
NOW at last the slowly-gathered, long-pent-up fury of the storm broke upon us. Four or five millions of men met each other in the first shock of the most merciless of all the wars of which record has been kept. Within a week the front in France, behind which we had been accustomed to dwell through the hard years of the former war and the opening phase of this, was to be irretrievably broken. Within three weeks the long-famed French Army was to collapse in rout and ruin, and our only British Army to be hurled into the sea with all its equipment lost. Within six weeks we were to find ourselves alone, almost disarmed, with triumphant Germany and Italy at our throats, with the whole of Europe open to Hitler’s power, and Japan glowering on the other side of the globe. It was amid these facts and looming prospects that I entered upon my duties as Prime Minister and Minister of Defence and addressed myself to the first task of forming a Government of all parties to conduct His Majesty’s business at home and abroad by whatever means might be deemed best suited to the national interest.
Five years later almost to a day it was possible to take a more favourable view of our circumstances. Italy was conquered and Mussolini slain. The mighty German Army had surrendered unconditionally. Hitler had committed suicide. In addition to the immense captures by General Eisenhower, nearly three million German soldiers were taken prisoners in twenty-four hours by Field-Marshal Alexander in Italy and Field-Marshal Montgomery in Germany. France was liberated, rallied, and revived. Hand in hand with our Allies, the two mightiest empires in the world, we advanced to the swift annihilation of Japanese resistance. The contrast was certainly remarkable. The road across these five years was long, hard, and perilous. Those who perished upon it did not give their lives in vain. Those who marched forward to the end will always be proud to have trodden it with honour.

In giving an account of my stewardship and in telling the tale of the famous National Coalition Government it is my first duty to make plain the scale and force of the contribution which Great Britain and her Empire, whom danger only united more tensely, made to what eventually became the Common Cause of so many States and nations. I do this with no desire to make invidious comparisons or rouse purposeless rivalries with our greatest Ally, the United States, to whom we owe immeasurable and enduring gratitude. But it is to the combined interest of the English-speaking world that the magnitude of the British war-making effort should be known and realised. I have therefore had a table made which I print on the opposite page, which covers the whole period of the war. This shows that until July 1944 Britain and her Empire had a substantially larger number of divisions in contact with the enemy than the United States. This general figure includes not only the European and African spheres but also all the war in Asia against Japan. Till the arrival in Normandy in the autumn of 1944 of the great mass of the American Army, we had always the right to speak at least as an equal and usually as the predominant partner in every theatre of war except the Pacific and the Australasian; and this remains also true, up to the time mentioned, of the aggregation of all divisions in all theatres for any given month. From July 1944 the fighting front of the United States, as represented by divisions in contact with the enemy, became increasingly predominant, and so continued, mounting and triumphant, till the final victory ten months later.
Another comparison which I have made shows that the British and Empire sacrifice in loss of life was even greater than that of our valiant Ally. The British total dead, and missing, presumed dead, of the armed forces amounted to 303,240, to which should be added over 109,000 from the Dominions, India, and the Colonies, a total of over 412,240. This figure does not include 60,500 civilians killed in the air raids on the United Kingdom, nor the losses of our Merchant Navy and fishermen, which amounted to about 30,000. Against this figure the United States mourn the deaths in the Army and Air Force, the Navy, Marines, and Coastguard, of 322,188.* I cite these sombre Rolls of Honour in the confident faith that the equal comradeship sanctified by so much precious blood will continue to command the reverence and inspire the conduct of the English-speaking world.
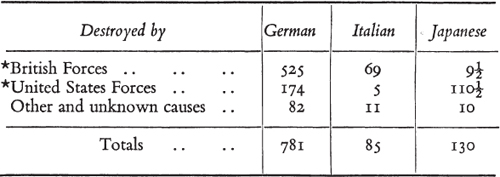
On the seas the United States naturally bore almost the entire weight of the war in the Pacific, and the decisive battles which they fought near Midway Island, at Guadalcanal, and in the Coral Sea in 1942 gained for them the whole initiative in that vast ocean domain, and opened to them the assault of all the Japanese conquests, and eventually of Japan herself. The American Navy could not at the same time carry the main burden in the Atlantic and the Mediterranean. Here again it is a duty to set down the facts. Out of 781 German and 85 Italian U-boats destroyed in the European theatre, the Atlantic and Indian Oceans, 594 were accounted for by British sea and air forces, who also disposed of all the German battleships, cruisers, and destroyers, besides destroying or capturing the whole Italian Fleet.
