Aarts, B., D. Denison, E. Keizer, and G. Popova (eds.) (2004). Fuzzy Grammar: A Reader. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Abbott, H. P. (2003). “Unnarratable Knowledge: The Difficulty of Understanding Evolution by Natural Selection.” In D. Herman (ed.), Narrative Theory and the Cognitive Sciences (pp. 143–62). Stanford, CA: Center for the Study of Language and Information.
Abbott, H. P. (2005). “Narration.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 339–44). London: Routledge.
Abbott, H. P. (2007). “Story, Plot, and Narration.” In D. Herman (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to Narrative (pp. 39–51). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Abbott, H. P. ([2002] 2008). The Cambridge Introduction to Narrative. 2nd edn. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Adam, J.-M. (1985). “Quels types de textes?” Le français dans le monde 192, 39–43.
Adams, J.-K. (1996). Narrative Explanation: A Pragmatic Theory of Discourse. Frankfurt: Peter Lang.
Alber, J. (2002). “The ‘Moreness’ or ‘Lessness’ of ‘Natural’ Narratology: Samuel Beckett’s ‘Lessness’ Reconsidered.” Style 36(1), 54–75.
Ankersmit, F. (2005a). “Historiography.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 217–21). London: Routledge.
Ankersmit, F. (2005b). “Narrative Explanation.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (p. 354). London:Routledge.
Atran, S. (1990). Cognitive Foundations of Natural History. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Baetens, J. (2002). “Revealing Traces: A New Theory of Graphic Enunciation.” In R. Varnum and C. Gibbons (eds.), The Language of Comics: Word and Image (pp. 145–55). Jackson, MS: University Press of Mississippi.
Bakhtin, M. M. ([1937–8] 1981). “Forms of Time and of the Chronotope in the Novel.” In M. Holquist (ed.), The Dialogic Imagination, trans. C. Emerson and M. Holquist (pp. 84–258). Austin: University of Texas Press.
Bakhtin, M. M. ([1953] 1986). “The Problem of Speech Genres,” trans. V. W. McGee. In C. Emerson and M. Holquist (eds.), Speech Genres and Other Late Essays (pp. 60–102). Austin: University of Texas Press.
Bal, M. ([1980] 1997). Narratology: Introduction to the Theory of Narrative, trans. C. van Boheemen. 2nd edn. Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Bamberg, M. (ed.) (1997a). Special issue on “Oral Versions of Personal Experience: Three Decades of Narrative Analysis.” Journal of Narrative and Life History 7(1–4), 1–415.
Bamberg, M. (1997b). “Positioning between Structure and Performance.” Journal of Narrative and Life History 7(1–4), 335–42.
Bamberg, M. (2004a). “Positioning with Davie Hogan: Stories, Tellings, and Identities.” In C. Daiute and C. Lightfoot (eds.), Narrative Analysis: Studying the Development of Individuals in Society (pp. 133–57). London: Sage.
Bamberg, M. (2004b). “Talk, Small Stories, and Adolescent Identities.” Human Development 47, 366–9.
Bamberg, M. (2005). “Positioning.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 445–6). London: Routledge.
Bamberg, M. (2006). Special issue on “Narrative – State of the Art.” Narrative Inquiry 16(1), 1–228.
Bamberg, M., and M. Andrews (eds.) (2004). Considering Counternarratives: Narrating, Resisting, Making Sense. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Banfield, A. (1982). Unspeakable Sentences: Narration and Representation in the Language of Fiction. Boston: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Barnes, B. (1990). “Sociological Theories of Scientific Knowledge.” In R. C. Olby, G. N. Cantor, J. R. R. Christie, and M. J. S. Hodge (eds.), Companion to the History of Modern Science (pp. 60–73). London: Routledge.
Barthes, R. ([1957] 1972).Mythologies, trans. A. Lavers. New York: Hill & Wang.
Barthes, R. ([1966] 1977). “Introduction to the Structural Analysis of Narratives,” trans. S. Heath. In Image Music Text (pp. 79–124). New York: Hill & Wang.
Barthes, R. ([1968] 1977). “From Work to Text,” trans. S. Heath. In Image Music Text (pp. 155–64). New York: Hill & Wang.
Benson, J. J. (ed.) (1990). New Critical Approaches to the Short Stories of ErnestHemingway. Durham: Duke University Press.
Beowulf (1993). Trans. E. T. Donaldson, in M. H. Abrams (ed.), The Norton Anthology of English Literature, vol. 1, 6th edn. (pp. 27–68). New York: W. W. Norton.
Berkenkotter, C., and T. N. Huckin (1995). Genre Knowledge in Disciplinary Communication: Cognition/Culture/Power. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Berlin, B. (1992). Ethnobiological Classification: Principles of Categorization of Plants and Animals in Traditional Societies. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Berlin, B., D. E. Breedlove, and P. H. Raven (1973). “General Principles of Classification and Nomenclature in Folk Biology.” American Anthropologist 75, 214–42.
Blackmore, S. (2004). Consciousness: An Introduction. Oxford: Oxford UniversityPress.
Blackmore, S. (2005). Consciousness: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Block, N., O. Flanagan, and G. Güzeldere (eds.) (1997). The Nature of Consciousness: Philosophical Debates. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Bolter, J. D., and R. Grusin (1999). Remediation: Understanding the New Media. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Booth, W. C. ([1961] 1983).The Rhetoric of Fiction. 2nd edn. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Booth, W. C. (2005). “Resurrection of the Implied Author: Why Bother.” In J. Phelan and P. J. Rabinowitz (eds.), A Companion to Narrative Theory (pp. 75–88). Oxford: Blackwell.
Borges, J. L. (1964). Labyrinths: Selected Stories and Other Writings, ed. D. A. Yates and J. E. Irby. New York: New Directions.
Bremond, C. (1964). “Le Message narratif.” Communications 4, 4–32.
Bremond, C. (1980). “The Logic of Narrative Possibilities,” trans. E. D. Cancalon. New Literary History 11, 387–411.
Bridgeman, T. (2005). “Figuration and Configuration: Mapping Imaginary Worlds in Bande Dessinee.” In C. Forsdick, L. Grove and L. McQuillan (eds.), The Francophone Bande Dessinee (pp. 115–36). Amsterdam: Rodopi, 2005.
