Chapter 17
Practice Exam 1: Answers and Explanations
After taking Practice Exam 1 in Chapter 16, use this chapter to check your answers and see how you did. Carefully review the explanations because doing so can help you understand why you missed the questions you did and also give you a better understanding of the thought process that helped you select the correct answers. If you’re in a hurry, flip to the end of the chapter for an abbreviated answer key.
Analytical Writing Sections
Have a friend read your essays: Refer that helpful person to Chapters 14 and 15 for scoring guidelines, and if the essays are clear, persuasive, and grammatically sound, you probably got it.
Section 1: Verbal Reasoning
- C. Corporate leaders would try to obfuscate (conceal) their intentions in order to maintain a competitive advantage. Occlude makes a good runner-up, but it carries a meaning more along the lines of blocking off access to something. None of the other three choices is close: Stipulate means to demand something specific, preclude means to prevent or prohibit, and abjure means to avoid or reject.
- E. Hubris is excessive pride or self-confidence, which is often characterized by a refusal to consider any criticism, as expressed in the opening phrase of the sentence. If it weren’t for that qualifier, any of the other answer choices would work: miscalculations can undermine a leader’s plans, ambivalence is uncertainty or indecisiveness, perfidy is treachery, and ineptitude is incompetence.
- B, F. The judge must have excoriated (severely criticized) the prosecutor in order for him to be despondent, and that despondency likely led to the defendant’s exoneration (acquittal), because the despondent prosecutor would be less effective. Otherwise, you could make a case for exoneration for the first blank and conviction for the second. Adjudication (a court order) is a legal term, but a judge doesn’t adjudicate a person, and a deposition is done by a witness, not a defendant.
- B, F. The report would have been gleaned (gathered) from internal documents, not coerced (gotten by force) or redacted (put into a suitable literary form). A company network is typically secure, so the transition “in fact” tells you that’s not the case and therefore not impregnable (able to withstand attack). Vulnerable would imply that security was stronger than IT had thought. Implacable means unable to be satisfied or appeased.
-
B, D, I. The second sentence references a democracy in early development, so it must be a nascent (emerging) democracy that would need to be built on certain precepts (principles or guidelines) in order to be strong. Otherwise, the government would be prone (disposed to) to evolving into a dictatorship.
For the first blank, you can rule out well-established, which is the opposite of nascent, and representative, which is just a type of democracy (direct or representative). For the second blank, both criteria and precedents would be good second choices, but because the second sentence mentions the right to vote and the rule of law, precepts is more accurate. For the third blank, you can rule out dedicated, because no democracy dedicates itself to becoming a dictatorship. You can rule out resolute (determined) for much the same reason.
- B, D, I. The reflection in a curved mirror would be an aberration (an abnormality), not a vacillation (wavering) or translucence (semi-transparency), so the reflection in the mirror would be a distortion (misrepresentation). For the second blank, divergence (deviation or departure) would be a good second choice, but distortion is more precise. Detraction (disparagement or denigration) doesn’t work. Some people find such a distorted reflection of themselves discomfiting (unsettling). Debilitating (incapacitating) is too strong a word, and humorous doesn’t work, because the last sentence is structured in a way that the missing word must be nearly the opposite of amusing.
- C. You may be tempted to select the last sentence because it presents a summary of the data, but the main conclusion in this passage is that fathers spend considerably less time with their children than do mothers.
- B, D, E. The paragraph defines paternal responsibility as “participation in key decisions, availability at short notice, involvement in the care of sick children, management and selection of alternative child care.” Choice (D), food, clothing, and housing, may be considered “key decisions” as a stretch; Choice (B), reading, and Choice (E), playing a game, may be considered involvement, but the other choices clearly fall under the paragraph definition of paternal responsibility.
- A, B. The passage focuses on two-parent families in which mothers are unemployed and only mentions “the small subgroup of fathers who assume high degrees of responsibility.” It doesn’t provide data related to single-parent families or two-parent families in which the father stays home with the children.
- A, C. Researchers did not include mention of financial support as a measure of parental responsibility, so you can rule out answer Choice (B). Engagement, accessibility, availability at short notice, and the care of sick children are all mentioned as measures of parental responsibility.
