
Through Bike Lanes

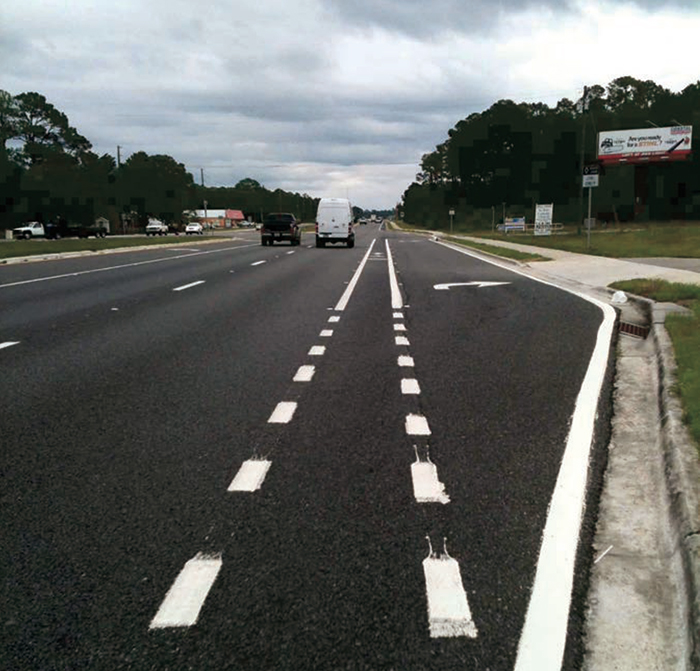
SANTA ROSA BEACH, FL
For bicyclists traveling in a conventional bike lane or from a truncated cycle track, the approach to an intersection with vehicular turn lanes can present a significant challenge. For this reason it is vital that bicyclists are provided with an opportunity to correctly position themselves to avoid conflicts with turning vehicles. This treatment specifically covers the application of a through bicycle lane or ‘bicycle pocket’ at the intersection. For other potential approaches to provide accommodations for bicyclists at intersections with turn lanes, please see bike box, combined bike lane/turn lane, bicycle signals, and colored bike facilities.

PORTLAND, OR
Benefits
Enables bicyclists to correctly position themselves to the left of right turn lanes or to the right of left turn lanes.
Reduces conflicts between turning motorists and bicycle through traffic.
Provides bicyclists with guidance to follow the preferred travel path.
Leads to more predictable bicyclist and motorist travel movements.
Alerts motorists to expect and yield to merging bicycle traffic.
Signifies an appropriate location for motorists to safely merge across the bike lane into the turn lane.

ST. PETERSBURG, FL
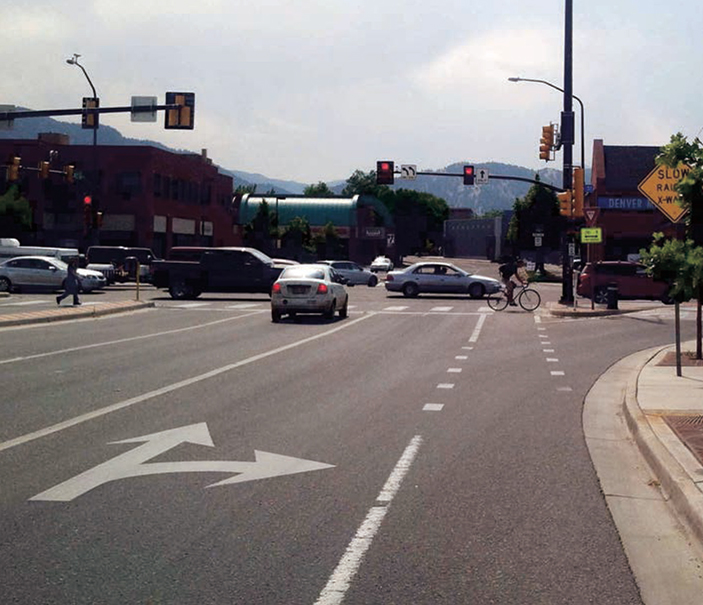

BOULDER, CO

CHICAGO, IL
Typical Applications
On streets with right-side bike lanes and right-turn only lanes at intersections.
On streets with left-side bike lanes and left-turn only lanes at intersections.
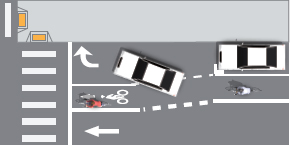
On streets with bike lanes and an auxiliary right-turn-only lane added in advance of the intersection.
On streets with bike lanes and a parking lane that transition into a turn lane at intersections.

