

Pablo Picasso entered the world howling. Seconds after he was born, one of the hospital physicians, his uncle Don Salvador, leaned down and blew a huge cloud of cigar smoke in the newborn’s face. The baby grimaced and bellowed in protest—and that’s how everyone knew he was healthy and alive. At that time, doctors were allowed to smoke in delivery rooms, but this little infant would have none of it. Even at birth, he refused to accept things as they had always been done.
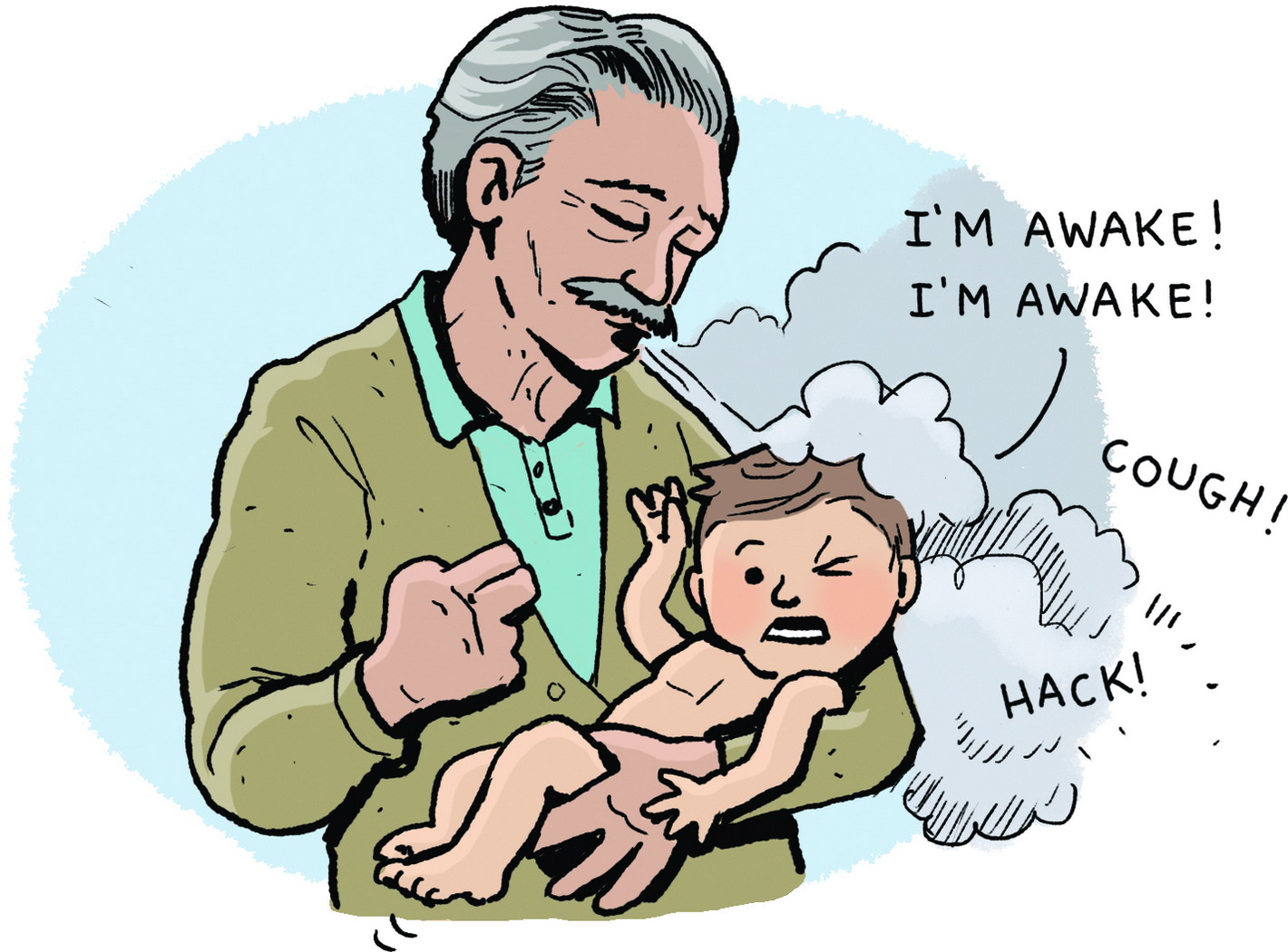

The baby was named Pablo Diego José Francisco de Paula Juan Nepomuceno María de los Remedios Cipriano de la Santísima Trinidad Martyr Patricio Clito Ruíz y Picasso—whew! He was known to his friends as Pablito, a nickname meaning “little Pablo,” and he learned to draw before he could walk. His first word was piz, short for lápiz, the Spanish word for pencil. It was an instrument that would soon become his most prized possession.
