E. Etches. 1st Royal Warwickshire Regiment
Lieut. A. D. Nicholson, 1st Cameron Highlanders
Lieut. Hon. R. F. Molyneux, Royal Horse Guards, attached 21st Lancers
Lieut. C. S. Nesham, 21st Lancers
Mr. C. Williams, correspondent of the DAILY CHRONICLE
EGYPTIAN ARMY
British Officers and N.C. Officer Wounded (6)
Capt. C. H. de Rougemont, R.A.
Capt. N. M. Smyth, Intelligence Staff
Lieut. H. A. Micklem, R.E.
Lieut. H. C. B. Hopkinson, Camel Corps
Lieut. C. F. S. Vandeleur, D.S.O.
Staff-Sergt. Hooper
Native Ranks
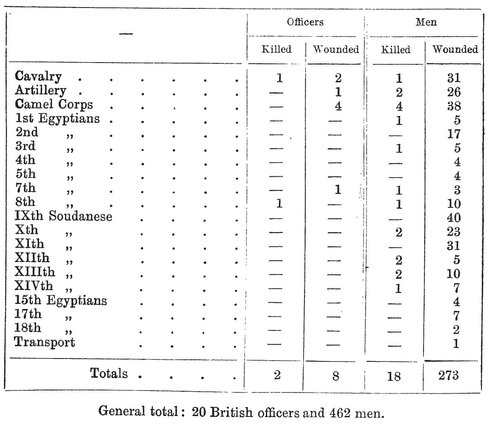
The Dervish losses were, from computations made on the field and corrected at a later date, ascertained to be 9,700 killed, and wounded variously estimated at from 10,000 to 16,000. There were, besides, 5,000 prisoners.