The dividing line between the Eastern and Western theatres is taken as a north/south line through Karachi.
The following are NOT taken as operational theatres:
N.W. Frontier of India; Gibraltar; West Africa; Iceland; Hawaii; Palestine; Iraq; Syria (except on July 1, 1941).
Malta is taken as an operational theatre; also Alaska from Jan. 1942 to July 1943.
Foreign contingents—e.g., Free French, Poles, Czechs—are NOT included.
The table of U-boat losses is as follows:
U-BOAT LOSSES
Grand total of U-boats destroyed: 996
In the air superb efforts were made by the United States to come into action, especially with their daylight Fortress bombers, on the greatest scale from the earliest moment after Pearl Harbour, and their power was used both against Japan and from the British Isles against Germany. However, when we reached Casablanca in January 1943 it is a fact that no single American bomber plane had cast a daylight bomb on Germany. Very soon the fruition of the great exertions they were making was to come, but up till the end of 1943 the British discharge of bombs upon Germany had in the aggregate exceeded by eight tons to one those cast from American machines by day or night, and it was only in the spring of 1944 that the preponderance of discharge was achieved by the United States. Here, as in the armies and on the sea, we ran the full course from the beginning, and it was not until 1944 that we were overtaken and surpassed by the tremendous war effort of the United States.
It must be remembered that our munitions effort from the beginning of Lend-Lease in January 1941 was increased by over one-fifth through the generosity of the United States. With the materials and weapons which they gave us we were actually able to wage war as if we were a nation of fifty-eight millions instead of forty-eight. In shipping also the marvellous production of Liberty Ships enabled the flow of supplies to be maintained across the Atlantic. On the other hand, the analysis of shipping losses by enemy action suffered by all nations throughout the war should be borne in mind. Here are the figures:

Of these losses 80 per cent. were suffered in the Atlantic Ocean, including British coastal waters and the North Sea. Only 5 per cent. were lost in the Pacific.
This is all set down, not to claim undue credit, but to establish on a footing capable of commanding fair-minded respect the intense output in every form of war activity of the people of this small Island, upon whom in the crisis of the world’s history the brunt fell.

It is probably easier to form a Cabinet, especially a Coalition Cabinet, in the heat of battle than in quiet times. The sense of duty dominates all else, and personal claims recede. Once the main arrangements had been settled with the leaders of the other parties, with the formal authority of their organisations, the attitude of all those I sent for was like that of soldiers in action, who go to the places assigned to them at once without question. The Party basis being officially established, it seemed to me that no sense of Self entered into the minds of any of the very large number of gentlemen I had to see. If some few hesitated it was only because of public considerations. Even more did this high standard of benaviour apply to the large number of Conservative and National Liberal Ministers who had to leave their offices and break their careers, and at this moment of surpassing interest and excitement to step out of official life, in many cases for ever.
The Conservatives had a majority of more than one hundred and twenty over all other parties in the House combined. Mr. Chamberlain was their chosen leader. I could not but realise that his supersession by me must be very unpleasant to many of them, after all my long years of criticism and often fierce reproach. Besides this, it must be evident to the majority of them how my life had been passed in friction or actual strife with the Conservative Party, that I had left them on Free Trade and had later returned to them as Chancellor of the Exchequer. After that I had been for many years their leading opponent on India, on foreign policy, and on the lack of preparation for war. To accept me as Prime Minister was to them very difficult. It caused pain to many honourable men. Moreover, loyalty to the chosen leader of the party is a prime characteristic of the Conservatives. If they had on some questions fallen short of their duty to the nation in the years before the war, it was because of this sense of loyalty to their appointed chief. None of these considerations caused me the slightest anxiety. I knew they were all drowned by the cannonade.
