Chapter 14
Air Force Officer Qualifying Test (AFOQT) Practice Test
The United States Air Force utilizes just one test for all its officer candidates, regardless of whether those candidates want to become aviators. The Air Force Officer Qualifying Test consists of 12 timed subtests, and the qualifying scores are combined into 5 composite scores that are designed to predict your success in various fields within the Air Force, including aviation. In addition to the five composite scores, you also receive a percentile score for each of the five composite areas.
Currently, the Air Force allows a candidate to take the test twice — an original and one retest. You have to wait at least six months between tests. Remember: The Air Force uses your most recent score, not your highest score, for selection criteria scoring.
The Subtests of the AFOQT
The AFOQT takes approximately three and a half hours to complete, including administrative periods (pre-test instruction) and a break. The 12 subtests are broken down as follows:
|
Subtest |
# of items |
Time |
|
1. Verbal Analogies (VA) |
25 |
8 minutes |
|
2. Arithmetic Reasoning (AR) |
25 |
29 minutes |
|
3. Word Knowledge (WK) |
25 |
5 minutes |
|
4. Math Knowledge (MK) |
25 |
22 minutes |
|
10-minute break |
||
|
5. Instrument Comprehension (IC) |
20 |
6 minutes |
|
6. Block Counting (BC) |
20 |
3 minutes |
|
7. Table Reading (TR) |
40 |
7 minutes |
|
8. Aviation Information (AI) |
20 |
8 minutes |
|
9. General Science (GS) |
20 |
10 minutes |
|
10. Rotated Blocks (RB) |
15 |
13 minutes |
|
11. Hidden Figures (HF) |
15 |
8 minutes |
|
12. Self-Description Inventory (SDI) |
220 |
40 minutes |
The five composite scores derived from the test are combined into the following categories. (Note: Various sections are weighted differently according to a secret formula, so you can’t find your composite score by just adding up the number of correct answers for each section.)
 Pilot (AR + MK + IC + TR + AI): This score predicts your success in the aviation field by measuring the knowledge and abilities the Air Force feels you need to successfully complete Air Force pilot training. The subtests included in this score measure mathematical ability, aeronautical knowledge, spatial relation of the aircraft to its systems and instruments, and perceptual speed. If you’re a pilot candidate, you must score at least 25 for this composite; if you’re a navigator candidate, you need to score at least 10.
Pilot (AR + MK + IC + TR + AI): This score predicts your success in the aviation field by measuring the knowledge and abilities the Air Force feels you need to successfully complete Air Force pilot training. The subtests included in this score measure mathematical ability, aeronautical knowledge, spatial relation of the aircraft to its systems and instruments, and perceptual speed. If you’re a pilot candidate, you must score at least 25 for this composite; if you’re a navigator candidate, you need to score at least 10.
 Navigator-technical (VA + AR + MK + BC + TR + GS): This grouping measures the abilities required to successfully complete Air Force navigator training. Unlike the pilot composite, this score doesn’t focus on aeronautical knowledge and spatial orientation. Pilot candidates need a minimum score of 10 for this composite; navigator candidates need a minimum score of 25.
Navigator-technical (VA + AR + MK + BC + TR + GS): This grouping measures the abilities required to successfully complete Air Force navigator training. Unlike the pilot composite, this score doesn’t focus on aeronautical knowledge and spatial orientation. Pilot candidates need a minimum score of 10 for this composite; navigator candidates need a minimum score of 25.
 Academic aptitude (VA + AR + WK + MK): This grouping measures verbal and quantitative knowledge, which is an important aspect of your career as a military officer. Good news: You don’t need a particular minimum score for this composite.
Academic aptitude (VA + AR + WK + MK): This grouping measures verbal and quantitative knowledge, which is an important aspect of your career as a military officer. Good news: You don’t need a particular minimum score for this composite.
 Verbal (VA + WK): This grouping measures verbal knowledge and abilities. The combined subtest determines the officer candidate’s ability to reason, understand synonyms, and recognize relationships between words. All candidates must achieve a minimum score of 15.
Verbal (VA + WK): This grouping measures verbal knowledge and abilities. The combined subtest determines the officer candidate’s ability to reason, understand synonyms, and recognize relationships between words. All candidates must achieve a minimum score of 15.
 Quantitative (AR + MK): This composite score measures the officer candidate’s math-related abilities and knowledge. All candidates must achieve a minimum score of 10.
Quantitative (AR + MK): This composite score measures the officer candidate’s math-related abilities and knowledge. All candidates must achieve a minimum score of 10.
You receive a score for each of the five areas but not a total combined score. In addition to the minimum composite scores, all pilot and navigator candidates must have a combined pilot and navigator-technical score of at least 50. If you’ve been keeping track of the math, you’ll realize that this requirement means that achieving the minimum scores in those sections isn’t good enough for these programs. However, you can perform marginally on one section (as long as you don’t go below the minimum) and make up the points in another, higher-scoring section. All commissioning sources determine how high these scores must be for the test-taker to be selected.
Subtest 1
Verbal Analogies
Time: 8 minutes for 25 questions
Description: This part of the exam measures your ability to reason and see relationships between words. Choose the answer that best completes the analogy developed at the beginning of each question.
Examples:
RED is to PINK as
(A) YELLOW is to ORANGE
(B) PURPLE is to LAVENDER
(C) BLUE is to BLACK
(D) WHITE is to GRAY
(E) GREEN is to GRASS
The correct answer is Choice (B).
BROOM is to SWEEP as SPONGE is to
(A) MOP
(B) CLEAN
(C) DETERGENT
(D) SCRUB
(E) GERMS
The correct answer is Choice (D).
1. CONCAVE is to CONVEX as
(A) CAVITY is to MOUND
(B) HILL is to HOLE
(C) OVAL is to OBLONG
(D) ROUND is to POINTED
(E) SQUARE is to ROUND
2. PERJURE is to STATE as
(A) ABANDON is to DESERT
(B) CONCENTRATE is to FOCUS
(C) MARVEL is to WONDER
(D) ROB is to STEAL
(E) TRESPASS is to ENTER
3. ANARCHIST is to DISORDER as
(A) YAWN is to BOREDOM
(B) MONTH is to YEAR
(C) GOOD is to BEST
(D) PACIFIST is to PEACE
(E) CONSTELLATION is to STARS
4. DOCTOR is to HEALING as
(A) PRISON is to GUARD
(B) DINOSAURS is to PALEONTOLOGIST
(C) AUTHOR is to WRITING
(D) CLAP is to HANDS
(E) PLANET is to UNIVERSE
5. AIRCRAFT is to FLY as BOAT is to
(A) STEER
(B) SINK
(C) SHIP
(D) LAND
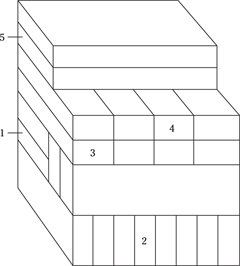
(E) SAIL
6. SHEEP is to LAMB as HORSE is to
(A) COLT
(B) DOE
(C) FAWN
(D) MARE
(E) RAM
7. BIRTH is to LIFE as
(A) RODENT is to SKUNK
(B) GENTRY is to NOBILITY
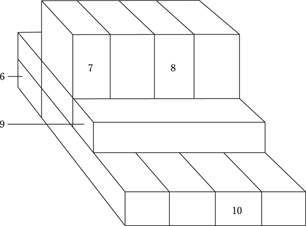
(C) PROLIFERATE is to CEASE
(D) WINCE is to JOY
(E) EXPOSURE is to INFECTION
8. HORIZONTAL is to VERTICAL as WARP is to
(A) COUNT
(B) PILE
(C) SELVAGE
(D) WEAVE
(E) WOOF
9. ISOLATION is to LONELINESS as
(A) SHORTEN is to NIP
(B) QUIET is to TACIT
(C) PROMOTION is to ADVANCEMENT
(D) MONOTONY is to HOMOGENOUS
(E) RUSTIC is to CITY
10. GROW is to MATURE as BLOOM is to
(A) ROSE
(B) PETAL
(C) FLOURISH
(D) DECAY
(E) BLOSSOM
11. ACTOR is to STAGE as
(A) PATIENT is to DOCTOR
(B) OUTSIDE is to BENCH
(C) GARAGE is to CAR
(D) TEACHER is to CLASSROOM
(E) METER is to ELECTRIC
12. CRUMB is to LOAF as
(A) PAINTER is to CANVAS
(B) PUDDLE is to OCEAN
(C) SOUND is to MICROPHONE
(D) PRIDE is to FALL
(E) FEATHER is to QUILL
13. CARROT is to VEGETABLE as
(A) DOGWOOD is to OAK
(B) FOOT is to PAW
(C) PEPPER is to SPICE
(D) SHEEP is to LAMB
(E) VEAL is to BEEF
14. IGNORE is to OVERLOOK as
(A) AGREE is to CONSENT
(B) ATTACH is to SEPARATE
(C) CLIMB is to WALK
(D) DULL is to SHARPEN
(E) LEARN is to REMEMBER
15. HALLOWED is to SACRED as
(A) SOLDIER is to ARMY
(B) GAMUT is to PROVINCIAL
(C) LIBEL is to PRAISE
(D) NOMADIC is to WANDERING
(E) OBLIVIOUS is to KEEN
16. GOWN is to GARMENT as GASOLINE is to
(A) COOLANT
(B) FUEL
(C) GREASE
(D) LUBRICANT
(E) OIL
17. PUSH is to SHOVE as CLIMB is to
(A) MOUNTAIN
(B) FALL
(C) WALK
(D) LINGER
(E) CLAMBER
18. FISHING ROD is to HOOK as KNIFE is to
(A) BLADE
(B) BULLET
(C) CUT
(D) STEAK
(E) HANDLE
19. SLOTH is to LAZINESS as
(A) GENTEEL is to VULGAR
(B) INSOMNIAC is to SLEEPLESSNESS
(C) HACKNEYED is to UNIQUE
(D) ACCEDE is to RESPECT
(E) CRYPT is to TOMB
20. BOOK is to CHAPTER as BUILDING is to
(A) ELEVATOR
(B) LOBBY
(C) ROOF
(D) STORY
(E) WING
21. BATHING is to CLEANLINESS as
(A) MEDICINE is to HARM
(B) SCHOOLING is to EDUCATION
(C) SPITE is to KINDNESS
(D) UTENSIL is to CHEF
(E) SEW is to CLOTHING
22. ELEVATOR is to HEIGHT as THRUST is to
(A) STAIRWAY
(B) CLIMBING
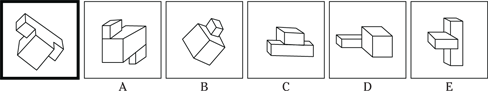
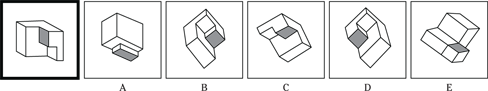
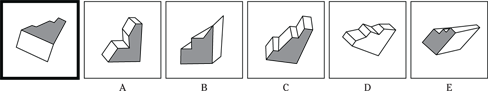
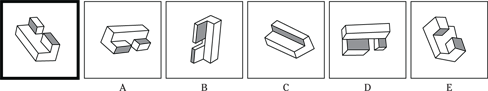
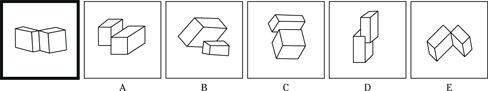
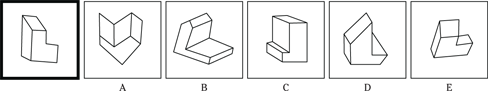
(C) ROCKET
(D) ALTITUDE
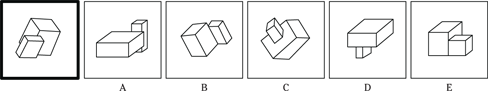
(E) FLIGHT
23. SANCTUARY is to REFUGE as
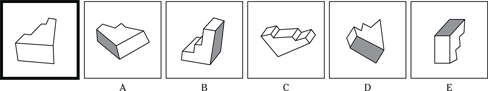
(A) FINGER is to HAND
(B) IMPRISONMENT is to PUNISHMENT
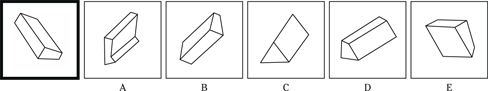
(C) BANJO is to COUNTRY
(D) BALLOON is to HELIUM
(E) SADNESS is to BLUES
24. OBEY is to COMPLY as REPLY is to
(A) QUESTION
(B) STATEMENT
(C) ANSWER
(D) REPOSE
(E) REWIND
25. SPEED is to DECELERATION as VELOCITY is to
(A) DISTANCE
(B) THRUST
(C) RAPIDITY
(D) BRAKING
(E) URGENCY

