
Minerals
Goji contains 21 trace minerals including:
Calcium
Copper
Geranium (anti-cancer mineral rarely found in foods)
Iron (11 mg/100g)
Magnesium
Phosphorus
Selenium
Zinc
Vitamins
Vitamin A (super-antioxidant, improves eye and nerve health)
Vitamin C (73mg/100g)
Vitamin B-complex (helps convert food into energy, increases energy, improves mood)
B1
B2
B6
Vitamin E (rarely found in fruits)
Amino Acids (Protein)
Contains 18 amino acids (of which eight are essential for life)
50 percent are free-form amino acids
More protein than whole wheat (13%)
A complete protein source

Very large, long-chain sugar molecules that are nourishment for macro phages (large white blood cells) in the gut wall. The macrophages are then transported to other immune cells, setting off a chain of defensive events in the human body.
Immune stimulant
Inhibits tumor growth
Anti-cancer
Neutralizes side effects of chemotherapy and radiation
Normalizes blood pressure
Balances blood sugar
Combats autoimmune disease
Anti-inflammatory
Balances immune function
Increases calcium absorption
Lowers cholesterol and blood lipids
Normalize cell growth
Restore and repair DNA
Scavenge free oxygen radicals
Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides (LBP 1–4)
glycoconjugates (essential cell sugars)
rhamnose
xylose
glucose
mannose
arabinose
galactose
Antioxidants
ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) 133 per gram
(Antioxidant measurement)
| Vitamin C | Super anti oxidant | |
| Beta-carotene Cystine | ImmunityImmunity and healthy stomach lining | |
| B2 (riboflavin) | Conversion of carbohydrates into fuel | |
| Manganese | Healthy blood, bone, cartilage | |
| Zinc | Wound healing, fertility, vision, immunity | |
| Copper | Energy, hormonal function, healthy skin | |
| Selenium | Healthy liver, thyroid, immunity, cancer protection |
Increases longevity
Beta-carotene (goji is one of the richest known sources) 26,000 and 8,000 IU/100g
Tetraterpenoids
Zeaxanthin (protects vision)
Physalin
Other Active Naturally Occurring Ingredients
Beta-Sitosterol
Anti-inflammatory
Lowers cholesterol
Treats sexual impotence
Treats prostate enlargement
Betaine (0.1%)
Protects DNA
Increases choline production by liver
Calms nervousness
Enhances memory
Promotes muscle growth
Protection against fatty liver disease
Aids in liver detoxification
Essential fatty acids
Produces hormones
Assists brain and nervous system function
Linoleic acid
Flavonoids
Antioxidant
Protect cell membranes
Solavetivone
Antifungal
Antibacterial
Physalin
Anti-cancer
Anti-leukemia
Immune system booster
Fights leukemia
Used in hepatitis B treatment
Sesquiterpenoids
Stimulates the glandular production of Humane Growth Hormone
Increase longevity
Cyperone (a sesquiterpene)
Used in the treatment of cervical cancer
Benefits heart and blood pressure
Relieves menstrual discomfort
Has been used with treatment of cervical cancer
Solavetivone
Tetraterpenoids
Zeaxanthin
Physalin
Sources
Mindell, Earl, and Rick Handel. Goji: the Himalayan Health Secret. Texas: Momentum Media, 2003.
Teeguarden, R. The Ancient Wisdom of the Chinese Tonic Herbs. New York: Warner Books, Inc., 1998.
Gross, P.M., X. Zhang, and R. Zhang. Wolfberry: Nature’s Bounty of Nutrition and Health. Booksurge Publishing, 2006.