In the first instance I had offered to Mr. Chamberlain, and he had accepted, the Leadership of the House of Commons, as well as the Lord Presidency. Nothing had been published. Mr. Attlee informed me that the Labour Party would not work easily under this arrangement. In a Coalition the Leadership of the House must be generally acceptable. I put this point to Mr. Chamberlain, and, with his ready agreement, I took the Leadership myself, and held it till February 1942. During this time Mr. Attlee acted as my deputy and did the daily work. His long experience in Opposition was of great value. I came down only on the most serious occasions. These were, however, recurrent. Many Conservatives felt that their party leader had been slighted. Everyone admired his personal conduct. On his first entry into the House in his new capacity (May 13) the whole of his party—the large majority of the House—rose and received him in a vehement demonstration of sympathy and regard. In the early weeks it was from the Labour benches that I was mainly greeted. But Mr. Chamberlain’s loyalty and support was steadfast, and I was sure of myself.
There was considerable pressure by elements of the Labour Party, and by some of those many able and ardent figures who had not been included in the new Government, for a purge of the “guilty men” and of Ministers who had been responsible for Munich or could be criticised for the many shortcomings in our war preparation. But this was no time for proscriptions of able, patriotic men of long experience in high office. If the censorious people could have had their way at least a third of the Conservative Ministers would have been forced to resign. Considering that Mr. Chamberlain was the Leader of the Conservative Party, it was plain that this movement would be destructive of the national unity. Moreover, I had no need to ask myself whether all the blame lay on one side. Official responsibility rested upon the Government of the time. But moral responsibilities were more widely spread. A long, formidable list of quotations from speeches and votes recorded by Labour, and not less by Liberal, Ministers, all of which had been stultified by events, was in my mind and available in detail. No one had more right than I to pass a sponge across the past. I therefore resisted these disruptive tendencies. “If the present,” I said a few weeks later, “tries to sit in judgment on the past it will lose the future.” This argument and the awful weight of the hour quelled the would-be heresy-hunters.

My experiences in those first days were peculiar. One lived with the battle, upon which all thoughts were centred, and about which nothing could be done. All the time there was the Government to form and the gentlemen to see and the party balances to be adjusted. I cannot remember, nor do my records show, how all the hours were spent. A British Ministry at that time contained between sixty and seventy Ministers of the Crown, and all these had to be fitted in like a jig-saw puzzle, in this case having regard to the claims of three parties. It was necessary for me to see not only all the principal figures but, for a few minutes at least, the crowd of able men who were to be chosen for important tasks. In forming a Coalition Government the Prime Minister has to attach due weight to the wishes of the party leaders as to who among their followers shall have the offices allotted to the party. By this principle I was mainly governed. If any who deserved better were left out on the advice of their party authorities, or even in spite of that advice, I can only express regret. On the whole however the difficulties were few.
In Clement Attlee I had a colleague of war experience long versed in the House of Commons. Our only differences in outlook were about Socialism, but these were swamped by a war soon to involve the almost complete subordination of the individual to the State. We worked together with perfect ease and confidence during the whole period of the Government. Mr. Arthur Greenwood was a wise counsellor of high courage and a good and helpful friend.
Sir Archibald Sinclair, as official Leader of the Liberal Party, found it embarrassing to accept the office of Air Minister, because his followers felt he should instead have a seat in the War Cabinet. But this ran contrary to the principle of a small War Cabinet. I therefore proposed that he should join the War Cabinet when any matter affecting fundamental political issues or party union was involved. He was my friend, and had been my second-in-command when in 1916 I commanded the 6th Royal Scots Fusiliers at Ploegsteert (“Plug Street”), and personally longed to enter upon the great sphere of action I had reserved for him. After no little intercourse this had been amicably settled. Mr. Ernest Bevin, with whom I had made acquaintance at the beginning of the war, in trying to mitigate the severe Admiralty demands for trawlers, had to consult the Transport and General Workers’ Union, of which he was secretary, before he could join the team in the most important office of Minister of Labour. This took two or three days, but it was worth it. The union, the largest of all in Britain, said unanimously that he was to do it, and stuck solid for five years till we won.
