4
Prepregnancy care, prenatal screening and fetal medicine
Examples of structural malformations identified on ultrasound (Figs 4.1–4.3) (see videos: Fetal echocardiogram 1, Fetal echocardiogram 2, Fetal myelomeningocele)
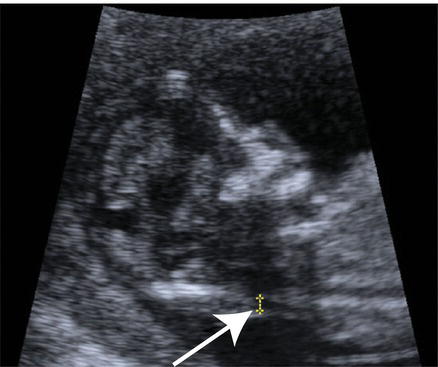
Fig. 4.1 Increased nuchal translucency associated with trisomy 21 (Down syndrome).
(Courtesy of Dr Venkhat Rahman.)
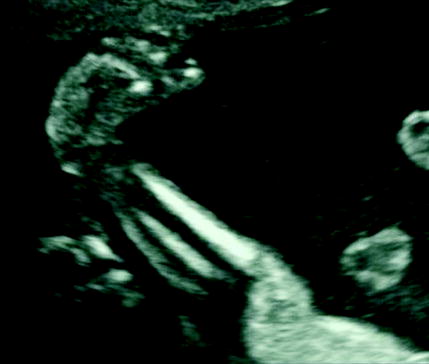
Fig. 4.3 Talipes equinovarus.
Fetal medicine
Fetal medicine (Fig. 4.4) may allow:
- identification of congenital abnormalities (structural and chromosomal) with varying specificity and sensitivity of detection.
- therapy (either indirectly or directly) to be given for a limited but increasing number of conditions, (e.g. fetal arrhythmias, intrauterine blood transfusion for severe rhesus disease)
- optimal multidisciplinary discussion to impart information on prognosis and allow parents to make informed decisions including option of termination of pregnancy for severe disorders
- optimal obstetric management of the fetus, e.g. timing of delivery
- neonatal management to be planned in advance, e.g. counseling and transfer to specialty center.
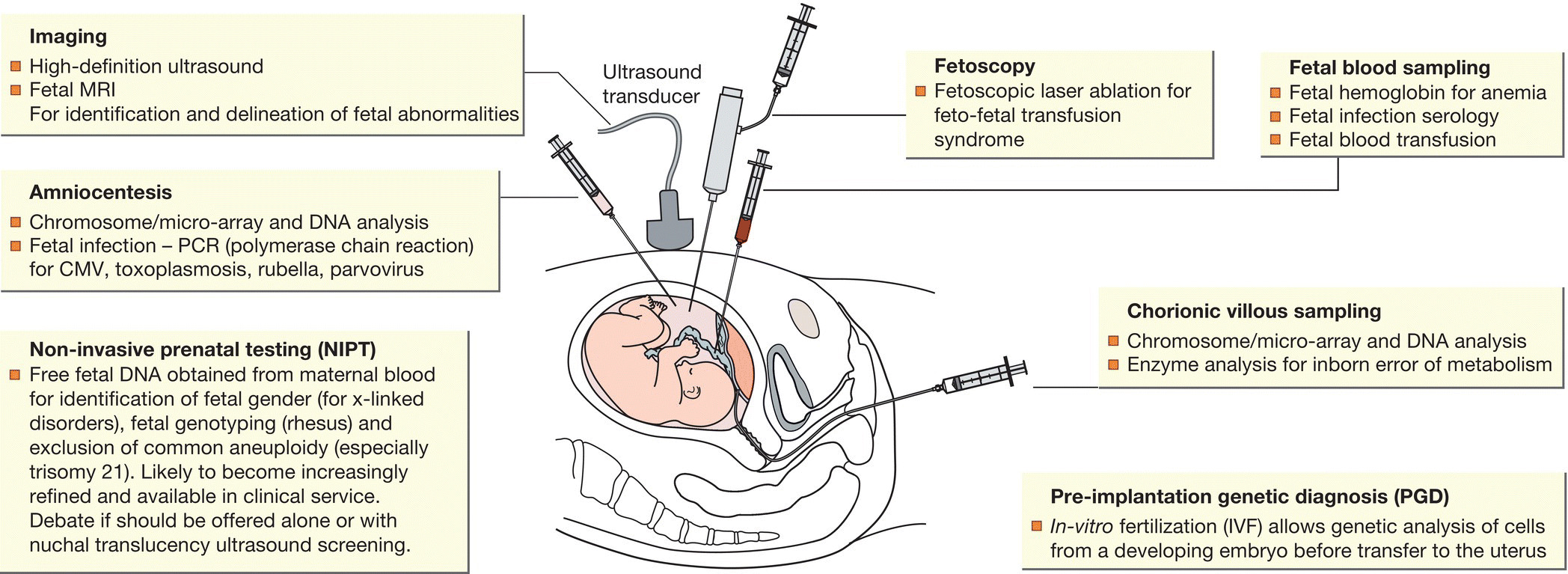
Fig. 4.4 Techniques in fetal medicine and their indications.