Required Features
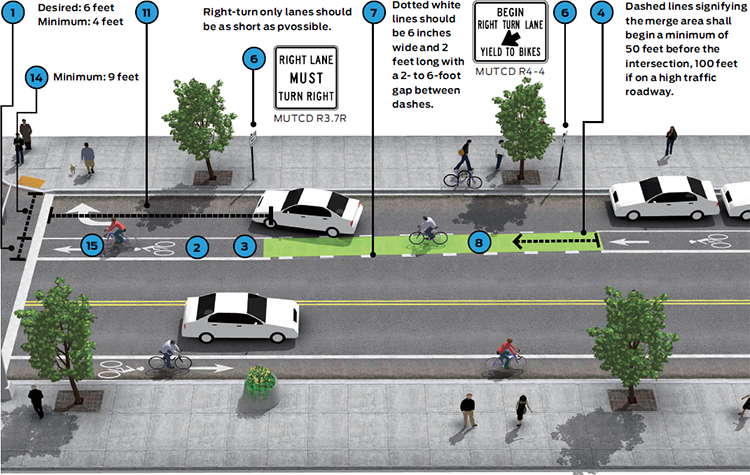
 The desired width of a dashed bike transition lane and through bike lane is 6 feet with a minimum width of 4 feet.
The desired width of a dashed bike transition lane and through bike lane is 6 feet with a minimum width of 4 feet.
 Bicycle lane word and/or symbol and arrow markings (MUTCD Figure 9C-3) shall be used to define the bike lane and designate that portion of the street for preferential use by bicyclists.
Bicycle lane word and/or symbol and arrow markings (MUTCD Figure 9C-3) shall be used to define the bike lane and designate that portion of the street for preferential use by bicyclists.
 The through bike lane shall be placed to the left of the right-turn only lane.
The through bike lane shall be placed to the left of the right-turn only lane.
 Dotted lines signifying the merge area shall begin a minimum of 50 feet before the intersection (MUTCD). Dotted lines should begin 100 feet before the intersection if along a high speed/ volume roadway.
Dotted lines signifying the merge area shall begin a minimum of 50 feet before the intersection (MUTCD). Dotted lines should begin 100 feet before the intersection if along a high speed/ volume roadway.
 Dotted lane line transition areas to through bike lanes shall not be used on streets with double right turn lanes. Double right turn lanes are extremely difficult for bicyclists to negotiate. Shared lane markings may be used in the center of the inside turn lane to designate the preferred path of through bicycle travel.
Dotted lane line transition areas to through bike lanes shall not be used on streets with double right turn lanes. Double right turn lanes are extremely difficult for bicyclists to negotiate. Shared lane markings may be used in the center of the inside turn lane to designate the preferred path of through bicycle travel.
Recommended Features
 Accompanying signage should include R3-7R “Right Lane Must Turn Right” and R4-4 “Begin Right Turn Yield to Bikes” (MUTCD).
Accompanying signage should include R3-7R “Right Lane Must Turn Right” and R4-4 “Begin Right Turn Yield to Bikes” (MUTCD).
 Dotted white lines should be 6 inches wide and 2 feet long with a 2- to 6-foot gap between dashes (MUTCD).
Dotted white lines should be 6 inches wide and 2 feet long with a 2- to 6-foot gap between dashes (MUTCD).
 Through bike lanes should be provided at any intersection approach where a right turn only auxiliary lane is created (also known as a right turn add lane). It is desirable for bicyclists to travel straight through the merging area to reinforce right-of-way.
Through bike lanes should be provided at any intersection approach where a right turn only auxiliary lane is created (also known as a right turn add lane). It is desirable for bicyclists to travel straight through the merging area to reinforce right-of-way.
 Dotted lane line transition areas to through bike lanes should not be provided at any intersection approach where a through travel lane transitions into a right turn only lane (also known as a right turn drop or trap lane). In such instances consider utilizing an exclusive bicycle signal phase with the bike lane remaining to the right, or not delineating the merging area connecting to the through lane. Shared lane markings may be used to provide additional guidance.
Dotted lane line transition areas to through bike lanes should not be provided at any intersection approach where a through travel lane transitions into a right turn only lane (also known as a right turn drop or trap lane). In such instances consider utilizing an exclusive bicycle signal phase with the bike lane remaining to the right, or not delineating the merging area connecting to the through lane. Shared lane markings may be used to provide additional guidance.
 At intersections with high right turning vehicle volumes, high bicyclist volumes, or along priority bicycle corridors, treatments beyond dotted white lines such as coloring and increased signing should be provided.
At intersections with high right turning vehicle volumes, high bicyclist volumes, or along priority bicycle corridors, treatments beyond dotted white lines such as coloring and increased signing should be provided.
 Right-turn only lanes should be as short as possible in order to limit the speed of cars in the right turn lane. Fast moving traffic on both sides can be uncomfortable for bicyclists.
Right-turn only lanes should be as short as possible in order to limit the speed of cars in the right turn lane. Fast moving traffic on both sides can be uncomfortable for bicyclists.
 Terminating the bike lane in advance of the intersection is discouraged.
Terminating the bike lane in advance of the intersection is discouraged.
 For intersections that lack the physical width to install a bicycle pocket, a combined bike/turn lane should be used.
For intersections that lack the physical width to install a bicycle pocket, a combined bike/turn lane should be used.
 Vehicle turn lane width should not be reduced to less than 9 feet.
Vehicle turn lane width should not be reduced to less than 9 feet.
 Bicycle detection should be provided within the through bike lane.
Bicycle detection should be provided within the through bike lane.
Optional Features
 On streets with a combined turn and through lane, shared lane markings may be used in the center of the lane.
On streets with a combined turn and through lane, shared lane markings may be used in the center of the lane.
 A bike box may be used in lieu of a designated through bike lane.
A bike box may be used in lieu of a designated through bike lane.
 Bicycle warning signs may be used in advance of the merge/ transition area.
Bicycle warning signs may be used in advance of the merge/ transition area.
Auxiliary Right-Turn-Only Lane Added
These are appropriate conditions for use of through
Auxiliary Right-Turn-Only Lane Added in Advance of an These are appropriate conditions for use of through bike lanes.
Parking lane into right-turn-only lane.
Through bike lanes provide bicycle priority within weaving area

