
Click here to download a PDF of Practice Test 1.
The Exam
SECTION I: Multiple-Choice Questions
DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
At a Glance
Total Time
1 hour and 30 minutes
Number of Questions
60
Percent of Total Score
50%
Writing Instrument
Pencil required
Instructions
Section I of this examination contains 60 multiple-choice questions.
Indicate all of your answers to the multiple-choice questions on the answer sheet. No credit will be given for anything written in this exam booklet, but you may use the booklet for notes or scratch work. After you have decided which of the suggested answers is best, completely fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Give only one answer to each question. If you change an answer, be sure that the previous mark is erased completely. Here is a sample question and answer.
Sample Question
Chicago is a
(A) state
(B) city
(C) country
(D) continent
Sample Answer

Use your time effectively, working as quickly as you can without losing accuracy. Do not spend too much time on any one question. Go on to other questions and come back to the ones you have not answered if you have time. It is not expected that everyone will know the answers to all the multiple-choice questions.
About Guessing
Many candidates wonder whether or not to guess the answers to questions about which they are not certain. Multiple-choice scores are based on the number of questions answered correctly. Points are not deducted for incorrect answers, and no points are awarded for unanswered questions. Because points are not deducted for incorrect answers, you are encouraged to answer all multiple-choice questions. On any questions you do not know the answer to, you should eliminate as many choices as you can, and then select the best answer among the remaining choices.
Section I
BIOLOGY
SECTION I
60 Questions
Time—90 minutes
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by four suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each case and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet.
1. The resting membrane potential depends on which of the following?
I. Active transport
II. Selective permeability
III. Differential distribution of ions across the axonal membrane
(A) III only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II, and III
2. The Krebs cycle in humans releases
(A) carbon dioxide
(B) pyruvate
(C) glucose
(D) lactic acid
3. A heterotroph
(A) obtains its energy from sunlight, harnessed by pigments
(B) obtains its energy by catabolizing organic molecules
(C) makes organic molecules from CO2
(D) obtains its energy by consuming exclusively autotrophs
4. Regarding meiosis and mitosis, one difference between the two forms of cellular reproduction is that in meiosis
(A) there is one round of cell division, whereas in mitosis there are two rounds of cell division
(B) separation of sister chromatids occurs during the second division, whereas in mitosis separation of sister chromatids occurs during the first division
(C) chromosomes are replicated during interphase, whereas in mitosis chromosomes are replicated during the first phase of mitosis
(D) spindle fibers form during interphase, whereas in mitosis the spindle fibers form during prophase
5. A feature of amino acids that is NOT found in carbohydrates is the presence of
(A) carbon atoms
(B) oxygen atoms
(C) nitrogen atoms
(D) hydrogen atoms
6. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of prokaryotic cells?
(A) Circular double-stranded DNA
(B) Membrane-bound cellular organelles
(C) Plasma membrane consisting of lipids and proteins
(D) Ribosomes that synthesize polypeptides
7. Which of the following best explains why a population is described as the evolutionary unit?
(A) Genetic changes can occur only at the population level.
(B) The gene pool in a population remains fixed over time.
(C) Natural selection affects individuals, not populations.
(D) Individuals cannot evolve, but populations can.
8. The endocrine system maintains homeostasis using many feedback mechanisms. Which of the following is an example of positive feedback?
(A) Infant suckling causes a mother’s brain to release oxytocin, which in turn stimulates milk production.
(B) An enzyme is allosterically inhibited by the product of the reaction it catalyzes.
(C) When ATP is abundant, the rate of glycolysis decreases.
(D) When blood sugar levels decrease to normal after a meal, insulin is no longer secreted.
9. A scientist carries out a cross between two guinea pigs, both of which have black coats. Black hair coat is dominant over white hair coat. Three quarters of the offspring have black coats, and one quarter have white coats. The genotypes of the parents were most likely
(A) bb bb
(B) Bb Bb
(C) Bb bb
(D) BB Bb
10. A large island is devastated by a volcanic eruption. Most of the horses die except for the heaviest males and heaviest females of the group. They survive, reproduce, and perpetuate the population. If weight is a highly heritable trait, which graph represents the change in population before and after the eruption?