Subtest 2
Arithmetic Reasoning
Time: 29 minutes for 25 questions
Description: This section tests your mathematic reasoning ability. Decide which answer choice is most correct.
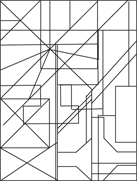
26. Tommy receives $30 for his birthday and $15 for cleaning the yard. If he spends $16 on a CD, how much money does he have left?
(A) $29
(B) $27
(C) $14
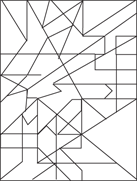
(D) $1
(E) $0.45
27. During a season, a high-school football quarterback attempted 82 passes and completed 57 of them. What was his completion percentage?
(A) 30.4 percent
(B) 69.5 percent
(C) 43.8 percent
(D) 81.7 percent
(E) 143.9 percent
28. A pound of margarine contains four equal sticks of margarine. The wrapper of each stick has markings that indicate how to divide the stick into eight 1-tablespoon sections. If a recipe calls for four tablespoons of margarine, the amount to use is
(A) 1/16 pound
(B) 1/8 pound
(C) 1/4 pound
(D) 1/2 pound
(E) 3/4 pound
29. George earns $8.40 an hour, plus an overtime rate equal to 11⁄2 times his regular pay for each hour worked above 40 hours per week. What are his total gross earnings for a 45-hour workweek?
(A) $336
(B) $370
(C) $399
(D) $567
(E) $599
30. Carrie earns an average of $22 an hour in tips as a waitress at a restaurant. If her hourly wage is $2.50 and she has to pay a 10-percent tip share to the hostesses and busboys, how much does she take home at the end of a day when she has worked from 10:30 a.m. to 5:30 p.m.?
(A) $32.90
(B) $121.11
(C) $138.60
(D) $156.10
(E) $171.50
31. An athlete jogs 15 laps around a circular track. If the total distance she jogs is 3 kilometers, what’s the distance around the track?
(A) 0.2 meters
(B) 2 meters
(C) 20 meters
(D) 200 meters
(E) 2,000 meters
32. Although an air assault infantry company has 131 soldiers authorized, B Company has only 125 total soldiers assigned, of whom 4 percent are officers. How many enlisted soldiers are assigned to B Company?
(A) 114
(B) 123
(C) 120
(D) 121
(E) 126
33. The fuel tank of a gasoline generator has enough capacity to operate the generator for 1 hour and 15 minutes. About how many times must the fuel tank be filled to run the generator from 6:15 p.m. to 7:00 a.m.?
(A) 9.4
(B) 10.2
(C) 10.8
(D) 11.5
(E) 12.0
34. On a map, 1 centimeter represents 4 miles. A distance of 10 miles would be how far on the map?
(A) 13⁄4 centimeters
(B) 2 centimeters
(C) 21⁄2 centimeters
(D) 4 centimeters
(E) 41⁄2 centimeters
35. One phone plan charges a $20 monthly fee and $0.08 per minute on every phone call made. Another phone plan charges a $12 monthly fee and $0.12 per minute for every phone call made. After how many minutes would the charge be the same for each phone plan?
(A) 60
(B) 90
(C) 120
(D) 200
(E) 320
36. A jar contains red, green, and yellow marbles, and 20 percent of these marbles are either red or green. What are the chances of randomly picking a yellow marble out of the jar?
(A) 1 out of 3
(B) 1 out of 5
(C) 2 out of 3
(D) 2 out of 5
(E) 4 out of 5
37. John found a chandelier for the dining room for $1,400. However, because the model had been discontinued and the display had no factory packaging material, the store manager discounted the price to $1,150. What was the percentage of the reduction?
(A) 1.78 percent
(B) 13.0 percent
(C) 15.0 percent
(D) 17.9 percent
(E) 21.7 percent
38. Tom donates 4/13 of his paycheck to his favorite charity. If he donates $26.80, what’s the amount of his paycheck?
(A) $8.25
(B) $82.50
(C) $87.10
(D) $137.50
(E) $348.40
39. A submarine sails x miles the first day, y miles the second day, and z miles the third day. What’s the average number of miles sailed per day?
(A) 3xyz
(B) 3(x + y + z)
(C) (x + y + z) ÷ 3
(D) (x + y + z)
(E) xyz ÷ 3
40. A passenger plane can carry two tons of cargo. A freight plane can carry six tons of cargo. If an equal number of both kinds of planes are used to ship 160 tons of cargo and each plane carries its maximum cargo load, how many tons of cargo are shipped on the passenger planes?
(A) 40 tons
(B) 60 tons
(C) 80 tons
(D) 100 tons
(E) 120 tons
41. When a highway was converted to a toll road, the traffic declined from 11,200 cars per day to 10,044. What was the percentage of the decline in traffic?
(A) 10.3 percent
(B) 11.5 percent
(C) 10.1 percent
(D) 8.9 percent
(E) 79.3 percent
42. If the weight of water is 62.4 pounds per cubic foot, the weight of the water that fills a 6-inch-x-6-inch-x-1 foot rectangular container is
(A) 3.9 pounds
(B) 7.8 pounds
(C) 15.6 pounds
(D) 31.2 pounds
(E) 62.4 pounds
43. What’s the volume of a container that is 23 feet long, 15 feet wide, and 11 feet high?
(A) 2,530 square feet
(B) 3,450 cubic feet
(C) 3,795 square feet
(D) 3,795 cubic feet
(E) 5,280 cubic feet
44. The area of circle A is four times as large as circle B (which has a radius of 3 inches). The radius of circle A is
(A) 12 inches
(B) 9 inches
(C) 8 inches
(D) 6 inches
(E) 4 inches
45. A theater contains x rows, with y seats in each row. How many total seats are in the theater?
(A) x + y
(B) x – y
(C) xy
(D) y – x
(E) 2x + y
46. Two runners finish a race in 80 seconds, another runner finishes the race in 72 seconds, and a fourth runner finishes the race in 68 seconds. The average of the runners’ times is
(A) 73 seconds
(B) 74 seconds
(C) 75 seconds
(D) 76 seconds
(E) 77 seconds
47. Mr. Jones earns a weekly salary of $300 plus a 10-percent commission on all sales. If he had $8,350 in sales last week, what were his total earnings?
(A) $835
(B) $865
(C) $1,135
(D) $1,835
(E) $1,925
48. When 550 gallons of oil are added to an oil tank that is 1/8 full, the tank becomes 1/2 full. The capacity of the oil tank is
(A) 1,350 gallons
(B) 1,390 gallons
(C) 1,430 gallons
(D) 1,470 gallons
(E) 1,510 gallons
49. A wheel has a 1-meter radius. How many meters will a point on the rim of that wheel travel if the wheel makes 35 rotations?
(A) 110
(B) 120
(C) 210
(D) 220
(E) 240
50. In the city of Trenton, houses are assessed at 80 percent of the purchase price. If Mr. Hall buys a home in Trenton for $120,000 and real estate taxes are $4.75 per $100 of assessed value, how much property tax must he pay each year?
(A) $3,648
(B) $5,472
(C) $4,560
(D) $4,845
(E) $5,700

