The Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit provides (as of writing) six assistants as shown in the following screenshot:
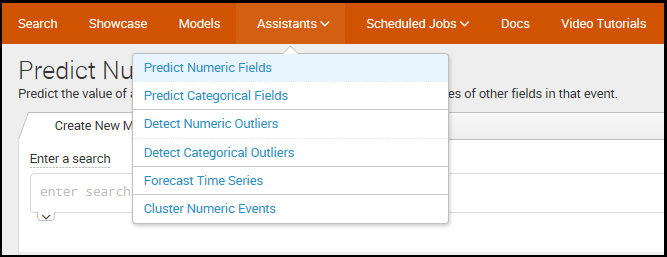
These assistants are provided to you as, sort of, wizards that provide step-by-step guidance to create a machine learning model with a particular purpose or objective.
The Splunk product describes these assistants as follows:
"Each assistant includes end-to-end examples with datasets, plus the ability to apply the visualizations and SPL commands to your own data..."
These six assisted models are based on six of (perhaps) the most common models a data scientist may build.
They include:
- Predict Numeric Fields (linear regression): For example, predict median house values
- Predict Categorical Fields (linear regression): For example, predict customer churn
- Detect Numeric Outliers (distribution statistics): For example, detect outliers in IT ops data
- Detect Categorical Outliers (probabilistic measures): For example, detect outliers in diabetes patient records
- Forecast Time Series: For example, forecast data center growth and capacity planning
- Cluster Numeric Events: For example, cluster hard drives by SMART metrics
We'll take a closer look at these assistants in the Build a model section of this chapter.