(A) A higher mean weight compared with their parents
(B) A lower mean weight compared with their parents
(C) The same mean weight as members of the original population
(D) A higher mean weight compared with members of the original population
11. All of the following play a role in early embryogenesis EXCEPT
(A) apoptosis
(B) regulatory factors
(C) operons
(D) differentiation
12. During the period when life is believed to have begun, the atmosphere on primitive Earth contained abundant amounts of all the following gases EXCEPT
(A) oxygen
(B) hydrogen
(C) ammonia
(D) methane
Questions 13–14 refer to the following passage.
The digestive system in humans can be divided into two parts: the alimentary canal and the accessory organs. The canal comprised of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines is where the food actually passes during its transition into waste. The accessory organs are any organs that aid in the digestion by supplying the organs in the alimentary canal with digestive hormones and enzymes.
13. The small intestine is the main site of absorption. It can accomplish it so efficiently because of villi and microvilli that sculpt the membrane into hair-like projections. They likely aid in reabsorption by
(A) increasing the surface area of the small intestine
(B) decreasing the surface area of the small intestine
(C) making the small intestine more hydrophilic
(D) making the small intestine more hydrophobic
14. The pancreas is a major accessory organ in the digestive system. Which of the following would destroy the function of the digestive products produced by the pancreas?
(A) A decrease in absorption rates within the alimentary canal
(B) Removing the excess water from the food waste
(C) Increased acidity due to the inability to neutralize stomach acid
(D) An increase in peristalsis and subsequent diarrhea
15. In animal cells, which of the following represents the most likely pathway that a secreted protein takes as it is synthesized in a cell?
(A) Plasma membrane–Golgi apparatus–ribosome–secretory vesicle–rough ER
(B) Ribosome–Golgi apparatus–rough ER–secretory vesicle–plasma membrane
(C) Plasma membrane–Golgi apparatus–ribosome–rough ER–secretory vesicle
(D) Ribosome–rough ER–Golgi apparatus–secretory vesicle–plasma membrane
16. All of the following statements are correct regarding alleles EXCEPT
(A) alleles are alternative forms of the same gene
(B) alleles are found on corresponding loci of homologous chromosomes
(C) a gene can have more than two alleles
(D) an individual with two identical alleles is said to be heterozygous with respect to that gene
17. Once specific genes, such as the gene coding for ampicillin, have been incorporated into a plasmid, the plasmid may be used to carry out a transformation, which is
(A) inserting it into a bacteriophage
(B) treating it with a restriction enzyme
(C) inserting it into a suitable bacterium
(D) running a gel electrophoresis
18. Although mutations occur at a regular and predictable rate, which of the following statements is the LEAST likely reason the frequency of mutation often appears to be low?
(A) Some mutations produce alleles that are recessive and may not be expressed.
(B) Some undesirable phenotypic traits may be prevented from reproducing.
(C) Some mutations cause such drastic phenotypic changes that they are soon removed from the gene pool.
(D) The predictable rate of mutation results in ongoing variability in a gene pool.
19. A scientist wants to test the effect of temperature on seed germination. Which of the following should be part of the experimental design?
(A) Use temperature as the dependent variable and alter the germination times
(B) Use temperature as the independent variable and measure the rate of germination
(C) Use temperature as the controlled variable and keep everything identical between groups
(D) Use the variable natural outside temperature as a control group
20. A mustard plant seed undergoes a polyploidy event resulting in the new plant’s pollen being unable to pollinate the plant that originally produced the seed despite them being less than a meter apart. This best exemplifies which of the following?
(A) Allopatric speciation because the plants remain in close contact
(B) Allopatric speciation because there is a significant geographic barrier
(C) Sympatric speciation because it is the simplest form of speciation
(D) Sympatric speciation because the plants are not separated
21. Which of the following is most correct concerning cell differentiation in vertebrates?
(A) Cells in different tissues contain different sets of genes, leading to structural and functional differences.
(B) Differences in the timing and expression levels of different genes lead to structural and functional differences.
(C) Differences in the reading frame of mRNA lead to structural and functional differences.
(D) Differences between tissues result from spontaneous morphogenesis.