Subtest 3
Word Knowledge
Time: 5 minutes for 25 questions
Description: This test measures your verbal comprehension and ability to understand written language. Select the best answer that means the same as the word given.
51. Tedious
(A) Demanding
(B) Dull
(C) Hard
(D) Simple
(E) Surprising
52. Assent
(A) Acquire
(B) Climb
(C) Consent
(D) Emphasize
(E) Participate
53. Equivalent
(A) Complicated
(B) Inferior
(C) Superior
(D) Evident
(E) Equal
54. Telemetry
(A) Mental communication
(B) Marketing goods or services by telephone
(C) Transmission of measurements made by automatic instruments
(D) Study of climactic variations
(E) Rashness
55. Succinct
(A) Concise
(B) Helpful
(C) Important
(D) Misleading
(E) Sweet
56. Centripetal
(A) Away from a center or axis
(B) Relating to the feet
(C) Having more than 100 petals
(D) Toward a center or an axis
(E) Circular
57. Counteract
(A) Criticize
(B) Conserve
(C) Erode
(D) Neutralize
(E) Retreat
58. Redundant
(A) Brilliant
(B) Held back
(C) Repetitive
(D) Unruly
(E) Isolated
59. Verify
(A) Alarm
(B) Confirm
(C) Explain
(D) Guarantee
(E) Question
60. Tacit
(A) Silent
(B) Sour
(C) Ornament
(D) Talkative
(E) Pleasing
61. Itinerary
(A) Migrant
(B) Not permanent
(C) Cure-all
(D) Schedule
(E) Character
62. Rebuff
(A) Forget
(B) Ignore
(C) Recover
(D) Polish
(E) Snub
63. Indolent
(A) Hopeless
(B) Lazy
(C) Lenient
(D) Rude
(E) Selfish
64. Mercurial
(A) Having compassion
(B) Specious
(C) Unpredictably changeable
(D) Metallic
(E) Containing mercury
65. Flexible
(A) Flammable
(B) Fragile
(C) Pliable
(D) Rigid
(E) Separable
66. Diagnose
(A) Predict the outcome
(B) Cut in two
(C) Identify a situation
(D) Antagonize
(E) Speak about
67. Altercation
(A) Controversy
(B) Defeat
(C) Irritation
(D) Substitution
(E) Vexation
68. Rectify
(A) Dealing with the digestive system
(B) Cause trouble or havoc
(C) Get back
(D) Correct
(E) Give fresh life to
69. Anachronistic
(A) Chronologically out of place
(B) Cursed
(C) Dealing with organism structure
(D) Attribution of conscious thoughts to inanimate objects or animals
(E) Existing before a war
70. Conducive
(A) Confusing
(B) Cooperative
(C) Energetic
(D) Helpful
(E) Respectful
71. Terse
(A) Faulty
(B) Lengthy
(C) Oral
(D) Pointed
(E) Written
72. Dilated
(A) Cleared
(B) Clouded
(C) Decreased
(D) Enlarged
(E) Tightened
73. Picayune
(A) Unnoticed
(B) Insignificant
(C) Intense
(D) Hot
(E) Unfortunate
74. Kinetic
(A) Relating to the motion of material bodies
(B) Referring to motion pictures
(C) Moving at a high speed
(D) Relating to a sensory experience
(E) Referring to a relative
75. Sullen
(A) Angrily silent
(B) Grayish yellow
(C) Mildly nauseated
(D) Soaking wet
(E) Very dirty