Pablo inherited his love of art from his father, Don José Ruiz y Blasco, a talented painter. Don José’s favorite subjects were the pigeons that flocked in the plaza outside the Picassos’ home in Málaga, a town on the southern coast of Spain. Sometimes he would allow Pablo to finish paintings for him. One of Pablo’s earliest solo artworks was a portrait of his little sister, which he painted with egg yolk.


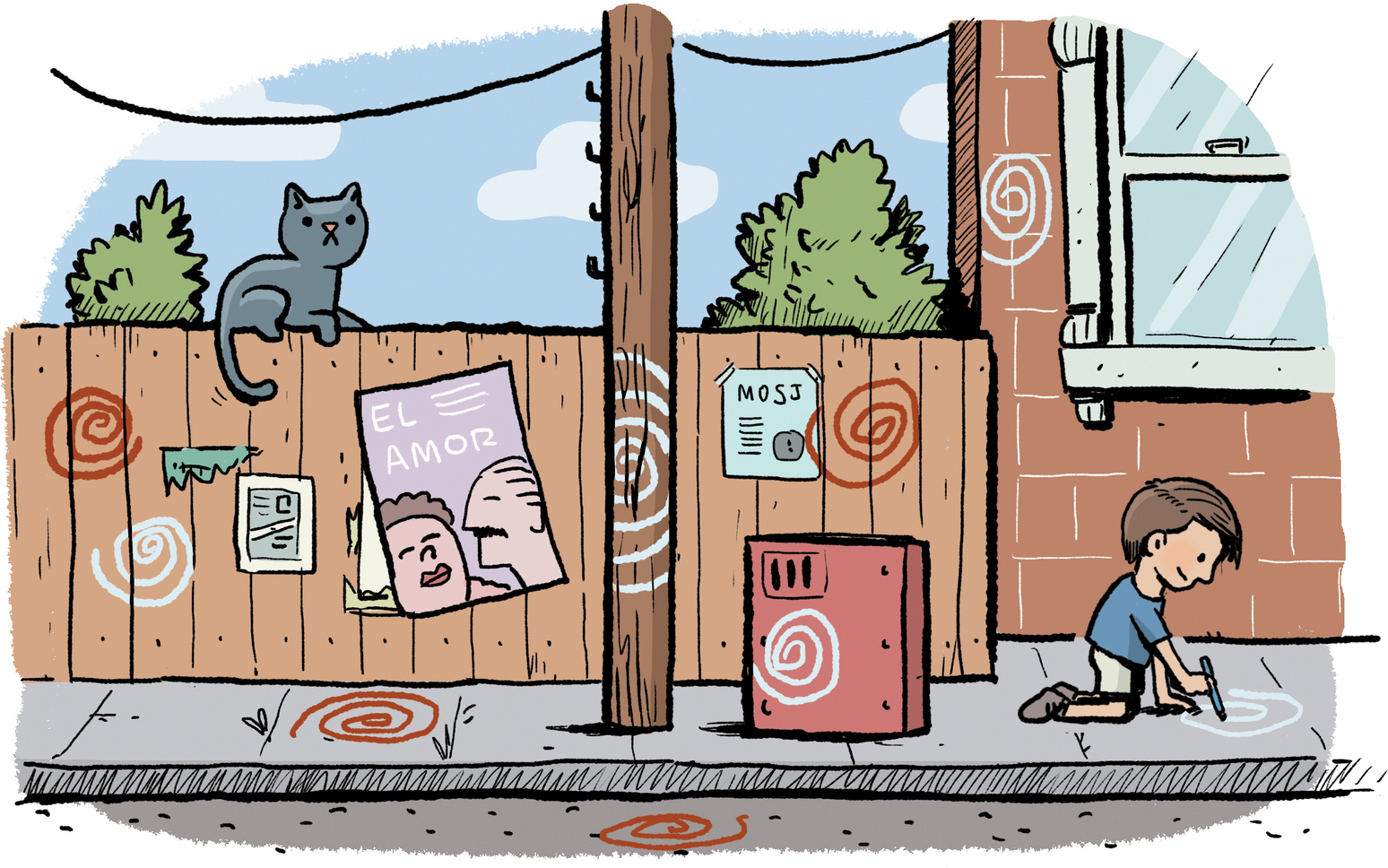
But painting was not yet his specialty. Drawing was. Pablo mostly liked to draw spirals. When people asked him why, he explained that they reminded him of churros, the fried-dough pastries sold at every streetcorner stand in Málaga. While other kids played underneath trees in the Plaza de la Merced, Pablo stood by himself scratching circles in the dirt with a stick.