Questions 22–23 refer to the following passage.
Pumping blood through the human heart must be carefully organized for maximal efficiency and to prevent backflow. In the figure below, the blood enters the heart through the vena cava (1), passes through the right atrium and right ventricle and then goes through the pulmonary artery toward the lungs. After the lungs, the blood returns through the pulmonary vein and then passes into the left atrium and the left ventricle before leaving the heart via the aorta.
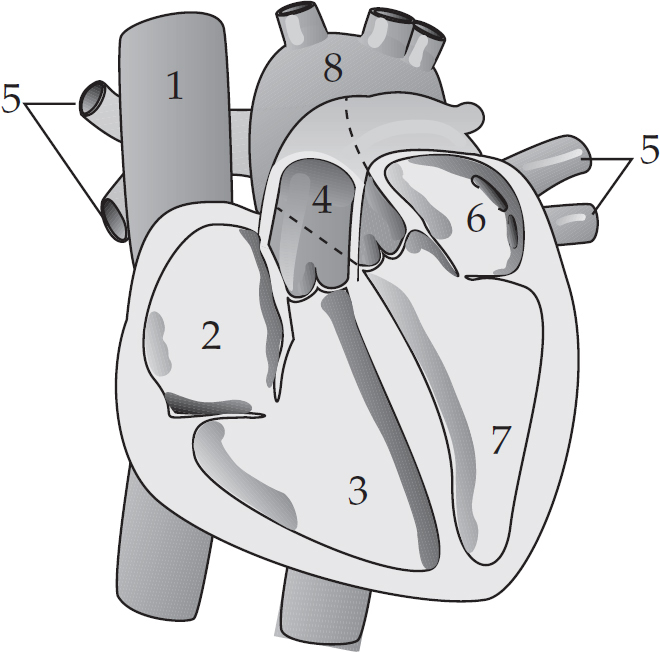
22. Which of the following chambers or vessels carry deoxygenated blood in the human heart?
(A) 1 only
(B) 2 and 3
(C) 1, 2, 3, 4
(D) 4 and 5
23. Blood is pumped via heart contractions triggered by action potentials spreading through the heart muscle. If there is a sudden increase in blood in chamber 3, which chamber of the heart received an increased number of action potentials?
(A) Left atrium
(B) Left ventricle
(C) Right atrium
(D) Right ventricle
24. Some strains of viruses can change normal mammalian cells into cancer cells in vitro. Which of the following is the best explanation for this impact on the mammalian cell?
(A) A pilus is formed between the mammalian cell and the virus.
(B) The viral genome incorporates into the mammalian cell’s nuclear DNA.
(C) The host’s genome is converted into the viral DNA.
(D) There is a viral release of spores into the mammalian cell.
25. All of the following correctly describe meiosis EXCEPT
(A) meiosis produces four haploid gametes
(B) homologous chromosomes join during synapsis
(C) sister chromatids separate during meiosis I
(D) crossing-over increases genetic variation in gametes
26. All of the following are examples of events that can prevent interspecies breeding EXCEPT
(A) the potential mates experience geographic isolation
(B) the potential mates experience behavioral isolation
(C) the potential mates have different courtship rituals
(D) the potential mates have different alleles
27. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of asexual reproduction in animals?
(A) Progeny cells have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
(B) Progeny cells are identical to the parent cell.
(C) The parent cell produces diploid cells.
(D) The progeny cells fuse to form a zygote.
28. Transpiration is a result of special properties of water. The special properties of water include all of the following EXCEPT
(A) cohesion
(B) adhesion
(C) capillary action
(D) hydrophobicity
Questions 29–32 refer to the following passage.
An experiment was performed to assess the growth of two species of plants when they were grown in different pHs, given different volumes of water, and watered at different times of day over 6 weeks. Two plants were grown of each species and the average heights (in cm) are shown in the table.

29. For which conditions do the species have different preferences?
(A) pH
(B) Volume
(C) Volume and watering time
(D) pH and volume and watering time
30. What are the preferred growth conditions for Species B?
(A) pH 7, 40 mL, any time of day
(B) pH 10, 40 mL, 7:00 A.M.
