H
H2 Antagonists
H2 ANTAGONISTS
| Name | Availability | Dosage Range | Side Effects |
| Cimetidine (Tagamet) |
T: 200 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg, 800 mg L: 300 mg/5 ml |
Treatment of DU: 800 mg at bedtime, 400 mg 2 times/day or 300 mg 4 times/day Maintenance of DU: 400 mg at bedtime Treatment of GU: 800 mg at bedtime or 300 mg 4 times/day GERD: 400 mg 4 times/day or 800 mg 2 times/day Hypersecretory: 300 mg 4 times/day. Maximum: 2,400 mg/day | Headaches, fatigue, dizziness, confusion, diarrhea, gynecomastia |
| Famotidine (Pepcid) |
T: 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg OS: 40 mg/5 ml I: 10 mg/ml |
Treatment of DU: 40 mg/day in 1 or 2 divided doses Maintenance of DU: 20 mg/day Treatment of GU: 40 mg/day at bedtime GERD: 20 mg 2 times/day for 6 wks Hypersecretory: Initially, 20 mg q6h. May increase up to 160 mg q6h | Headaches, dizziness, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, tinnitus |
| Nizatidine (Axid) |
OS: 15 mg/ml C: 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg |
Treatment of GU: 300 mg at hs or 150 mg 2 times/day GERD: 150 mg 2 times/day Treatment of DU: 300 mg at hs or 150 mg 2 times/day Maintenance of DU: 150 mg/day at bedtime | Fatigue, urticaria, abdominal pain, constipation, nausea |
| Ranitidine (Zantac) |
T: 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg C: 150 mg, 300 mg Syrup: 15 mg/ml I: 25 mg/ml |
Treatment of DU: 300 mg at hs or 150 mg 2 times/day Maintenance of DU: 150 mg/day at bedtime Treatment of GU: 150 mg 2 times/day GERD: 150 mg 2 times/day Hypersecretory: 150 mg 2 times/day. Maximum: 6 g/day Erosive Esophagitis: Treatment: 150 mg 4 times/day. Maintenance: 150 mg 2 times/day | Blurred vision, constipation, nausea, abdominal pain |
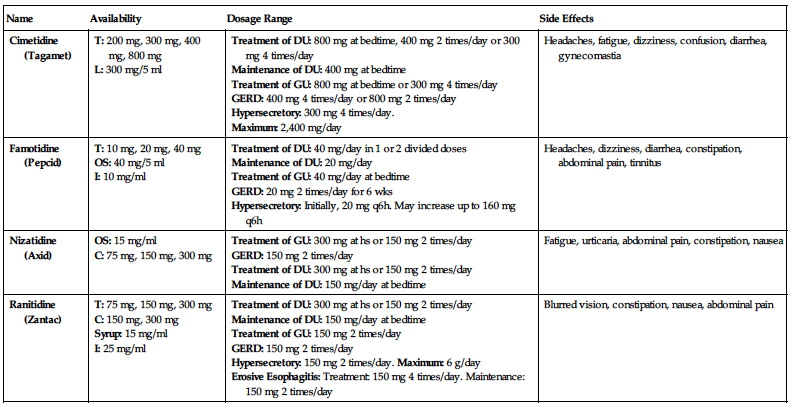
C, Capsules; DT, disintegrating tablets; DU, duodenal ulcer; GERD, gastroesophageal reflux disease; GU, gastric ulcer; I, injection; L, liquid; OS, oral suspension; T, tablets.