Bruner, J. (1986). Actual Minds, Possible Worlds. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Bruner, J. (1987). “Life as Narrative.” Social Research 54, 11–32.
Bruner, J. (1990). Acts of Meaning. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Bruner, J. (1991). “The Narrative Construction of Reality.” Critical Inquiry 18, 1–21.
Buchholz, S., and M. Jahn (2005). “Space in Narrative.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 551–5). London: Routledge.
Carrier, D. (2000). The Aesthetics of Comics. University Park, PA: Pennsylvania State University Press.
Chafe, W. (1994). Discourse, Consciousness, and Time: The Flow and Displacement of Conscious Experience in Speaking and Writing. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Chalmers, D. J. (1996). The Conscious Mind: In Search of a Fundamental Theory. New York: Oxford University Press.
Chatman, S. (1978). Story and Discourse: Narrative Structure in Fiction and Film. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Chatman, S. (1990). Coming to Terms: The Rhetoric of Narrative in Fiction and Film. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Clark, A. (1998). “Embodied, Situated, and Distributed Cognition.” In W. Bechtel and G. Graham (eds.), A Companion to Cognitive Science (pp. 506–17). Oxford: Blackwell.
Clark, G. (1990). Beowulf. Boston: Twayne.
Clover, C. J. (1980). “The German Context of the Unfer3 Episode.” Speculum 55, 444–68.
Clowes, D. (1997). Ghost World. Seattle, WA: Fantagraphics Books.
Cohn, D. (1978). Transparent Minds: Narrative Modes for Presenting Consciousness in Fiction. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Cohn, D. (1999). The Distinction of Fiction. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Crystal, D. (1997). A Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics. 4th edn. Oxford: Blackwell.
Culler, J. (1975). Structuralist Poetics: Structuralism, Linguistics, and the Study of Literature. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Culler, J. (1998). A Very Short Introduction to Literary Theory. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Dannenberg, H. (2008). Convergent and Divergent Lives: Plotting Coincidence and Counterfactuality in Narrative Fiction. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Danto, A. C. (1985). Narration and Knowledge (including the integral text of Analytical Philosophy of History). New York: Columbia University Press.
Davies, M. (1999). “Consciousness.” In R. A. Wilson and F. C. Keil (eds.), The MIT Encyclopedia of the Cognitive Sciences (pp. 190–3). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Dennett, D. (1991). Consciousness Explained. Boston: Little, Brown.
Dennett, D. (1997). “Quining Qualia.” In N. Block, O. Flanagan, and G. Güzeldere (eds.), The Nature of Consciousness: Philosophical Debates (pp. 619–42). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Derrida, J. ([1980] 1991). “The Law of Genre.” In D. Attridge (ed.), Acts of Literature (pp. 221–52). New York: Routledge.
Dole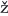 el, L. (1980). “Truth and Authenticity in Narrative.” Poetics Today 1, 7–25.
el, L. (1980). “Truth and Authenticity in Narrative.” Poetics Today 1, 7–25.
Dole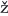 el, L. (1998). Heterocosmica: Fiction and Possible Worlds. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
el, L. (1998). Heterocosmica: Fiction and Possible Worlds. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Drew, P., and J. Heritage (eds.) (1992). Talk at Work. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Dubrow, H. (1982). Genre. London: Methuen.
Edwards, D. (1997). Discourse and Cognition. London: Sage.
Edwards, D. (2006). “Discourse, Cognition and Social Practices: The Rich Surface of Language and Social Interaction.” Discourse Studies 8(1), 41–9.
Edwards, D., and J. Potter (1992). Discursive Psychology. London: Sage.
Eggins, S., and D. Slade (1997). Analysing Casual Conversation. London: Cassell.
Eisner, W. (1996). Graphic Storytelling and Visual Narrative. Tamarac: PoorhousePress.
Ellen, R. (1993). The Cultural Relations of Classification. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Emmott, C. (1997). Narrative Comprehension: A Discourse Perspective. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Ewert, J. C. (2004). “Art Spiegelman’s Maus and the Graphic Narrative.” In M.-L. Ryan (ed.), Narrative Across Media: The Languages of Storytelling (pp. 178–93). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Ewert, J. C. (2005). “Comics and Graphic Novel.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 71–3). London: Routledge.
Flanagan, O. (1998). “Consciousness.” In W. Bechtel and G. Graham (eds.), A Companion to Cognitive Science (pp. 176–85). Oxford: Blackwell.
Fludernik, M. (1993). The Fictions of Language and the Languages of Fiction: The Linguistic Representation of Speech and Consciousness. London: Routledge.
Fludernik, M. (1996). Towards a “Natural” Narratology. London: Routledge.
Fludernik, M. (2000). “Genres, Text Types, or Discourse Modes?” Style 34(2), 274–92.
Fludernik, M. (2003). “Natural Narratology and Cognitive Parameters.” In D. Herman (ed.), Narrative Theory and the Cognitive Sciences (pp. 243–67). Stanford, CA: Center for the Study of Language and Information.
Fludernik, M. (2005). “Histories of Narrative Theory (II): From Structuralism to the Present.” In J. Phelan and P. J. Rabinowitz (eds.), A Companion to Narrative Theory (pp. 36–59). Oxford: Blackwell.
Fludernik, M. (2007). “Identity/Alterity.” In D. Herman (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to Narrative (pp. 260–73). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Frawley, W. (1992). Linguistic Semantics. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum
Freeman, A. (2003). Consciousness: A Guide to the Debates. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-Clio.
Gallagher, S. (2006). “The Narrative Alternative to Theory of Mind.” In R. Menary (ed.), Radical Enactivism: Intentionality, Phenomenology, and Narrative: Focus on the Philosophy of Daniel D. Hutto (pp. 223–9). Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Garcia Landa, J. A. (2004). “Overhearing Narrative.” In J. Pier (ed.), The Dynamics of Narrative Form: Studies in Anglo-American Narratology (pp. 191–214). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Garfinkel, H. (1967). Studies in Ethnomethdology. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Genette, G. ([1972] 1980).Narrative Discourse: An Essay in Method, trans. J. E. Lewin. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Genette, G. ([1966] 1982). “Frontiers of Narrative.” In Figures of Literary Discourse, trans. A. Sheridan (pp. 127–42). New York: Columbia University Press.