Analytical Report (Cacao Nibs www.sacredchocolate.com)
All results are reflected per 100 grams
| Protein | 15.4 grams |
| Carbohydrate (Total) | 29.4 grams |
| Fat (Total) | 48.0 grams |
| Moisture | 3.9 grams |
| Ash | 3.3 grams |
| Calories | 611 |
| Calories from Fat | 432 |
| Saturated Fat | 27.6 grams |
| Trans Fat | 0.25 grams |
| Dietary Fiber | 22.3 grams |
| Sugars | 0.1 grams |
| Sodium | 53 mg |
| Calcium | 58 mg |
| Iron | 202 mg |
| Magnesium | 342 mg |
| Vitamin A | 20 (IU) |
| Vitamin C | 44 mg |
*Northeast Laboratories, Inc.; Cacao Nibs, Analytical Report
The Cacao Bean’s Natural Chemical Constituents and Their Concentrations (when available)
Acetic acid 1,520–7,100 ppm
Alanine 10,400 ppm
Amylase
Anandamide
Arabinose
Arginine 800+ ppm
Ascorbic acid 31 ppm
Aspariginase
Beta Theosterol
Caffeic acid
Caffeine, Petiole 51–525 ppm or 500–12,900 ppm, Skin 130–723 ppm
Calcium 800–1,100 ppm
Camposterol
Carbohydrates 347,000–445,000 ppm
Catalase
Catechins 30,000–35,000 ppm
Chloride 120 ppm
Chromium (10 times more than whole wheat, highest of any major food)
Citric acid 4,500–7,500 ppm
Copper 24 ppm
Coumarin
Cyanidin-glycoside 4,000–5,000 ppm
Dopamine
Epigallocatechin
Ergosterol
Fat 371,000–582,300 ppm
Fiber 59,000–89,000 ppm
Glucose 3,000 ppm
Glutamic acid 10,200 ppm
Glycine 900 ppm
Histamine
Histidine 800 ppm
Iron 36–37 ppm
Iron oxide 40 ppm
Isoleucine 5,600 ppm
L-epicatechin 27,000 ppm
Lactic acid
Leucine
Leucocyanidins 14,000–35,000 ppm
Linalol 5 ppm
Linoleic acid
Linolenic acid
Lipase
Lysine 800 ppm
Lysophosphatidylcholine
Magnesium
Mannose
N-linoleoylethanolamine—Anandamide reuptake inhibitor
N-oleolethanolamine—Anandamide reuptake inhibitor
Niacin 17–18 ppm
Nicotinamide 21 ppm
Nitrogen 22,800 ppm
Oleic acid 190,000–217,000 ppm
Oleo-Dipalmatin 76,500–92,800 ppm
Oxalic acid 1,520–5,000 ppm
Palmitic acid
Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5)13 ppm
Pectin
Pentose
Peroxidase
Phenylacetic acid
Phenylalanine 5,600 ppm
Phenylethylamine
Phosphatidyl-choline 92–1,328 ppm
Phospholipids
Phosphorus 3,600–5,571 ppm
Polyphenols 78,000–100,000 ppm
Proline 7,200 ppm
Protein 120,000–180,000 ppm
Purine 30,000–40,000 ppm
Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) 1 ppm
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) 1–4 ppm
Serine 8,800 ppm
Serotonin
Sitosterol
Starch 60,000 ppm
Stearic acid
Tannins 75,400 ppm
Theobromine 10,000–33,500 ppm
Theophylline 3,254–4,739 ppm—Theophylline is a methylxanthine with diuretic and bronchial smooth muscle relaxant properties.
Thiamine (Vitamin B1)1–3 ppm
Threonine 1,400 ppm
Tocopherol (beta, gamma, Vitamin E)
Tryptophan
Tyramine
Tyrosine 5,700 ppm
Valine 5,700 ppm
Vanillic acid
Water 36,000 ppm
Xylose
Sources
Wolfe, David, and Shazzie. Naked Chocolate. Berkeley: North Atlantic Books, 2005.
Dr. Duke’s Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
Minerals
Calcium (higher than potatoes) (350–500mg/100g)
Copper
Iron (higher than potatoes)
Magnesium
Phosphorus (300–350mg/100g)
Potassium (1600–2000mg/100g)
Iodine
Zinc
Sulfur
Iron
Sodium
Manganese
Aluminum
Tin
Vitamins
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin)
Vitamin C
Vitamin E
Alanine
Arginine
Aspartic acid
Glutamine
Glycine
Histidine
OH-proline
Isoleucine
Leucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Proline
Sarcosine
Serine
Threonine
Tyrosine
Valine
More Nutrients and Facts
| Carbohydrates | 59% |
| Protein | 10.2% |
| Fiber | 8.5% |
| Lipids | 2.2% |
Sterols
Brassicasterol
Erogosterol
Ergostadienol
Campesterol
Sitosterol
Stigmasterol
Fatty Acids
Oleic
Lauric
Myristic
Palmitic
Palmitoleic
Linoleic
Arachidic
Steric
Behanic
Nervonic
Lignoceric
Tridecanoic
7-tridecanoic
Perntadecanoic
7-pentadecanoic
Heptadecanoic
9-heptadecanoic
Nonadecanoic
11-nonadecanoic
15-eicosenoic
Alkaloids
Macaina 1-4 (Chacón)
Macamides
Macaenes (Zheng)
Glucosinolates (anti-cancer, antimutagenic, anticarcinogenic)
Indole3-carbinol
Isothiocyanates
P-methoxybenzyl isothi ocyanate (aphrodisiac properties)
Sources
Ley, B.M. MACA: Adaptogen and Hormonal Regulator. Minnesota: BL Publications, 2003.