(C) pH 7, 80 mL, any time of day
(D) pH 10, 80 mL, 12:00 P.M.
31. Which pH and volume were likely used for the watering time experiment?
(A) pH 4 and 40 mL
(B) pH 7 and 40 mL
(C) pH 4 and 80 mL
(D) pH 7 and 80 mL
32. Which of the following would most improve the statistical significance of the results?
(A) Let the plants grow for a longer period of time.
(B) Add more conditions to test, such as amount of light and amount of soil.
(C) Test the same plants with more pHs and more volumes and times of day.
(D) Increase the number of plants in each group.
33. Photoperiodism in plants, in which plants respond to the stimulus of the day lengthening or shortening, can be best compared to which of the following phenomena in animals?
(A) Viral infection
(B) Increased appetite
(C) Meiotic cell divison
(D) Circadian rhythms
34. In most ecosystems, gross primary productivity, the total amount of chemical energy that producers create in a given time, is not entirely available for the consumers to utilize due to which explanation below?
(A) Not all solar energy is in the correct spectrum for plants to absorb it.
(B) Plants utilize some energy for the cellular respiration.
(C) Heterotrophs do not absorb energy from autotrophs.
(D) Very little biomass is available at the producer level.
35. Hawkmoths are insects that are similar in appearance and behavior to hummingbirds. Which of the following is LEAST valid?
(A) These organisms are examples of convergent evolution.
(B) These organisms were subjected to similar environmental conditions.
(C) These organisms are genetically related to each other.
(D) These organisms have analogous structures.
36. Which of the following describes a mutualistic relationship?
(A) A tapeworm feeds off its host’s nutrients, causing the host to lose large amounts of weight.
(B) Certain plants grow on trees in order to gain access to sunlight, not affecting the tree.
(C) Remora fish eat parasites off sharks. The sharks stay free of parasites, and the remora fish are protected from predators.
(D) Meerkats sound alarm calls to warn other meerkats of predators.
37. The pancreas is an organ that makes insulin and glucagon in its beta and alpha cells, respectively. Insulin is released when blood glucose is high and glucagon is released when blood glucose is low. Anti-beta cell antibodies, which bind to their target and inhibit functionality, will cause which of the following to occur?
(A) Glucagon secretion will stop, and blood glucose levels will not decrease.
(B) Glucagon secretion will stop, and blood glucose levels will decrease.
(C) Glucagon secretion will stop, and digestive enzymes will be secreted.
(D) Insulin secretion will stop, and blood glucose levels will not decrease.
Questions 38–40 refer to the following passage.
The rainfall and biomass of several trophic levels in an ecosystem were measured over several years. The results are shown in the graph below.

38. Which of the following concepts is best demonstrated by this experiment?
(A) Populations with higher genetic variation can withstand droughts better.
(B) Meteorological impacts will affect the evolution of populations.
(C) Environmental changes can affect all the levels of the ecosystem.
(D) Unoccupied biological niches are dangerous because they attract invasive species.
39. If it rained 120 inches, what would you project the primary consumer biomass to be?
(A) 150–200
(B) 60
(C) 45
(D) 20
40. Which of the following graphs best depicts the projected biomass of secondary consumers if they were measured?


41. The calypso orchid, Calypso bulbosa, grows in close association with mycorrhizae fungi. The fungi penetrate the roots of the flower and take advantage of the plant’s food resources. The fungi concentrate rare minerals, such as phosphates, in the roots and make them readily accessible to the orchid. This situation is an example of
(A) parasitism
(B) commensalism
(C) mutualism
(D) endosymbiosis
42. Which of the following are characteristics of both bacteria and fungi?
(A) Cell wall, DNA, and plasma membrane
(B) Nucleus, organelles, and unicellularity
(C) Plasma membrane, multicellularity, and Golgi apparatus
(D) Cell wall, unicellularity, and mitochondria
43. The synthesis of new proteins necessary for lactose utilization by the bacterium E. coli using the lac operon is regulated by the ability of RNA polymerase to bind and advance. This regulation can best be described as
(A) bacterial regulation
(B) pre-transcriptional regulation
(C) pre-translational regulation
(D) post-translational regulation
44. Trypsin is a digestive enzyme. It cleaves polypeptides after lysine and arginine amino acid residues. Which of the following statements about trypsin is NOT true?