The greatest difficulty was with Lord Beaverbrook. I believed he had services to render of a very high quality. I had resolved, as the result of my experiences in the previous war, to remove the supply and design of aircraft from the Air Ministry, and I wished him to become the Minister of Aircraft Production. He seemed at first reluctant to undertake the task, and of course the Air Ministry did not like having their Supply Branch separated from them. There were other resistances to his appointment. I felt sure however that our life depended upon the flow of new aircraft; I needed his vital and vibrant energy, and I persisted in my view.
In deference to prevailing opinions expressed in Parliament and the Press it was necessary that the War Cabinet should be small. I therefore began by having only five members, of whom one only, the Foreign Secretary, had a department. These were naturally the leading party politicians of the day. For the convenient conduct of business it was necessary that the Chancellor of the Exchequer and the Leader of the Liberal Party should usually be present, and as time passed the number of “constant attenders” grew. But all the responsibility was laid upon the five War Cabinet Ministers. They were the only ones who had the right to have their heads cut off on Tower Hill if we did not win. The rest could suffer for departmental shortcomings, but not on account of the policy of the State. Apart from the War Cabinet, any one could say: “I cannot take the responsibility for this or that.” The burden of policy was borne at a higher level. This saved many people a lot of worry in the days which were immediately to fall upon us.

In my long political experience I had held most of the great offices of State, but I readily admit that the post which had now fallen to me was the one I liked the best. Power, for the sake of lording it over fellow-creatures or adding to personal pomp, is rightly judged base. But power in a national crisis, when a man believes he knows what orders should be given, is a blessing. In any sphere of action there can be no comparison between the positions of number one and number two, three, or four. The duties and the problems of all persons other than number one are quite different and in many ways more difficult. It is always a misfortune when number two or three has to initiate a dominant plan or policy. He has to consider not only the merits of the policy but the mind of his chief; not only what to advise but what it is proper for him in his station to advise; not only what to do but how to get it agreed, and how to get it done. Moreover, number two or three will have to reckon with numbers four, five, and six, or maybe some bright outsider, number twenty. Ambition, not so much for vulgar ends, but for fame, glints in every mind. There are always several points of view which may be right, and many which are plausible. I was ruined for the time being in 1915 over the Dardanelles, and a supreme enterprise was cast away, through my trying to carry out a major and cardinal operation of war from a subordinate position. Men are ill-advised to try such ventures. This lesson had sunk into my nature.
At the top there are great simplifications. An accepted leader has only to be sure of what it is best to do, or at least to have made up his mind about it. The loyalties which centre upon number one are enormous. If he trips he must be sustained. If he makes mistakes they must be covered. If he sleeps he must not be wantonly disturbed. If he is no good he must be pole-axed. But this last extreme process cannot be carried out every day; and certainly not in the days just after he has been chosen.
The fundamental changes in the machinery of war direction were more real than apparent. “A Constitution,” said Napoleon, “should be short and obscure.” The existing organisms remained intact. No official personalities were changed. The War Cabinet and the Chiefs of Staff Committee at first continued to meet every day as they had done before. In calling myself, with the King’s approval, Minister of Defence I had made no legal or constitutional change. I had been careful not to define my rights and duties. I asked for no special powers either from the Crown or Parliament. It was however understood and accepted that I should assume the general direction of the war, subject to the support of the War Cabinet and of the House of Commons. The key change which occurred on my taking over was of course the supervision and direction of the Chiefs of Staff Committee by a Minister of Defence with undefined powers. As this Minister was also the Prime Minister, he had all the rights inherent in that office, including very wide powers of selection and removal of all professional and political personages. Thus for the first time the Chiefs of Staff Committee assumed its due and proper place in direct daily contact with the executive head of the Government, and in accord with him had full control over the conduct of the war and the armed forces.