At school, Pablo found it hard to concentrate. Rather than completing classwork, he filled the margins of his notebook with pencil sketches of animals, birds, and people. His teacher grew exasperated with his lack of attention. She wrote a note to his mother saying: “Pablo should stop drawing in class and pay attention to his lessons.”
It was clear that Pablo hated rules, and he took every opportunity to disobey them. When adults told him what to do, he did the opposite. He once got in trouble for coloring the sky a bright red instead of the “normal” blue. Pablo was often banished to the “calaboose,” a bare cell with white walls and a bench, which served as a holding pen for unruly students.
“I liked it there, because I took along a sketch pad and drew incessantly,” Pablo later said. “I could have stayed there forever drawing without stopping.” He even began misbehaving on purpose so that he would be sentenced to detention and sent to the calaboose.
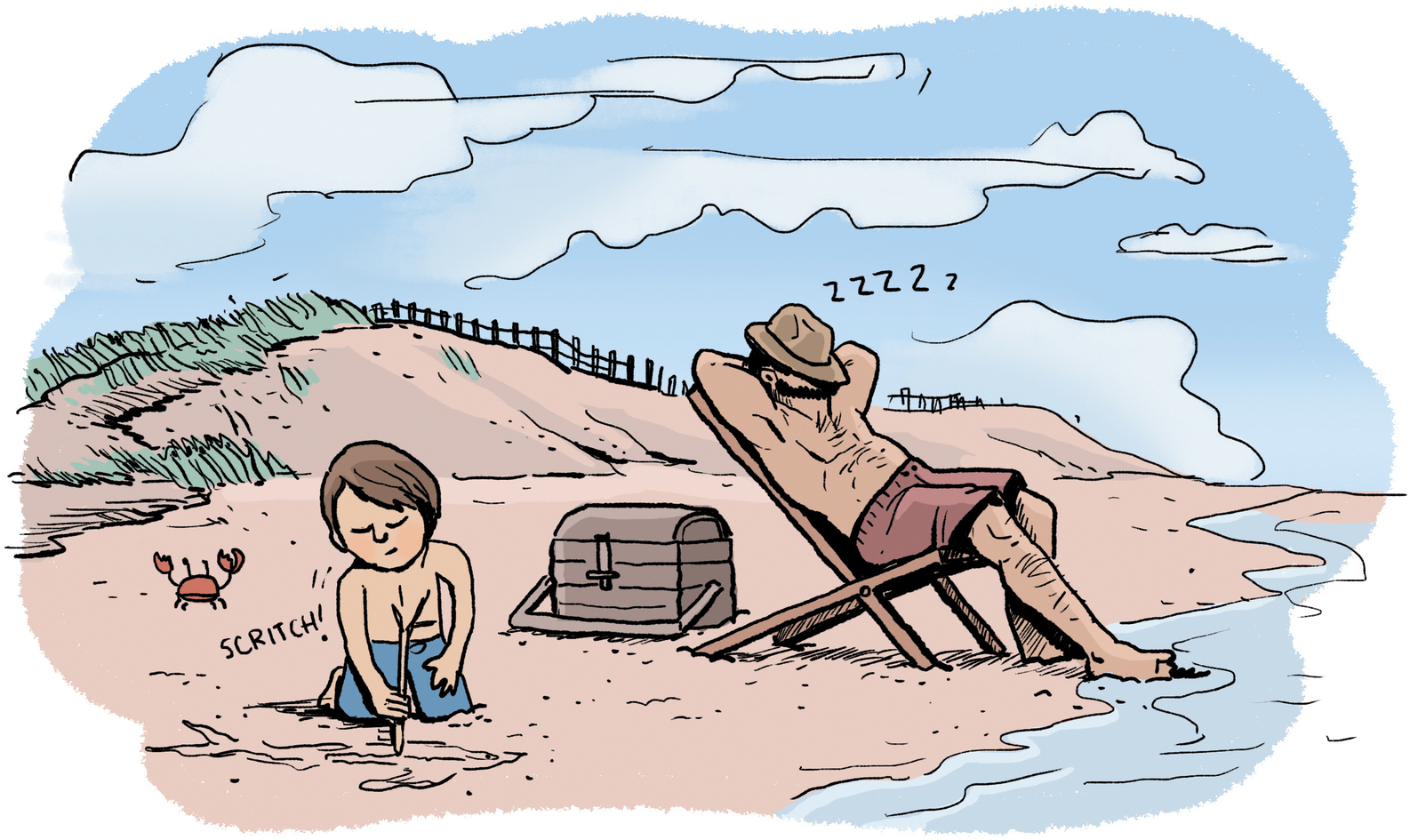