Genette, G. ([1983] 1988).Narrative Discourse Revisited, trans. J. E. Lewin. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Genette, G. ([1991] 1993). Fiction and Diction, trans. Catherine Porter. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Genette, G. ([1982] 1997). Palimpsests: Literature in the Second Degree, trans. C. Newman and C. Doubinsky. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Georgakopoulou, A. (2005). “Text-Type Approach to Narrative.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), The Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 594–6). London: Routledge.
Georgakopoulou, A. (2007).Small Stories, Interaction and Identities. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Gerrig, R. J. (1993). Experiencing Narrative Worlds: On the Psychological Activities of Reading. New Haven: Yale University Press.
Goffman, E. (1974). Frame Analysis: An Essay on the Organization of Experience. New York: Harper & Row.
Goffman, E. (1981). Forms of Talk. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press.
Goodman, N. (1978). Ways of Worldmaking. Indianapolis: Hackett.
Goodwin, M. H. (1990). He-Said-She-Said: Talk as Organization among Black Children. Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
Görlach, M. (2004). Text Types and the History of English. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
Green, G. M. (1989). Pragmatics and Natural Language Understanding. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Greimas, A. J. ([1966] 1983).Structural Semantics: An Attempt at a Method, trans. D. McDowell, R. Schleifer, and A. Velie. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Groensteen, T. (2007). The System of Comics, trans. Bart Beaty and Nick Nguyen. Jackson: University of of Mississippi Press.
Gumperz, J. J. (1982). Discourse Strategies. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Halliday, M. A. K. (1994).An Introduction to Functional Grammar. 2nd edn. London: Edward Arnold.
Hamburger, K. ([1957] 1993). The Logic of Literature. 2nd, revised, edn., trans. M. J. Rose. Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
Hamon, P. (1982). “What Is a Description?” In P. Hamon (ed.), French Literary Theory Today (pp. 147–78). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Hansen, P. K. (2007). “Reconsidering the Unreliable Narrator.” Semiotica 165(1/4), 227–46.
Harré, R. (2001). “The Discursive Turn in Social Psychology.” In D. Schiffrin, D. Tannen, and H. E. Hamilton (eds.), The Handbook of Discourse Analysis(pp. 688–706). Oxford: Blackwell.
Harré, R., and G. Gillett (1994). The Discursive Mind. London: Sage.
Harré, R., and L. van Langenhove (eds.) (1999). Positioning Theory: Moral Contexts of Intentional Action. Oxford: Blackwell.
Harré, R., and P. Stearns (eds.) (1995). Discursive Psychology in Practice. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Hemingway, E. ([1927] 1987). “Hills Like White Elephants.” In The Complete Short Stories of Ernest Hemingway (pp. 211–14). New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Hempel, C. ([1948] 1998). “Studies in the Logic of Explanation.” In E. D. Klemke, R. Hollinger, and D. W. Rudge, with A. D. Kline (eds.), Introductory Readings in the Philosophy of Science (pp. 206–24). Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
Herman, D. (1998). “Narrative, Science, and Narrative Science.” Narrative Inquiry 8(2), 379–90.
Herman, D. (1999a). “Introduction.” In David Herman (ed.), Narratologies: New Perspectives on Narrative Analysis (pp. 1–30). Columbus: Ohio State University Press.
Herman, D. (1999b). “Towards a Socionarratology.” In D. Herman (ed.), Narratologies: New Perspectives on Narrative Analysis (pp. 1–30). Columbus: Ohio State University Press.
Herman, D. (2000). “Pragmatic Constraints on Narrative Processing: Actants and Anaphora Resolution in a Corpus of North Carolina Ghost Stories.” Journal of Pragmatics 32(7), 959–1001.
Herman, D. (2001a). “Spatial Reference in Narrative Domains.” TEXT: An Interdisciplinary Journal for the Study of Discourse 21(4), 515–41.
Herman, D. (2001b). “Sciences of the Text.” Postmodern Culture 11(3) <http://www.iath.virginia.edu/pmc/text-only/issue.501/11.3herman.txt>.
Herman, D. (2002a). Story Logic: Problems and Possibilities of Narrative. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Herman, D. (2002b). “Narrative: A User’s Manual.” Style 36(2), 560–8.
Herman, D. (2003a). “Stories as a Tool for Thinking.” In D. Herman (ed.), Narrative Theory and the Cognitive Sciences (pp. 163–92). Stanford, CA: Publications of the Center for the Study of Language and Information.
Herman, D. (2003b). “Regrounding Narratology: The Study of Narratively Organized Systems for Thinking.” In T. Kindt and H.-H. Müller (eds.), What Is Narratology? Questions and Answers Regarding the Status of a Theory (pp. 303–32). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Herman, D. (2004). “Toward a Transmedial Narratology.” In M.-L. Ryan (ed.), Narrative across Media: The Languages of Storytelling (pp. 47–75). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Herman, D. (2005a). “Histories of Narrative Theory (I): A Genealogy of Early Developments.” In J. Phelan and P. J. Rabinowitz (eds.), The Blackwell Companion to Narrative Theory (pp. 19–35). Oxford: Blackwell.
Herman, D. (2005b). “Quantitative Methods in Narratology: A Corpus-Based Study of Motion Events in Stories.” In J.-C. Meister (ed.), Narratology Beyond Literary Criticism (pp. 125–49). (Edited in cooperation with T. Kindt, W. Schernus, and M. Stein). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Herman, D. (2006a). “Narrative: Cognitive Approaches.” In K. Brown (ed.), Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics, 2nd edn., vol. 8 (pp. 452–9). (Section editor C. Emmott.) Oxford: Elsevier.
Herman, D. (2006b). “Dialogue in a Discourse Context: Scenes of Talk in Fictional Narrative.” Narrative Inquiry 16(1), 79–88.
Herman, D. (2006c). “Genette Meets Vygotsky: Narrative Embedding and Distributed Intelligence.” Language and Literature 15(4), 375–98.
