| Alevis |
community of Muslims whose beliefs combine elements of Shi’a Islam and Sufi traditions |
| aliyah bet |
illegal Jewish immigration to Mandate-era Palestine |
| bey |
gentleman; man of rank |
| caique |
narrow, oared boat used on the Bosphorus and Golden Horn |
| caliph |
supreme spiritual leader in Islam; title claimed by Ottoman sultans until the caliphate’s abolition in 1924 |
çar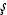 af af |
Islamic female covering, typically black and draping the entire body |
| cherkeska |
long tunic with small ammunition-holders on the chest worn by men from the Caucasus |
| Circassians |
cultural group with ties to the historic region of Circassia in the northwest Caucasus in modern-day Russia |
| dervish |
adherent of a Sufi religious order |
| Emniyet |
Turkish secret police |
| esnaf |
guild of tradesmen or artisans |
| ezan |
Islamic call to prayer |
| gazi |
conqueror or hero in Islamic warfare |
| hamal |
porter |
| han |
hostel or boardinghouse, typically for traveling traders |
| hanım |
lady; woman of rank |
| harem |
household; wives and concubines of the sultan or other Ottoman men of rank |
| haremlik; Harem |
private portion of a traditional household reserved for family use |
| imam |
leader in Islamic worship |
| inkılâp |
revolution |
| janissaries |
elite infantry of the Ottoman Empire before the 1820s |
| lâiklik |
secularism; state management of religious institutions |
| Karagöz |
traditional entertainment featuring semitransparent puppets on a backlit screen |
| Kemalism |
political ideology of modernity and secularism associated with Mustafa Kemal Atatürk |
| Ladino |
language of Sephardic Jews, based on Spanish and written in either Hebrew or Latin script; also called Judeo-Spanish |
| mahalle |
neighborhood |
| meyhane |
restaurant typically serving wine, raki, and small plates of food |
| millet |
Ottoman legal category defined by membership in a religious community (e.g., Muslims, Orthodox Christians, Armenian Apostolic Christians, Jews) |
| millet system |
religious self-government in the Ottoman Empire, based on quasi autonomy of millets |
| muezzin |
cantor who delivers the Islamic call to prayer |
| muhacirs |
Muslim refugees, especially from the Balkans and the Caucasus |
| OGPU |
Stalinist secret police and predecessor of KGB |
| OSS |
Office of Strategic Services; American intelligence organization and predecessor of CIA |
| oud |
musical instrument resembling a Western lute |
| pasha |
military general or high-ranking official |
| patriarch |
supreme leader of an independent Orthodox Christian church |
| raki |
anise-flavored liqueur |
| rebetiko |
urban folk music associated with Greeks originally from Smyrna and Istanbul (also spelled rembetiko) |
| selâmlık |
public portion of a traditional household used for business or receiving guests; also, the sultan’s public procession to Friday prayers |
| Sephardim |
Jews from the Iberian Peninsula who immigrated to the Ottoman Empire in the fifteenth century |
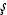 eyhülislam eyhülislam |
chief Islamic cleric |
| sharia |
Islamic canon law |
| sheikh |
Islamic religious leader or saint, especially in Sufi orders |
| Shi’a |
community of Muslims who recognize the spiritual successors to the Prophet Muhammad through Ali, his son-in-law |
| SOE |
Special Operations Executive; British intelligence service |
| Sufi |
general term for a number of ecstatic or mystical religious orders in Islam, typically associated with a founding sage |
| sultan |
ruler of the Ottoman Empire |
| Sunni |
community of Muslims who recognize the spiritual successors to the Prophet Muhammad through a line of caliphs |
| sürgün |
forced resettlement |
| Tanzimat |
period of centralization, reform, and modernization in the Ottoman Empire, 1839–1876 |
| tekke |
Sufi lodge or meeting house |
| tulumbacı |
foot-borne fireman |
| türbe |
mausoleum, especially of an Islamic sage or holy person |
| Unionists |
members of the Committee of Union and Progress, the makers of the 1908 revolution; also known as Young Turks |
| wagon-lit |
sleeping carriage on a train |
| yalı |
house near the water on the Bosphorus, typically made from ornately mitered wood |
| yishuv |
Jewish community in Mandate-era Palestine |
| Young Turks |
see Unionists |
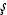 af
af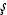 eyhülislam
eyhülislam