(A) It is an organic compound made of proteins.
(B) It is a catalyst that alters the rate of a reaction.
(C) It is operative over a wide pH range.
(D) The rate of catalysis is affected by the concentration of substrate.
45. In DNA replication, which of the following does NOT occur?
(A) Helicase unwinds the double helix.
(B) DNA ligase links the Okazaki fragments.
(C) RNA polymerase is used to elongate both chains of the helix.
(D) DNA strands grow in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
46. Which of the following is true about genetic variation?
(A) Mutation is the greatest source of genetic variation.
(B) Ecosystems with high levels of genetic variation are not resistant to stress.
(C) Mitosis provides genetic variation to most somatic cells.
(D) Crossing-over prevents plants from undergoing speciation.
47. The energy given up by electrons as they move through the electron transport chain is used to
(A) break down glucose
(B) make glucose
(C) produce ATP
(D) make NADH
48. If a plant undergoing the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis began to release 18O2 instead of normal oxygen, one could most reasonably conclude that the plant had been supplied with
(A) H2O containing radioactive oxygen
(B) CO2 containing radioactive oxygen
(C) C6H12O6 containing radioactive oxygen
(D) NO2 containing radioactive oxygen
49. Yeast haploid cells secrete pheromones to other yeast to indicate they want to mate, and others respond by growing toward these potential mates. The pheromones bind to a receptor which eventually leads to increased expression of transcription factors required for this growth. This best exemplifies which of the following?
(A) Chemical inhibition due to the intracellular binding site
(B) Passive transport since the haploid cells require less energy
(C) Mitotic division due to anaphase elongation
(D) Signal transduction affecting cell function
50. Homologous structures are often cited as evidence for the process of natural selection. All of the following are examples of homologous structures EXCEPT
(A) the forearms of a cat and the wings of a bat
(B) the flippers of a whale and the arms of a man
(C) the pectoral fins of a porpoise and the flippers of a seal
(D) the forelegs of an insect and the forelimbs of a dog
51. Certain populations of finches have long been isolated on the Galapagos Islands off the western coast of South America. Compared with the larger stock population of mainland finches, these separate populations exhibit far greater variation over a wider range of species. The variation among these numerous finch species is the result of
(A) convergent evolution
(B) divergent evolution
(C) disruptive selection
(D) stabilizing selection
52. Which of the following contributes the MOST to genetic variability in a population?
(A) Sporulation
(B) Binary fission
(C) Vegetative propagation
(D) Mutation
Questions 53–55 refer to the following information and table.
A marine ecosystem was sampled in order to determine its food chain. The results of the study are shown below.
|
Type of Organism |
Number of Organisms |
|
Shark |
2 |
|
Small crustaceans |
400 |
|
Mackerel |
20 |
|
Phytoplankton |
1,000 |
|
Herring |
100 |
53. Which of the following organisms in this population are secondary consumers?
(A) Sharks
(B) Phytoplankton
(C) Herrings
(D) Small crustaceans
54. Which of the following organisms has the largest biomass in this food chain?
(A) Phytoplanktons
(B) Mackerels
(C) Herrings
(D) Sharks
55. If the herring population is reduced by predation, which of the following would most likely be a secondary effect on the ecosystem?
(A) The mackerels will be the largest predator in the ecosystem.
(B) The small crustacean population will be greatly reduced.
(C) The phytoplankton population will be reduced over the next year.
(D) The small crustaceans will become extinct.
Questions 56–57 refer to the following information and diagram.
Scientists used embryology, morphology, paleontology, and molecular biology to create the phylogenetic tree below.

56. Which of the following is the least closely related according to the phylogenetic tree?
(A) B. physalus and B. brydei
(B) B. boreales and B. brydei
(C) B. musculus and B. brydei
(D) B. musculus and Eschrichtius robustus
57. Which of the sources of evolutionary evidence would be the most reliable of those listed?
(A) Embryology
(B) Morphology
(C) Paleontology
(D) Molecular biology
58. The brain of the frog is destroyed. A piece of acid-soaked paper is applied to the frog’s skin. Every time the piece of paper is placed on its skin, one leg moves upward. Which of the following conclusions is best supported by the experiment?