Minerals
Calcium
Phosphorus
Potassium
Iron
Copper
Iodine
Zinc
Sulfur
Sodium
Chlorine
Magnesium
Manganese
Molybdenum
Boron
Silica
Titanium
Vitamins
Provitamin A
B-1 Thiamin
B-2 Riboflavin
B-3 Niacin
B-5
B-6 Pyridoxine
B-12 (cyanocobalamin)
Pantothenic Acid
Vitamin C
Vitamin F
Vitamin D
Vitamin E
Vitamin H
Vitamin K
Vitamin P
Folic Acid
Choline
Inositol
Rutin
Other Nutrients
Amino acids
Carbohydrates
Fatty acids
Enzymes and coenzymes
Fats
Average Composition of Honey (all values % except for pH)
| Component | Average | Range |
| Moisture | 17.2% | 12.2–22.9% |
| Fructose | 38.4 | 30.9–44.3 |
| Glucose | 30.3 | 22.9–40.7 |
| Sucrose | 1.3 | 0.2–7.6 |
| Maltose | 7.3 | 2.7–16.0 |
| Higher Sugars | 1.4 | 0.1–3.8 |
| Acid as Gluconic | 0.57 | 0.17–1.17 |
| Ash | 0.169 | 0.02–1.03 |
| Nitrogen | 0.041 | 0.00–0.13 |
| pH | 3.91 | 3.42–6.10 |
Sources
Kacera, Walter “Shantree.” Pollen Power: Nectar of Life. Ayurvedic Nutritionist and Herbalist, 2002.
Analysis of royal jelly reveals all major vitamins: A, B-complex, C, D, and E. It contains a natural antibiotic—decanoic acid—sulfur, and over 5% fatty acids, 12% protein, and nearly 3% “unidentifiable” substances. The moisture content is 66%. Natural hormones, essential sugars, nucleic acids, vegetable gelatin, gamma globulin, and other fascinating nutrients are also found in royal jelly.
Like all beehive products, propolis is made of locally gathered substances of plant origin. Propolis differs in composition from place to place. It typically consists of:
30% beeswax
55% resins
10% aromatic ethers and essential oils
5% pollen.
A sampling of chemical ingredients often includes:
| B vitamins | ferulic acid |
| caffeic acid | iron |
| Calcium | manganese |
| Chrysin | silicon |
| cinnamic acid | tectochrysin |
| cinnamyl alcohol | vanadium |
| Copper | vanillan |
| E vitamins | vitamin C |
Propolis may contain up to 27 additional compounds that are not clearly scientifically understood in their composition and/or effects.
Essential Minerals and Trace Elements
| Mineral | Amount |
| Potassium | 15,400 mg/kg |
| Calcium | 1,315 mg/kg |
| Zinc | 39 mg/kg |
| Magnesium | 1,915 mg/kg |
| Manganese | 25 mg/kg |
| Selenium | 0.40 ppm |
| Iron | 580 mg/kg |
| Phosphorus | 8,942 mg/kg |
Minerals (per 10 grams)
| Mineral | Amount |
| Calcium | 12 mg |
| Magnesium | 14.4 mg |
| Iron | 3.18 mg |
| Phosphorus | 31.2 mg |
| Potassium | 45.6 mg |
| Sodium | 21.9 mg |
| Manganese | 78 mcg |
| Zinc | 36 mcg |
| Boron | 30 mcg |
| Copper | 3 mcg |
| Molybdenum | 3 mcg |
Vitamins (per 10 grams)
| Vitamin | Amount |
| Beta-carotene | 10 mg |
| Vitamin A (100% | 15,030 IU |
| as Beta-carotene) | |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 102 mcg |
| Vitamin B2 | 99 mcg |
| (Riboflavin) | |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 621 mcg |
| Vitamin B6 | 13 mcg |
| Vitamin B12 | 6.6 mcg |
| Inositol | 2.04 mg |
| Biotin | 0.969 mg |
| Folic Acid | 0.9 mcg |
| Pantothenic | 12 mcg |
| Pyridoxine (B6) | 3 mg/kg |
| Biotin | 0.4 mg/kg |
| Cobalamin (B12) | 2 mg/kg |
| Pantothenic Acid | 11 mg/kg |
| Folic Acid | 0.5 mg/kg |
| Inositol | 350 mg/kg |
| Niacin | 118 mg/kg |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 40 mg/kg |
| Thiamine (B1) | 55 mg/kg |