- C. Vertiginous means spinning, whirling — movement that would cause someone to become dizzy. Because this passage describes the variety of literature as overwhelming, in both positive and negative ways, the variety of authors and countries is considered vertiginous. You can immediately rule out the first two options, which both mean something along the lines of believable. Although literature may be enlightening (informative) and edifying (intellectually enriching), the variety of authors and countries would probably not be considered enlightening or edifying in this context.
- B, C. Gao Xingjian is mentioned as a French citizen who continues to write in Chinese, while Tashi Dawa blends elements drawn from Tibetan folklore and international magical realism for his writings in Chinese. This question is a little tricky, because cultural hybridity isn’t mentioned until the second example of it is presented. Choice (A) is wrong because in this passage, cultural hybridity refers to the blending of cultures within a literary work, not the exchange of literary works between countries or cultures, although such exchanges no doubt promote cultural hybridity in literature.
- C. The fact that a character-impact compound can be associated with a particular smell would help, not hinder, the ability to associate an odor with a specific volatile compound.
- B. All of the answer choices are definitions of volatile, but because the passage discusses molecules being distributed through the air, evaporating rapidly is the most accurate meaning.
- D. The first bolded portion states the conclusion that heavy farm equipment compacts the soil, and the second bolded portion concludes that farmers must employ various strategies to reduce soil compaction. You can rule out Choice (A) because although the first states a conclusion, the second doesn’t provide supporting evidence. Rule out Choice (B) because although the first states a problem, the second describes a possible solution to the problem, not the effects of that problem. Rule out Choices (C) and (E) because the second bolded portion doesn’t oppose or counter the first.
- E. This argument assumes that other states operate the same way as California. Choice (E) states, however, that other states divert monies from schools, which means that the lottery money does not actually increase revenue for education: Any money coming in from the lottery would be diverted right out. Choices (A) and (C) are out of scope, while Choice (B) supports the argument, and (D) simply states that lottery funding represents a small portion of the total education budget in a state.
- A, C. The victor was exhausted, but the transition “though” tells you that he showed the opposite during his speech: vivacious (energetic) and ebullient (enthusiastic). You can easily rule out lugubrious, which means sad or gloomy; laconic, which means terse or concise, and mendacious and disingenuous, both meaning dishonest.
- C, F. The deeds described here would be fake — counterfeit or spurious. Extenuated means severe and explained, as in extenuating circumstance, inadvertent means unintentional, and exculpated means freed from blame. Pilfered means stolen, but there is no other answer choice with a similar meaning, and anyway, filing a stolen deed wouldn’t help the con artist transfer ownership of the property — it would have the true owner’s name on it.
- B, E. Think of something broadcast that can be harmful to young viewers but cannot be easily regulated. Because Turpitude and depravity both mean immorality, and the passage focuses on indecent programming, these two choices are best. Truculence and impertinence both imply disrespectful behavior, but these are not particularly harmful to youth. Asperity, which means harshness or sternness, has no choice comparable in meaning. Choice (D), infidelity, is tempting, but the answer choices don’t contain a word similar in meaning.
- B, C. If the speaker exceeded her allotted time, she must have been loquacious or voluble, which both imply long-winded. She may have also been eloquent and articulate (well-spoken), but these wouldn’t necessarily cause her to exceed her allotted speaking time. Vivacious means lively or energetic, and voluminous means large, neither of which has a comparable word in the list of answer choices and neither of which would necessarily cause the keynote speaker to run past her allotted time.
Section 2: Quantitative Reasoning
- B. Take it step by step.
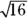 becomes 4, and the one-half power is a square root, so
becomes 4, and the one-half power is a square root, so 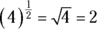
-
C. You find the probability of an event (selecting one grape candy from the first bowl) by putting the number of possibilities (three grape candies) over the total number of outcomes (five candies total). Thus, the probability of selecting a grape candy from the first bowl is
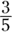 . Similarly, the probability of selecting a grape candy from the second bowl is
. Similarly, the probability of selecting a grape candy from the second bowl is 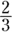 .
.The probability of two independent events occurring together (selecting a grape candy each from the first and second bowls) is the product of the first probability and the second probability:
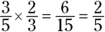
-
5. The units digit is the digit in the ones place, just before where the decimal point would be. For example, in the number 123, the units digit is 3. When you’re multiplying two whole numbers, the units digits of the multipliers produce the units digit of the product. So when you multiply
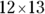 , for example, the 2 in 12 times the 3 in 13 produces the 6 in the product, 156.