(A) Reflex actions are not automatic.
(B) Some reflex actions can be inhibited.
(C) All behaviors in frogs are primarily reflex responses.
(D) This reflex action does not require the brain.
Questions 59–60 refer to the figure and chart below.


59. Which of the following DNA strands is the template strand that led to the amino acid sequence shown above?
(A) 3’-ATGCGACCAGCACGT-5’
(B) 3’-AUGCCACUAGCACGU-5’
(C) 3’-TACGGTGATCGTGCA-5’
(D) 3’-UACGGUGAUCGUGCA-5’
60. Immediately after the translation of methionine, a chemical is added which deletes all remaining uracil nucleotides in the mRNA. Which of the following represents the resulting amino acid sequence?
(A) Serine–histidine–serine–threonine
(B) Methionine–proline–glutamine–histidine
(C) Methionine–proline–leucine–alanine–arginine
(D) Methionine–proline–alanine–arginine–arginine
STOP
END OF SECTION I
IF YOU FINISH BEFORE TIME IS CALLED, YOU MAY CHECK YOUR WORK ON THIS SECTION. DO NOT GO ON TO SECTION II UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
Section II
BIOLOGY
SECTION II
6 Questions
Writing Time—90 minutes
Directions: Questions 1 and 2 are long free-response questions that should require about 25 minutes each to answer and are worth 8–10 points each. Questions 3 through 6 are short free-response questions that should require about 10 minutes each to answer and are worth 4 points each.
Read each question carefully and completely. Write your response in the space provided following each question. Only material written in the space provided will be scored. Answers must be written out in paragraph form. Outlines, bulleted lists, or diagrams alone are not acceptable unless specifically requested.
1. At what level does natural selection operate: the individual or the group? This is a central question in the field of sociobiology. In 1962, V. C. Wynne Edwards put forth his revolutionary group selection thesis, which states that animals avoid overexploitation of their habitats, especially with regard to food supply. In his theory, they accomplish this by altruistic restraint on the part of individuals who reduce their reproduction, or refrain altogether, to avoid overpopulation. Thus altruism is favored by natural selection.