| Tocopherol (Vit E) | 190 mg/kg |
Eight Essential Amino Acids
| Amino Acid | % |
| Isoleucine | 4.13% |
| Leucine | 5.80% |
| Lysine | 4.00% |
| Methionine | 2.17% |
| Phenylalanine | 3.95% |
| Threonine | 4.17% |
| Tryptophan | 1.13% |
| Valine | 6.00% |
Non-essential Amino Acids
| Amino Acid | % |
| Alanine | 5.82% |
| Arginine | 5.98% |
| Aspartic Acid | 6.34% |
| Cystine | 0.67% |
| Glutamic Acid | 8.94% |
| Glycine | 3.50% |
| Histidine | 1.08% |
| Proline | 2.97% |
| Serine | 4.00% |
| Tyrosine | 4.60% |
Chemical Analysis of Spirulina
| Protein | 71% |
| Crude Fiber | 0.90% |
| Carbohydrates | 16.90% |
| Fat | 7.00% |
| Cholesterol (less than) | 0.05% |
| Moisture | 7.00% |
General Composition Analysis of Another Spirulina
| Protein | 60% |
| Carbohydrates | 19% |
| Lipids | 6% |
| Minerals | 8% |
| Moisture | 7% |
Vitamin Analysis of Spirulina (average)
| Biotin | 0.4 mg/kg |
| Vitamin B12 | 2 mg/kg |
| D-Ca-Pantothenate | 11 mg/kg |
| Folic Acid | 0.5 mg/kg |
| Inositol | 350 mg/kg |
| Nicotinic Acid | 118 mg/kg |
| Vitamin B6 | 3 mg/kg |
| Vitamin B2 | 40 mg/kg |
| Vitamin B1 | 55 mg/kg |
| Vitamin E | 190 mg/kg |
Mineral Analysis of Spirulina (average)
| Calcium | 1,315 mg/kg |
| Phosphorus | 8,942 mg/kg |
| Iron | 580 mg/kg |
| Sodium | 412 mg/kg |
| Magnesium | 1,915 mg/kg |
| Manganese | 25 mg/kg |
| Zinc | 39 mg/kg |
| Potassium | 15,400 mg/kg |
| Selenium | 0.4 mg/kg |
Other Components (average)
| Nucleic Acids | 4.50% |
| Carotenoids | 0.40% |
| Chlorophyll | 0.80% |
| Crude Protein | 71% |
Essential Amino Acids
| Isoleucine | 4.10% |
| Leucine | 5.80% |
| Lysine | 4.00% |
| Methionone | 2.20% |
| Phenylalanine | 4.00% |
| Threonine | 4.20% |
| Tryptophan | 1.10% |
| Valine | 6.00% |
| Alanine | 5.80% |
| Arginine | 6.00% |
| Aspartic Acid | 6.40% |
| Cystine | 0.70% |
| Glutamic Acid | 8.90% |
| Glycine | 3.50% |
| Histidine | 1.10% |
| Proline | 3.00% |
| Serine | 4.00% |
| Tyrosine | 4.60% |
Polysaccharides and Phytonutrients per 10 grams (% spirulina)
| Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA) | 130 mg 1.3% |
| Glycolipids (Lipid) | 200 mg 2.0% |
| Sulfolipids (Glycolipids) | 10 mg 0.1% |
| Polysaccharides | 460 mg 4.6% |
Antioxidants per 10 grams
| Beta-carotene 9-cis | 1.60 mg |
| Beta-carotene 13-cis | 0.52 mg |
| Beta-carotene 15-cis | 0.12 mg |
| Beta-carotene all-trans | 7.80 mg |
| Zeaxanthin | 0.95 mg |
| Chlorophyll | 23.70 mg |
| Total carotenoids* | 14 mg |
| Phycocyanin | 333 mg |
| Superoxide | 2,640 units |
| Dismutase** | |
| *Includes alpha carotene, beta cryptoxanthin, and others. | |
| **Reported as units Ferric S.O.D. | |
Carotenoid Profile
| Carotenoid | Amount |
| Alpha-carotene | traces |
| Beta-carotene | 1,700 mg/kg |
| Xanthophylls | 1,000 mg/kg |
| Cryptoxanthin | 556 mg/kg |
| Echinenone | 439 mg/kg |
| Zeaxanthin | 316 mg/kg |
| Lutein | 289 mg/kg |
Other Active Naturally Occurring Ingredients (per 10 grams)
| Omega-6 Family Gamma-Linolenic (GLA) | 30 mg |
| Essential Linoleic | 33 mg |
| Dihomogamma Linolenic | 1.59 mg |
Omega-3 Family
| Alpha-Linolenic | 0.0435 mg |
| Docosahexaenoic (DHA) | 0.0435 mg |
Monoenoic Family
| Palmitoleic | 5.94 mg |
| Oleic | 0.51 mg |
| Erucic | 0.072 mg |
Sources
Challem, Jack J. Spirulina. New Canaan, CT: Keats Publishing, 1981.