Herman, D. (2007a). “Nonfactivity, Tellability, and Narrativity.” Presentation for a Workshop on “Events, Eventfulness, and Tellability” sponsored by the University of Hamburg’s Interdisciplinary Centre for Narratology and the University of Ghent; Ghent, Belgium, February 2007.
Herman, D. (2007b). “Storytelling and the Sciences of Mind: Cognitive Narratology, Discursive Psychology, and Narratives in Face-to-Face Interaction.”Narrative 15(3), 306–34.
Herman, D. (2007c). “Cognition, Emotion, and Consciousness.” In D. Herman (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to Narrative (pp. 245–59). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Herman, D. (2008a). “Narrative Theory and the Intentional Stance.” Partial Answers 6(2), 233–60.
Herman, D. (2008b). “Narrative and Intentionality.” Presentation for a panel on “Intentionalities” at the annual meeting of the International Society for the Study of Narrative; Austin, Texas, May 2008.
Herman, D. (forthcoming a). “Narrative Theory after the Second Cognitive Revolution.” In L. Zunshine (ed.),Introduction to Cognitive Cultural Studies. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Herman, D. (forthcoming b). “Description, Narrative, and Explanation: Text-Type Categories and the Cognitive Foundations of Discourse Competence.” Poetics Today 29(3).
Herman, D. (forthcoming c). “Word-Image/Utterance-Gesture: Case Studies in Multimodal Storytelling.” New Perspectives on Narrative and Multimodality. Ed. R. Page. London: Routledge.
Herman, D., and B. Childs (2003). “Narrative and Cognition in Beowulf.” Style 37(2), 177–202.
Herman, D., and S. Moss (2007). “Plant Names and Folk Taxonomies: Frameworks for Ethnosemiotic Inquiry.” Semiotica 167(1/4), 1–11.
Herman, L., and B. Vervaeck (2005a). Handbook of Narrative Analysis. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Herman, L., and B. Vervaeck (2005b). “Postclassical Narratology.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), The Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 450–1). London: Routledge.
Hogan, P. C. (2003). Cognitive Science, Literature, and the Arts: A Guide for Humanists. London: Routledge.
Hutto, D. D. (1999). The Presence of Mind. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Hutto, D. D. (2000). Beyond Physicalism. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Hutto, D. D. (2006a). “Narrative Practice and Understanding Reasons: Reply to Gallagher.” In R. Menary (ed.), Radical Enactivism: Intentionality, Phenomenology, and Narrative: Focus on the Philosophy of Daniel D. Hutto (pp. 231–47). Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Hutto, D. D. (2006b). “Impossible Problems and Careful Expositions: Reply to Myin and De Nul.” In R. Menary (ed.),Radical Enactivism: Intentionality, Phenomenology, and Narrative: Focus on the Philosophy of Daniel D. Hutto
(45–64). Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Hutto, D. D. (2007). “The Narrative Practice Hypothesis: Origins and Applications of Folk Psychology.” In D. D. Hutto (ed.), Narrative and Understanding Persons (pp. 43–68). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Hutto, D. D. (2008). Folk Psychological Narratives: The Sociocultural Basis of Understanding Reasons. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Hutto, D. D., and M. Ratcliffe (eds.) (2007). Folk Psychology Re-assessed. Dordrecht: Springer.
Hymes, D. (1974). Foundations in Sociolinguistics: An Ethnographic Approach. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press.
Hyvärinen, M. (2006). “Towards a Conceptual History of Narrative.” <http://www.helsinki.fi/collegium/e-series/volumes/volume_1/001_04_hyvarinen.pdf>. In M. Hyvärinen, A. Korhonen, and J. Mykkänen (eds.), The Travelling Concept of Narrative (pp. 20–41). Helsinki: Helsinki Collegium for Advanced Studies. <http://www.helsinki.fi/collegium/e-series/vol.s/vol._1/index.htm>.
Iser, W. (1974). The Implied Reader: Patterns of Communication in Prose Fiction from Bunyan to Beckett. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Jackson, F. (1982). “Epiphenomenal Qualia.” Philosophical Quarterly 32, 127–36.
Jahn, M. (1996). “Windows of Focalization: Deconstructing and Reconstructing a Narratological Concept.” Style 30(3), 241–67.
Jahn, M. (1997). “Frames, Preferences, and the Reading of Third-Person Narratives: Towards a Cognitive Narratology.” Poetics Today 18, 441–68.
Jahn, M. (1999). “More Aspects of Focalization: Refinements and Applications.” GRAAT 21 (Groupes de Recherches Anglo-Américaines de Tours) [Issue Topic: “Recent Trends in Narratological Research”], 85–110.
Jahn, M. (2005). “Focalization.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 173–7). London: Routledge.
Jahn, M. (2007). “Focalization.” In D. Herman (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to Narrative (pp. 94–108). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Jakobson, R. (1960). “Closing Statement: Linguistics and Poetics.” In T. A. Sebeok (ed.), Style in Language (pp. 350–77). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Jannidis, F. (2003). “Narratology and the Narrative.” In T. Kindt and H.-H. Müller (ed.), What Is Narratology? Questions and Answers Regarding the Status of a Theory (pp. 35–54). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Jauss, H. R. (1982). Toward an Aesthetic of Reception, trans. Timothy Bahti. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Jefferson, G. (1984). “Transcription Notation.” In J. M. Atkinson and J. Heritage (eds.), Structures of Social Action: Studies in Conversation Analysis (pp. ix–xvi). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Jewitt, C. (2006). Technology, Literacy, and Learning: A Multimodal Approach. London: Routledge.
Johnston, K. G. (1987). The Tip of the Iceberg: Hemingway and the Short Story. Greenwood, FL: Penkevill.
Johnstone, B. (2000). Qualitative Methods in Sociolinguistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Kafalenos, E. (2006). Narrative Causalities. Columbus: Ohio State University Press.
Keen, S. (2007). Empathy and the Novel. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Kendall, T. (2007). “Enhancing Sociolinguistic Data Collections: The North Carolina Sociolinguistic Archive and Analysis Project.” Penn Working Papers in Linguistics13(2), 15–26. <http://repository.upenn.edu/pwpl/vol13/0iss2/>.
Kindt, T., and H.-H. Müller (2006). The Implied Author: Concept and Controversy. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Kirk, R. (2003). “Zombies.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2003 edn.).<http://plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2003/entries/zombies/>.