Right-turn-only lane added at intersection with throat widening.
Through bike lanes provide bicycle priority within weaving area.
Through Travel Lane Transitions into Right-Turn-Only Lane
These are generally inappropriate conditions for use of through bike lanes.Consider alternate treatments.
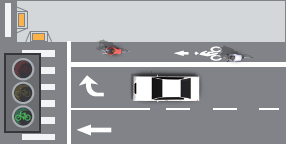
Exclusive bicycle signal phase used to separate conflicting movements.
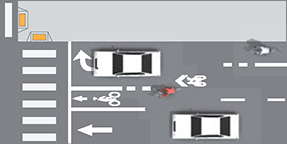
Bicycle lane dropped in advance of the intersection encourages bicyclists to merge across as gaps permit. Shared lane markings may be used to provide additional guidance.

Bicyclists are not provided priority in weaving area and must use caution to merge across potentially high-speed motor vehicle traffic. Dotted lane line transition areas to through bike lanes should not be provided at these locations.

PORTLAND, OR
Maintenance
Routine roadway maintenance is needed.
Dashed lines should be installed with thermoplastic to increase durability and resist tire wear.
Because the effectiveness of markings depends entirely on their visibility, maintaining markings should be a high priority.
Treatment Adoption and Professional Consensus
Bicycle lanes are the most common bicycle facility in use in the US, and most jurisdictions are familiar with their design and application as described in the MUTCD and AASHTO Guide for the Development of Bicycle Facilities. Many US cities offer through bicycle lanes at intersections; some offer increased levels of comfort and security to bicyclists through the application of some of the recommended and optional elements noted within this guide.