McCauley, B. Confessions of a Body Builder. Lansing, MI: Spartan Enterprises, 2000.
http://www.mallorcaspirit.com/Alternative_Medicine_directory/spirulina.html
Minerals
| Boron | 0.05 mg |
| Calcium | 4.86 mg |
| Chloride | 0.02 mg |
| Chromium | 0.18 mcg |
| Cobalt | 0.69 mcg |
| Copper | 1.49 mcg |
| Fluoride | 13.21 mcg |
| Germanium | 0.09 mcg |
| Iodine | 18 mcg |
| Iron | 121.69 mcg |
| Magnesium | 0.76 mg |
| Manganese | 11.12 mcg |
| Molybdenum | 1.15 mcg |
| Nickel | 1.84 mcg |
| Potassium | 4.16 mcg |
| Phosphorus | 1.82 mcg |
| Selenium | 0.23 mcg |
| Silicon | 65.2 mcg |
| Sodium | 0.94 mg |
| Tin | 0.172 mcg |
| Titanium | 16.17 mcg |
| Vanadium | 0.96 mcg |
| Zinc | 6.51 mcg |
Minerals (per gram)
| Boron | 14.0 mcg |
| Calcium | 12.70 mg |
| Chloride | 0.47 mg |
| Chromium | 0.53 mcg |
| Cobalt | 2.00 mcg |
| Copper | 4.30 mcg |
| Fluoride | 38.00 mcg |
| Germanium | 0.27 mcg |
| Iodine | 0.53 mcg |
| Iron | 0.37 mg |
| Magnesium | 2.20 mg |
| Manganese | 32.0 mcg |
| Molybdenum | 3.30 mcg |
| Nickel | 5.3 mcg |
| Phosphorus | 5.20 mg |
| Potassium | 12.00 mcg |
| Selenium | 0.67 mcg |
| Silicon | 186.70 mcg |
| Sodium | 2.70 mg |
| Tin | 0.47 mcg |
| Titanium | 23.3 mcg |
| Vanadium | 2.70 mcg |
| Zinc | 18.70 mcg |
Vitamins
| Provitamin A Beta-carotene | 1890 IU |
| Thiamin (B1) | 27 mcg |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 49 mcg |
| Niacin (B3) | 0.05 mg |
| Pantothenic Acid (B5) | 2.38 mcg |
| Pyridoxine (B6) | 3.85 mcg |
| Inositol | 55.50 mcg |
| Vitamin E | 0.59 IU |
| Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) | 2.34 mcg |
| Biotin | 0.10 mcg |
| Folic Acid | 0.73 mcg |
| Choline | 0.80 mcg |
| Cobalamin (B12) | 2.80 mcg |
| Vitamin K | 34 mcg |
Vitamins (AFA Algae)
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin)
Vitamin B3 (niacin)
Pantothenic acid (B5)
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
Folic Acid (B9)
Vitamin B12
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
Choline
Biotin
Vitamin E
Typical Amino Acid Content (per 15ml)
Essential Amino Acids
| Arginine | 13.19 mg |
| Histidine | 3.12 mg |
| Isoleucine | 10.06 mg |
| Leucine | 18.04 mg |
| Lysine | 12.15 mg |
| Methionine | 2.43 mg |
| Phenylalanine | 8.68 mg |
| Threonine | 11.52 mg |
| Tryptophan | 2.42 mg |
| Valine | 11.10 mg |
Non-essential Amino Acids
| Alanine | 16.30 mg |
| Asparagine | 15.91 mg |
| Aspartic Acid | 2.43 mg |
| Cystine | 0.69 mg |
| Glutamic Acid | 1.39 mg |
| Glutamine | 27.06 mg |
| Glycine | 10.06 mg |
| Proline | 10.13 mg |
| Serine | 10.01 mg |
| Tyrosine | 5.89 mg |
| Essential | Semi-Essential | Non-Essential |
| Isoleucine | Arginine | Alanine |
| Leucine | Histidine | Aspartic Acid |
| Lysine | Cystine | |
| Methionine | Glutamic Acid | |
| Tryptophan | Proline | |
| Threonine | Serine | |
| Phenylalanine | Tyrosine | |
| Valine |
Other Occurring Nutrients
Essential Fatty Acids
Alpha-Linolenic Acid (Omega 3) 10.70 mg
Gamma-Linolenic Acid (Omega 6) 2.15 mg
Typical Nutrient Composition (15ml)
| Protein | < 1 gram |
| Fat | < 1 gram |
| Carbohydrate | < 1 gram |
| Fiber | 1.50% |
| Moisture | 94 to 95% |
| Chlorophyll | 0.59% |
| Calories | 3.9 Cal/0.016 kJ |
Beta-carotene
1–2% Chlorophyll
Helps the body obtain more oxygen
Aids digestion
Anti-inflammatory
Fights gum disease
Prevents infection
Minimizing the effects of pollution
Accelerates wound healing
Internal deodorizer
Combats bad breath and body odor
Stimulates regeneration of damaged liver cells
Increases circulation
Balances alkalinity
Aids in transmission of nerve impulses that control contraction in the heart
Strong cleansing and detoxification
15% Phycocyanin (blue pigments that increase stem cell production)
Lipids (omega-3 fatty acids that protect the nervous system)
Complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides that support long-term energy and improve the immune system).
Sources
McKeith, Gillian. Miracle Superfood: Wild Blue-Green Algae. Los Angeles: Keats Publishing, 1999.