Subtest 4
Math Knowledge
Time: 22 minutes for 25 questions
Description: This subtest deals with your general understanding of and ability to use mathematical relationships in problem solving. Each problem is followed by five possible answers, and you must determine which answer is most correct. Use scratch paper to do your calculations and then mark the correct answer. (Note: We don’t provide any scratch paper with this book, but you’ll receive paper at your test site.)
76. John took five midterm tests for five different college classes; his average for all five tests was 88. That night at home, he could only remember his first 4 scores: 78, 86, 94, and 96. What was his score on the fifth test?
(A) 82
(B) 86
(C) 84
(D) 88
(E) 87
77. Solve for z: 3z – 5 + 2z = 25 – 5z
(A) z = 1
(B) z = 3
(C) z = –3
(D) z = 0
(E) No solution
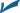
78. The expression 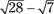 reduces to
reduces to
(A) 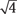
(B) 
(C) 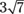
(D) 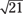
(E) 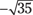
79. If 5x + 3y = 29 and x – y = 1, x equals
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
80. Find the square root of 85, correct to the nearest tenth.
(A) 9.1
(B) 9.2
(C) 9.3
(D) 9.4
(E) 9.5
81. The volume of a cylinder with a radius of r and a height of h is
(A) πrh
(B) 2πrh
(C) 2πr2h
(D) 4πr2h
(E) None of the above
82. An airplane is flying a circular or “racetrack” orbit around a 4,000-meter-high mountaintop. Assuming the pilot flies a perfectly circular course, how far does he need to travel in kilometers for each orbit if the distance between the mountaintop and the outer edge of his orbit is 40 kilometers?
(A) 13 kilometers
(B) 25 kilometers
(C) 126 kilometers
(D) 251 kilometers
(E) 503 kilometers
83. If x is an odd integer, which of the following is an even integer?
(A) 2x + 1
(B) 2x – 1
(C) x(2 + x)
(D) (2 + x – 1)
(E) None of the above
84. A new wildlife preserve is laid out in a perfect circle with a radius of 14 kilometers. The lion habitat is shaped like a wedge and has an 8-foot-high razor wire fence around its two inner sides that meet at a 90-degree angle in the center of the preserve. What’s the area of the lion habitat?
(A) 140 square kilometers
(B) 3.5 square kilometers
(C) 210 square kilometers
(D) 154 square kilometers
(E) 35 square kilometers
85. The sum of the angle measures of a pentagon is
(A) 360 degrees
(B) 540 degrees
(C) 720 degrees
(D) 900 degrees
(E) 1,180 degrees
86. 2(a – b) + 4(a + 3b) =
(A) 6a – 10b
(B) 6a + 2b
(C) 8a + 2b
(D) 6a – 2b
(E) 6a + 10b
87. The area of a square with a perimeter of 40 yards is
(A) 100 square feet
(B) 180 square feet
(C) 900 square feet
(D) 300 square yards
(E) 1,600 square feet
88. If 3n = 9, what’s the value of 4n + 1?
(A) 24
(B) 48
(C) 64
(D) 108
(E) None of the above
89. Two circles have the same center. If their radii are 7 centimeters and 10 centimeters, find the area that is part of the larger circle but not part of the smaller one.
(A) 3 square centimeters
(B) 17 square centimeters
(C) 51π square centimeters
(D) 71π square centimeters
(E) 91π square centimeters
90. The ratio of 3x to 5y is 1:2. What’s the ratio of x to y?
(A) 1:2
(B) 2:3
(C) 3:4
(D) 4:5
(E) 5:6
91. The reciprocal of 7 to the nearest thousandth is
(A) 0.143
(B) 1.428
(C) 14
(D) 21
(E) 49
92. Which of the following is the smallest prime number greater than 200?
(A) 201
(B) 205
(C) 211
(D) 214
(E) 223
93. One million may be represented as
(A) 104
(B) 105
(C) 106
(D) 107
(E) 108
94. 10x divided by 10y equals
(A) 
(B) 10xy
(C) 10x + y
(D) 10x – y
(E) None of the above
95. The cube root of 729 is equal to the square of
(A) 11
(B) 9
(C) 7
(D) 5
(E) 3
96. A cook is mixing fruit juice from concentrate for a catered event. Ten ounces of liquid contain 20 percent fruit juice and 80 percent water. He then further dilutes the mixture by adding 40 additional ounces of water. What’s the percent of fruit juice in the new solution?
(A) 4 percent
(B) 10 percent
(C) 14 percent
(D) 18 percent
(E) 20 percent
97. A cylindrical container has a radius of 7 inches and a height of 15 inches. How many gallons of hydraulic fluid can it hold? (Note: There are 231 cubic inches in a gallon.)
(A) 15 gallons
(B) 14 gallons
(C) 140 gallons
(D) 10 gallons
(E) 23.1 gallons
98. If one angle of a triangle measures 115 degrees, the degree sum of the other two angles is
(A) 245
(B) 75
(C) 195
(D) 65
(E) None of the above
99. An equilateral triangle has a perimeter divisible by both 3 and 5. Which of the following can be the length of each of its sides?
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
(E) 7
100. If one of the angles of a right triangle is 30 degrees, what are the degree measurements of the other two angles?
(A) 30 and 120
(B) 60 and 45
(C) 60 and 90
(D) 45 and 90
(E) 45 and 120