The position of the First Lord of the Admiralty and of the Secretaries of State for War and Air was decisively affected in fact though not in form. They were not members of the War Cabinet, nor did they attend the meetings of the Chiefs of Staff Committee. They remained entirely responsible for their departments, but rapidly and almost imperceptibly ceased to be responsible for the formulation of strategic plans and the day-to-day conduct of operations. These were settled by the Chiefs of Staff Committee acting directly under the Minister of Defence and Prime Minister, and thus with the authority of the War Cabinet. The three Service Ministers, very able and trusted friends of mine whom I had picked for these duties, stood on no ceremony. They organised and administered the ever-growing forces, and helped all they could in the easy, practical English fashion. They had the fullest information by virtue of their membership of the Defence Committee, and constant access to me. Their professional subordinates, the Chiefs of Staff, discussed everything with them and treated them with the utmost respect. But there was an integral direction of the war to which they loyally submitted. There never was an occasion when their powers were abrogated or challenged, and anyone in this circle could always speak his mind; but the actual war direction soon settled into a very few hands, and what had seemed so difficult before became much more simple—apart of course from Hitler. In spite of the turbulence of events and the many disasters we had to endure the machinery worked almost automatically, and one lived in a stream of coherent thought capable of being translated with great rapidity into executive action.

Although the awful battle was now going on across the Channel, and the reader is no doubt impatient to get there, it may be well at this point to describe the system and machinery for conducting military and other affairs which I set on foot and practised from my earliest days of power. I am a strong believer in transacting official business by the Written Word. No doubt, surveyed in the after-time, much that is set down from hour to hour under the impact of events may be lacking in proportion or may not come true. I am willing to take my chance of that. It is always better, except in the hierarchy of military discipline, to express opinions and wishes rather than to give orders. Still, written directives coming personally from the lawfully-constituted Head of the Government and Minister specially charged with defence counted to such an extent that, though not expressed as orders, they very often found their fruition in action.
To make sure that my name was not used loosely, I issued during the crisis of July the following minute:
Let it be very clearly understood that all directions emanating from me are made in writing, or should be immediately afterwards confirmed in writing, and that I do not accept any responsibility for matters relating to national defence on which I am alleged to have given decisions unless they are recorded in writing.
When I woke about 8 a.m. I read all the telegrams, and from my bed dictated a continuous flow of minutes and directives to the departments and to the Chiefs of Staff Committee. These were typed in relays as they were done, and handed at once to General Ismay, Deputy-Secretary (Military) to the War Cabinet, and my representative on the Chiefs of Staff Committee, who came to see me early each morning. Thus he usually had a good deal in writing to bring before the Chiefs of Staff Committee when they met at ten-thirty. They gave all consideration to my views at the same time as they discussed the general situation. Thus between three and five o’clock in the afternoon, unless there were some difficulties between us requiring further consultation, there was ready a whole series of orders and telegrams sent by me or by the Chiefs of Staffs and agreed between us, usually giving all the decisions immediately required.
In total war it is quite impossible to draw any precise line between military and non-military problems. That no such friction occurred between the military staff and the War Cabinet staff was due primarily to the personality of Sir Edward Bridges, Secretary to the War Cabinet. Not only was this son of a former Poet Laureate an extremely competent and tireless worker, but he was also a man of exceptional force, ability, and personal charm, without a trace of jealousy in his nature. All that mattered to him was that the War Cabinet Secretariat as a whole should serve the Prime Minister and War Cabinet to the very best of their ability. No thought of his own personal position ever entered his mind, and never a cross word passed between the civil and military officers of the Secretariat.
In larger questions, or if there were any differences of view, I called a meeting of the War Cabinet Defence Committee, which at the outset comprised Mr. Chamberlain, Mr. Attlee, and the three Service Ministers, with the Chiefs of Staff in attendance. These formal meetings got fewer after 1941.* As the machine began to work more smoothly I came to the conclusion that the daily meetings of the War Cabinet with the Chiefs of Staff present were no longer necessary. I therefore eventually instituted what came to be known among ourselves as the “Monday Cabinet Parade”. Every Monday there was a considerable gathering—all the War Cabinet, the Service Ministers, and the Minister of Home Security, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, the Secretaries of State for the Dominions and for India, the Minister of Information, the Chiefs of Staff, and the official head of the Foreign Office. At these meetings each Chief of Staff in turn unfolded his account of all that had happened during the previous seven days; and the Foreign Secretary followed them with his story of any important developments in foreign affairs. On other days of the week the War Cabinet sat alone, and all important matters requiring decision were brought before them. Other Ministers primarily concerned with the subjects to be discussed attended for their own particular problems. The members of the War Cabinet had the fullest circulation of all papers affecting the war, and saw all important telegrams sent by me. As confidence grew the War Cabinet intervened less actively in operational matters, though they watched them with close attention and full knowledge. They took almost the whole weight of home and party affairs off my shoulders, thus setting me free to concentrate upon the main theme. With regard to all future operations of importance I always consulted them in good time; but, while they gave careful consideration to the issues involved, they frequently asked not to be informed of dates and details, and indeed on several occasions stopped me when I was about to unfold these to them.