Earth’s Essential Elements E3Live,™ DATA SHEET Klamath Lake Blue-Green Algae. Klamath Falls, OR: Vision, Inc., n.d.
Minerals
| Elements | Result |
| Boron | 2.843 mcg/75mg |
| Calcium | 142.500 mcg/75mg |
| Chromium | 0.014 mcg/75mg |
| Copper | 0.384 mcg/75mg |
| Iodine | 1.210 mcg/75mg |
| Iron | 90.000 mcg/75mg |
| Magnesium | 286.500 mcg/75mg |
| Manganese | 19.800 mcg/75mg |
| Molybdenum | 0.023 mcg/75mg |
| Phosphorus | 960.000 mcg/75mg |
| Potassium | 975.000 mcg/75mg |
| Selenium | <0.010 mcg/75mg |
| Sodium | 682.500 mcg/75mg |
| Sulfur | 504.000 mcg/75mg |
| Vanadium | <0.069 mcg/75mg |
| Zinc | 1.673 mcg/75mg |
Vitamins
| Folic Acid | 0.053 mcg/75mg |
| Vitamin A | 30.00 mcg/75mg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) | 1.300 mcg/75mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 7.000 mcg/75mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 11.00 mcg/75mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) | 8.000 mcg/75mg |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) | 0.990 mcg/75mg |
Amino Acids
| Isoleucine | 1.275 mg/75mg |
| Leucine | 2.625 mg/75mg |
| Lysine | 2.175 mg/75mg |
| Methionine | 0.825 mg/75mg |
| Phenylalanine | 1.350 mg/75mg |
| Proline | 2.925 mg/75mg |
| Threonine | 1.725 mg/75mg |
| Tryptophan | 0.600 mg/75mg |
| Valine | 1.800 mg/75mg |
| Alanine | 2.325 mg/75mg |
| Arginine | 2.325 mg/75mg |
| Aspartic Acid | 3.225 mg/75mg |
| Glutamic Acid | 4.650 mg/75mg |
| Glycine | 1.800 mg/75mg |
| Histidine | 0.600 mg/75mg |
| Tyrosine | 1.050 mg/75mg |
Marine Phytoplankton (Nannochloropsis) preserved in ocean-derived mineral concentrate
(Serving Size = 0.2 tsp), Ionic Trace
Mineral Solution
Serving Size = 1.52 gm
Fatty Acids
More Composition Info on Gesundheit Marine Phytoplankton (dried) Nutritional Proxy Test
| Parameter | Result |
| Protein | 47.50% |
| Ash | 7.20% |
| Energy | 422 Cal/ 100 gm |
| Energy | 1765 KJ/ 100 gm |
| Carbohydrates | 29.40% |
| Fat | 12.70% |
| Moisture | 3.20% |
| Crude Fiber | 0.10% |
Fatty Acid Profile
EPA 9.3 mg/gm
DHA 4.9 mg/gm
Omega-6 Fatty Acid (Linoleic Acid) 3.4 mg/gm
Gamma-Linolenic 3.4 mg/gm
Beta-carotene (by HPLC)*
Vitamin C (by HPLC)**
Iodine (as per USP)***
*A number of carotenoids were found to be present in the sample. It could be Xanthophyll or other types of carotenoids.
**Vitamin C is present but could not be quantified.
***Iodine is present but could not be quantified.
Macro Nutrients
| Carbohydrates | 27.00 mg/75mg |
| Lipids | 2.445 mg/75mg |
| Proteins | 36.375 mg/75mg |
| Ash | 6.600 mg/75mg |
| Moisture | 3.490 mg/75mg |
| Nitrogen | 5.820 mg/75mg |
| Calories | 3.670 Kcal/g |
| Total Pigments | 23.300 mcg/75mg |
Minerals
In parts per million (ppm) when available
| Calcium | 4,600 |
| Chlorine | |
| Chromium | |
| Cobalt | |
| Copper | |
| Germanium | |
| Iron | 300 |
| Magnesium | 930 |
| Manganese | 0.6 |
| Phosphorus | 940 |
| Potassium | 850 |
| Selenium | 2.3 |
| Silicon | 2.2 |
| Sodium | 510 |
| Sulfur | |
| Tin | 11 |
| Zinc | 770 |
Vitamins
In parts per million (ppm) when available