Hepatitis C Virus
ANTI-HEPATITIS C VIRUS PREPARATIONS
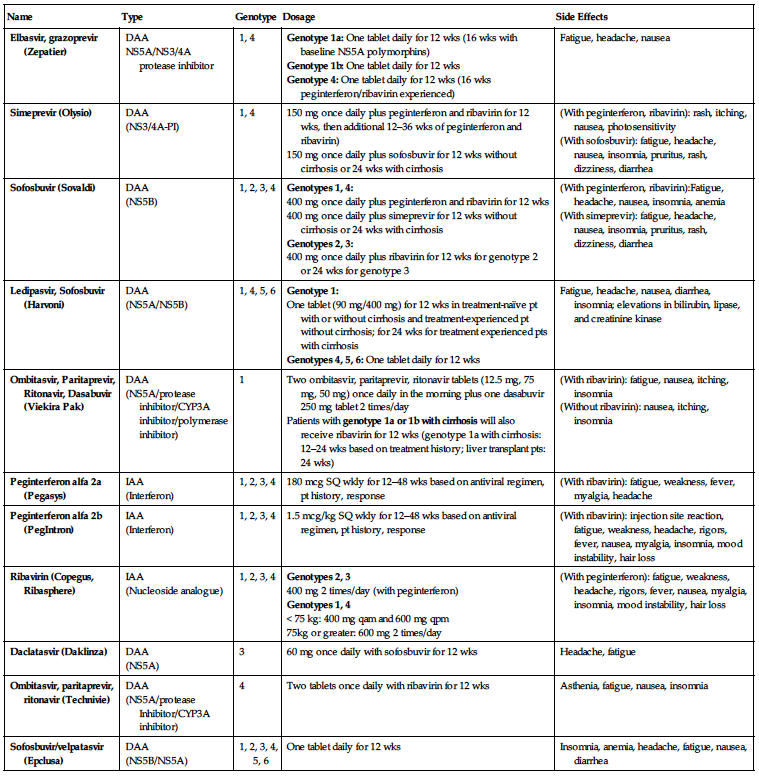
| Name | Type | Genotype | Dosage | Side Effects |
| Elbasvir, grazoprevir (Zepatier) |
DAA NS5A/NS3/4A protease inhibitor | 1, 4 |
Genotype 1a: One tablet daily for 12 wks (16 wks with baseline NS5A polymorphins) Genotype 1b: One tablet daily for 12 wks Genotype 4: One tablet daily for 12 wks (16 wks peginterferon/ribavirin experienced) | Fatigue, headache, nausea |
| Simeprevir (Olysio) |
DAA (NS3/4A-PI) | 1, 4 |
150 mg once daily plus peginterferon and ribavirin for 12 wks, then additional 12–36 wks of peginterferon and ribavirin) 150 mg once daily plus sofosbuvir for 12 wks without cirrhosis or 24 wks with cirrhosis |
(With peginterferon, ribavirin): rash, itching, nausea, photosensitivity (With sofosbuvir): fatigue, headache, nausea, insomnia, pruritus, rash, dizziness, diarrhea |
| Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) |
DAA (NS5B) | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
Genotypes 1, 4: 400 mg once daily plus peginterferon and ribavirin for 12 wks 400 mg once daily plus simeprevir for 12 wks without cirrhosis or 24 wks with cirrhosis Genotypes 2, 3: 400 mg once daily plus ribavirin for 12 wks for genotype 2 or 24 wks for genotype 3 |
(With peginterferon, ribavirin):Fatigue, headache, nausea, insomnia, anemia (With simeprevir): fatigue, headache, nausea, insomnia, pruritus, rash, dizziness, diarrhea |
| Ledipasvir, Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) |
DAA (NS5A/NS5B) | 1, 4, 5, 6 |
Genotype 1: One tablet (90 mg/400 mg) for 12 wks in treatment-naïve pt with or without cirrhosis and treatment-experienced pt without cirrhosis; for 24 wks for treatment experienced pts with cirrhosis Genotypes 4, 5, 6: One tablet daily for 12 wks | Fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhea, insomnia; elevations in bilirubin, lipase, and creatinine kinase |
| Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, Ritonavir, Dasabuvir (Viekira Pak) |
DAA (NS5A/protease inhibitor/CYP3A inhibitor/polymerase inhibitor) | 1 |
Two ombitasvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir tablets (12.5 mg, 75 mg, 50 mg) once daily in the morning plus one dasabuvir 250 mg tablet 2 times/day Patients with genotype 1a or 1b with cirrhosis will also receive ribavirin for 12 wks (genotype 1a with cirrhosis: 12–24 wks based on treatment history; liver transplant pts: 24 wks) |
(With ribavirin): fatigue, nausea, itching, insomnia (Without ribavirin): nausea, itching, insomnia |
| Peginterferon alfa 2a (Pegasys) |
IAA (Interferon) | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 180 mcg SQ wkly for 12–48 wks based on antiviral regimen, pt history, response | (With ribavirin): fatigue, weakness, fever, myalgia, headache |
| Peginterferon alfa 2b (PegIntron) |