Kittay, J. (1981). “Descriptive Limits.” Yale French Studies 61, 225–43.
Klemke, E. D., R. Hollinger, and D. W. Rudge, with A. D. Kline (eds.) (1998). Introductory Readings in the Philosophy of Science. Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
Kraus, W. (2005). “The Eye of the Beholder: Narratology as Seen by Social Psychology.” In J.-C. Meister (ed.), Narratology Beyond Literary Criticism (pp. 265–87). (Edited in cooperation with T. Kindt, W. Schernus, and M. Stein). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Kreiswirth, M. (2005). “Narrative Turn in the Humanities.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 377–82). London: Routledge.
Kress, G., and T. van Leeuwen (2001). Multimodal Discourse: The Modes and Media of Contemporary Communication. London: Arnold.
Labov, W. (1972). “The Transformation of Experience in Narrative Syntax.” In Language in the Inner City (pp. 354–96). Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press.
Labov, W., and J. Waletzky (1967). “Narrative Analysis: Oral Versions of Personal Experience.” In J. Helm (ed.), Essays on the Verbal and Visual Arts (pp. 12–44). Seattle: University of Washington Press.
Lacey, A. R. (1986). A Dictionary of Philosophy. 2nd edn. London: Routledge.
Lakoff, G. (1987). Women, Fire and Dangerous Things: What Categories Reveal about the Mind. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Lakoff, G. ([1987] 2004). “The Importance of Categorization.” In B. Aarts, D. Denison, E. Keizer, and G. Popova (eds.), Fuzzy Grammar: A Reader (pp. 139–77). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Lambert, K., and G. Britten ([1970] 1998). “Laws and Conditional Statements.” In E. D. Klemke, R. Hollinger, and D. W. Rudge, with A. D. Kline (eds.), Introductory Readings in the Philosophy of Science (pp. 225–32). Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
Lambrou, M. (2008). “Oral Narratives of Personal Experiences: When Is a Narrative not a Narrative but a Recount?” In M. Lambrou and P. Stockwell (eds.), Contemporary Stylistics (pp. 196–208). London: Continuum.
Lanser, S. S. (1981). The Narrative Act: Point of View in Prose Fiction. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Lanser, S. S. (1992). Fictions of Authority: Women Writers and Narrative Voice. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Leech, G., and M. Short ([1981] 2007). Style in Fiction: A Linguistic Introduction to English Fictional Prose. 2nd edn. Harlow: Pearson/Longman.
Lejeune, P. (1989). “The Autobiographical Pact.” In On Autobiography, ed. P. J. Eakin, trans. K. Leary (pp. 3–30). Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Levi, P. (1961). Survival in Auschwitz, trans. S. Woolf. New York: Collier.
Levin, J. (1999). “Qualia.” In R. A. Wilson and F. C. Keil (eds.), The MIT Encyclopedia of the Cognitive Sciences (pp. 693–4). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Levine, J. (1983). “Materialism and Qualia: The Explanatory Gap.” Pacific Philosophical Quarterly 64(4), 354–61.
Levinson, S. ([1979] 1992). “Activity Types and Language.” In P. Drew and J. Heritage (eds.), Talk at Work (pp. 66–100). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Lewis, D. (1979). “Scorekeeping in a Language Game.” Journal of Philosophical Logic 8, 339–59.
Linde, C. (1993). Life Stories: The Creation of Coherence. New York: Oxford University Press.
Lodge, D. (2002). “Consciousness and the Novel.” In Consciousness and the Novel: Connected Essays (pp. 1–91). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Longino, H. (1990). Science as Social Knowledge: Values and Objectivity in Scientific Inquiry. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Longino, H. (2002). “The Social Dimensions of Scientific Knowledge.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. <http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/scientific-knowledge-social/>.
Lönneker, B. (2005). “Narratological Knowledge for Natural Language Generation.” In G. Wilcock, K. Jokinen, C. Mellish, and E. Reiter (eds.), Proceedings of the 10th European Workshop on Natural Language Generation (= ENLG 2005) (pp. 91–100). Aberdeen, Scotland, August 8–10, 2005. <http://www1.uni-hamburg.de/story-generators//Birte/Narratological_Knowledge.pdf>.
Lord, A. B. (1995). The Singer Resumes the Tale, ed. M. L. Lord. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Lubbock, P. ([1921] 1957). The Craft of Fiction. London: Jonathan Cape.
Lukács, G. ([1936] 1970). “Narrate or Describe?” In Writer and Critic and Other Essays, trans. and ed. A. D. Kahn (pp. 110–48). New York: Grosset & Dunlap.
Lyotard, J.-F. ([1979] 1984).The Postmodern Condition: A Report on Knowledge, trans. G. Bennington and B. Massumi. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
MacIntyre, A. (1984). After Virtue: A Study of Moral Theory. 2nd edn. South Bend: University of Notre Dame Press.
Mallinson, C. (2006). “The Dynamic Construction of Race, Class, and Gender through Linguistic Practice among Women in a Black Appalachian Community.” Unpublished doctoral dissertation. Department of Sociology, North Carolina State University.
Mallinson, C. (2008). “The Linguistic Negotiation of Complex Racialized
Identities by Black Appalachian Speakers.” In K. King, N. Schilling-Estes, L. Fogle, J. Lou, and B. Soukup (eds.), Sustaining Linguistic Diversity: Endangered and Minority Languages and Language Varieties (pp. 67–80). Washington, DC: Georgetown University Press.
Malt, B. C. (1995). “Category Coherence in Cross-Cultural Perspective.” Cognitive Psychology 29, 85–148.
Margolin, U. (1990a). “The What, the When, and the How of Being a Character in a Literary Narrative.” Style 24, 453–68.
Margolin, U. (1990b). “Individuals in Narrative Worlds: An Ontological Perspective.” Poetics Today 11, 843–71.
Margolin, U. (1999). “Of What Is Past, Is Passing, or To Come: Temporality, Aspectuality, Modality, and the Nature of Narrative.” In D. Herman (ed.), Narratologies: New Perspectives on Narrative Analysis (pp. 142–66). Columbus: Ohio State University Press.