Subtest 5
Instrument Comprehension
Time: 6 minutes for 20 questions
Description: In this subtest, you have to determine the position of an airplane in flight by looking at two dials: one showing the artificial horizon and the other showing the compass heading. From these dials, you have to determine the amount of climb or dive, the degree of bank to left or right, and the heading. Choose the airplane silhouette from the answer choices (A) through (D) that most nearly represents the position indicated on the dials.
Directions: Below are shown two sets of dials, labeled artificial horizon and compass. The heavy black line on the artificial horizon represents the horizon line. If the airplane is above the horizon, it’s climbing. If it’s below the horizon, it’s diving. The greater amount of climb or dive, the farther up or down the horizon line is seen. The artificial horizon dial also has a black arrowhead showing the degree of bank to left or right. If the airplane has no bank, the arrowhead points to zero. If it’s banked to the left, the arrowhead points to the right of zero. If the airplane is banked to the right, the arrowhead points to the left of zero.
101.
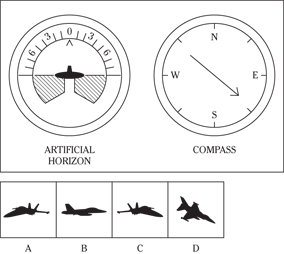
102.
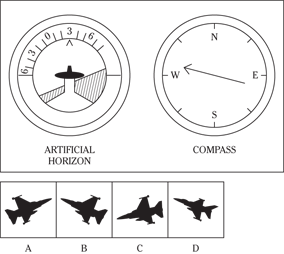
103.
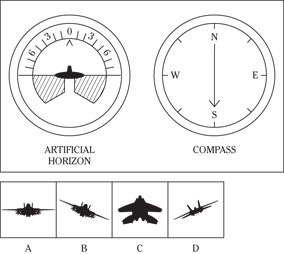
104.
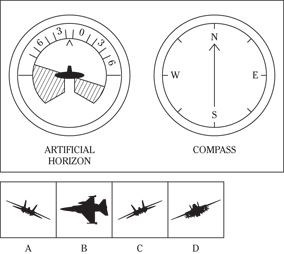
105.
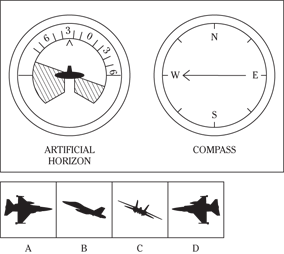
106.
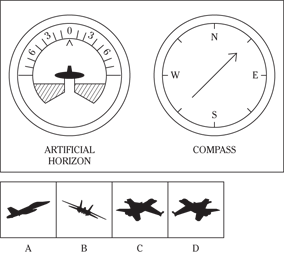
107.
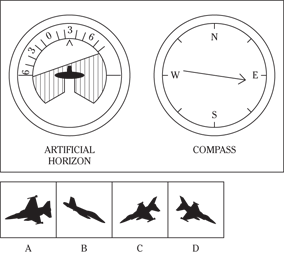
108.
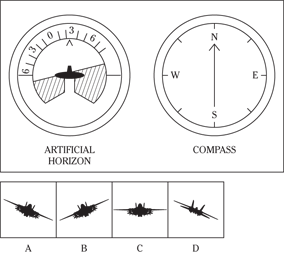
109.
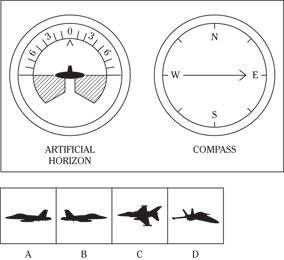
110.
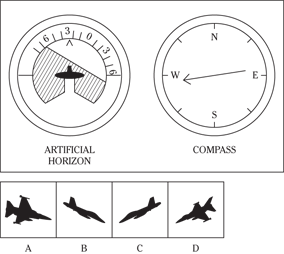
111.
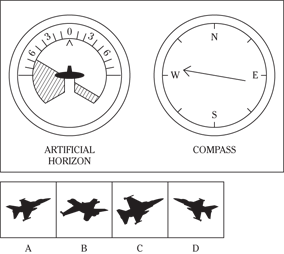
112.
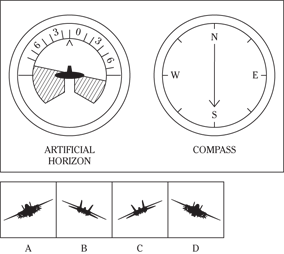
113.
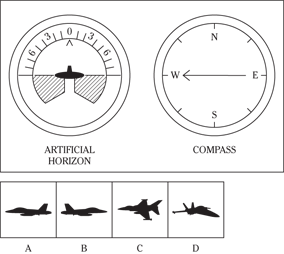
114.
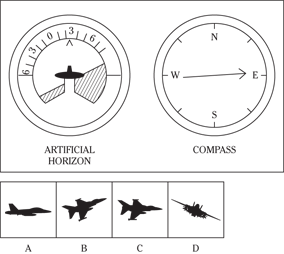
115.
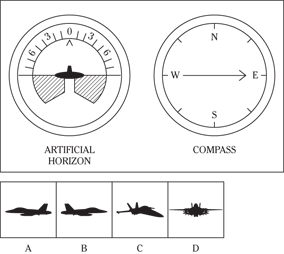
116.
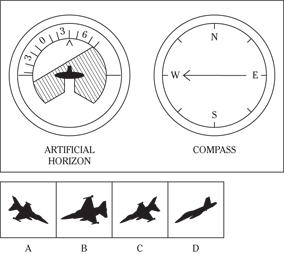
117.
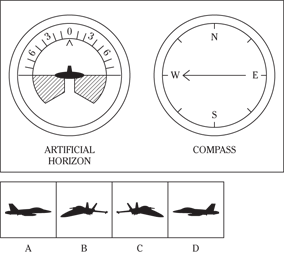
118.
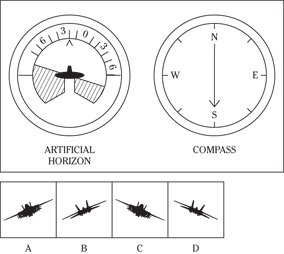
119.
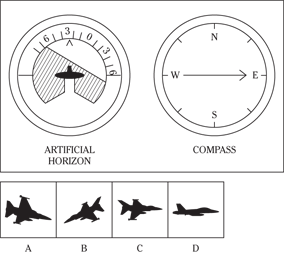
120.
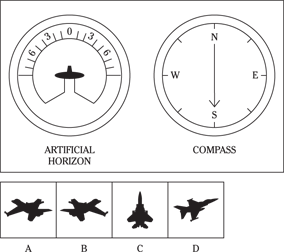

Subtest 6
Block Counting
Time: 3 minutes for 20 questions
Description: This section of the test measures your ability to see and comprehend a three-dimensional viewpoint of a pile of blocks. Given a specific numbered block, you must determine how many other blocks it touches.
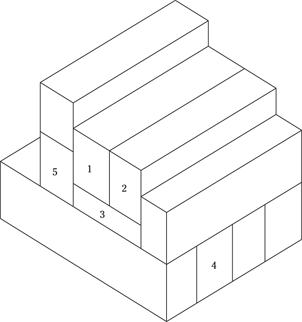
121. Block 1 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
122. Block 2 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
123. Block 3 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 8
(B) 7
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
124. Block 4 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
125. Block 5 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 7
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
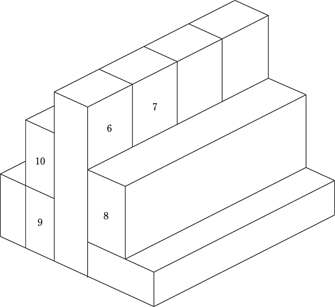
126. Block 6 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 6
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
127. Block 7 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 7
(B) 6
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
128. Block 8 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 5
(D) 4
(E) 7
129. Block 9 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 7
(B) 6
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
130. Block 10 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
131. Block 1 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 6
(B) 10
(C) 7
(D) 4
(E) 5
132. Block 2 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
133. Block 3 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 6
(B) 5
(C) 7
(D) 4
(E) 3
134. Block 4 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
135. Block 5 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
136. Block 6 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
137. Block 7 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
138. Block 8 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
139. Block 9 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
140. Block 10 touches how many other blocks?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5

Subtest 7
Table Reading
Time: 7 minutes for 40 questions
Description: This test gauges your ability to read a table quickly and accurately. For this test, you use the given value to find the entry that occurs at the intersections of the corresponding row and column.
For questions 141 to 145, use the following table. Note that the x values are shown at the bottom of the table and the y values are shown at the left side of the table. Given x and y, choose the answer that represents the intersecting value.
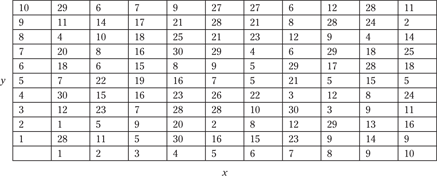
141. x = 4; y = 6
(A) 16
(B) 8
(C) 24
(D) 4
(E) 32
142. x = 2; y = 8
(A) 16
(B) 12
(C) 24
(D) 28
(E) 10
143. x = 3; y = 3
(A) 10
(B) 6
(C) 7
(D) 42
(E) 16
144. x = 5; y = 1
(A) 16
(B) 22
(C) 9
(D) 25
(E) 7
145. x = 9; y = 6
(A) 28
(B) 22
(C) 21
(D) 18
(E) 9
Questions 146 to 150 are based on the following table of commuter train schedules.

