When Black gets quick equality, should he risk it and play for more?
Robert Wade White
Nikola Karaklajic Black
Monte Carlo 1967
Ruy Lopez, Exchange Variation C69
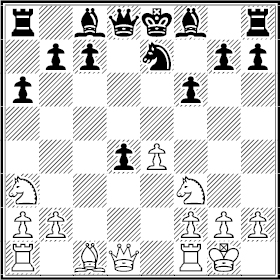
1 e4 e5 2 ♘f3 ♘c6 3 ♗b5 a6 4 ♗xc6 dxc6 5 0-0 f6 6 c3 c5 7 ♘a3 ♘e7 8 d4! cxd4 9 cxd4 exd4

10 e5?
The endgame is equal after 10 ♕xd4 ♕xd4.
Question 300: What happens on 10 ♘xd4 c5 11 ♕h5+ ?
10...♗g4!
Black is equal after 10...fxe5. To play for more requires speculating or calculating far ahead.
11 exf6 gxf6 12 ♕xd4
White remains a pawn down after 12 h3 ♗xf3 13 ♕xf3 ♕d5 14 ♕xd5 ♘xd5. He might even get mated after 14 ♕xf6? ♖g8 15 g3 0-0-0.
12...♗xf3!
To play this Black had to conclude 13 ♕xd8+ ♔xd8 14 gxf3 ♘c6 favors him (15...♗xa3, 15...♘d4 or 15...♘e5).
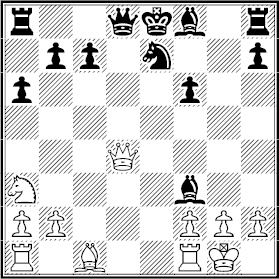
13 ♕xf6 ♗xg2!
Now 14 ♔xg2 ♖g8+ 15 ♔h1 ♕d5+ 16 f3 0-0-0.
14 ♕xh8 ♗xf1 15 ♗h6 ♕d5!
The threat of ...♕g2 mate prevents 16 ♕xf8+ ♔d7.
16 ♖xf1 0-0-0 17 ♗xf8 ♘g6 18 ♕g7 ♖xf8 19 f3 ♖g8 20 ♕f6 ♘f4+ White resigns.
Black mates after 21 ♔h1 ♕d3 or 21...♘h3.
Robert Huebner White
Mikhail Tal Black
Wijk aan Zee 1982
1 e4 e5 2 ♘f3 ♘c6 3 ♗b5 a6 4 ♗xc6 dxc6 5 0-0 f6 6 d4 ♗g4 7 dxe5 ♕xd1 8 ♖xd1 fxe5 9 ♖d3 ♗d6 10 ♘bd2 ♘f6 11 ♘c4 0-0 12 ♘cxe5? ♗h5! 13 ♗f4? ♗xf3! White resigned. (14 ♖xf3 or 14 gxf3 allow 14...♘h5!)