INDEX
B-smooth number
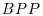
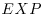
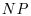
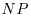 -complete
-complete
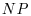 -hard
-hard
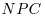
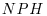
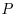
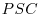
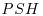
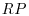
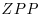
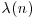
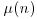
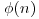
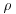 -factoring method
-factoring method
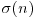
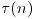
b-sequence
kth (higher) power nonresidue
kth (higher) power residue
kth power nonresidue
kth power residue
n−1 primality test
p−1 factoring algorithm
A
additive group
additive identity
additive inverse
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
affine transformation
AKS algorithm
AKS primality test
algebraic computation law
algebraic equation
algebraic integer
algebraic number
almostfield
anomalous curve
arithmetic function
arithmetic progression of consecutive primes
arithmetic progression of prime numberss
associativity
asymmetric key cryptography
authentication
authorization
B
baby-step giant-step algorithm
biological (DNA) cryptography
Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture
blinding attack
block cipher
BSD conjecture
C
Caesar cipher
Carmichael’s 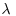 -function
-function
Carmichael’s theorem
CFRAC factoring algorithm
CFRAC method
character cipher
Chinese Remainder theorem (CRT)
chosen plaintext attack
chosen-ciphertext attack
chosen-plaintext attack
Church–Turing thesis
ciphers
ciphertext
ciphertext-only attack
closure
coding-based cryptography
coin-tossing states
common modulus attack
common multiple
commutative group
commutative ring
commutativity
complete system of residues
completely multiplicative function
complexity theory
composite number
composite numbers
computability theory
computation theory
computational number theory
computationally infeasible
computationally secure
conditionally unbreakable
confidentiality
congruence
congruence classes
congruent
conic
conjectured intractable problems
consecutive pairs of quadratic residues
consecutive triples of quadratic residues
Continued FRACtion (CFRAC) method
continued fraction algorithm
convergent
convergents
Converse of the Fermat little theorem
Converse of Wilson’s theorem
Cook–Karp thesis
cryptanalysis
cryptanalytic attacks
cryptographic system
cryptography
cryptology
cryptosystem
cubic Diophantine equation
cubic integer
cyclic group
D
Data Encryption Standard (DES)
decryption
degree of polynomial
deterministic cryptosystem
deterministic encryption
DHM assumption
Diffie-Hellman-Merkle key-exchange (DHM)
digital signature algorithm (DSA)
Digital Signature Standard (DSS)
digital signature system
digital signatures
Diophantine geometry
discrete logarithm
Discrete Logarithm Problem (DLP)
Disquisitiones Arithmeticae
dividend
division algorithm
division ring
divisor
DNA-based biological computation
domain
double encryption
E
ECC challenge problems
ECDLP assumption
ECM (Elliptic Curve Factoring Method)
ECPP (elliptic curve primality proving)
elementary attacks on RSA
ElGamal cryptography
ElGamal signature scheme
elite class
elliptic curve
elliptic curve cryptography (ECC)
Elliptic Curve DHM
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA)
Elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem (ECDLP)
Elliptic Curve ElGamal
Elliptic Curve Massey–Omura
elliptic curve primality tests
Elliptic Curve RSA
elliptic curves
elliptic function
elliptic integral
embedding messages on elliptic curves
encryption
equivalence classes
equivalence relation
Euclid
Euclid’s algorithm
Euler’s (totient) 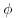 -function
-function
Euler’s criterion
Euler’s theorem
even number
exclusive or (XOR)
exponential-time algorithm
extended Euclid’s algorithm
F
factor
factoring by trial divisions
feasibility/infeasibility theory
Federal Information Processing Standard
Fermat’s little theorem
field
finite fields
finite group
finite order of a point on an elliptic curve
finite simple continued fraction
FIPS
FIPS
FIPS
FIPS
fixed-point
fixed-point attack
forward search attack
Function Field Sieve (FFS)
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
G
Galois field
Gauss’s lemma
Gaussian integer
Gaussian prime
general purpose factoring algorithms
geometric composition law
GNFS (General Number Field Sieve)
greatest common divisor (gcd)
Gross–Zagier theorem
group
group laws on elliptic curves
guessing d attack
guessing plaintext M attack
guessing plaintext attack
H
Heegner points
height
high-order congruence
Hill n-cipher
Hill cipher
I
identity
IFP-based cryptography
incongruent
index calculus for DLP
index of a to the base g
index of an integer modulo n
infinite fields
infinite group
infinite order of a point on an elliptic curve
infinite simple continued fraction
information-theoretic security
Integer Factorization Problem (IFP)
integral domain
integrity
inverse
invertible function
irrational numbers
irreducible polynomial
J
Jacobi symbol
K
Kerckhoff principle
key bundle
known-plaintext attack
Knuth’s Factoring Challenge Problem
L
lattice-based cryptography
least common multiple (lcm)
least non-negative residue
least residue
Legendre symbol
Legendre, A. M.