IAA (Interferon) | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 1.5 mcg/kg SQ wkly for 12–48 wks based on antiviral regimen, pt history, response | (With ribavirin): injection site reaction, fatigue, weakness, headache, rigors, fever, nausea, myalgia, insomnia, mood instability, hair loss |
| Ribavirin (Copegus, Ribasphere) |
IAA (Nucleoside analogue) | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
Genotypes 2, 3 400 mg 2 times/day (with peginterferon) Genotypes 1, 4 < 75 kg: 400 mg qam and 600 mg qpm 75kg or greater: 600 mg 2 times/day | (With peginterferon): fatigue, weakness, headache, rigors, fever, nausea, myalgia, insomnia, mood instability, hair loss |
| Daclatasvir (Daklinza) |
DAA (NS5A) | 3 | 60 mg once daily with sofosbuvir for 12 wks | Headache, fatigue |
| Ombitasvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir (Technivie) |
DAA (NS5A/protease Inhibitor/CYP3A inhibitor) | 4 | Two tablets once daily with ribavirin for 12 wks | Asthenia, fatigue, nausea, insomnia |
| Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (Epclusa) |
DAA (NS5B/NS5A) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 | One tablet daily for 12 wks | Insomnia, anemia, headache, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea |
Hormones
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection
ANTIRETROVIRAL AGENTS FOR TREATMENT OF HIV INFECTION
| Name | Availability | Dosage Range | Side Effects |
| Nucleoside Analogues | |||
| Abacavir (Ziagen) |
T: 300 mg OS: 20 mg/ml | A: 300 mg 2 times/day or 600 mg once daily | Nausea, vomiting, malaise, rash, fever, headaches, asthenia, fatigue, hypersensitivity reactions |
| Didanosine (Videx EC) |
DR: 125 mg, 200 mg, 250 mg, 400 mg OS: 2 g/bottle, 4 g/bottle |
DR (weighing 60 kg or more): 400 mg once daily; (weighing 25–59 kg): 250 mg once daily; (weighing 20–24 kg): 200 mg once daily OS (weighing more than 60 kg): 200 mg q12h or 400 mg once daily; (weighing less than 60 kg): 125 mg q12h or 250 mg once daily | Peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headaches, insomnia, rash, hepatitis, seizures |
| Emtricitabine (Emtriva) |
C: 200 mg OS: 10 mg/ml |
A: 200 mg/day (C) 240 mg/day (OS) | Headaches, insomnia, depression, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rhinitis, asthenia, rash |
| Lamivudine (Epivir) |
T: 100 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg OS: 5 mg/ml, 10 mg/ml |
A: 150 mg 2 times/day or 300 mg once daily C: 4 mg/kg 2 times/day | Diarrhea, malaise, fatigue, headaches, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, peripheral neuropathy, arthralgia, myalgia, skin rash |
| Stavudine (Zerit) |
C: 15 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg OS: 1 mg/ml | A (weighing more than 60 kg): 40 mg 2 times/day (20 mg 2 times/day if peripheral neuropathy occurs); (weighing 60 kg or less): 30 mg 2 times/day (15 mg 2 times/day if peripheral neuropathy occurs) | Peripheral neuropathy, anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia |
| Zidovudine (Retrovir) |