| Vitamin B1: Thiamin | 0.8 |
| Vitamin B2: Riboflavin | |
| Vitamin B3: Niacin | 64 |
| Vitamin B9: Folic Acid | 200 |
| Vitamin C | 6,260 |
| Vitamin E | |
| Choline |
Amino Acids and Amino Acid Groups
In parts per million (ppm) when available
Sugars and Polysaccharides
In parts per million (ppm) when available
| Arabinose | |
| Fructose | |
| Glucose | 1,030 |
| Galactose | 100 |
| Mannose | |
| Rhamnose | |
| Xylose |
Antioxidants
In parts per million (ppm) when available
| Beta-carotene | 3 |
Enzymes
In parts per million (ppm) when available
| Amylase | 20 |
| Catalase | |
| Lipase | 16 |
Other Biologically Active Components
In parts per million (ppm) when available
| Anthraquinones | 300,000 |
| Aloins | 300,000 |
| Purine | 56 |
Sources
Dr. Duke’s Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
http://sun.arsgrin.gov:8080/npgspub/xsql/duke/plantdisp.xsql?taxon=58
Minerals
| Phosphorus | 36.46% |
| Calcium | 23.64% |
| Potassium | 20.28% |
| Silica | 11.90% |
| Magnesium | 5.70% |
| Iron | 1.00% |
| Sodium | 0.78% |
| Sulfur | 0.19% |
| Chlorine | 0.08% |
Vitamins
| Vitamin E | 30 mg/g |
| Vitamin C | 14 mg/g |
| Vitamin B1 | 9 mg/g |
| Vitamin B2 | 11 mg/g |
| Vitamin B3 | 25 mg/g |
| Vitamin B6 | 3 mg/g |
Amino Acids (Whole Hempseed) (mg/g hempseed)
Components
| Protein | 22.5% |
| Carbohydrates | 35.8% |
| Fat | 30% |
| Moisture | 5.7% |
| Ash | 5.9% |
| Calories | 503 per 100 g |
| Dietary fiber (3.0% soluble) | 35.1% |
| Nitrogen-free extract | 40.59 |
Polysaccharides
| Carotene International Units/gram | 7.63 |
Other Active Naturally Occurring Ingredients
(Hempseed Oil average % Main Fatty Acids) (76.78% of the Total Fat-Oil)
| Linoleic (omega-6) | 54.0 |
| G-Linolenic (omega-6) | 1.68 |
| Linolenic (omega-3) | 21.1 |
More on Hempseed Oil
| Vitamin A | 19,140 IU/kg |
| Insoluble Matter | 0.01% |
| Chlorophyll | 6 ppm |
| Free Fatty Acids | 0.94% |
| Fat Stability AOM | 5 hours |
| Phosphatides | 0.03% |
| Unsaponified matter | 0.28% |
| Saponification Value | 192.8 |
| Melting point | (–8°C) |
| Flash Point | 141°C |
| Smoke Point | 165°C |
| Peroxide value | 7.0 meg/kg |
| Moisture | 19% |
| Specific Gravity | 0.9295 @20°C |
Fatty Acids in Hempseed Oil

Coconut meat, raw
Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz)
| Energy | 350 kcal |
| 1480 kJ | |
| Carbohydrates | 15.23 g |
| Sugars | 6.23 g |
| Dietary fiber | 9.0 g |
| Fat | 33.49 g |
| Saturated | 29.70 g |
| Monounsaturated | 1.43 g |
| Polyunsaturated | 0.37 g |
| Protein | 3.3 g |
| Thiamin (Vit. B1) | 0.066 mg 5% |
| Riboflavin (Vit. B2) | 0.02 mg 1% |
| Niacin (Vit. B3) | 0.54 mg 4% |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) | 0.300 mg 6% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.054 mg 4% |
| Folate (Vit. B9) | 26 mg 7% |
| Vitamin C | 3.3 mg 6% |
| Calcium | 14 mg 1% |
| Iron | 2.43 mg 19% |
| Magnesium | 32 mg 9% |
| Phosphorus | 113 mg 16% |
| Potassium | 356 mg 8% |
| Zinc | 1.1 mg 11% |
(Percentages are relative to U.S. recommendations for adults.)