, for example, the 2 in 12 times the 3 in 13 produces the 6 in the product, 156.For this question, 5 times itself any number of times results in a product with a units digit of 5:
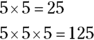
and so on.
- 3. First, determine the value at the top of the fraction (the numerator): Multiply the
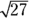 by the
by the 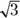 for the
for the 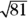 , which equals 9. Determining the value at the bottom of the fraction (the denominator) is easy, because the square root of 9 is 3. Divide the numerator by the denominator for the correct answer:
, which equals 9. Determining the value at the bottom of the fraction (the denominator) is easy, because the square root of 9 is 3. Divide the numerator by the denominator for the correct answer:
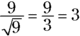
- B. To determine Quantity A, calculate the average parcel weight by totaling the weight of the parcels and then dividing the total weight by the number of parcels. You can use the following equation for weighted average:
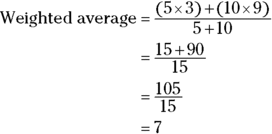
Quantity A is 7 pounds, which is 1 pound less than Quantity B’s 8 pounds, so Quantity B is greater.
- A. To determine Quantity A, simplify the exponents and the fraction. To simplify each negative exponent, place a 1 on top:
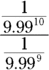
To divide the fractions, flip the bottom fraction and multiply it by the top fraction:
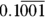
You simplify the resulting fraction with the on-screen calculator;
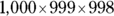 is slightly greater than 0.1, so Quantity A is greater.
is slightly greater than 0.1, so Quantity A is greater. - B. Simplify the quantities so that A reads
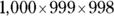
and B reads
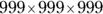
These products are still too big for the on-screen calculator. To resolve this, eliminate one 999 from each quantity so that A reads
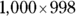
and B reads
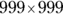
Using the on-screen calculator, find the resulting values as 998,000 and 998,001. You see that Quantity B is greater.
- B.
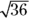 equals 6, so
equals 6, so 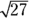 is less than 6.
is less than 6. - D. Given
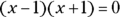 , x equals either 1 or –1. You don’t know which one, so you can’t determine which quantity is greater based on the information given.
, x equals either 1 or –1. You don’t know which one, so you can’t determine which quantity is greater based on the information given. - C. If the angle CAB measures
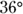 , minor arc BC also measures
, minor arc BC also measures 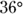 , making it one tenth of the circle:
, making it one tenth of the circle:
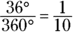
A circle with a radius of 5 has a circumference of
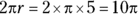 . Multiply this circumference by the fraction of the circle, giving you a minor arc length of
. Multiply this circumference by the fraction of the circle, giving you a minor arc length of 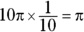 . Therefore, the two values are equal.
. Therefore, the two values are equal. - C. You can find the area of a trapezoid with the formula
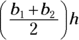
where
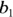 represents one base,
represents one base, 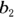 represents the other base, and h represents the height. To find the height, set the formula equal to the area and simplify it:
represents the other base, and h represents the height. To find the height, set the formula equal to the area and simplify it: 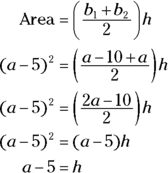
Therefore, the two quantities are equal.
- 24. If total sales are $150,000 and Humboldt County spent $36,000, you can find the percent by placing the Humboldt County sales over the total sales:
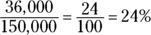
You can’t type the percent symbol into the answer box. Because the percent symbol is already in place and the question asks for the percent, the correct answer is 24, not 0.24.
- E. You can compare the box prices of each brand by estimating the ratio of sales dollars to units sold. The higher the ratio, the higher the brand’s average selling price. Sugar Choc has the highest ratio of dollar sales to units sold, making it the highest-priced brand of cereal.
-
D. Though actual numbers aren’t provided, you can use the bar graph to approximate the ratios. Because the question asks for an “approximate” answer and the answer choices are far apart, you can eyeball your numbers from the graphs.
Lucky Shapes and Sugar Choc show similar numbers of units sold, but the Lucky Shapes sales number in Glenn County, at $9,000, is about one third that of Sugar Choc in Trinity County, at $27,000. This means, box for box, the price of Lucky Shapes is approximately one third that of Sugar Choc, for a ratio of 1:3.
