Glossary
Note on pronunciation: In romanized Indic-language names and italicized terms, short a is pronounced like the u in “but”; the other vowels have roughly the same values as in Spanish or Italian; 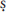 and
and  are pronounced like English sh; c is pronounced like English ch; and h after any other consonant simply adds extra breath, without changing the sound of the preceding consonant (thus, not ph as in “physics” or th as in “thin”). Other letters may be given their usual English values.
are pronounced like English sh; c is pronounced like English ch; and h after any other consonant simply adds extra breath, without changing the sound of the preceding consonant (thus, not ph as in “physics” or th as in “thin”). Other letters may be given their usual English values.
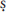 and
and  are pronounced like English sh; c is pronounced like English ch; and h after any other consonant simply adds extra breath, without changing the sound of the preceding consonant (thus, not ph as in “physics” or th as in “thin”). Other letters may be given their usual English values.
are pronounced like English sh; c is pronounced like English ch; and h after any other consonant simply adds extra breath, without changing the sound of the preceding consonant (thus, not ph as in “physics” or th as in “thin”). Other letters may be given their usual English values.
E = English; H = Hindi (or related North Indian language); L = Latin; S = Sanskrit
Most Sanskrit terms can be used in Hindi (usually dropping final -a).
 c c ra ra |
(S) custom, practice; customary rule; local law
|
adhik ra ra |
(S) competence, qualification; authorization; responsibility
|
  rama rama |
(S) at first, a way of life (such as that of a married householder or ascetic); the M
 nava Dharma nava Dharma  stra canonized the ideal of four sequential stra canonized the ideal of four sequential   ramas (hence, “life-stages”: student, householder, hermit, and homeless ascetic [yati; later, sa ramas (hence, “life-stages”: student, householder, hermit, and homeless ascetic [yati; later, sa ny ny sin]; see Olivelle 1993) sin]; see Olivelle 1993)
|
| bhakti |
(S) devotion experienced as a direct personal contact or union with God; a largely vernacular devotional movement originating
in seventh-century South India
|
bh 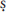 ya ya |
(S) “commentary,” a prose text structured as a running explication or interpretation of a s
 tra or tra or   stra stra |
| communis error facit ius |
(L) “A common error makes law”
|
| Dalit |
(E < H) “oppressed,” label often used to denote castes formerly known as “low caste” or “Untouchable,” and often adopted today by members of such castes
|
da 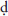 a a |
(S) “staff; royal scepter”; punishment, symbol of the king’s authority to punish the guilty
|
de adharma adharma |
(S) law peculiar to a region
|
| dharma |
(S) righteousness, duty, law; (H) religion
|
dharm dhik dhik rin, -k rin, -k r r |
(S, H) state-appointed official, properly an expert in Dharma
  stra, concerned especially with the enforcement of pr stra, concerned especially with the enforcement of pr ya ya citta and caste penalties citta and caste penalties
|
dharma  stra stra |
(S) canonical treatise on dharma; dharma literature in general (capitalized in this sense); compare
  stra stra |
dharma  strin, - strin, -  str str |
(S, H) expert in Dharma
  stra stra
|
| diaspora |
(E) the dispersal or spread of people of a common religion or ethnicity due to political or economic pressures, leading to
their long-term or permanent resettlement abroad; collectively, the people thus dispersed
|
| divya |
(S) “divine” proof, i.e., oath or ordeal
|
diwani (d v v n n ) )
|
(E < H) revenue collection under Islamic or colonial administration
|
| jayapattra |
(S) document recording success in a legal suit
|
kacahr |
(H) court of law, cutchery
|
k vya vya |
(S) ornate courtly poetry in Sanskrit
|
| laukika |
(S) “of this world; customary” (as opposed to “divine” or “sacred”)
|
| lekha, lekhya |
(S) written document
|
manaut |
(H) pledge, votive petition
|
| Mandal Commission |
a committee created in 1979, chaired by B. P. Mandal, to reassess government policies intended to benefit “backward classes,” i.e., those socially or economically disadvantaged because of their caste status
|
| mantrin |
(S) minister, appointed high official of the state
|
m la la |
(S) “root” or source (e.g., of dharma)
|
| nibandha |
(S) topically organized digest of quotations from various sm
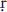 tis tis
|
ny ya ya |