I had never intended to embody the office of Minister of Defence in a department. This would have required legislation, and all the delicate adjustments I have described, most of which settled themselves by personal goodwill, would have had to be thrashed out in a process of ill-timed constitution-making. There was however in existence and activity under the personal direction of the Prime Minister the Military Wing of the War Cabinet Secretariat, which had in pre-war days been the Secretariat of the Committee of Imperial Defence. At the head of this stood General Ismay, with Colonel Hollis and Colonel Jacob as his two principals, and a group of specially-selected younger officers drawn from all three Services. This Secretariat became the staff of the office of the Minister of Defence. My debt to its members is immeasurable. General Ismay, Colonel Hollis, and Colonel Jacob rose steadily in rank and repute as the war proceeded, and none of them was changed. Displacements in a sphere so intimate and so concerned with secret matters are detrimental to continuous and efficient dispatch of business.
After some early changes almost equal stability was preserved in the Chiefs of Staff Committee. On the expiry of his term as Chief of the Air Staff, in September 1940, Air Marshal Newall became Governor-General of New Zealand, and was succeeded by Air Marshal Portal, who was the accepted star of the Air Force. Portal remained with me throughout the war. Sir John Dill, who had succeeded General Ironside in May 1940, remained C.I.G.S. until he accompanied me to Washington in December 1941. I then made him my personal Military Representative with the President and head of our Joint Staff Mission. His relations with General Marshall, Chief of Staff of the United States Army, became a priceless link in all our business, and when he died in harness some two years later he was accorded the unique honour of a resting-place in Arlington Cemetery, the Valhalla hitherto reserved exclusively for American warriors. He was succeeded as C.I.G.S. by Sir Alan Brooke, who stayed with me till the end.
From 1941, for nearly four years, the early part of which was passed in much misfortune and disappointment, the only change made in this small band either among the Chiefs or in the Defence staff was due to the death in harness of Admiral Pound. This may well be a record in British military history. A similar degree of continuity was achieved by President Roosevelt in his own circle. The United States Chiefs of Staff—General Marshall, Admiral King, and General Arnold, subsequently joined by Admiral Leahy—started together on the American entry into the war, and were never changed. As both the British and Americans presently formed the Combined Chiefs of Staff Committee this was an inestimable advantage for all. Nothing like it between allies has ever been known before.
I cannot say that we never differed among ourselves even at home, but a kind of understanding grew up between me and the British Chiefs of Staff that we should convince and persuade rather than try to overrule each other. This was of course helped by the fact that we spoke the same technical language, and possessed a large common body of military doctrine and war experience. In this ever-changing scene we moved as one, and the War Cabinet clothed us with ever more discretion, and sustained us with unwearied and unflinching constancy. There was no division, as in the previous war, between politicians and soldiers, between the “Frocks” and the “Brass Hats”—odious terms which darkened counsel. We came very close together indeed, and friendships were formed which I believe were deeply valued.
The efficiency of a war Administration depends mainly upon whether decisions emanating from the highest approved authority are in fact strictly, faithfully, and punctually obeyed. This was achieved in Britain in this time of crisis owing to the intense fidelity, comprehension, and whole-hearted resolve of the War Cabinet upon the essential purpose to which we had devoted ourselves. According to the directions given, ships, troops, and aeroplanes moved, and the wheels of factories spun. By all these processes, and by the confidence, indulgence, and loyalty by which I was upborne, I was soon able to give an integral direction to almost every aspect of the war. This was really necessary, because times were so very bad. The method was accepted because everyone realised how near were death and ruin. Not only individual death, which is the universal experience, stood near, but, incomparably more commanding, the life of Britain, her message, and her glory.

