
Multivariate Models from Chapter 2

TABLE A.1
Effect of personal experiences on issue importance of unemployment
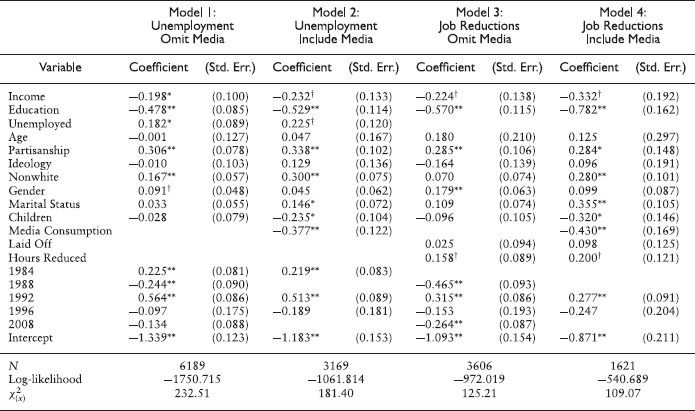
Note: All columns report maximum likelihood estimates of coefficients and standard errors for a probit model of considering unemployment costs to be most important. See Appendix G for details on coding of control variables.
† p < .10
*p < .05
**p < .01 (two-tailed tests)
TABLE A.2
Effect of personal experience on issue importance of health care costs
Variable |
Coefficient |
(Std. Err.) |
Income |
0.907∗∗ |
(0.346) |
Education |
0.135 |
(0.250) |
Unemployed |
−0.083 |
(0.319) |
Age |
0.058 |
(0.218) |
Partisanship |
0.096 |
(0.263) |
Ideology |
0.123 |
(0.315) |
Nonwhite |
−0.248† |
(0.219) |
Gender |
−0.232 |
(0.138) |
Marital Status |
−0.063 |
(0.145) |
Children |
−0.032 |
(0.225) |
Media Consumption |
−0.053 |
(0.328) |
Delayed Health Care |
0.312† |
(0.164) |
1992 |
1.227∗∗ |
(0.221) |
Intercept |
−3.453∗∗ |
(0.453) |
N |
2217 |
|
Log-likelihood |
−171.364 |
|
χ2(13) |
64.64 |
|
Note: Columns report maximum likelihood estimates of coefficients and standard errors for a probit model of considering health care costs to be most important. See Appendix G for details on coding of control variables.
† p <.10
**p < .01 (two-tailed tests)
TABLE A.3
Effect of personal experiences on issue importance of retirement costs
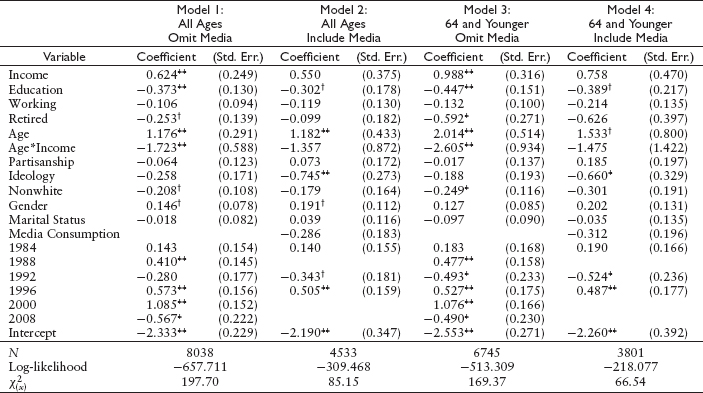
Note: All Columns report maximum likelihood estimates of coefficients and standard errors for a probit model of considering retirement costs to be most important. See Appendix G for details on coding of control variables.
† p <.10
*p < .05
**p < .01 (two-tailed tests)
TABLE A.4
Effect of personal experiences on issue importance of education costs
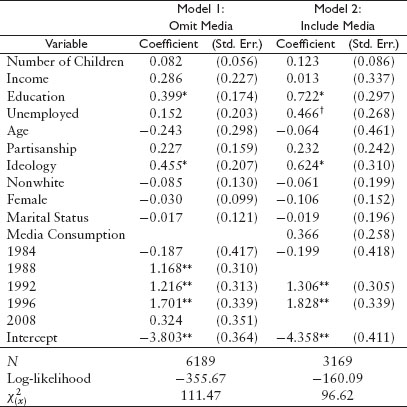
Note: All columns report maximum likelihood estimates of coefficients and standard errors for a probit model of considering education costs to be most important. See Appendix G for details on coding of control variables.
† p < .10
*p < .05
**p < .01 (two-tailed tests)