- 2. Reduce the exponents by converting
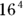 to
to 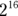 :
:
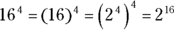
Now reduce the fraction by subtracting the exponents:
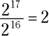
- B. Set up the equation and substitute 5 for y:
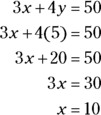
- D. Suppose
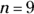 . You’re looking for
. You’re looking for 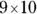 , which is the same as
, which is the same as 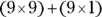 , or
, or 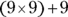 . Substitute n for 9, and you have
. Substitute n for 9, and you have 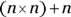 , or
, or 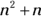 .
. - E. You’re given the number of kilometers per hour, and you need to determine the number of meters per second, so focus on the units of measurement: 25 kilometers is 25,000 meters, and 1 hour is 60 minutes times 60 seconds, or 3,600 seconds. You know that the sled is travelling 25,000 kilometers per 3,600 seconds for 18 seconds. Once you set it up, the math is simple:
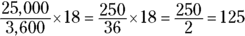
-
C. First, identify the unknown. You know that you end up with 15 liters of a solution, but you don’t know what its saline concentration is, so you have 15 liters of x.
Ten liters of 6 percent solution plus 5 liters of 9 percent solution gives you 15 liters of x, so set up the equation and simplify:
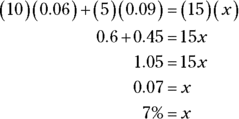
- A, B. Don’t let the circle with the dot confound you. The question indicates that its value is
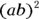 . However, because
. However, because 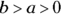 and they’re both integers, a is always at least 1 less than b. If b is 4, a can’t be more than 3, and so forth. So try the possibilities, and the highest a and b can be is 2 and 3, because
and they’re both integers, a is always at least 1 less than b. If b is 4, a can’t be more than 3, and so forth. So try the possibilities, and the highest a and b can be is 2 and 3, because 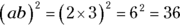 . Also, a and b can be 1 and 2, making
. Also, a and b can be 1 and 2, making 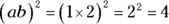 . However, 3 and 4 don’t work, because
. However, 3 and 4 don’t work, because 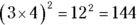 . Therefore a can only be 1 or 2, but not 3 or higher. So try the possibilities, and a can be 1 or 2, because
. Therefore a can only be 1 or 2, but not 3 or higher. So try the possibilities, and a can be 1 or 2, because 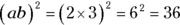 , but 3 doesn’t work because
, but 3 doesn’t work because 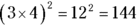 .
.
Section 3: Verbal Reasoning
- C. Ubiquitous means existing everywhere, which among conservation-minded commuters is what the electric car is likely to become. Inaccessible and scarce convey nearly the opposite meaning. Electric cars can’t really be considered indispensable, because commuters have been just fine without them. Salubrious doesn’t fit, because it means conducive to good health.
- A. Taciturn means aloof or uncommunicative, which describes the lecturer who leaves without checking with his audience for questions. Effusive means outwardly enthusiastic, so you can immediately rule out Choice (B). Indignant means outraged or annoyed, but there’s no mention of this. Despondent means depressed or dejected, which could work, but the passage contains nothing to indicate that he was depressed. And malevolent would indicate that the lecturer was dangerous, which also isn’t mentioned in the text.
- C, E. Epigenetics is the study of changes in gene activity that can be passed down to future generations. To some degree, it repudiates (rejects) Darwin’s theory of evolution because a gene’s expression can change; genes are not immutable (unchangeable). For the first blank, obviates (takes steps to render something unnecessary) doesn’t work, nor does expatiates, which would imply that epigenetics elaborates on Darwin’s theory of evolution. For the second blank, imperturbable would be a good second choice, but it means something more along the lines of being calm, cool, and collected. Inimitable (incomparable) just doesn’t fit.
- B, D. Financial experts are often depicted as being prudent (fiscally cautious), but when it comes to investing, they become the opposite — audacious (bold, daring). You can rule out dissident (rebellious) and confident based on the meaning of the second sentence — the word however indicates that the quality mentioned in the first sentence will be opposite of the quality in the second sentence. The opposite of prudent makes these individuals audacious (aggressive) when investing, not pusillanimous (timid) or aloof (standoffish).
- B, F. With a paucity (too little) of livestock and a surfeit (too much) of corn, farmers would be more likely to market their corn for use in biofuel production instead of using it as feed. For the first blank, the other choices — plethora and overabundance — mean the opposite of paucity. For the second blank, the other choices — dearth and scarcity — are the opposite of surfeit.