146. The metro line A is scheduled to arrive at Wilks Station at
(A) 3:15 p.m.
(B) 3:16 p.m.
(C) 4:10 p.m.
(D) 3:46 p.m.
(E) 3:55 p.m.
147. The metro line B is scheduled to arrive at Wilks Station at
(A) 4:22 p.m.
(B) 4:11 p.m.
(C) 4:16 p.m.
(D) 3:10 p.m.
(E) 4:18 p.m.
148. The metro line B will arrive at Plymouth Station at
(A) 4:21 p.m.
(B) 3:55 p.m.
(C) 4:48 p.m.
(D) 4:35 p.m.
(E) 4:55 p.m.
149. Metro line C departs Plymouth Station at
(A) 4:55 p.m.
(B) 4:28 p.m.
(C) 4:44 p.m.
(D) 4:52 p.m.
(E) 4:21 p.m.
150. Metro line C arrives at Central Station at
(A) 5:01 p.m.
(B) 4:52 p.m.
(C) 4:57 p.m.
(D) 5:58 p.m.
(E) 4:48 p.m.
Questions 151 to 155 are based on the following mileage chart listed in the back of a U.S. travel atlas.
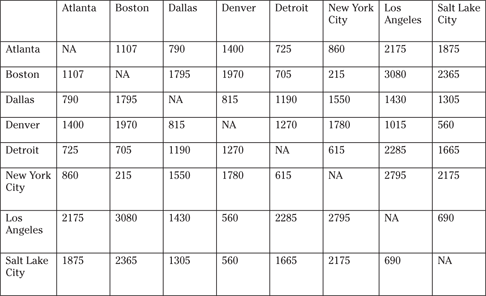
151. How far is it from Dallas to Detroit?
(A) 849 miles
(B) 1,500 miles
(C) 1,722 miles
(D) 1,640 miles
(E) 1,190 miles
152. How far is it from Atlanta to New York City?
(A) 970 miles
(B) 1,213 miles
(C) 860 miles
(D) 775 miles
(E) 1,055 miles
153. How far is it from Atlanta to Denver if you first go to Dallas and then to Denver?
(A) 1,230 miles
(B) 1,547 miles
(C) 1,449 miles
(D) 1,605 miles
(E) 1,190 miles
154. How far is it from Salt Lake City to Denver?
(A) 777 miles
(B) 640 miles
(C) 560 miles
(D) 305 miles
(E) 435 miles
155. How far is it from Boston to Los Angeles?
(A) 3,080 miles
(B) 3,410 miles
(C) 2,905 miles
(D) 2,490 miles
(E) 3,216 miles
Questions 156 to 160 cover the military compensation tables.

156. What does an 0-2 (1st Lieutenant in the Air Force) with 3 years of service earn per month for base pay?
(A) $4,216.50
(B) $4,347.00
(C) $3,990.22
(D) $4,479.00
(E) $3,660.76
157. When you first get your commission and enter flight school (less than 1 year of service), what is your base pay?
(A) $2,876.40
(B) $2,890.84
(C) $2,858.00
(D) $3,163.50
(E) $3,216.63
158. What does a Captain (0-3) make in base pay after 6 years of service in the Air Force?
(A) $4,895.52
(B) $5,572.48
(C) $5,101.00
(D) $5,361.60
(E) $4,790.25
159. You’re a 2nd Lieutenant with 6 years of prior enlisted service. What’s your base pay per month?
(A) $4,290.60
(B) $3,455.00
(C) $3,864.60
(D) $3,910.23
(E) $3,245.75
160. A Lieutenant Colonel (0-5) with more than 16 years of service makes how much base pay per month?
(A) $7,216.00
(B) $7,086.20
(C) $8,254.46
(D) $8,045.10
(E) $7,895.10
Questions 161 to 165 involve data from the acceptable military height and weight tables.
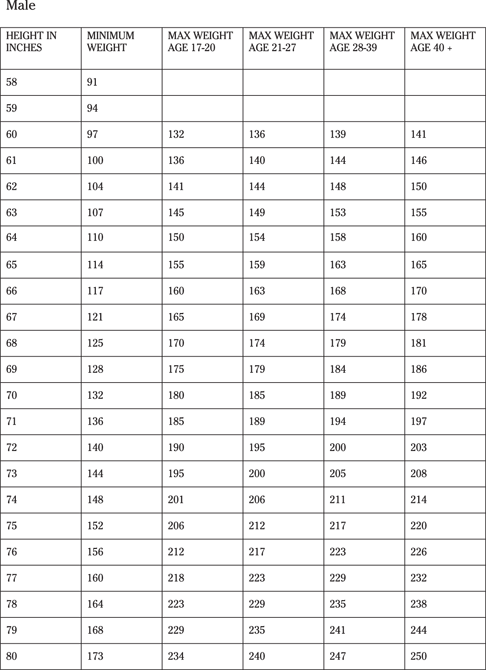

161. A 27-year-old male who is 74 inches tall can weigh up to
(A) 202 pounds
(B) 206 pounds
(C) 198 pounds
(D) 201 pounds
(E) 212 pounds
162. A 42-year-old male who is 71 inches tall can weigh up to
(A) 199 pounds
(B) 204 pounds
(C) 189 pounds
(D) 197 pounds
(E) 199 pounds
163. A 32-year-old female who is 66 inches tall can weight up to
(A) 158 pounds
(B) 151 pounds
(C) 148 pounds
(D) 160 pounds
(E) 164 pounds
164. A 38-year-old male who is 70 inches tall can weigh up to
(A) 188 pounds
(B) 189 pounds
(C) 192 pounds
(D) 204 pounds
(E) 212 pounds
165. A 22-year-old female who is 62 inches tall can weigh up to
(A) 108 pounds
(B) 126 pounds
(C) 144 pounds
(D) 130 pounds
(E) 138 pounds
Questions 166 to 170 are based on the following table. The x values are shown along the horizontal plane, and the y values are on the vertical plane. Given the x and y values, determine the appropriate value.
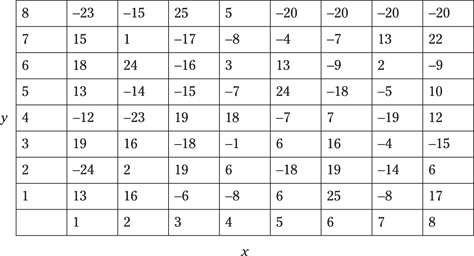
166. x = 2; y = 3
(A) 16
(B) –22
(C) –16
(D) 8
(E) 24
167. x = 6; y = 7
(A) –1
(B) –21
(C) –7
(D) 7
(E) 48
168. x = 1; y = 6
(A) 15
(B) 18
(C) –1
(D) 11
(E) –11
169. x = 4; y = 1
(A) 4
(B) 6
(C) 8
(D) 12
(E) –8
170. x = 5; y = 4
(A) 6
(B) 14
(C) –7
(D) –5
(E) 3
Questions 171 to 175 concern the calculations of federal tax with the following table and criteria given.
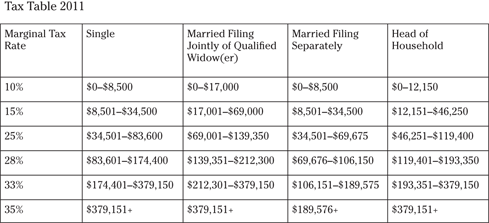
171. You’re a married head of a household with two children; after deductions, your income is $46,280. What tax bracket do you fall in?
(A) 15 percent
(B) 28 percent
(C) 33 percent
(D) 0 percent
(E) 25 percent
172. You’re single with no dependents and have an after-deduction taxable amount of $22,500. What tax bracket do you fall in?
(A) 15 percent
(B) 28 percent
(C) 33 percent
(D) 0 percent
(E) 25 percent
173. You’re married with no children, are filing jointly, and have an after-deduction earnings of $82,300. What tax bracket do you fall in?
(A) 15 percent
(B) 28 percent
(C) 33 percent
(D) 35 percent
(E) 25 percent
174. You’re the head of a household and earn $126,200 after deductions. What tax bracket do you fall in?
(A) 15 percent
(B) 28 percent
(C) 33 percent
(D) 35 percent
(E) 25 percent
175. You’re single and, after all deductions, you have taxable earnings of $10,150. What tax bracket do you fall in?
(A) 15 percent
(B) 28 percent
(C) 33 percent
(D) 35 percent
(E) 25 percent
Questions 176 to 180 deal with the grading cutoff for a recently taken course with an assigned instructor curve. Given your score in both the lab course and classroom, find your overall grade
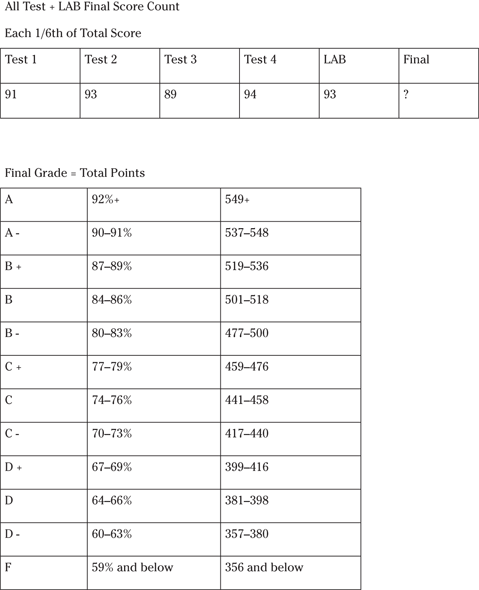
176. Last test equals 88 percent
(A) A–
(B) A
(C) B+
(D) B
(E) B–
177. Last test equals 74 percent
(A) A–
(B) A
(C) B+
(D) B
(E) B–
178. Last test equals 96 percent
(A) A–
(B) A
(C) B+
(D) B
(E) B–
179. Last test equals 92 percent
(A) A–
(B) A
(C) B+
(D) B
(E) B–
180. Last test equals 84 percent
(A) A–
(B) A
(C) B+
(D) B
(E) B–