Any account of the methods of government which developed under the National Coalition would be incomplete without an explanation of the series of personal messages which I sent to the President of the United States and the heads of other foreign countries and the Dominions Governments. This correspondence must be described. Having obtained from the Cabinet any specific decisions required on policy, I composed and dictated these documents myself, for the most part on the basis that they were intimate and informal correspondence with friends and fellow-workers. One can usually put one’s thoughts better in one’s own words. It was only occasionally that I read the text to the Cabinet beforehand. Knowing their views, I used the ease and freedom needed for the doing of my work. I was of course hand-in-glove with the Foreign Secretary and his department, and any differences of view were settled together. I circulated these telegrams, in some cases after they had been sent, to the principal members of the War Cabinet, and, where he was concerned, to the Dominions Secretary. Before dispatching them I of course had my points and facts checked depart-mentally, and nearly all military messages passed through Ismay’s hands to the Chiefs of Staff. This correspondence in no way ran counter to the official communications or the work of the Ambassadors. It became however in fact the channel of much vital business, and played a part in my conduct of the war not less, and sometimes even more, important than my duties as Minister of Defence.
The very select circle, who were entirely free to express their opinion, were almost invariably content with the drafts and gave me an increasing measure of confidence. Differences with American authorities for instance, insuperable at the second level, were settled often in a few hours by direct contact at the top. Indeed, as time went on the efficacy of this top-level transaction of business was so apparent that I had to be careful not to let it become a vehicle for ordinary departmental affairs. I had repeatedly to refuse the requests of my colleagues to address the President personally on important matters of detail. Had these intruded unduly upon the personal correspondence they would soon have destroyed its privacy and consequently its value.
My relations with the President gradually became so close that the chief business between our two countries was virtually conducted by these personal interchanges between him and me. In this way our perfect understanding was gained. As Head of the State as well as Head of the Government, Roosevelt spoke and acted with authority in every sphere; and, carrying the War Cabinet with me, I represented Great Britain with almost equal latitude. Thus a very high degree of concert was obtained, and the saving in time and the reduction in the number of people informed were both invaluable. I sent my cables to the American Embassy in London, which was in direct touch with the President at the White House through special coding machines. The speed with which answers were received and things settled was aided by clock-time. Any message which I prepared in the evening, at night, or even up to two o’clock in the morning, would reach the President before he went to bed, and very often his answer would come back to me when I woke the next morning. In all I sent him nine hundred and fifty messages, and received about eight hundred in reply. I felt I was in contact with a very great man, who was also a warm-hearted friend and the foremost champion of the high causes which we served.

On Monday, May 13, 1940, I asked the House of Commons, which had been specially summoned, for a vote of confidence in the new Administration. After reporting the progress which had been made in filling the various offices, I said: “I have nothing to offer but blood, toil, tears, and sweat.” In all our long history no Prime Minister had ever been able to present to Parliament and the nation a programme at once so short and so popular. I ended:
You ask, What is our policy? I will say: It is to wage war, by sea, land, and air, with all our might and with all the strength that God can give us: to wage war against a monstrous tyranny, never surpassed in the dark, lamentable catalogue of human crime. That is our policy. You ask, What is our aim? I can answer in one word: Victory—victory at all costs, victory in spite of all terror; victory, however long and hard the road may be; for without victory there is no survival. Let that be realised: no survival for the British Empire; no survival for all that the British Empire has stood for, no survival for the urge and impulse of the ages, that mankind will move forward towards its goal. But I take up my task with buoyancy and hope. I feel sure that our cause will not be suffered to fail among men. At this time I feel entitled to claim the aid of all, and I say, “Come, then, let us go forward together with our united strength.”
Upon these simple issues the House voted unanimously, and adjourned till May 21.
Thus then we all started on our common task. Never did a British Prime Minister receive from Cabinet colleagues the loyal and true aid which I enjoyed during the next five years from these men of all parties in the State. Parliament, while maintaining free and active criticism, gave continuous, overwhelming support to all measures proposed by the Government, and the nation was united and ardent as never before. It was well indeed that this should be so, because events were to come upon us of an order more terrible than anyone had foreseen.