- C, F, G. The nature of the situation must have been involute (complex) to require input from trenchant (clever) advisors so that the CEO could make sagacious (shrewd) decisions. By starting at the end of the passage, you know that the decisions needed to be wise and not salacious (obscene) or sententious (self-righteous). Conscientious or confidential advisors wouldn’t be the best qualified to advise the CEO on making wise decisions; they’d be better in situations that were delicate or sensitive in nature and that probably wouldn’t lead to greatly improving the company’s market share.
- C, D, H. If teachers are claiming that charter schools have an unfair advantage, they must be critical of charter schools, so they would deprecate (express disapproval of) them, not extoll (praise) or advocate (speak or write in favor of) them. For the second blank, if charter schools have the power to set very selective admissions standards, they must be unencumbered (free of) Department of Education policies, not hampered or constrained, which both mean constricted or limited by. And given that they’re unencumbered by Department of Education policies, they must be free to forge their own policies. Disallow means prohibited, which is opposite of the meaning this blank calls for, and correlate means to arrange in some orderly fashion, which doesn’t quite fit.
- B. Schumacher classifies energy sources as two categories: capital, which is available in limited quantities, and income, which is clean and renewable. Hydroelectricity is the only answer choice that represents a renewable energy source. All the other energy sources (heating oil, natural gas, uranium, and coal) are nonrenewable.
- A, C. In the first sentence of the passage, Schumacher scorns the idea that problems in the industrialized world had been solved. Near the end of the passage, the author mentions that Schumacher’s message was derided by the majority of people. Derided and scorned are synonymous.
- C. The only specific human activity that’s described is the use of coal, oil, and gas. You may be tempted to choose (E), which mentions “we have started to distinguish … and to invest,” but that phrase is not as specific as the use of natural resources.
- B. This passage is primarily about the need to establish and enforce sound financial policies. You can rule out Choice (A) because the passage doesn’t mention the need to pay off debt; in fact, it mentions the possibility of defaulting on debt. Choices (C), (D), and (E) are all specific problems that occur when sound financial policies are not in place or not enforced; they serve as evidence to support the author’s main point in the passage, but they are not the main point.
- D. Moribund means declining or not progressing, stagnant. Robust and stout carry the opposite meaning and would be used to describe a healthy economy. The economy described in the passage is still a working economy, so it can’t be extinct (nonexistent) or dead (kaput).
- A, B. The passage states that the 2008 EESA/TARP bill failed to cure bad lending decisions by banks, Choice (A), and that Dodd-Frank failed to force transparency on derivatives, Choice (B). States of the economy and employment are results, not contributors, of the economic crisis.
- E. The main point of this passage is that the United States can expand its influence in the world by building trust. The passage does imply that humanitarian aid is more effective than military might in improving how the world views the United States (Choice [A]), but this is only one example of how to build trust — it’s supporting evidence, not the main point. You can rule out Choice (B) because the passage doesn’t mention the United States using its military and economic power for anything evil. You can also rule out Choice (D) because it’s not mentioned in the passage. Choice (C) represents an assumption on which the main point of the article is based, but it’s not the main point.
- C. Choice (C) points out that the Iraq War removed the corrupt Iraqi president from power. Political corruption is second on the list of concerns from citizens around the world, as stated in the first paragraph. Choices (A) and (B) are examples of United States’ initiatives developed to help other countries pursue their interests. The passage doesn’t state that the United States doesn’t have such programs in place, so these choices don’t challenge a claim made in the passage. Choice (D) is irrelevant. Choice (E) suggests that the United States serves its own internal interests while reaching out to help other countries.
- D. One of the costs of the failure to treat mental illness is the $9 billion annually to house those with mental illness in the prison system. If you chose the sentence immediately after the question, you fell for a common trap. Although that sentence answers the question, it doesn’t offer evidence — specific data or an example — to support the question.
- B, E. If the violence were counterproductive, then politicians from both parties would encourage their constituents to avoid or eschew violence, which carry nearly the same meaning. Embrace, appropriate, and incite would actually promote violence, which isn’t something politicians would encourage if it were counterproductive. Denounce means to condemn, which sort of works in the sentence, but none of the other answer choices conveys a similar meaning.
- C, D. Calculating the cubic volume of a meal before partaking in it would be a quirk or idiosyncrasy. Passions and obsessions make a fairly good pairing, but the behavior being described isn’t ordinary, so these two choices aren’t the best. Likewise, calculating the cubic volume of a meal may be considered an endowment (talent), but idiosyncrasies and quirks are more fitting choices; besides, none of the other answer choices is similar in meaning to endowment. Assimilation means the acquisition of something, such as a cultural trait; again, this isn’t the best choice, and it has no synonym in the answer choices.