(S) logic; legal reasoning; a judicial ruling (ny
 ya-v ya-v da); by extension, “justice” in a legal proceeding da); by extension, “justice” in a legal proceeding
|
| Other Backward Classes |
(E) category used in Article 340 of the Indian Constitution to designate a roster of castes other than the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes and women as beneficiaries of reservations under Indian law; commonly abbreviated “OBCs”
|
| pañcagavya |
(S) the five pure products of the cow: milk, curd, butter, urine, manure
|
pandit (pa 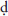 ita) ita)
|
(E < S, H) learned man; expert in traditional learning
|
pram  a a |
(S) criterion or means of correct knowledge; authoritativeness; proof
|
pr m m  ya ya |
(S) authority
|
pr ya ya citta citta |
(S) penance, ritual expiation according to Brahmanical Hindu ritual and Dharma
  stra stra
|
| purohita |
(S) chief Brahmin priest of a king, responsible for performing his consecration and other rites of state
|
| quod fieri non debuit factum valet |
(L) “What ought not to have been done is valid, once done”
|
r jadharma jadharma |
(S) the dharma of a king according to Dharma
  stra stra
|
r jan jan |
(S) king
|
| reservations |
(E) legally mandated quotas for lower castes and women in the public sphere, a form of compensatory discrimination or “affirmative action”
|
sabh |
(S) council of Brahmins constituted to make decisions or hear cases
|
| sabhya |
(S) appointed member of a sabh
 |
| samaya |
(S) established convention, sometimes recorded in a document (pattra / patra / p
 tra) tra)
|
 apatha apatha |
(S) oath, an appeal to divine authority when used in court
|
  sana sana |
(S) command, especially a written royal decree, grant, or ruling
|
  stra stra |
(S) canonical treatise, composed mainly in verse, with any commentary thereon; field of scholastic expertise
|
  strin / strin /   str str |
(S/H) expert in
  stra stra |
sat |
(S) devoted wife who immolates herself on her husband’s funeral pyre; in British usage (“suttee”), the (ostensibly voluntary)
act itself
|
| Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes |
(E) the categories used in Indian law to designate specifically enumerated castes and tribes to whom the policy of reservations applies; abbreviated SCs and STs
|
sm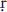 ti ti |
(S) “memory” of Vedic precepts as recorded in s
 tras, dharma tras, dharma  stras, and other Sanskrit works; often used as a synonym of “dharma stras, and other Sanskrit works; often used as a synonym of “dharma  stra” stra”
|
 ruti ruti |
(S) the “audible” Vedic scriptures as preserved orally through rote memorization, held in M
 m m  s s and Dharma and Dharma  stra to have
the highest authority of all sources of knowledge (pram stra to have
the highest authority of all sources of knowledge (pram  as); contrasted with sm as); contrasted with sm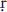 ti, which is considered second to ti, which is considered second to  ruti in authority ruti in authority
|
| stare decisis |
(L) “Stand by prior decisions”
|
| sthiti |
(S) rule based on customary norms (
 c c ra), sometimes recorded in a document (pattra / patra / p ra), sometimes recorded in a document (pattra / patra / p tra) tra)
|
s tra tra |
(S) code of rules composed in compressed, aphoristic style in Sanskrit, generally one of the older canonical texts of tradition; the dharmas
 tras were the earliest works devoted to the rules of dharma tras were the earliest works devoted to the rules of dharma |
| suttee |
see sat
 |
| svadharma |
(S) the dharma appropriate to oneself
|
| twice migrants |
(E) members of the Hindu diaspora of one adopted country who relocate to another
|
var a a |
(S) caste category in the fourfold hierarchy taught in Brahmanical doctrine: Brahmin, K
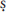 atriya, Vai atriya, Vai ya, ya, 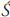  dra dra
|
var   ramadharma ramadharma |
(S) dharma defined in relation to caste (var
 a) and stage of life ( a) and stage of life (  rama), a concept established in the M rama), a concept established in the M nava Dharma nava Dharma  stra stra |
| vijaya |
(S) victory, success in litigation, sometimes recorded in a document (pattra / patra / p
 tra) tra)
|
vyavah ra ra |
(S) in general: social intercourse, commerce; in the Artha
  stra: legally recognized transaction; in Dharma stra: legally recognized transaction; in Dharma  stra: lawsuit, legal procedure stra: lawsuit, legal procedure
|
vyavasth |
(S) ruling, decision, determination of a case by a pandit serving as law officer to a court, sometimes recorded in a document (pattra / patra / p
 tra) tra)
|