Margolin, U. (2005a). “Character.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 52–7). London:
Routledge. Margolin, U. (2005b). “Authentication.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 32–3). London: Routledge.
Margolin, U. (2007). “Character.” In D. Herman (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to Narrative (pp. 66–79). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Martin, T. (2004). Poiesis and Possible Worlds: A Study in Modality and Literary Theory. Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Martin, W. (1986). Recent Theories of Narrative. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Mateas, M., and P. Senger (2003). Narrative Intelligence. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
McCloud, S. (1993). Understanding Comics. New York: HarperCollins.
McEwan, I. (1978). The Cement Garden. London: Jonathan Cape.
McHale, B. (1987). Postmodernist Fiction. London: Methuen.
Meister, J. C. (2003). Computing Action: A Narratological Approach. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Menary, R. (2006). “Introduction: What is Radical Enactivism?” In R. Menary (ed.), Radical Enactivism: Intentionality, Phenomenology, and Narrative: Focus on the Philosophy of Daniel D. Hutto (pp. 1–12). Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Mildorf, J. (2007). Storying Domestic Violence: Constructions and Stereotypes of Abuse in the Discourse of General Practitioners. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Miller, C. R. (1984). “Genre as Social Action.” Quarterly Journal of Speech 70, 151–67.
Miller, J. E. (ed.) (1972). Theory of Fiction: Henry James. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Mink, L. (1978). “Narrative Form as Cognitive Instrument.” In R. H. Canary and H. Kozicki (eds.), The Writing of History: Literary Form and Historical Understanding (pp. 129–49). Madison: University of Wisconsin Press.
Moisinnac, L. (2008). “Positioning in Conversational Stories: Advances in Theory and Practice.” Prospectus of panel discussion held at the Georgetown University Roundtable in Linguistics, March 2008. <http://www8.georgetown.edu/college/gurt/2008/>.
Moore, A., D. Gibbons, and J. Higgins (1987). Watchmen. New York: DC Comics.
Morgan, R. (2002). Altered Carbon. New York: Del Rey.
Morrison, J. (forthcoming). “Narrative Theory in the Film Studies Classroom; or, Old Movies and the New Disorder.” In D. Herman, B. McHale, and J. Phelan (eds.), Teaching Narrative Theory. New York: Modern Language Association of America.
Mosher, H. F., Jr. (1991). “Towards a Poetics of Descriptized Narration.” Poetics Today 3, 425–45.
Nagel, T. (1974). “What Is It Like To Be a Bat?” The Philosophical Review 83(4), 435–50.
Nelson, L. H. (1990). Who Knows: From Quine to Feminist Empiricism. Philadelphia, PA: Temple University Press.
Nieragden, G. (2002). “Focalization and Narration: Theoretical and Terminological Refinements.” Poetics Today 23(4), 685–97.
Norrick, N. R. (1992). “Twice-Told Tales: Collaborative Narration of Familiar Stories.” Language in Society 26, 199–220.
Norrick, N. R. (2000). Conversational Narrative. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Norrick, N. R. (2007). “Conversational Storytelling.” In D. Herman (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to Narrative (127–41). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Nünning, A. (1997). “Deconstructing and Reconceptualizing the Implied Author.” Anglistik 8(2), 95–116.
Nünning, A. (2003). “Narratology or Narratologies? Taking Stock of Recent Developments: Critique and Modest Proposals for Future Usages of the Term.” In T. Kindt and H.-H. Müller, What Is Narratology? Questions and Answers Regarding the Status of a Theory (pp. 239–75). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Nünning, A. (2005). “Reconceptualizing Unreliable Narration.” In J. Phelan and P. J. Rabinowitz (eds.), A Companion to Narrative Theory (pp. 89–107). Oxford: Blackwell.
Oatley, K. (1999). “Emotions.” In R. A. Wilson and F. C. Keil (eds.), The MIT Encyclopedia of the Cognitive Sciences (pp. 273–5). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Ochs, E., and L. Capps (2001).Living Narrative: Creating Lives in Everyday Storytelling. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Ochs, E., C. Taylor, D. Rudolph, and R. Smith (1992). “Storytelling as TheoryBuilding Activity.” Discourse Processes 15, 37–72.
Page, R. (2006). Literary and Linguistic Approaches to Feminist Narratology. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Palmer, A. (2003). “The Mind Beyond the Skin.” In D. Herman (ed.), Narrative Theory and the Cognitive Sciences (pp. 322–48). Stanford, CA.: Center for the Study of Language and Information.
Palmer, A. (2004). Fictional Minds. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Pavel, T. (1976). Syntaxe narrative des tragédies de Corneille. Paris: Klincksieck.
Pavel, T. (1985). The Poetics of Plot. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Pavel, T. (1986). Fictional Worlds. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Pflugmacher, T. (2005). “Description.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 101–2). London: Routledge.
Phelan, J. (1989). Reading People, Reading Plots. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Phelan, J. (2005a). Living to Tell about It: A Rhetoric and Ethics of Character Narration. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Phelan, J. (2005b). “Who’s Here? Thoughts on Narrative Identity and Narrative Imperialism.” Narrative 13(3), 205–10.
Pike, K. L. (1982). Linguistic Concepts: An Introduction to Tagmemics. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Plotnitsky, A. (2005). “Science and Narrative.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 514–18). London: Routledge.
Plum, G. A. (1988). “Text and Contextual Conditioning in Spoken English: A Genre-Based Approach.” Unpublished doctoral dissertation. University of Sydney.
Potter, J., and M. Wetherell (1987). Discourse and Social Psychology. London: Sage.
Pratt, M. L. (1977). Toward a Speech Act Theory of Literary Discourse. Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
Prince, G. (1973). A Grammar of Stories. The Hague: Mouton.
Prince, G. (1980). “Aspects of a Grammar of Narrative.” Poetics Today 1, 49–63.
Prince, G. (1982). Narratology: The Form and Functioning of Narrative. The Hague: Mouton.
Prince, G. (1983). “Narrative Pragmatics, Message, and Point.” Poetics 12, 527–36.
Prince, G. (1999). “Revisiting Narrativity.” In W. Grünzweig and A. Solbach (eds.), Transcending Boundaries: Narratology in Context (pp. 43–51). Tübingen: Narr.