- B, E. The second and third sentences express the pivotal nature of the career choice — you can envision an arrow turning around a pivot point depending on which career choice is made. The closest match to pivotal is paramount, which means “of great importance.” Choices (A), (C), and (D) would make good pairings but mean the opposite of pivotal and paramount. The meaning of urgent, Choice (F), is more in line with pivotal and paramount but conveys more of a sense of requiring immediate action.
- B. The definition of domestication in this passage is activity that “results in genetic change brought about through conscious or unconscious human selection,” meaning certain specimens are selected and bred for their characteristics. Farm-raised catfish is an example of cultivation, but the individual catfish are not selected for their characteristics.
Section 4: Quantitative Reasoning
- D. First convert the
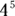 into
into 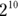 . Then simplify the fraction by subtracting the exponents:
. Then simplify the fraction by subtracting the exponents:
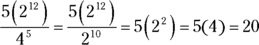
-
C. Factor the
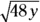 into
into 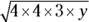 . The lowest possible value of y is 3, because in order for the square root of 48y to be an integer, the factors inside the square root must form numbers squared — you have one
. The lowest possible value of y is 3, because in order for the square root of 48y to be an integer, the factors inside the square root must form numbers squared — you have one 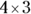 , and you need to multiply it by another
, and you need to multiply it by another 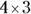 to square it.
to square it.You could also plug in the answer choices, starting with the lowest value and working your way up:
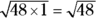 , which isn’t an integer.
, which isn’t an integer. 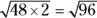 , which isn’t an integer.
, which isn’t an integer. 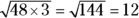 , which is an integer. Factoring is faster though.
, which is an integer. Factoring is faster though. -
A, C, D, E.
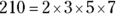 , so n could be any product of 2, 3, 5, and 7, as long as any factor is used only once. 12 is wrong, because it uses the factor 2 twice.
, so n could be any product of 2, 3, 5, and 7, as long as any factor is used only once. 12 is wrong, because it uses the factor 2 twice.You could also solve this one by plugging in answer choices, but that’s a lot of math.
- C. Regardless of the distribution, no child will receive six candies. After giving each child two candies, three candies are left over. If these are given to one child, he will have a total of five.
- A. You can find the average speed by placing the entire distance over the entire time. If Davis travels at 40 miles per hour for two hours, he travels 80 miles during that time. Combine this with 60 miles for one hour for a total of 140 miles in three hours:
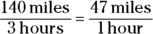
- C. Simplify the radical:
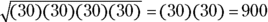
- D. Given that
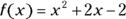 and
and 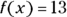 , set up and simplify the equation with 13 as the
, set up and simplify the equation with 13 as the 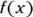 :
:
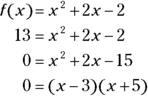
Therefore,
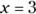 or –5, but you don’t know which one, so Quantity A could be either equal to or less than Quantity B. Because you don’t know, go with Choice (D).
or –5, but you don’t know which one, so Quantity A could be either equal to or less than Quantity B. Because you don’t know, go with Choice (D). - B. Any number between zero and one becomes smaller when multiplied by itself. For example,
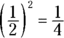
Each time you multiply 0.99 by itself, the quantity becomes smaller and remains less than 1.
- C. Simplify the factorial expressions:
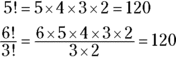
- B. You can find the volume of a right circular cylinder with
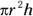 , where r is the radius and h is the height. If r and h are integers, the only way the volume can be
, where r is the radius and h is the height. If r and h are integers, the only way the volume can be 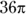 is if r is 3 and h is 4, with a sum of 7, or r is 2 and h is 9, with a sum of 11. Either way, the sum is less than 12.
is if r is 3 and h is 4, with a sum of 7, or r is 2 and h is 9, with a sum of 11. Either way, the sum is less than 12. - A. The question asks for an “approximate” ratio, so eyeball the graph and compare the bars. The C bar is half the B bar, making the ratio 1:2.
- C. If the 211 Creede students are earning A’s, the remaining 894 students are earning all the other grades. Looking at the bar chart, the B bar is the length of the C, D, and F bars put together. This means that about half the remaining students are earning B’s. Bayfield has 306 students, so approximately half that is 150.