Source: USDA Nutrient Database for Standard
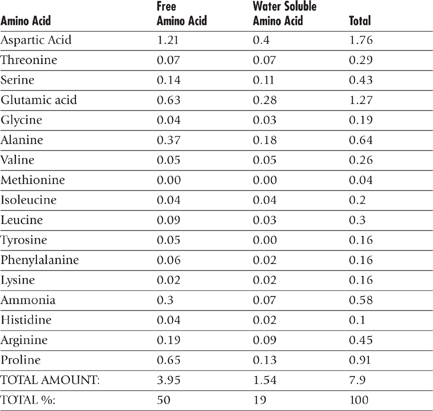
Amino Acid Content of Coconut Water
| Amino Acid | mg/100g | mg/cup |
| Tryptophan | 8 | 19 |
| Threonine | 26 | 62 |
| Isoleucine | 28 | 27 |
| Leucine | 53 | 127 |
| Lysine | 32 | 77 |
| Methionine | 13 | 31 |
| Cystine | 14 | 34 |
| Phenylalanine | 37 | 89 |
| Tyrosine | 22 | 53 |
| Valine | 44 | 106 |
| Arginine | 118 | 283 |
| Histidine | 17 | 41 |
| Alanine | 37 | 89 |
| Aspartic Acid | 70 | 168 |
| Glutamic Acid | 165 | 396 |
| Glycine | 34 | 82 |
| Proline | 30 | 72 |
| Serine | 37 | 89 |
| Source: USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard | ||
| Note: Coconut water contains 18 amino acids. Sports drinks contain none. | ||
Sugar Content in Juices
| Juice (1 cup) | Sugar (g) | Calories (kcal) |
| Coconut Water | 6.26 | 46 |
| Vegetable Cocktail | 7.99 | 46 |
| Tomato | 8.65 | 41 |
| Carrot | 9.23 | 94 |
| Grapefruit | 22.48 | 96 |
| Orange | 20.83 | 112 |
| Apple | 27.03 | 117 |
| Pineapple | 31.43 | 130 |
| Grape | 35.27 | 142 |
| Source: USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard | ||
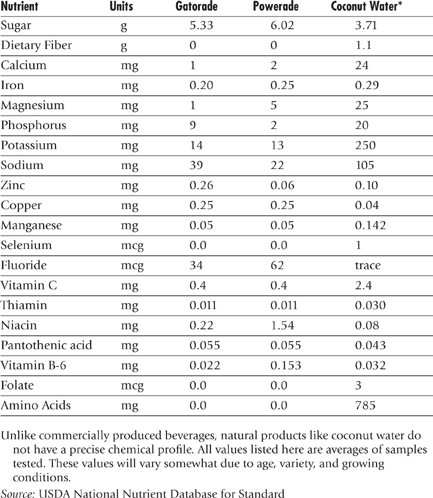
Nutrient Content in Gatorade, Powerade, and Coconut Water (Value per 100 grams)
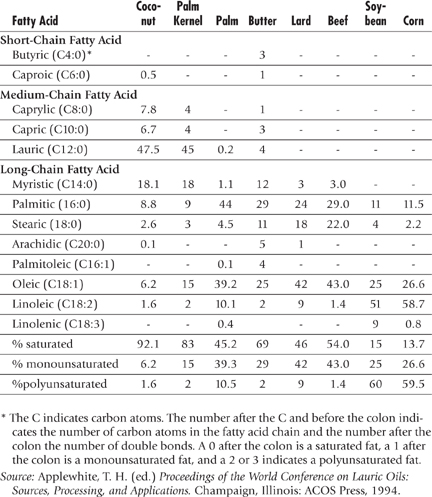
Fatty Acid Composition of Various Fats and Oils
Published medical studies show that MCFA’s in coconut oil kill bacteria, fungi, and other organisms that cause the following illnesses and conditions:
Bacterial Infections
Throat and sinus infections
Urinary tract infections
Pneumonia
Ear infections
Rheumatic fever
Dental cavities and gum disease
Food poisoning
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Gonorrhea
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Lymphogranuloma venereum
Conjunctivitis
Parrot fever
Gastric ulcers
Septicemia
Endocarditis
Enterocolitis
Viral Infections
Influenza
Measles
Herpes
Mononucleosis
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Hepatitis C
AIDS
SARS
Fungal Infections
Ringworm
Athlete’s Foot
Jock Itch
Candidiasis
Diaper Rash
Thrush
Toenail Fungus
Parasite Infections
Giardiasis
Medical research has identified a number of pathogenic organisms that are inactivated by medium-chain fatty acids in coconut oil. Below is a listing of some of the organisms reported in the medical literature.
Viruses
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
SARS coronavirus
Measles virus
Rubeola virus
Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1 and-2)
Herpes viridae
Sarcoma virus
Syncytial virus
Human lymphotropic virus (Type 1)
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)
Visna virus
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Epstein-Barr virus
Influenza virus
Leukema virus
Pneumonovirus
Hepatitis C virus
Coxsackie B4 virus
Bacteria
Listeria monocytogenes
Helicobacter pylori
Hemophilis influenza
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus agalactiae
Escherichia coli
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Acinetobacter aeruginosa
Acinetobacter baumannii
Neisseria
Chlamydia tracchomatis
Steptococci Groups A, B, F, & G
Gram-positive organisms
Gram-negative organisms
(if pretreated with chelator)
Parasites
Giardia
Ciliate protozoa
Studies show that coconut oil tempers or blocks the harmful effects of many toxins including the following:
Ethanol
MSG
N-nitrosomethylurea
Azoxymethane
Benzpyrene
Azaserine
Diamethylbenzanthracene
Dimethylhydrazine
Dimethynitrosamine
Methylmethanesulfonate
Tetracycline
Streptococci endotoxin/exotoxin
Staphylococci endotoxin/exotoxin
E. coli endotoxin
Aflatoxin
Sources
Fife, B. Coconut Cures. Colorado Springs, CO: Piccadilly Books, 2005.
———. Coconut Water. Colorado Springs, CO: Piccadilly Books, 2008.