Prince, G. ([1987] 2003). A Dictionary of Narratology. 2nd edn. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Prince, G. (2005). “Narrativity.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 387–8). London: Routledge.
Propp, V. ([1928] 1968). Morphology of the Folktale, 2nd edn. trans. L. Scott; revised L. A. Wagner. Austin: University of Texas Press.
Quine, W. V. O. (1951). “Two Dogmas of Empiricism.” The Philosophical Review 60, 20–43.
Rabinowitz, P. J. ([1977] 1996). “Truth in Fiction: A Reexamination of Audiences.” In D. H. Richter (ed.), Narrative/Theory (pp. 209–26). White Plains, NY: Longman.
Rabinowitz, P. J. (1998). Before Reading: Narrative Conventions and the Politics of Interpretation. Columbus: Ohio State University Press.
Reddy, M. J. (1979). “The Conduit – Metaphor a Case of Frame Conflict in Our Language about Language.” In A. Ortony (ed.), Metaphor and Thought (pp. 284–324). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Richardson, B. (2006). Unnatural Voices: Extreme Narration in Modern and Contemporary Fiction. Columbus: Ohio State University Press.
Ricoeur, P. (1990). Time and Narrative. Vol. 1. Trans. K. McLaughlin and D. Pellauer. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Rimmon-Kenan, S. ([1983] 2002). Narrative Fiction: Contemporary Poetics. 2nd edn. London: Routledge.
Robbe-Grillet, A. ([1957, 1959] 1965). Two Novels, by Robbe-Grillet [La Jalousie and Dans le labyrinthe], trans. R. Howard. New York: Grove Press.
Roberts, C. (1999). “Discourse.” In R. A. Wilson and F. C. Keil (eds.), The MIT Encyclopedia of the Cognitive Sciences (pp. 231–2). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Ronen, R. (1994). Possible Worlds in Literary Theory. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Ronen, R. (1997). “Description, Narrative, and Representation.” Narrative 3, 274–86.
Rosch, E. (1973). “Natural Categories.” Cognitive Psychology 4, 328–50.
Rosch, E. ([1978] 2004). “Principles of Categorization.” In B. Aarts, D. Denison, E. Keizer, and G. Popova (eds.), Fuzzy Grammar: A Reader (pp. 91–108). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Rosch, E., C. Mervis, W. Gray, D. Johnson, and P. Boyes-Braem (1976). “Basic Objects in Natural Categories.” Cognitive Psychology 8, 382–439.
Ryan, M.-L. (1991). Possible Worlds, Artificial Intelligence, and Narrative Theory. Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
Ryan, M.-L. (2001a). Narrative as Virtual Reality: Immersion and Interactivity in Literature and Electronic Media. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Ryan, M.-L. (2001b). “The Narratorial Functions: Breaking Down a Theoretical Primitive.” Narrative 9(2), 146–52.
Ryan, M.-L. (ed.) (2004). Narrative across Media: The Languages of Storytelling. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Ryan, M.-L. (2005a). “Narrative.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 344–8). London: Routledge.
Ryan, M.-L. (2005b). “Possible-Worlds Theory.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 446–50). London: Routledge.
Ryan, M.-L. (2005c). “Tellability.” In D. Herman, M. Jahn, and M.-L. Ryan (eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory (pp. 589–91). London: Routledge.
Ryan, M.-L. (2006). Avatars of Story. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Ryan, M.-L. (2007). “Toward a Definition of Narrative.” In D. Herman (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to Narrative (pp. 22–35). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Sacco, J. (1994). Palestine. Seattle, WA: Fantagraphics Books.
Sacco, J. (2000). Safe Area Gorazde. Seattle, WA: Fantagraphics Books.
Sacks, H. (1992). Lectures on Conversation. Vols. 1 and 2, ed. G. Jefferson. Oxford: Blackwell.
Sacks, H., E. Schegloff, and G. Jefferson (1974). “A Simplest Systematics for the Organization of Turn-Taking for Conversation.” Language 50, 696–735.
Salway, A., M. Graham, E. Tomadaki, and Y. Xu (2003). “Linking Video and Text via Representations of Narrative.”Intelligent Media Management: Papers from the AAAI 2003 Spring Symposium: Technical Report SS-03-08 (pp. 104–12). Menlo Park, CA: American Association for Artificial Intelligence.
Saussure, F. de ([1916] 1959). Course in General Linguistics, ed. C. Bally and A. Sechehaye, in collaboration with A. Riedlinger, trans. W. Baskin. New York: The Philosophical Library.
Saville-Troike, M. (2002).The Ethnography of Communication: An Introduction. 3rd edn. Oxford: Blackwell.
Schechtman, M. (1997). The Constitution of Selves. Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
Schegloff, E. A. (1981). “Discourse as an Interactional Achievement.” In D. Tannen (ed.), Analyzing Discourse: Text and Talk(pp. 71–93). Washington, DC: Georgetown University Press.
Schegloff, E. A. (1997). “Narrative Analysis Thirty Years Later.” Journal of Narrative and Life History 7(1–4), 97–106.
Schegloff, E. A. (n.d.). “Transcription Module.” <http://www.sscnet.ucla.edu/soc/faculty/schegloff/TranscriptionProject/index.xhtml>.
Schiffrin, D. (1987). Discourse Markers. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Scholes, R., and R. Kellogg (1966). The Nature of Narrative. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Schutz, A. (1962). “Common-Sense and the Scientific Interpretation of Human Action.” In Collected Papers, vol. 1, ed. M. Natanson (pp. 3–47). The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff.
Searle, J. R. (1992). The Rediscovery of the Mind. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Searle, J. R. (1997). The Mystery of Consciousness. New York: The New York Review of Books.
Sebald, W. G. ([1992] 1996). The Emigrants, trans. M. Hulse. New York: New Directions.
Sebald, W. G. (2001). Austerlitz, trans. A. Bell. New York: Random House.
Segal, E. M. (1995). “Narrative Comprehension and the Role of Deictic Shift Theory.” In J. F. Duchan, G. A. Bruder, and L. E. Hewitt (eds.), Deixis in Narrative: A Cognitive Science Perspective (pp. 3–17). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Shaw, H. (2005). “Why Won’t Our Terms Stay Put? The Narrative Communication Diagram Scrutinized and Historicized.” In J. Phelan and P. J. Rabinowitz (eds.), A Companion to Narrative Theory (pp. 299–311). Oxford: Blackwell.