-
C. From the bar chart, about
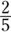 of the grades are B grades, so about
of the grades are B grades, so about 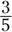 are the other grades. De Beque has 115 students, and the only answer choice that’s about
are the other grades. De Beque has 115 students, and the only answer choice that’s about 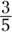 of that is 70.
of that is 70.An approximate estimate is usually good enough for these questions. The answer 70 isn’t really close to the other answers, so if you eyeball the graph differently, you’ll still get the right answer.
-
A, C. The range is the difference between the lowest and highest numbers. If the range of set S is 9 and none of the given numbers are 9 apart, x has to be either 0 or 11.
The median is the middle number of the set. If x is 0, the median is 5; if x is 11, the median is 7.
-
0. The correct answer is 0.
The trap here is doing a lot of extra math work. Drop the parentheses to avoid this trap:
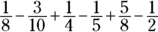
Now give the fractions common denominators of either 8 or 10:
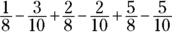
The
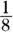 ,
, 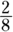 , and
, and 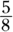 add up to 1, and the
add up to 1, and the 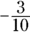 ,
, 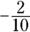 , and
, and 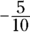 add up to –1. The sum, therefore, equals 0.
add up to –1. The sum, therefore, equals 0.Note that there are other ways to simplify the fractions. On the GRE, especially with fractions, you’re looking for ways to cancel and simplify.
-
36. The correct answer is 36.
Combine
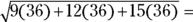 into
into 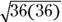 , which equals 36.
, which equals 36. - C, D, E. If
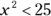 , x is either less than 5 or greater than –5, which you can write as
, x is either less than 5 or greater than –5, which you can write as
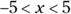
the value x cannot be equal to 5 or –5. It’s greater than –5 and less than 5, so from the list of answer choices, x could be equal to –3, 0, or 3.
- B. First find the area of the square:
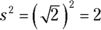
For the area of the circle, you need its radius. Cut the square in half, corner to corner, to form two 45-45-90 triangles, where each hypotenuse is the diameter of the circle. If the side of this triangle is
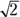 , the hypotenuse is 2, because in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is the sum of the squares of the other two sides:
, the hypotenuse is 2, because in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is the sum of the squares of the other two sides: 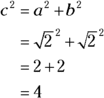
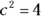 , so
, so 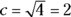 is the circumference of the circle, and the radius of the circle is half the diameter, or 1. Now for the area of the circle:
is the circumference of the circle, and the radius of the circle is half the diameter, or 1. Now for the area of the circle: 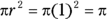
Subtract the area of the square from the area of the circle for your answer:
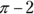
- 21. For the area of a triangle, multiply the base by the height and divide by 2. The base of this triangle is 7 and the height is 6, for an area of 21. The 2 in the drawing has no bearing.
- A, B, C, E, F. $600 is
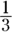 of $1,800 and
of $1,800 and 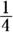 of $2,400. This means that Clarissa’s monthly income is greater than $1,800 and less than $2,400. Multiply these values by 12 for an annual income greater than $21,600 and less than $28,800. Note that her income can’t equal these amounts: It’s greater than the lower number and less than the higher number. Common trap: missing the word “not” in the question.
of $2,400. This means that Clarissa’s monthly income is greater than $1,800 and less than $2,400. Multiply these values by 12 for an annual income greater than $21,600 and less than $28,800. Note that her income can’t equal these amounts: It’s greater than the lower number and less than the higher number. Common trap: missing the word “not” in the question.
Answer Key for Practice Exam 1
Section 1: Verbal Reasoning
- C
- E
- B, F
- B, F
- B, D, I
- B, D, I
- C
- B, D, E
- A, B
- A, C
- C
- B, C
- C
- B
- D
- E
- A, C
- C, F
- B, E
- B, C
Section 2: Quantitative Reasoning
- B
- C
- 5
- 3
- B
- A
- B
- B
- D
- C
- C
- 24
- E
- D
- 2
- B
- D
- E
- C
- A, B
Section 3: Verbal Reasoning
- C
- A
- C, E
- B, D
- B, F
- C, F, G
- C, D, H
- B
- A, C
- C
- B
- D
- A, B
- E
- C
- D
- B, E
- C, D
- B, E
- B
Section 4: Quantitative Reasoning
- D
- C
- A, C, D, E
- C
- A
- C
- D
- B
- C
- B
- A
- C
- C
- A, C
- 0
- 36
- C, D, E
- B
- 21
- A, B, C, E, F