The one person who understood that Pablo wasn’t acting out for no reason was his father. One day when Pablo’s mother caught him drawing on the wall with a nail, Don José took him to the beach to blow off steam. As Don José stretched out to take a nap, Pablo sat beside him and drew a dolphin in the wet sand. When Don José awoke, he was astonished by the beauty of his son’s drawing. “Could it be Pablo who drew this?” he wondered.

That afternoon, Don José took a closer look at the image Pablo had drawn on their living room wall. What at first looked like random scratches soon took shape. Don José recognized a reindeer and a bison running away from a group of men on horseback who were armed with bows and arrows. At that moment, Don José knew what to do to get Pablo to stop misbehaving. He decided to take him into his studio and teach his son how to paint.
From that day onward, Pablo and his father were inseparable art partners. In search of new subjects to portray, they began going to the bullfights. Pablo was mesmerized by the sight of the brave picadors as they charged ferocious bulls.
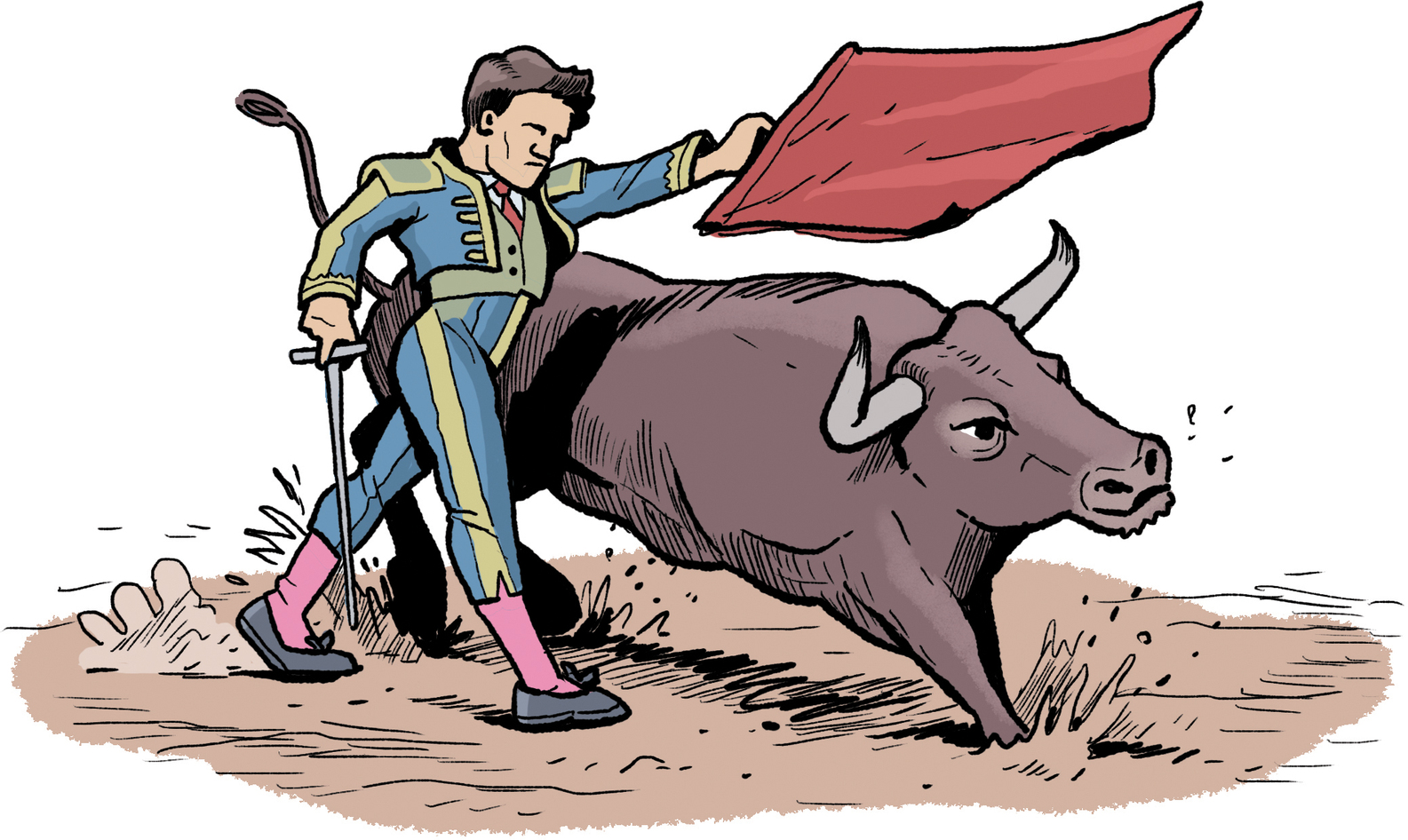