C: 100 mg T: 300 mg Syrup: 50 mg/5 ml, 10 mg/ml | A: 300 mg 2 times/day | Anemia, granulocytopenia, myopathy, nausea, malaise, fatigue, insomnia |
| Nucleotide Analogues | |||
| Tenofovir TAF (Vemlidy) | T: 25 mg | A: 25 mg once daily | Headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, cough, nausea, back pain |
| Tenofovir TDF (Viread) | T: 300 mg | A: 300 mg once daily | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, fatigue |
| Non-nucleoside Analogues | |||
| Delavirdine (Rescriptor) | T: 100 mg, 200 mg | A: 200 mg 3 times/day for 14 days, then 400 mg 3 times/day | Rash, nausea, headaches, elevated hepatic function tests |
| Efavirenz (Sustiva) |
C: 50 mg, 200 mg T: 600 mg |
A: 600 mg/day C: 200–600 mg/day based on weight | Headaches, dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, rash, nightmares |
| Etravirine (Intelence) | T: 100 mg, 200 mg | A: 200 mg 2 times/day | Skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme), nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting |
| Nevirapine (Viramune, Viramune XR) |
T: 200 mg T (ER): 400 mg S: 50 mg/ml | A: 200 mg/day for 14 days, then (if no rash) 200 mg 2 times/day | Rash, nausea, fatigue, fever, headaches, abnormal hepatic function tests |
| Rilpivirine (Edurant) | T: 25 mg | A: 25 mg once daily with a meal | Depression, insomnia, headache, rash |
| Protease Inhibitors | |||
| Atazanavir (Reyataz) | C: 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg | A: 400 mg/day or 300 mg (with 100 mg ritonavir) once daily | Headaches, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, rash |
| Darunavir (Prezista) | T: 400 mg, 600 mg | A: 600 mg 2 times/day (with ritonavir 100 mg) or 800 mg once daily with ritonavir 100 mg | Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headaches, skin rash, constipation |
| Fosamprenavir (Lexiva) |
T: 700 mg OS: 50 mg/ml | A: 1,400–2,800 mg/day with 100 mg ritonavir | Headaches, fatigue, rash, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain |
| Indinavir (Crixivan) | C: 200 mg, 400 mg | A: 800 mg q8h or 800 mg 2 times/day with ritonavir 100 mg | Nephrolithiasis, hyperbilirubinemia, abdominal pain, asthenia, fatigue, flank pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, insomnia, dizziness, altered taste |
| Lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra) |
C: 133/33 mg OS: 80/20 mg |
A: 400 mg/100 mg 2 times/day or 800 mg/200 mg once daily C (4–12 yrs): 10–13 mg/kg 2 times/day | Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, headaches, rash |
| Nelfinavir (Viracept) |
T: 250 mg Oral Powder: 50 mg/g |
A: 750 mg q8h or 1,250 mg 2 times/day C: 20–25 mg/kg q8h | Diarrhea, fatigue, asthenia, headaches, hypertension, impaired concentration |
| Ritonavir (Norvir) |
C: 100 mg OS: 80 mg/ml | A: Titrate up to 800 mg/day based on protease inhibitor | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, altered taste, fatigue, elevated LFT and triglyceride levels |
| Saquinavir (Invirase) |