For example, small birds of the species Parus major typically produce nine or ten eggs per clutch, although they have been observed to produce as many as thirteen eggs per clutch. Data show that a clutch size larger than nine or ten actually produces fewer surviving offspring. See Figure 1; the vertical axis gives the percent occurrence of each brood size, and the numbers labelling the dots indicate the number of known survivors per nest.
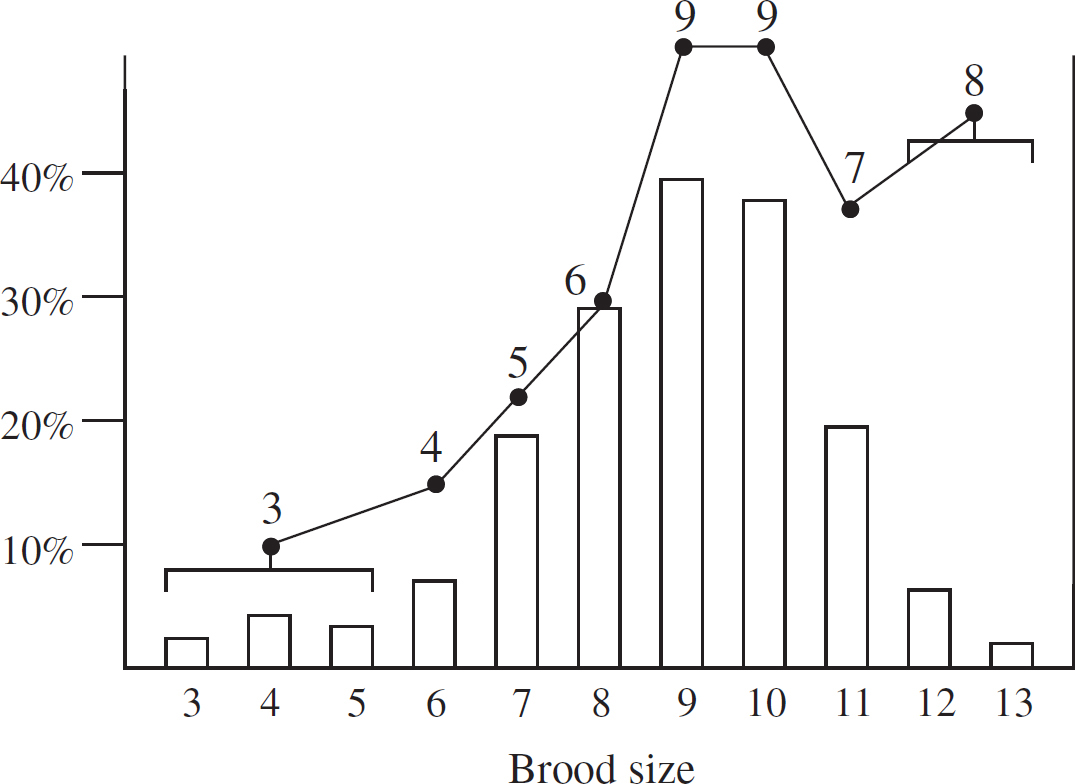
Figure 1
Additional evidence for the group-selection theory is that there appears to be a relationship between reproductive success of individuals and the density of the population. When density is low, mortality is likewise low and reproductive rate high. At high numbers resources are more scarce, and it is more difficult to stay alive and to reproduce, so mortality is high and reproductivity low. Figure 2 shows the number of surviving offspring per mating pair plotted against the number of breeding adults present (the graph covers several years).
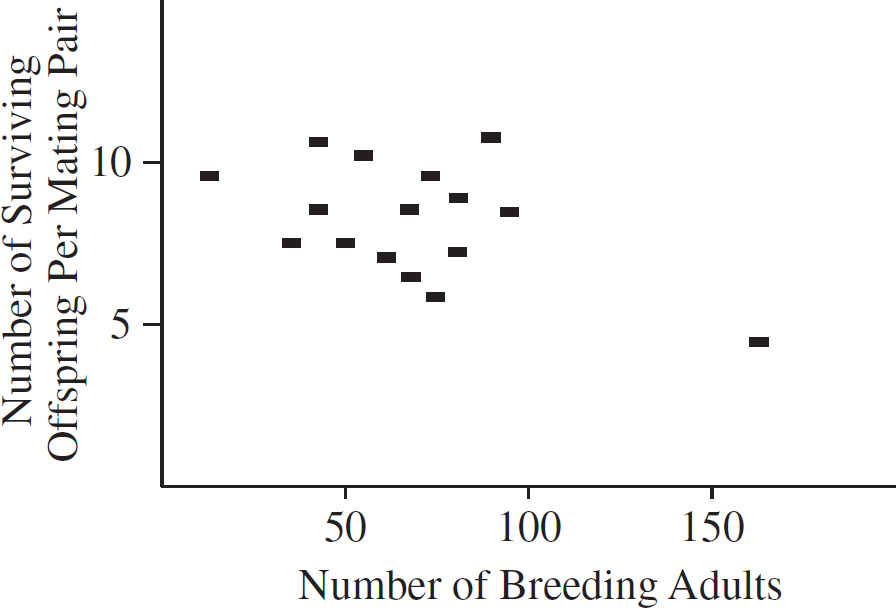
Figure 2
(a) Describe the carrying capacity in a population. Can a brood size have a carrying capacity? Justify your choice.
(b) This study involved observing birds in their natural habitat. Identify the independent variable in this brood size vs. percent survival study. Describe what makes an observational study different from a study inside a lab environment.
(c) Describe the brood size(s) in which 100% of the offspring survive. Identify which brood size has the highest percent of mortality.
(d) Over many more years the number of breeding adults was measured, and it was found that over a long time the number of breeding adults averaged around 100. Describe how this would change the information in Figure 1. Justify your answer.
2. Diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2DM) is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance on the part of the body’s tissues. Onset is usually much later in life and highly associated with obesity. A recent study evaluated the relative dysfunction of mitochondria of individuals who were lean, obese, and diabetic (type 2). Muscle biopsies were taken both prior to and after a twenty-week exercise program. The mitochondrial mass was measured by cardiolipin, the citric acid cycle was measured by citrate synthase, and electron transport chain activity was measured by NADH oxidase levels. The results are shown below in the table.

Table 1 Mean (upper rows) and standard error (lower rows) measurements for markers of ETC activity, in relative units normalized to creatine kinase activity.
(a) Explain how the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain are related and how they are affected by exercise.
(b) Construct a graph of the data indicating citric acid cycle activity. Be sure to use error bars.
(c) Identify which group did not show an increase in cardiolipin after exercise was done. Justify your choice with data.
(d) If another measure of the citric acid cycle were added in a future experiment, explain what results you would expect.
3. Maternal inheritance is one pattern of inheritance which does not follow the rules of Mendelian genetics. It is an example of uniparental inheritance in which all progeny have the genotype and phenotype of the female parent.
Maternal inheritance can be demonstrated in the haploid fungus Neurospora by crossing the fungi in such a way that one parent contributes the bulk of the cytoplasm to the progeny. This cytoplasm-contributing parent is called the female parent, even though no true sexual reproduction occurs. The inheritance patterns of a mutant strain of Neurospora called poky have been studied using such crosses. Poky differs from the wild-type in that it is slow-growing and has abnormal quantities of cytochromes.
Investigators suspected that the poky mutation was carried in the mitochondria, instead of in the nuclear genome. The following experiments were designed to test this hypothesis.
Step 1:
Mitochondria were extracted from poky Neurospora mutants.
Step 2:
An ultrafine needle and syringe was used to inject these mitochondria into wild-type Neurospora cells.
Step 3:
These recipient cells were cultured for several generations, and the phenotypes were examined.
Results:
The poky phenotype was observed in some of the cultured fungi.
(a) In mitochondrial inheritance the offspring have the genotype and phenotype of the mother. Under Mendelian inheritance it is possible for the offspring to have a different genotype but the same phenotype as the mother. Describe how this is possible.
(b) Explain what important control(s) the scientists should do to account for the procedure in Step 2.
(c) If the nuclear DNA was injected into the wild-type Neurospora cells instead of the mitochondria, explain whether the resulting fungi would have the poky phenotype?
(d) Justify your prediction.
4. A diverse flock of finches that can eat many sizes of seeds lives on a small island in Polynesia, which recently experienced a drought. Trees producing robust, medium-sized seeds died out in large numbers but more resilient trees that produced both small and large-sized seeds are thriving. The finches can shelter in the trees or in burrows underground. The island is home to several tree species that do not produce edible seeds and small rodents that also eat the seeds.
(a) Finches are incapable of digging burrows yet approximately 25% of the finches found on the island live in underground dwellings. Describe the source of the finch dwellings.
(b) Describe the relationship between the finches and rodents on the island.
(c) Protein HITB8 is found to be present in high levels in medium-sized beak finches and less so in other finch types. Predict what will happen to the frequency of this protein product in the finch population after two generations if the drought continues.
(d) Justify your answer to (c).

(a) Describe the importance of being the sole occupant of a niche in an ecosystem.
(b) Describe the impact of an invasive species that competes with phytoplankton and zooplankton.
(c) Identify the number of species with no natural predator on this food web.
(d) Explain why toxins are more of a concern for tertiary consumers than they are for primary consumers.
6. A teacher observes squirrels frequently crossing the road and wants to determine if squirrels prefer one side of the road to the other. At 4:00 P.M. for three non-consecutive days the teacher counts the number of squirrels on each side. The north side has predominantly pine trees, while the south side has mostly red maple trees.
|
|
North Side |
South Side |
|
Monday |
21 |
15 |
|
Wednesday |
18 |
18 |
|
Friday |
22 |
14 |
|
Average |
|
|
Table 1
(a) Identify the null hypothesis of this experiment.
(b) Complete the table with the average data and values necessary to test the hypothesis. (All white empty blanks should be filled.)

(c) Use statistics to determine whether the null hypothesis should be rejected.
(d) Explain how the results of the experiment support the theory that animal behavior changes as their environment changes.
STOP
END OF EXAM