Subtest 8
Aviation Information
Time: 8 minutes for 20 questions
Description: This section is a test of your aeronautical knowledge. You will be given questions or incomplete statements with five possible choices. Pick the most-correct answer.
181. What’s the critical angle of attack?
(A) The angle of attack required for lifting action on the wing
(B) The angle of attack that is critical to achieve during takeoff
(C) The angle at which the wing on an aircraft will stall
(D) The angle of attack that is critical to achieve during approach
(E) The angle in which the aircraft will have the lowest amount of parasite drag
182. When flaps are extended, or lowered, the aircraft experiences
(A) Less lift and less drag
(B) Less lift and more drag
(C) More lift and less drag
(D) More lift and more drag
(E) No change in lift or drag
183. The four forces acting on an airplane are
(A) Lift, pressure, drag, and power
(B) Drag, thrust, acceleration, and weight
(C) Drag, airspeed, gravity, and friction
(D) Lift, drag, power, and thrust
(E) Lift, drag, power, and weight
184. Induced drag is greatest at
(A) High airspeeds
(B) Low airspeeds
(C) Diving flight
(D) Shallow turns
(E) Straight and level flight
185. Which doesn’t affect density altitude?
(A) Altitude
(B) Temperature
(C) Humidity
(D) Aircraft gross weight
(E) Atmospheric pressure
186. Va is defined as the
(A) Stall speed
(B) Best rate of climb airspeed
(C) Minimum rate of descent airspeed
(D) Maneuvering airspeed
(E) Takeoff airspeed
187. Flying with a CG that is aft results in
(A) No difference
(B) Less stability at slow airspeeds
(C) Less stability at all airspeeds
(D) Less stability at high airspeeds
(E) A higher angle of attack
188. Which of the following statements is true in respect to the forces acting on an aircraft in stable, straight, and level flight?
(A) Lift equals drag; thrust equals weight.
(B) Lift equals weight; thrust equals drag.
(C) Lift is greater than drag; thrust equals weight.
(D) Lift equals drag; thrust is greater than weight.
(E) Lift is greater than weight; thrust is greater than drag.
189. On a final approach aligned with the runway, you see both rows of VASI approach lights indicating white. This display means that
(A) You’re above the glide path.
(B) You’re below the glide path.
(C) You’re slightly to the left of the centerline.
(D) You’re slightly to the right of the centerline.
(E) You’re cleared for landing.
190. The wings of an airplane are curved on the top and flat on the bottom in order to
(A) Reduce drag
(B) Increase drag
(C) Produce lift
(D) Decrease noise
(E) Increase rotational turn rate
191. Nighttime airport taxiway identifiers are what color?
(A) Red
(B) White
(C) Green
(D) Blue
(E) Orange
192. Bernoulli’s principle indicates that
(A) The faster airflow over the greater curvature of the upper wing decreases pressure and lift.
(B) The slower airflow over the greater curvature of the upper wing increases pressure and lift.
(C) The faster airflow over the flat surface of the bottom of the wing increases pressure and lift.
(D) The faster airflow over the flat surface of the bottom of the wing decreases pressure and lift.
(E) The faster airflow over the greater curvature of the upper wing decreases pressure and increases lift.
193. On a conventional aircraft, what primary flight control produces motion around the longitudinal axis?
(A) The rudder
(B) The aircraft trim tab
(C) The elevators
(D) The ailerons
(E) The flaps
194. A solid green light signal from the tower to an aircraft in flight means
(A) You’re cleared to land.
(B) Caution for other traffic.
(C) Depart the air traffic area.
(D) Go around for another approach.
(E) Contact the tower on standard frequency.
195. How is a closed runway identified?
(A) The runway has stripes painted every 500 feet.
(B) The runway has a large yellow X painted on both approach ends.
(C) The runway has obstacles placed at either approach end.
(D) Large “Closed” signs are painted on the runway.
(E) Large red “Do not land” signs are painted on the runway.
196. What’s the transponder code for “emergency”?
(A) 1200
(B) 7667
(C) 7777
(D) 7700
(E) 6666
197. Displaced thresholds are for what type of airport operations?
(A) Takeoffs only
(B) Landings only
(C) Aircraft pre-takeoff checks
(D) Takeoffs, landings, and taxi operations
(E) Takeoffs and taxi operations only
198. The ratio of aircraft speed in relation to the speed of sound is the
(A) Mach number
(B) Warp number
(C) Air/sound speed
(D) Aerodynamic velocity
(E) True airspeed
199. An airport windsock tells you
(A) The direction the wind is coming from
(B) The airport density altitude
(C) The wind direction, a rough idea of velocity, and gusts
(D) Whether the runway is open
(E) Which runway is the only legal one to operate on
200. Induced drag has the least effect at
(A) Cruise flight
(B) Slow airspeeds
(C) High airspeeds
(D) During steep turns
(E) In a dive