C: 200 mg T: 500 mg | A: 1,000 mg 2 times/day with ritonavir 100 mg | Diarrhea, elevated LFTs, hypertriglycerides, cholesterol, abnormal fat accumulation, hyperglycemia |
| Tipranavir (Aptivus) |
C: 250 mg OS: 100 mg/ml | A: 500 mg (with 200 mg ritonavir) 2 times/day | Diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, headaches, vomiting |
| Fusion Inhibitors | |||
| Enfuvirtide (Fuzeon) | I: 108 mg (90 mg when reconstituted) | Subcutaneous: 90 mg 2 times/day | Insomnia, depression, peripheral neuropathy, decreased appetite, constipation, asthenia, cough |
| CCR5 Antagonists | |||
| Maraviroc (Selzentry) | T: 150 mg, 300 mg |
A: 300 mg 2 times/day CYP3A4 inducers: 600 mg 2 times/day CYP3A4 inhibitors: 150 mg 2 times/day | Cough, pyrexia, upper respiratory tract infections, rash, musculoskeletal symptoms, abdominal pain, dizziness |
| Integrase Inhibitor | |||
| Raltegravir (Isentress) | T: 400 mg | A: 400 mg 2 times/day | Nausea, headache, diarrhea, pyrexia |
| Dolutegravir (Tivicay) | T: 50 mg | A: 50 mg once daily or 50 mg bid (with CYP3A inducers or resistance) | Insomnia, headache |
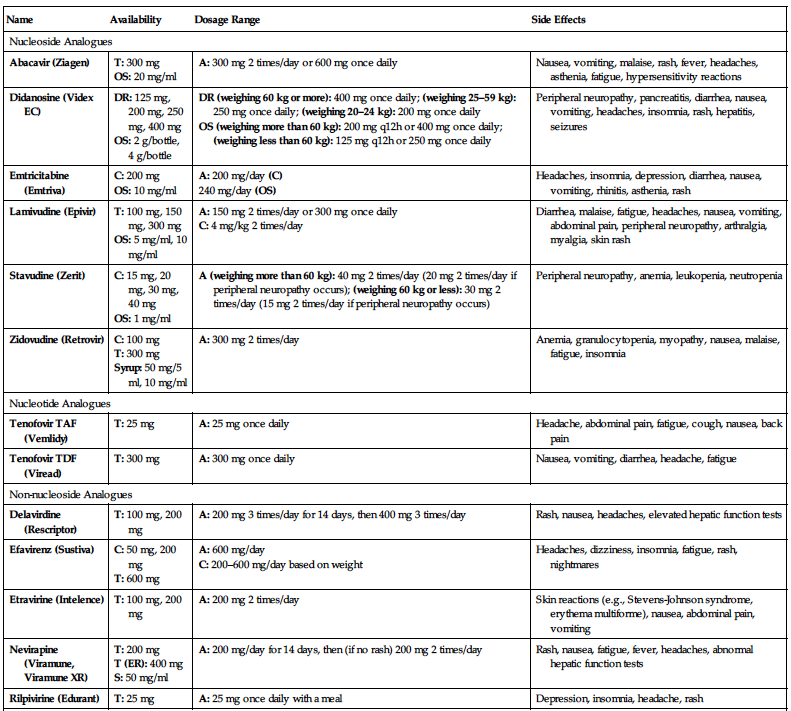
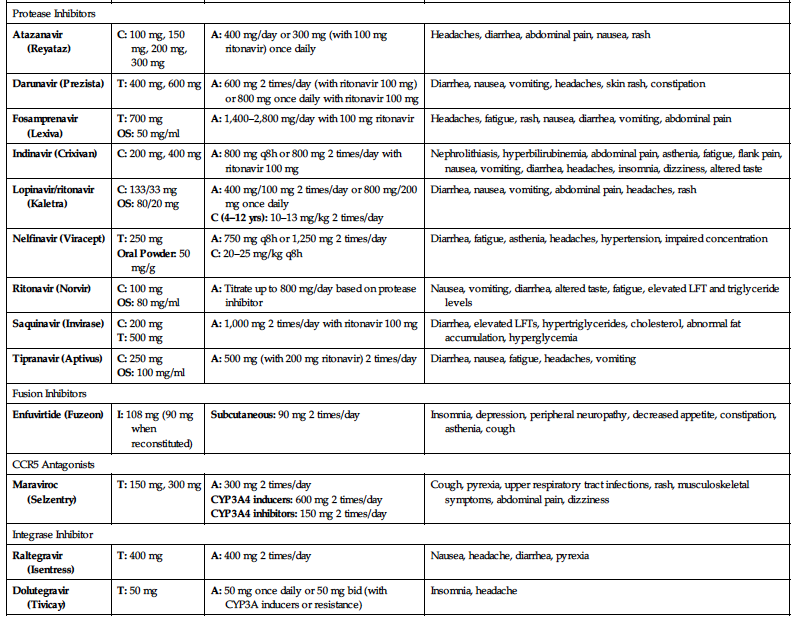
A, Adults; C, capsules; C (dosage), children; DR, delayed-release; ER, extended-release; I, injection; OS, oral solution; S, suspension; T, tablets; TAF, tenofovir alafenamide; TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
FIXED-COMBINATION THERAPIES
| Brand Name | Generic Name | Dosage |
| Atripla |
Efavirenz 600 mg Emtricitabine 200 mg Tenofovir (TDF) 300 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
| Combivir |
Lamivudine 150 mg Zidovudine 300 mg | 1 tablet twice daily |
| Complera |
Emtricitabine 200 mg Rilpivirine 27.5 mg Tenofovir (TDF) 300 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
| Descovy |
Emtricitabine 200 mg Tenofovir (TAF) 25 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
| Epzicom |
Abacavir 600 mg Lamivudine 300 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
| Evotaz |
Atazanavir 300 mg Cobicistat 150 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
| Genvoya |
Cobicistat 150 mg Elvitegravir 150 mg Emtricitabine 200 mg Tenofovir (TAF) 10 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
| Odefsey |
Emtricitabine 200 mg Rilpivirine 25 mg Tenofovir (TAF) 25 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
| Prezcobix |
Cobicistat 150 mg Darunavir 800 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
| Stribild |
Cobicistat 150 mg Elvitegravir 150 mg Emtricitabine 200 mg Tenofovir (TDF) 300 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
| Triumeq |
Abacavir 600 mg Dolutegravir 50 mg Lamivudine 300 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
| Trizivir |
Abacavir 300 mg Lamivudine 150 mg Zidovudine 300 mg | 1 tablet twice daily |
| Truvada |
Emtricitabine 200 mg Tenofovir (TDF) 300 mg | 1 tablet once daily |
TAF, tenofovir alafenamide; TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.