He saw El Lagartijo—“The Lizard”—one of the most famous bullfighters in Spain, and he met Cara Ancha, the celebrated Andalusian matador. When he was only nine years old, Pablo completed his first painting, Le Picador, a portrait of a man riding a horse in the bullring.
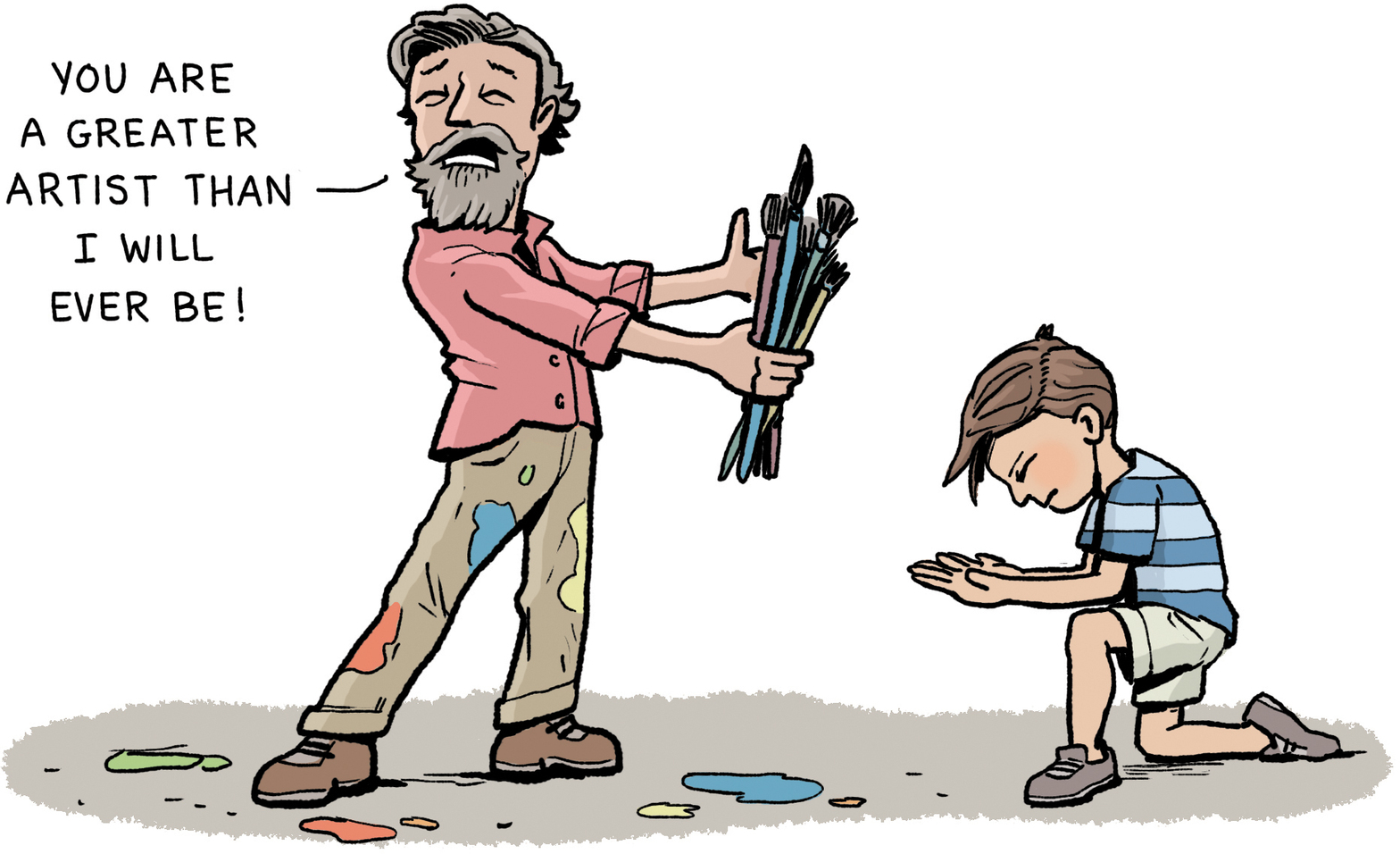
Two years later, Pablo’s family moved to a new town, La Coruña, on Spain’s Atlantic coast. Don José got a job as an art teacher at the local college. Even though he was much younger than the other students, Pablo enrolled in his father’s class. He also took courses in figure drawing and landscape painting. By the time he turned thirteen, Pablo’s skill level had surpassed his father’s. Don José was so impressed that he handed his son his brushes and vowed never to paint again.


When Pablo was fourteen years old, his family moved again, this time to Barcelona, where Pablo enrolled in the prestigious School of Fine Arts. His teachers quickly noticed his skills and allowed him to skip two grades. But just as in Málaga, Pablo had trouble adhering to the school’s rules. Before long he was back to his old tricks, cutting class so that he could wander the city streets, sketching interesting scenes that he observed along the way.

Pablo repeated this behavior at his next school, the Royal Academy of San Fernando in Madrid. This time, Pablo’s father refused to tolerate his son’s antics and stopped his allowance. At age sixteen, Pablo found himself on his own for the first time, forced to support himself on nothing but his artistic ability.
It has been said that the older Pablo grew, the more childlike his art became. During some periods he painted almost entirely in blue or depicted only circus performers. During his Cubist period, he painted people and objects broken down into geometric shapes. When he died in 1973, at the age of ninety-one, Pablo left behind more than fifty thousand artworks in a wide variety of styles and materials—paintings, prints, ceramics, sculpture, and more. He was considered the world’s best-known artist.
When it came to making art, Pablo Picasso lived by his own rules. Wherever inspiration led him, he followed—something that would not have surprised anyone who had known him as a child growing up in his native Spain.