Subtest 9
General Science
Time: 10 minutes for 20 questions
Description: This section tests your knowledge of general scientific principles. You will be given questions or incomplete statements with five possible choices. Pick the most-correct answer.
201. Fats and oils that are found in foods are called
(A) Carbohydrates
(B) Lipids
(C) Amino acids
(D) Proteins
(E) Trace elements
202. When a substance transfers directly from a solid to a gas, it’s called
(A) Condensation
(B) Reduction
(C) Boyle’s melting
(D) Sublimation
(E) Direct transformation
203. Which organ is responsible for detoxification and protein synthesis?
(A) Liver
(B) Heart
(C) Lungs
(D) Bladder
(E) Pancreas
204. What type of energy is derived from the core heating ability, or stored energy, of the earth?
(A) Fossil
(B) Solar
(C) Geothermal
(D) Volcanic
(E) Hydroelectric
205. The study of interactions between organisms and their physical environment is known as
(A) Biology
(B) Embryology
(C) Ecology
(D) Cytology
(E) Physiology
206. The function of an enzyme is to
(A) Speed up a chemical reaction
(B) Slow down a chemical reaction
(C) Absorb energy during a chemical reaction
(D) Transfer energy during a chemical reaction
(E) Be the by-product of a chemical reaction
207. A woman with type O blood and a man with type AB blood can have an offspring with what blood type?
(A) Type AB
(B) Type B
(C) Type A
(D) Type O
(E) Type A or B
208. Which of the following animals has the highest metabolic rate?
(A) Lion
(B) Elephant
(C) Sloth
(D) Rabbit
(E) Cheetah
209. In the electromagnetic spectrum, which has the longest wavelength and the lowest frequency?
(A) X-rays
(B) Radio waves
(C) Sunlight
(D) Microwaves
(E) Gamma rays
210. Most of the nutrients in food are absorbed in the body’s
(A) Stomach
(B) Gall bladder
(C) Large intestine
(D) Small intestine
(E) Kidneys
211. The measurement of electrical resistance to oppose the current or flow of electrons is
(A) Watts
(B) Amperes
(C) Volts
(D) Joules
(E) Ohms
212. Lack of vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, causes which disease?
(A) Goiter
(B) Alzheimer’s
(C) Scurvy
(D) Epilepsy
(E) Rickets
213. After salt is added to water, the water’s freezing level
(A) Increases
(B) Stays the same
(C) Becomes variable
(D) Increases and then decreases
(E) Decreases
214. Inside a cell, DNA is located within the
(A) Nucleus
(B) Golgi apparatus
(C) Lysosome
(D) Endoplasmic reticulum
(E) Centriole
215. The International System (SI) standard uses what base unit for weight?
(A) Pound
(B) Ton
(C) Joule
(D) Gram
(E) Kilogram
216. If one parent has a dominant trait gene (dD) and the other parent doesn’t have the trait (dd), what’s the chance that their offspring will have the dominant trait?
(A) 25 percent
(B) 50 percent
(C) 75 percent
(D) 100 percent
(E) Varies
217. When heat is given off during a chemical reaction, the process is called
(A) Hot
(B) Thermal
(C) Endothermic
(D) Exothermic
(E) A reduction
218. Of the various elements in the air, the most abundant is
(A) Helium
(B) Nitrogen
(C) Oxygen
(D) Carbon dioxide
(E) Argon
219. A 120-volt power source results in 3 amps to the load. The total power delivered is
(A) 100 watts
(B) 300 watts
(C) 360 watts
(D) 240 watts
(E) 120 watts
220. The process of dividing one cell nucleus into two nuclei is called
(A) Division
(B) Subtration
(C) Cytokinesis
(D) Cell division
(E) Mitosis

Subtest 10
Rotated Blocks
Time: 13 minutes for 15 questions
Description: This section tests your ability to visualize and manipulate objects. In each initial picture, you see a 3-D representation of a block. Identify which of the five possible choices best represents the same block.
221.
222.

223.
224.
225.

226.

227.

228.

229.
230.
231.
232.
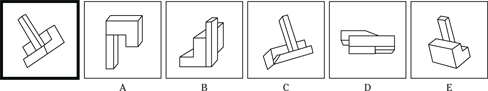
233.
234.
235.

Subtest 11
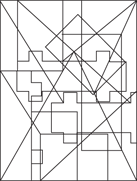
Hidden Figures
Time: 8 minutes for 15 questions
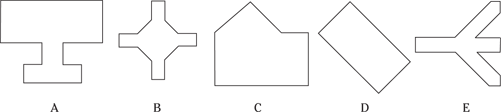
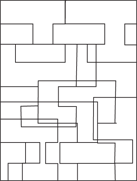
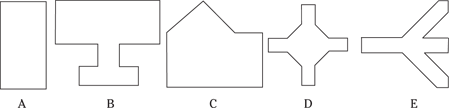
Description: This section tests your ability to recognize a simple figure in a complex drawing. Before each set of questions, you see five figures lettered A, B, C, D, and E. For each question, identify which simple figure (A through E) is in the complex drawing.
236.–240.
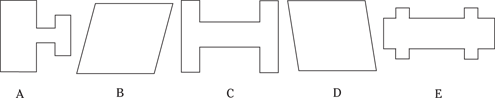
236.
237.
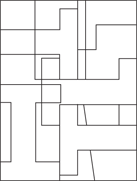
238.
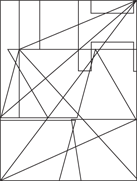
239.
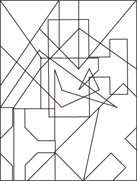
240.

241.–245.
241.
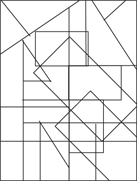
242.
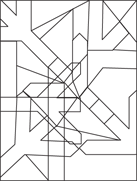
243.
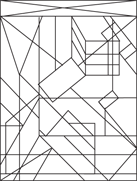
224.
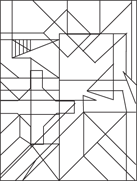
245.
246.–250.
246.
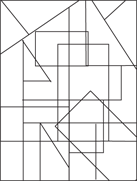
247.
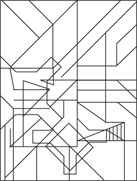
248.

249.
250.

Subtest 12
Self-Description Inventory (Sample Questions)
Time: 40 minutes for 220 questions
Description: This inventory uses 220 questions to measure your personal traits and attitudes. The inventory consists of a series of statements that may be personal or controversial. Read each statement carefully, decide how well it describes you, and mark the corresponding level of agreement. Don’t spend a lot of time on the answers; choose based on your first impression. There is no right or wrong answer.
Here are some examples of self-description questions your test may ask (don’t worry, we don’t include 220 of them):
251. I like being where the action is.
(A) Strongly disagree
(B) Moderately disagree
(C) Neither agree nor disagree
(D) Moderately agree
(E) Strongly agree
252. I like new challenges.
(A) Strongly disagree
(B) Moderately disagree
(C) Neither agree nor disagree
(D) Moderately agree
(E) Strongly agree
253. I always try to finish what I start.
(A) Strongly disagree
(B) Moderately disagree
(C) Neither agree nor disagree
(D) Moderately agree
(E) Strongly agree
254. I generally get along well with most people.
(A) Strongly disagree
(B) Moderately disagree
(C) Neither agree nor disagree
(D) Moderately agree
(E) Strongly agree
255. I get nervous if I have to speak in public.
(A) Strongly disagree
(B) Moderately disagree
(C) Neither agree nor disagree
(D) Moderately agree
(E) Strongly agree
256. People often get upset with me for not showing up on time.
(A) Strongly disagree
(B) Moderately disagree
(C) Neither agree nor disagree
(D) Moderately agree
(E) Strongly agree
257. I like to listen to many different kinds of music.
(A) Strongly disagree
(B) Moderately disagree
(C) Neither agree nor disagree
(D) Moderately agree
(E) Strongly agree
258. I usually let my work goals take priority over my personal interests.
(A) Strongly disagree
(B) Moderately disagree
(C) Neither agree nor disagree
(D) Moderately agree
(E) Strongly agree
259. I am not comfortable supervising others.
(A) Strongly disagree
(B) Moderately disagree
(C) Neither agree nor disagree
(D) Moderately agree
(E) Strongly agree
260. I am pleased when friends drop in to see me.
(A) Strongly disagree
(B) Moderately disagree
(C) Neither agree nor disagree
(D) Moderately agree
(E) Strongly agree
Here are other sample questions that may appear in this test section:
 I don’t like to be involved in group activities.
I don’t like to be involved in group activities.
 I have higher work standards than do most people.
I have higher work standards than do most people.
 I am neater than most people I know.
I am neater than most people I know.
 I keep my promises.
I keep my promises.
 I sympathize with those who are worse off than me.
I sympathize with those who are worse off than me.
 I love life.
I love life.
 I look at the bright side of life.
I look at the bright side of life.
 I tend to make rash decisions.
I tend to make rash decisions.
 I excel in what I do.
I excel in what I do.
 I would cheat to get ahead.
I would cheat to get ahead.
 I keep my emotions under control.
I keep my emotions under control.
 I am easily hurt.
I am easily hurt.
 I enjoy being the center of attention.
I enjoy being the center of attention.
 I act wild and crazy.
I act wild and crazy.
 I rarely notice my emotional reactions.
I rarely notice my emotional reactions.