Lehman’s method
Lenstra’s Elliptic Curve Method (ECM)
linear congruence
linear Diophantine equation
logarithms
M
Möbius 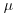 -function
-function
Möbius inversion formula
Massey-Omura cryptography
mathematical cryptography
McEliece’s coding-based cryptography
Menezes–Vanstone ECC
Mersenne primes
message digest
Miller-Rabin test
Miller–Rabin test
Miller–Selfridge–Rabin test
minimal polynomial
modern cryptography
modular inverse
Modular Polynomial Root Finding Problem (MPRFP)
modulus
monic
monographic cipher
MPRFP
multiple
multiple encryption
Multiple Polynomial Quadratic Sieve (MPQS)
multiplicative function
multiplicative group
multiplicative identity
multiplicative inverse
N
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
non-secret encryption
nonrepudiation
nonsingular curve
nonsingular elliptic curve
nontrivial divisor
nontrivial square root of
nonwitness
nonzero field element
norm
NTRU cryptosystem
Number Field Sieve (NFS)
number theory
number-theoretic cryptography
O
odd number
one-time pad (OTP)
one-way function
Order Finding Problem (OFP)
order of a modulo n
order of a field
order of a group
order of a point on an elliptic curve
order of an element a in group g
order of an element x modulo n
P
padding process
partial quotients
perfect secrecy
perfect square
period
periodic simple continued fraction
plaintext
Pocklington’s theorem
Pohlig–Hellman cryptosystem
point at infinity
polarization
Pollard’s 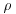 factoring algorithm
factoring algorithm
Pollard’s 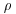 Method
Method
polygraphic cipher
polynomial
polynomial congruence
polynomial congruential equation
polynomial security
polynomial-time algorithm
polynomial-time computable
polynomial-time equivalent
polynomial-time reducible
polynomially secure
positive integers
post-quantum cryptography
powerful number
practical secure
practical/conjectured secure
Pratt’s primality proving
presumably intractable problems
Primality test based on order of integers
Primality test based on primitive roots
Primality test by trial divisions
Primality Test Problem (PTP)
Primality Testing Problem (PTP)
prime factor
Prime Factorization Problem (PFP)
prime field
prime number
Prime Number theorem
prime numbers
prime power
primitive root of n
privacy
private key
probabilistic encryption
probabilistic Turing machine (PTM)
proper divisor
provable intractable problems
provably secure
pseudofield
public key
public-key cryptography
public-key cryptosystem
purely periodic simple continued fraction
Q
quadratic congruence
quadratic integer
quadratic irrational
quadratic non-residue
Quadratic reciprocity law
quadratic residue
quadratic residuosity based cryptosystem
Quadratic Residuosity Problem (QRP)
Quadratic Sieve (QS)
quantum algorithm for discrete logarithms
quantum algorithm for integer factorization
quantum algorithms for elliptic curve discrete logarithms
quantum computational number theory
quantum cryptographic protocol
quantum cryptography
quantum factoring attack
Quantum Integer Factorization
quantum order finding
quantum order finding attack
quantum register
quantum resistant cryptography
qubit
quotient
R
Rabin cryptosystem
Rabin’s M2 encryption
randomized cryptosystem
randomized encryption
randomized Turing machine (RTM)
rank of an elliptic curve
rank of elliptic curve
rational integer
rational integers
rational line
rational number
rational numbers
rational point
rational prime
real base logarithm
real number
real-valued function
rectilinear polarization
reduced system of residues modulo n
reflexive
relatively prime
remainder
Repeated Doubling Method
residue
residue class
residue classes
residue of x modulo n
RFP
Riemann hypothesis
ring
ring with identity
Rivest’s Factoring Challenge Problem
Root Finding Problem (RFP)
root of polynomial
RSA assumption
RSA Cryptography
RSA cryptosystem
RSA numbers
S
salting process
secret key
secret-key cryptography
secret-key cryptosystem
security
semantic security
Shanks’ baby-step giant-step method for discrete logarithms
Shanks’ class group method
Shanks’ SQUFOF method
shift transformation
short plaintext attack
Shortest Vector Problem (SVP)
Sieve of Eratosthenes
signature generation
signature verification
Silver–Pohlig–Hellman algorithm
simple continued fraction
singular curve
size of point on elliptic curve
smooth number
SNFS (Special Number Field Sieve)
special purpose factoring algorithms
SQRT Problem
square number
square root method
Square Root Problem (SQRT)
strong probable prime
strong pseudoprimality test
strong pseudoprime
strong psudoprimality test
subexponential-time complexity
subgroup
substitution cipher
succinct primality certification
SVP
symmetric
symmetric key cryptography
T
test tube
the short d attack
theory of computations
torsion group
torsion subgroup
transitive
trapdoor
trapdoor one-way function
trial division
Triple DES (TDES)
triple prime numbers
triplet primes
trivial divisor
Turing machine
twin prime conjecture
twin prime constant
twin prime numbers
U
unbreakability
unconditionally secure
unconditionally unbreakable
US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
W
Williams’ M2 encryption
Williams’ M3 encryption
Wilson’s primality test
Wilson’s theorem
witness
X
xedni calculus for ECDLP
Z
zero of polynomial
zero-knowledge proof
zero-knowledge technique
zero-knowlege Identification