Shklovskii, V. ([1929 [1990]). Theory of Prose, trans. B. Sher. Elmwood Park, IL: Dalkey Archive Press.
Stanzel, F. K. ([1979] 1984).A Theory of Narrative, trans. C. Goedsche. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Sternberg, M. (1978). Expositional Modes and Temporal Ordering in Fiction. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Sternberg, M. (1981). “Ordering the Unordered: Time, Space and Descriptive Coherence.” Yale French Studies 61, 61–88.
Sternberg, M. (1982). “Proteus in Quotation-Land: Mimesis and the Forms of Reported Discourse.” Poetics Today 3(2), 107–56.
Sternberg, M. (1990). “Telling in Time (I): Chronology and Narrative Theory.” Poetics Today 11, 901–48.
Sternberg, M. (1992). “Telling in Time (II): Chronology, Teleology, Narrativity.” Poetics Today 13, 463–541.
Sternberg, M. (2001). “How Narrativity Makes a Difference.” Narrative 9(2), 115–22.
Strawson, G. (2004). “Against Narrativity.” Ratio 17, 428–52.
Tammi, P. (2006). “Against Narrative: A Boring Story.” Partial Answers 4(2), 19–40.
Tannen, D. (ed.) (1993).Framing in Discourse. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Taylor, Charles (1989). Sources of the Self. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Taylor, Craig (2001). “Girls World.” The Guardian, Saturday, November 3, 2001. <http://www.guardian.co.uk/Archive/Article/0,4273,4290067,00.xhtml>
Teahan, S. (1995). The Rhetorical Logic of Henry James. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press.
Todorov, T. (1968). “La Grammaire du récit.” Langages 12, 94–102.
Todorov, T. (1969). Grammaire du “Décaméron.” The Hague: Mouton.
Todorov, T. ([1978] 1990).Genres in Discourse, trans. Catherine Porter. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Tomasello, M. (1999). The Cultural Origins of Human Cognition. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Tomasello, M. (2003). Constructing a Language: A Usage-Based Theory of Language Acquisition. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Tomashevskii, B. ([1925] 1965). “Thematics.” In L. T. Lemon and M. J. Reis (eds.), Russian Formalist Criticism (pp. 61–95). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Toolan, M. ([1988] 2001). Narrative: A Critical Linguistic Introduction. 2nd edn. London: Routledge.
Turner, M. (ed.) (2006).The Artful Mind: Cognitive Science and the Riddle of Human Creativity. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Tye, M. (2003). “Qualia.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Summer 2003 edn.). <http://plato.stanford.edu/archives/sum2003/entries/qualia/>.
Van Gulick, R. (2004). “Consciousness.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2004 edn.). <http://plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2004/entries/consciousness/>.
Virtanen, T. (1992). “Issues of Text Typology: Narrative-a ‘Basic’ Type of Text?” TEXT 12, 293–310.
Virtanen, T., and B. Wårvik (1987). “Observations sur les types de texte.” Communications: Recontre des professeurs de français de l’enseignement supérieur 8, 161–9.
Wagner-Martin, L. (ed.) (1998). Ernest Hemingway: Seven Decades of Criticism. East Lansing: Michigan State University Press.
Walsh, R. (2007). The Rhetoric of Fictionality: Narrative Theory and the Idea of Fiction. Columbus: Ohio State University Press.
Walton, K. (1990). Mimesis as Make-Believe: On the Foundations of the Representational Arts. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Ward, G., and J. Hirschberg (1985). “Implicating Uncertainty: The Pragmatics of Fall-Rise Intonation.” Language 61(4), 747–76.
Warhol, R. (1989). Gendered Interventions: Narrative Discourse in the Victorian Novel. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press.
Warhol, R. (2003). Having a Good Cry: Effeminate Feelings and Popular Forms. Columbus: Ohio State University Press.
Warhol, R. (2005). “Neonarrative; or, How to Render the Unnarratable in Realist Fiction and Contemporary Film.” In J. Phelan and P. J. Rabinowitz (eds.), A Companion to Narrative Theory (pp. 220–31). Oxford: Blackwell.
Welty, E. ([1941] 2006). “A Worn Path.” In E. V. Roberts and H. E. Jacobs (eds.), Literature: An Introduction to Reading and Writing, 8th edn. (pp. 138–43). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Werlich, E. (1975). Typologie der Texte: Entwurf eines textlinguistischen Modells zur Grundlegung einer Textgrammatik. Heidelberg: Quelle & Meyer.
Werlich, E. (1983). A Text Grammar of English, 2nd edn. Heidelberg: Quelle & Meyer.
Werth, P. (1999). Text Worlds: Representing Conceptual Space in Discourse. London: Longman.
Wilson, R., and F. Keil (eds.) (1999). The MIT Encyclopedia of the Cognitive Sciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Wimsatt, W., and M. Beardsley ([1947] 2001). “The Intentional Fallacy.” In V. B. Leitch et al. (eds.), The Norton Anthology of Theory and Criticism (pp. 1374–89). New York: W. W. Norton.
Wittgenstein, L. ([1953] 1958). Philosophical Investigations, ed. G. E. M. Anscombe and R. Rhees, trans. G. E. M. Anscombe, 3rd edn. Oxford: Blackwell.
Woodward, J. (2003). “Scientific Explanation.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. <http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/scientific-explanation/>.
Young, K. G. (1987). Taleworlds and Storyrealms: The Phenomenology of Narrative. Dordrecht: Martinus Nijhoff.
Zoran, G. (1984). “Towards a Theory of Space in Narrative.” Poetics Today 5(2), 309–35.
Zubin, D., and L. E. Hewitt (1995). “The Deictic Center: A Theory of Deixis in Narrative.” In J. F. Duchan, G. A. Bruder, and L. E. Hewitt (eds.), Deixis in Narrative: A Cognitive Science Perspective (pp. 129–55). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Zunshine, L. (2006). Why We Read Fiction: Theory of Mind and the Novel. Columbus: Ohio State University Press.
Zwigoff, T. (2001). Ghost World. MGM.