27 |
Text by Carin van Ginkel |
|---|---|
The largest group of living seedless plants, with about 12,000 species. Stems are underground rhizomes; roots are simple. Reproduce via spores carried in sporangia or sporocarps. In some, the sporangia form clusters (sori).
1 Kariba weed
Salvinia molesta


© C. GRIFFITHS
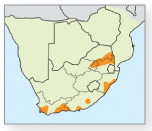
Floating, alien invasive fern, with horizontal rhizome-bearing leaves in whorls of three, consisting of two roundish ‘unwettable’ leaves covered in fine hairs, and a feathery submerged leaf resembling roots. Often forms dense mats on water surface. Size: Rhizomes up to 200mm in length, typically 2–3cm in height. Biology: In standing water at altitudes of 5–1,500m. Category 1 invasive weed; can choke waterways; introduced from South America as an ornamental. Reproduces from fragments. The tiny weevil Cyrtobagous salviniae (p.206, 3) is an effective biocontol agent against this species.
2 Saddle-shaped water clover
Marsilea ephippiocarpa

© A. LINTSTROM

© C. VAN GINKEL

© C. VAN GINKEL

© C. CILLIERS

© C. CILLIERS
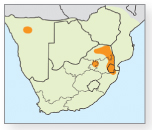
Creeping, indigenous aquatic fern. Stem slender, leaves broadly ovate and streaked, with dark lines when floating. Reproductive sporocarps dark brown and hairy when young, in clusters of 3–10, with a distinctly concave upper surface. Size: Typically 8–30cm in height. Biology: In seasonally flooded areas and along lake or dam edges in eastern Mpumalanga and Limpopo; also in Namibia and Swaziland. Form ground covers that can withstand drought. RELATED SPECIES: Powdery water clover (M. farinosa) (2a, 2b) has leaves broadly divided, almost smooth, with margins rounded or deeply rippled. Sporocarps in clusters held at 90–180°, hairy and bean-shaped. Attains 8–25cm and found in riverbeds, seasonal vleis and pans in areas within KwaZulu-Natal, Free State and Namibia. Large fruit water clover (M. macrocarpa) (2c) has slender stem and broadly divided, almost smooth leaves with concave flanks; sporocarps (2d) solitary; variable in size and form. Attains 8–35cm and found in permanently running water or seasonal vleis and pans. Widespread throughout South Africa and Namibia.
3 Creeping fern
Gleichenia polypodioides

© C. VAN GINKEL

© C. GRIFFITHS
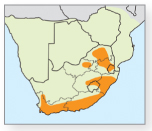
Erect, creeping, shrub-like fern growing around margins of water bodies. Widely creeping rhizome; fronds widely spaced and deeply incised (3a). Sori sunken into the leaf blade. Size: Typically 0.30–9.14m in height. Biology: Found in crevices on moist cliff faces, along stream banks and on forest margins, in exposed or deeply shaded areas at altitudes of 90–500m; may be invasive in plantations.
4 Horsetail fern
Equisetum ramosissimum

© C. VAN GINKEL (BOTH)
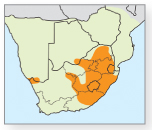
Erect, grass-like indigenous fern. Aerial stems much-branched, hollow and ribbed, with roots at each node; leaves scale-like. Strobili (reproductive structures with spores) terminal on stems (inset). Size: Typically 0.5–1.52m in height. Biology: Found in open woodland, rock crevices, in and along rivers and in shallow waterlogged areas at altitudes of 10–2,105m. Considered ‘living fossils’, poisonous to stock and used as traditional medicine.
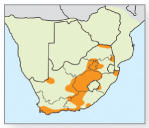
5 Red water fern
Azolla filiculoides

© C. CILLIERS
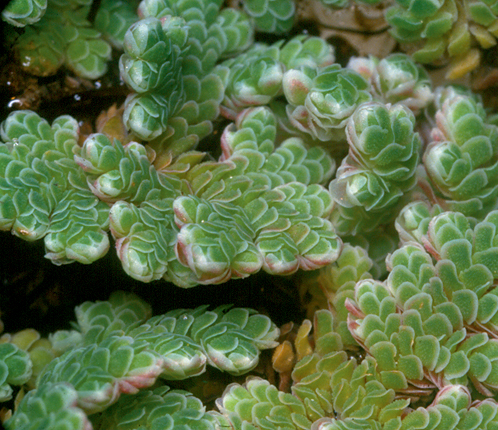
Free-floating invasive fern introduced as garden plant from tropical South America around 1948. Stem branching with solitary, smooth, curled-tipped roots. Leaves silvery green and often red during winter. Size: <10mm in height. Biology: In rivers, dams and vleis; regularly dominant in large open water bodies at altitudes below 1,700m and often in association with cyanobacteria (p.332) that can bind nitrogen. A Caterory 1 declared weed, but an effective biological control agent has been introduced in South Africa. RELATED SPECIES: Mosquito fern (A. pinnata), an indigenous fern with more feather-like leaves, found in pools and backwaters of rivers in KwaZulu-Natal and the Okavango swamps.
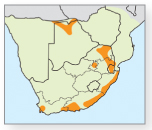
6 Swamp cyclosorus
Cyclosorus interruptus

© C. GRIFFITHS
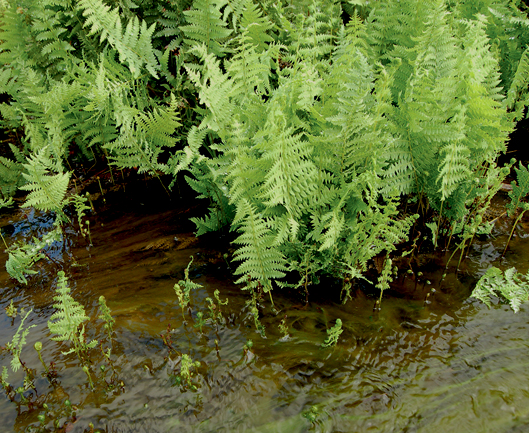
Erect, spreading, indigenous fern that has dispersed around the world. Stems creeping widely, fronds spaced widely apart, with margins of pinnae (smaller leaflets) incised by a third of their breadth. Sori circular, forming a zig-zag pattern underneath. Size: Typically 0.4–1.6m in height. Biology: On river banks and other marshy areas at 10–1,300m. Rare in the Western Cape. Used in water features and as a soil stabiliser. Aromatic; also used medicinally for treating burns, coughs, malaria and general sickness.